social inequality: race, gender, and social mobility in Canada
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
studying inequality
all societies exhibit systematic inequalities that differentiate people based on their membership in some social category
like all other observed patterns in sociology, in most cases patterned inequalities are statistical regularities, not absolute laws
the presence of exceptions does not negate the empirical reality of the pattern
when studying inequality, the first question we want to ask ourselves is: inequality in regard to what? what is unequally distributed?
things that differentiate people in their membership
things are incredibly different from one society to the next
social inequality: possible dependent variables
there are all kinds of material and social resources that exhibit pattered inequalities
wealth, access to material resources
income inequality, wealth inequality, access to housing, food security → things that people use wealth to obtain
the social theorist Pierre Bourdieu refers to these inequalities with the phrase “proximity to necessity”
safety
freedom from violence, freedom from state persecution
access to education → social resource that is unequal
health outcomes
mortality rates, likelihood of good outcomes after a health emergency, chronic health concerns → who most likely have a family doctor
social recognition
the ability to be included in the public sphere as one’s authentic self
can you show up as your authentic self?
social inequality: independent variables
class
gender
race
ethnicity
nationality
immigration status
disability status
sexuality
3% of population lives unsheltered → various factors have increased risked
native
LGBTQ+
non-white
immigrant
exhibit pattern inequalities

intersectionality
in sociology, we often talk various demographic variables like race, gender, immigration status, etc.
these variables can be isolated in a statistic model, but they are never isolated in experience
intersectionality: intersecting identities are often associated with specific experiences of social inequality
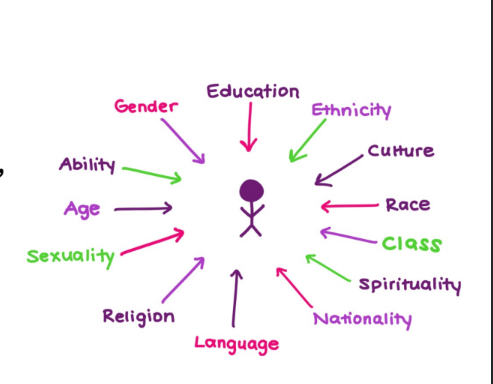
inequality in lived experience
are the disadvantages associated with group membership additive, or are there interaction effects?
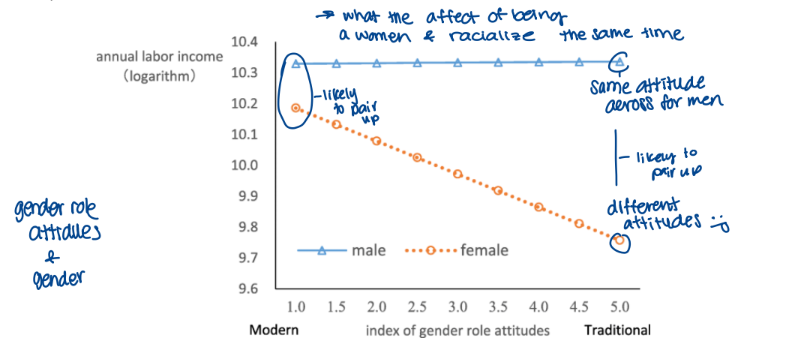
what the effect of being a women and racialized at the same time
race and social inequality in Canada
race is a variable that exhibits patterned inequality in Canada
wealth and income
safety, victimization and access to police protection
access to education
health outcomes, including life expectancy
social recognition
race
physical difference
ethnicity
shared culture (language, religion, material culture/ traditions)
nationality
country of original citizenship
racialization
the processes through which physical differences (i.e skin colour) gets signified as a fundamental category
observing race and social inequality
the sociological study of race and inequality can address this relationship at each of the level of analysis: macro, meso, and micro
what does an investigation of the relation between race and inequality look like if one is interested in the macro-level o analysis?

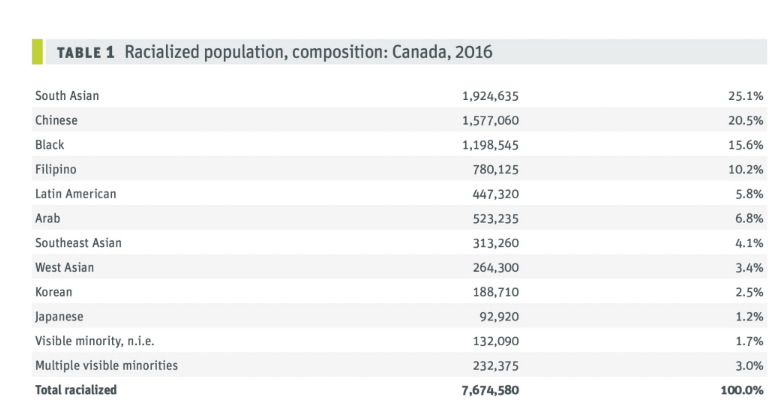
racial minorities in Canadian society (2016 census)
macro level
% of the racialized population (nonwhite people)
labour market participation, by race
whether or not someone has a job or not
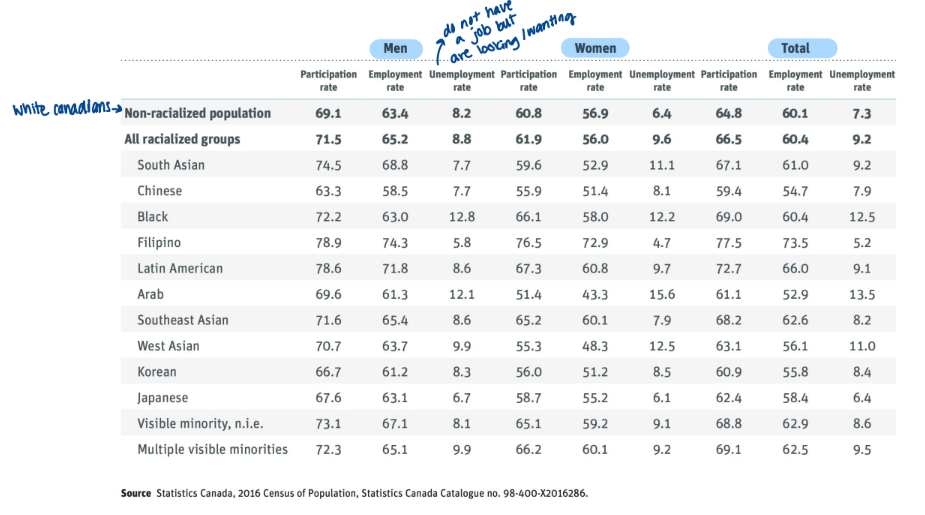
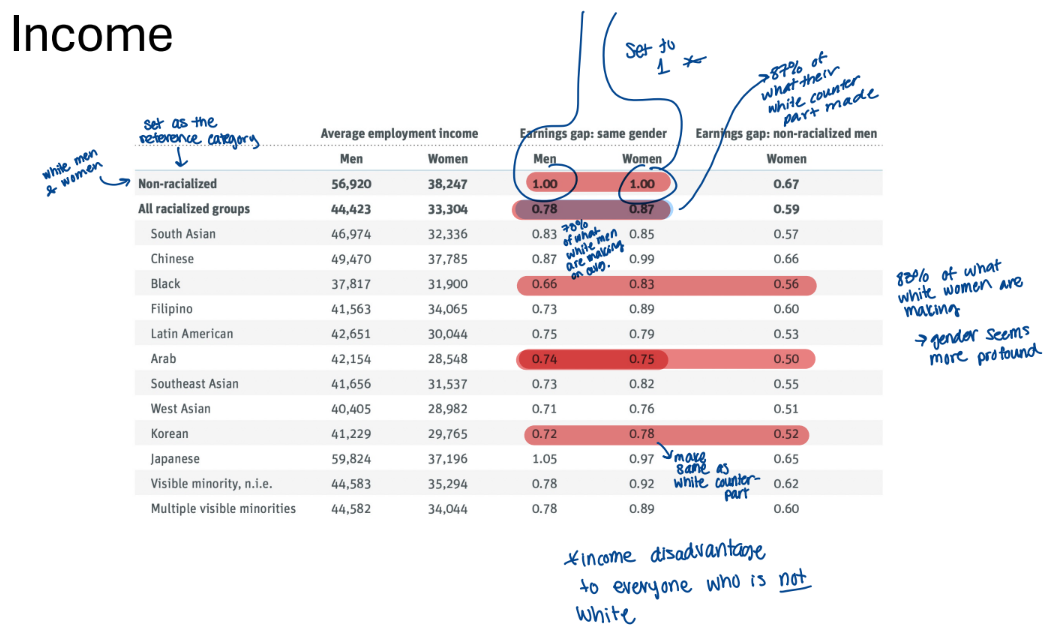
income
white women and men are set as the reference category
income disadvantage to everyone who is not white
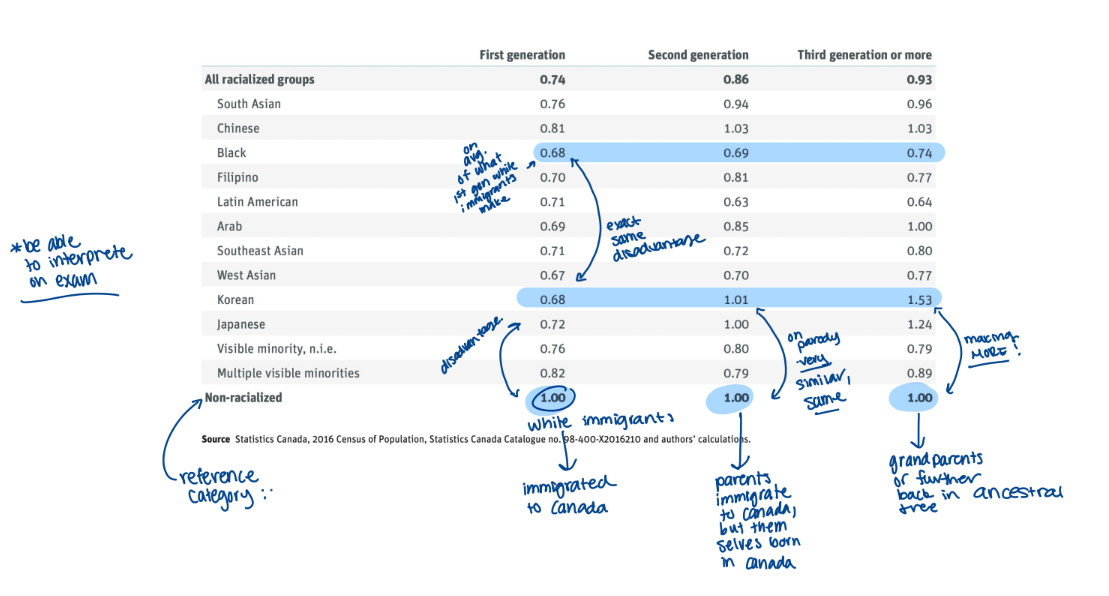
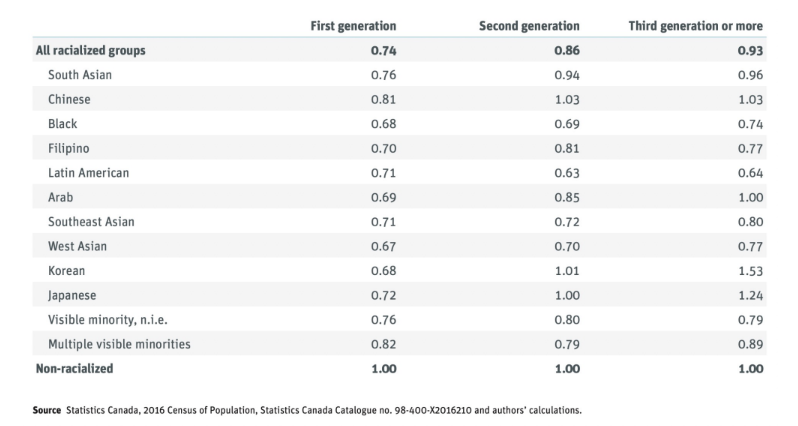
immigration status effects
the subjective experience of racialization
the sociological study of race and inequality can address this relationship at each level of analysis: macro, meso, and micro
what does an investigation of the relationship between race and inequality look like if one is interested in the micro-level of analysis?
try to flesh out individual interactions responsible for macro
Du Bois: The Souls of Black Folk
black Americans experience double-consciousness → unique experiences of the self where one understands you live in a dominant culture that has expectations that surround you
consciousness of one’s self; one’s own self-understanding
consciousness of how one is perceived, both by white individuals and by the dominant white culture more generally
The Souls of Black Folks
(p. 127) Black Americans are “born with a veil, and gifted with second-sight in this American world- a world which yields him no true self-consciousness, but only lets him see himself through the revelation of the other world”
veil → obscures the face, can’t see the face from the outside
race → race obscures you
people see him first as black (race) before him as Du Bois
the veil
Du Boi’s concept of the veil describes the inability of escaping racial categorization for non-whites
Barak Obama
first black president of U.S
veil → this is always the way he is perceived
Justin Trudeau
never hear “Justin Trudeau, the 41st white president”
his whiteness does not get in the way
Asians are good at math → not bad to be good at math, positive dominant culture

integrating macro- and micro-level observations: race and upward social mobility
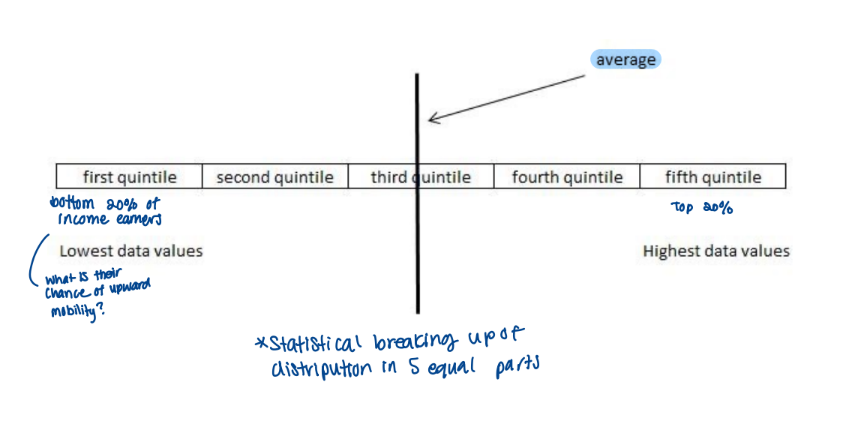
income quintiles
upward mobility in Canadian society
linear relationship of income of parents with having high income as an adult
probability of upward mobility (top 20%)
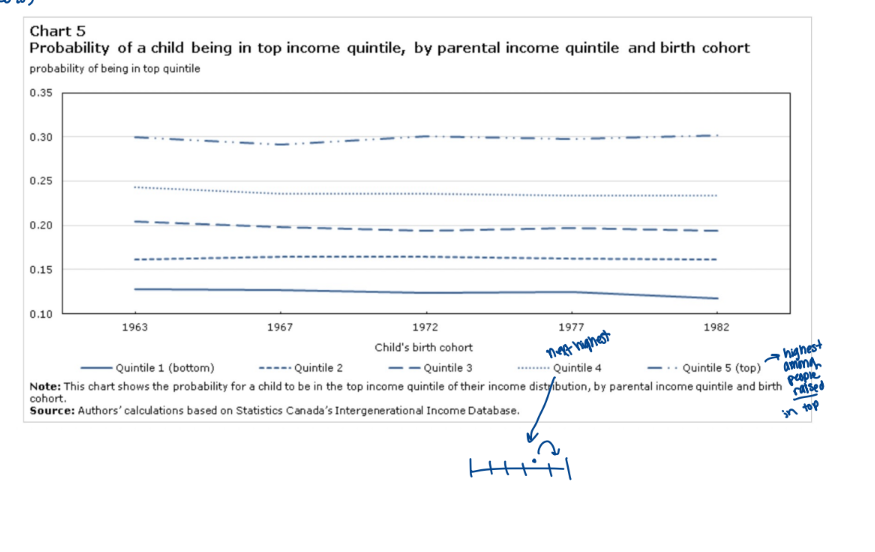
upward mobility in Canadian society - findings show that the correlation between a child’s income rank as an adult and their parents’ income ran has been on an increasing trend
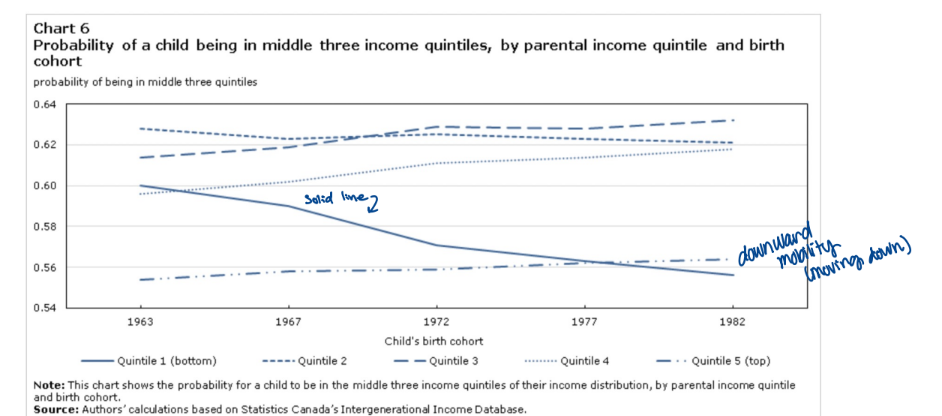
probability of just getting in middle 2, 3, 4
what your parents make increasingly predicts your income as an adult
education
while the relationship between post-secondary education and upward mobility is decreasing in Canada, education remains the single most important predictor of upward mobility
getting a post-secondary education is by no means a guarantee of upward mobility
for most upward mobile individuals, education is an essential component for upward mobility
observe pattern
people with more connections have better job opportunity → positive employment outcomes
ADVICE → number of people that are networking (eventually gets dilutes)
university degree → increase income → increase number of people attending university
all in Ray are in the bottom quintile
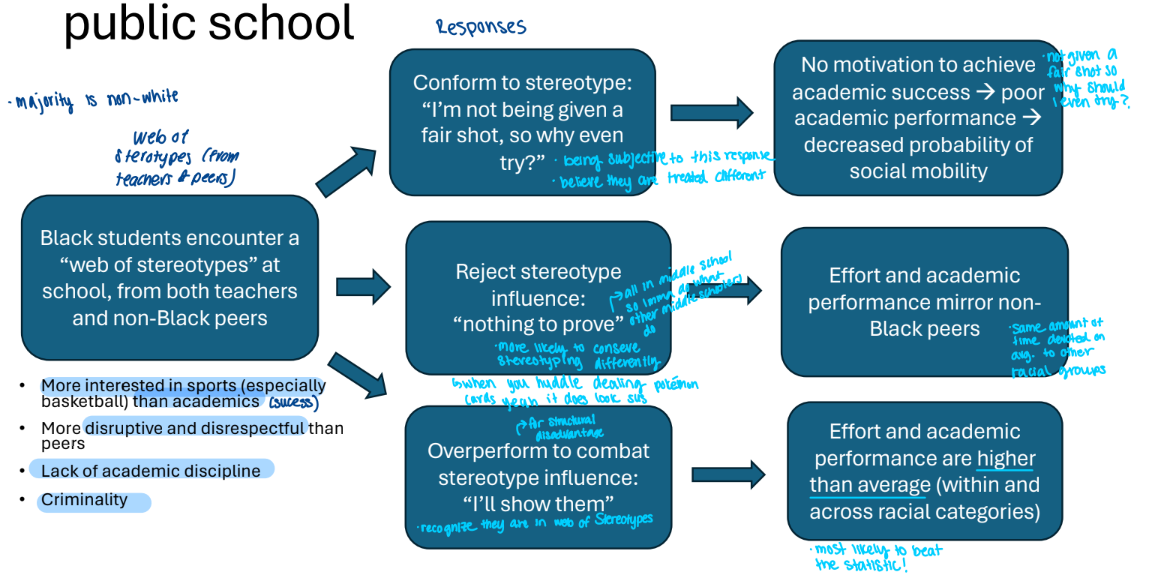
James (2019): “adapting, disrupting, and resisting” Canadian journal of sociology
Study of Black middle school students in the GTA (Greater Toronto Area), in grades 6-8
Qualitative data gathered via focus groups
group qualitative interview, multiple research participants conversing with each other
Quantitative observations:
Black students have lower academic performance than their white peers
Black students are among the least likely to attend a 4-year degree program
50% of Black students who enroll in a 4-year degree program will not graduate → going into debt for a program you didn’t or did complete
“Most schools have embraced the pervasive neoliberal discourse of individualism and merit, but in reality, the educational achievements or successes of Black youth do not depend solely on hard work, commitment, and persistence.”
very similar to a connection Ray makes → flow of education → commitment and discipline → but there are there factors not at individual level that affect
The classroom is not the same environment for Black students as it is for other students
James 2019: Double consciousness in public school
Cano and Hofmeister (2023) the intergenerational transmission (ideas) of gender
quantitative study
study of heterosexual families with children in Australia
children born between March 1999-February 2000
representative sample, N = 2796 children
for each child, both mother and father completed surveys
longitudinal survey data: the same people were surveyed 6 times, over the curse of 10 years (children ages 4-14)
dependent variable → what are children thinking about with relation to gender
dependent variable” gender-role attitudes
How strongly do you agree with the following statements:
a. It is better for the family if the husband is the principle breadwinner outside the home and the wife has primary responsibility for the home and children
b. If both, husband and wife, work, they should share equally in the household and childcare
c. Ideally, there should be as many women as men in important positions in government and business
all are Likert questions
At age 14, children answered each of these questions by responding to a 5- point Likert scale (strongly agree-strongly disagree)
Scores for all three questions were averaged
taken average of scores
independent variables
parenting style (warm/ sensitive vs. authoritative)
time spent doing childcare (ratio level variable)
time spent doing unpaid housework
ratio level
hours per week
unpaid domestic tasks
measured these variables for both fathers and mothers (6 independent variables in total)
warm mother, authoritative father
aut. mother, warm father
aut. mother, aut father
warm mother, warm father
what’ the child exposed to at different development stages
traditional attitudes —————————————————— egalitarian attitudes

results: fathers’ influence on their children’s gender-role attitudes
Father’s time spent on childcare is associated with more egalitarian gender role attitudes at age 14
Effect holds even when the gender role attitudes of the father and mother are introduced as variables (although the inclusion of these variables decreases the effect size)
Implicit vs explicit socialization!
Father’s time spent on unpaid household labour when children are young is associated with more egalitarian attitudes about gender roles at age 14
Largest effect size
Father’s parenting style (warm vs. authoritative) had no effect on gender role attitudes
more time spent witnessing dad vacuum, clean, cook increases egalitarian attitude in children → less traditional
just doing childcare shifts the attitude of children towards egalitarian attitudes
results: mothers’ influence on their children’s gender role attitudes
Mothers’ time spent on childcare had no effect on children’s gender role attitudes (direct care)
Mothers’ time spent on housework had a negative effect on gender role attitudes (opposite effect as dad)
Mothers’ parenting style had the largest effect on gender role attitudes, which children raised by more warm/sensitive mothers having more egalitarian gender role attitudes than children raised by authoritative mothers (regardless of father being aut. or arm)
Largest effect size