Labour, Wages, and Unemployment
0.0(0)Studied by 3 people
Card Sorting
1/16
Earn XP
Last updated 11:27 AM on 4/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
1
New cards
What is the difference between active and potential labour force?
Active labour force includes:
* Employed (self-employed, employees, those on gov. schemes, unpaid workers)
* Unemployed
\
Potential labour force includes the active labour supply as well as:
* Inactive:
* Looking after family
* Short-term sickness
* Discouraged workers
* Long-term sickness
* Students
* Retired
* Employed (self-employed, employees, those on gov. schemes, unpaid workers)
* Unemployed
\
Potential labour force includes the active labour supply as well as:
* Inactive:
* Looking after family
* Short-term sickness
* Discouraged workers
* Long-term sickness
* Students
* Retired
2
New cards
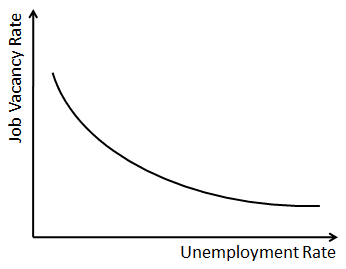
What is the Beveridge curve?
The Beveridge curve suggests that there is a negative relationship between job vacancies and the level of unemployment (as vacancies rise, the amount of unemployment falls).
3
New cards
What does the Beveridge curve illustrate in the economy?
The Beveridge curve illustrates cyclical unemployment: during growth phases, unemployment increases and vacancies decreases; vice versa during a recession
4
New cards
What is the natural rate of unemployment?
The natural rate of unemployment (NRU) is the rate of unemployment when the labour market is in equilibrium (aka. the unemployment caused by structural/supply-side factors).
\
It is around 3.7% in the UK.
\
It is around 3.7% in the UK.
5
New cards
Set up the bathtub model.
The bathtub model illustrates people “flowing” from unemployment to employment and vice versa **at the same time**. It states how employment and unemployment evolve over time.
\
Two endogenous variables: employment E and unemployment U.
* E = total pool of employed
* U = total pool of unemployed
Two exogenous variables:
* s bar = job separation rate (% of those fired/separated)
* f bar = job finding rate (% of those unemployment pool that find a job)
\
Two endogenous variables: employment E and unemployment U.
* E = total pool of employed
* U = total pool of unemployed
Two exogenous variables:
* s bar = job separation rate (% of those fired/separated)
* f bar = job finding rate (% of those unemployment pool that find a job)
6
New cards
Equation for the size of the labour force
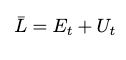
7
New cards
Equation for the change in unemployment
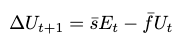
8
New cards
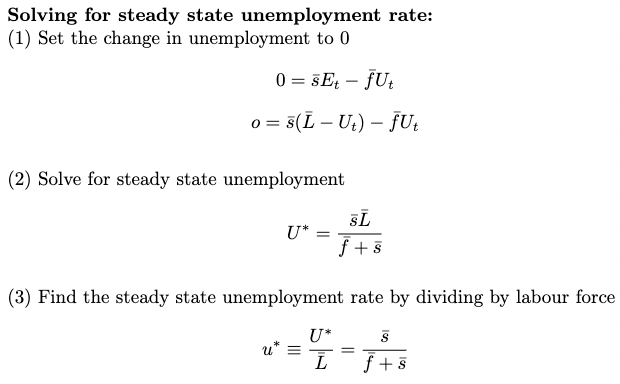
How do you find the steady state unemployment rate?
* Set the change in unemployment to 0
* Solve for steady state unemployment (U\*)
* Find the steady state unemployment rate by dividing by labour force (L bar)
* Solve for steady state unemployment (U\*)
* Find the steady state unemployment rate by dividing by labour force (L bar)
9
New cards
How can you alter the natural rate of unemployment/steady state unemployment?
* Change the job finding rate
* Change the job separation rate
* Change the job separation rate
10
New cards
What are the factors affecting job separation and matching?
* Structural, technological, and demographic change in the economy and workforce: stochastic volatility in demands and supplies
* Search costs: the costs of gathering information about job vacancies and labour availabilities
* Costs of mobility → geographical, housing, etc.
* Incentives for job search → affected by the tax/benefit system
* Employee protection regulation (affects finding rate as well as separation rate)
* Real wage rigidity
* Search costs: the costs of gathering information about job vacancies and labour availabilities
* Costs of mobility → geographical, housing, etc.
* Incentives for job search → affected by the tax/benefit system
* Employee protection regulation (affects finding rate as well as separation rate)
* Real wage rigidity
11
New cards
How high or low would the finding and separation rate be during a recession?
The finding rate would be low, and the separation rate would be high during a recession
12
New cards
What is real wage rigidity?
Real wage rigidity is when wages in an economy do not adjust quickly in response to changes in labor market conditions, such as changes in labor demand or labor productivity
13
New cards
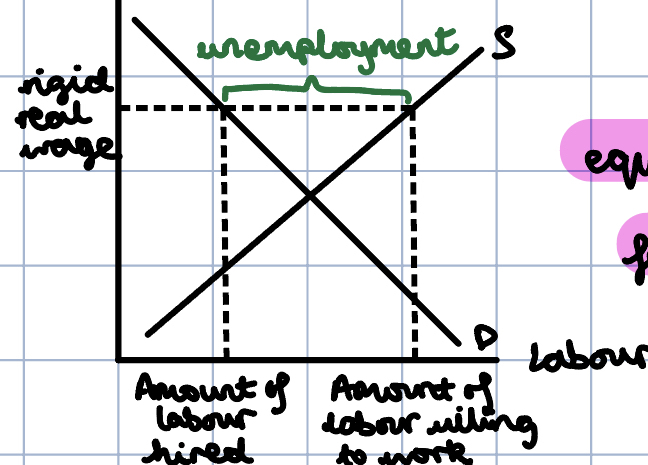
Draw a diagram illustrating rigid real wages when it is above its equilibrium. What does this mean?
This means that there are fewer jobs than there are willing workers
14
New cards
What are the causes of real wage rigidity
* Exercise of market power by incumbent workers through unions and collective bargaining
* Unduly high minimum wage laws
* ‘Efficiency wage’ reasons
* Unduly high minimum wage laws
* ‘Efficiency wage’ reasons
15
New cards
What is the efficiency wage theory?
This is the theory which suggests that paying higher wages to workers can lead to increased productivity and profitability for firms.
This is due to:
* Greater work effort and reduces ‘shirking’ → more output (‘moral hazard’)
* Attract better quality workers (more output) (‘adverse selection’)
* Less turnover → recruitment hiring and training cost saving
* Improve health of works (esp.in developing countries)
This is due to:
* Greater work effort and reduces ‘shirking’ → more output (‘moral hazard’)
* Attract better quality workers (more output) (‘adverse selection’)
* Less turnover → recruitment hiring and training cost saving
* Improve health of works (esp.in developing countries)
16
New cards
How might NRU change over time?
* Changes in factors affecting job separation and matching
* Changes in the causes of real wage rigidity
* Hysteresis: history dependence
* Still atrophy during periods of unemployment
* Loss of employability
* Long-term developemnet
* Changes in the causes of real wage rigidity
* Hysteresis: history dependence
* Still atrophy during periods of unemployment
* Loss of employability
* Long-term developemnet
17
New cards