Microeconomics Chapter 6: Taxes and Subsidies
1/27
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
When a tax is imposed on buyers, the economic burden...
is identical to that of an equivalent tax imposed on sellers.
The economic burden of a tax would fall most heavily on buyers of...
electricity
If sellers are required to pay a $5 tax per laptop, then the supply curve shifts...
up by $5
Sellers are required to pay a tax per bicycle. If the tax increases from $50 to $60, then the supply curve shifts...
down by $60
Buyers are required to pay a tax per coat. If the tax increases from $10 to $30, then the demand curve shifts...
up by $30
What is deadweight loss?
the decrease in total surplus that results from an inefficient level of production
Why do taxes create deadweight losses?
they prevent some buyers and sellers from making mutually-beneficial trades
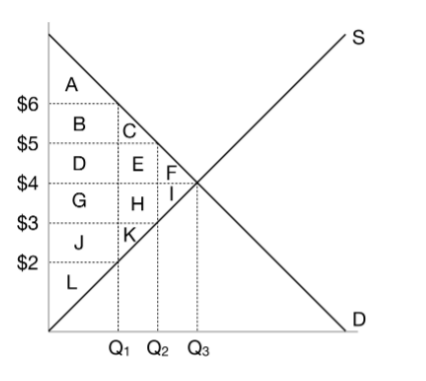
When the government imposes a $2 tax on this market, what is the price that buyers pay?
$5
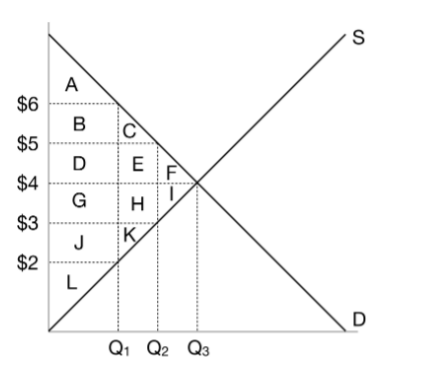
When the government imposes a $2 tax on this market, what is the price that sellers receive?
$3
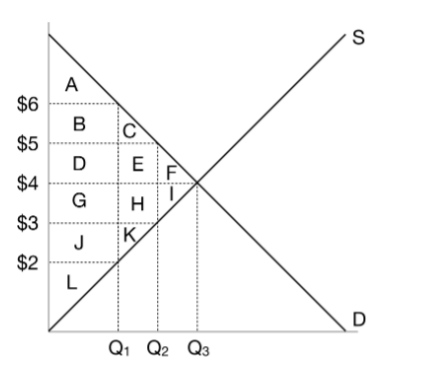
When the government imposes a $2 tax on this market, what is the quantity?
Q2
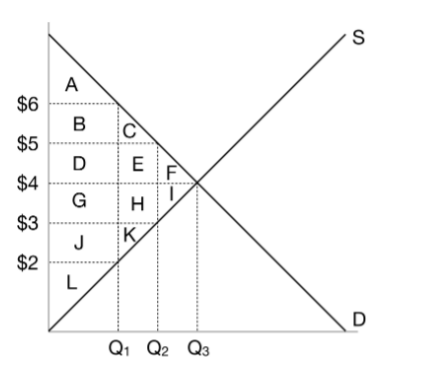
When the government imposes a $2 tax on this market, what is the consumer surplus?
A+B+C
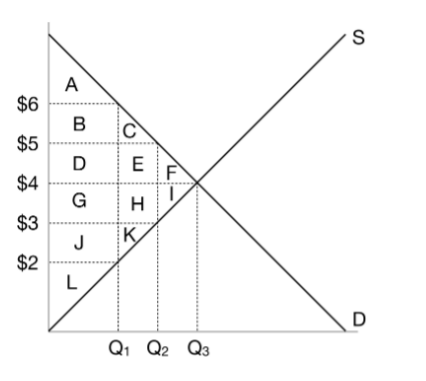
When the government imposes a $2 tax on this market, what is the producer surplus?
J+K+L
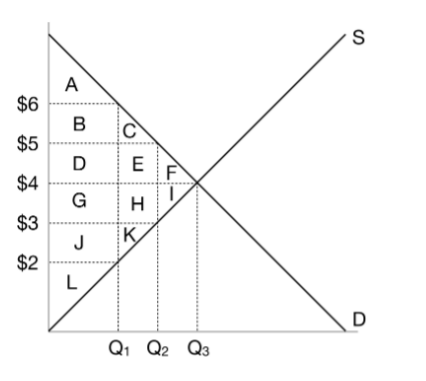
When the government imposes a $2 tax on this market, what is the tax revenue?
D+E+G+H
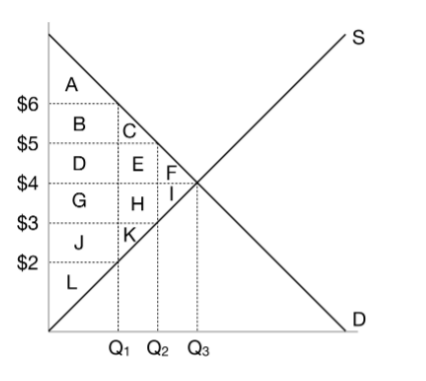
When the government imposes a $2 tax on this market, what is the deadweight loss?
F+I
A $5 tax creates the smallest deadweight loss when it is imposed on a product with...
price inelastic supply and demand
There is a $1 tax on soda. If the number of substitutes to soda increases, then demand becomes more...
price elastic, and deadweight loss increases
Which of the following increases the deadweight loss from a tax?
None of the above are correct.
San Francisco imposed a tax on broadband Internet service when broadband was new. What happened?
Tax revenue increased. Total surplus decreased.
If the economic burden of a soda tax falls mostly on sellers, which of the following is correct?
Soda demand is more elastic than price supply.
Which of the following would explain why the economic burden of a cigarette tax falls mostly on buyers?
Cigarettes are addictive, so demand is more price inelastic than supply.
The government places a tax on yachts. The goal is to raise revenue from buyers who tend to be wealthy.
The supply curve of yachts is relatively steep, and the demand curve is relatively flat. Who feels more of the
economic burden of the tax?
Sellers feel more of the burden because supply is more price inelastic than demand.
The government is considering three proposals for a $100 tax. In proposal A, all of the tax is collected from
buyers. In proposal B, all of the tax is collected from sellers. In proposal C, half is collected from buyers, and
half is collected from sellers. Which of the following is correct?
All of the proposals place the same economic burdens on buyers.
If the government imposes a tax on workers, what happens to the wage?
The wage that employers pay rises. The wage that workers receive falls.
The labor supply curve for high-income workers is price elastic. The labor supply curve for low-income
workers is price inelastic. The labor demand curve for both workers is identical. If the government imposes
the same tax on all workers, who feels more of the economic burden?
Low-income workers feel more of the burden than high-income workers do.
In the summer, all gas refineries are working at full capacity. What does this imply about the market for gas?
The supply curve is vertical.
During a gas tax holiday, which of the following happens in the market for gas?
Demand shifts up.
Suppose buyers pay a gas tax of $2, and the supply curve is vertical. If there is a gas tax holiday, how much
of the benefit goes to buyers?
$0
Suppose buyers pay a gas tax of $2, and the supply curve is vertical. If there is a gas tax holiday, how much
of the benefit goes to sellers?
$2