Developmental Biology: Fertilization Processes and Mechanisms
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is fertilization?
The union of sex cells that begins the formation of a new organism.
What is polyspermy?
The entry of more than one sperm into the oocyte, which is prevented during fertilization.
What is pronuclear fusion?
Also known as amphimixis, it is the fusion of the genetic materials of the sperm and the oocyte.
What are the two phases of oocyte metabolism activation during fertilization?
Early metabolic responses and late metabolic responses.
What is external fertilization?
A type of fertilization that occurs outside the female body, characteristic of aquatic vertebrates like fish and amphibians.
What is the role of the jelly coat in external fertilization?
It secretes chemoattractants for species-specific recognition of sex cells in the aquatic environment.
What is internal fertilization?
A type of fertilization that occurs inside the female reproductive tract, characteristic of avians and mammals.
What is the acrosomal reaction?
The breakdown of the acrosomal cap of the sperm, releasing enzymes to penetrate the jelly coat and vitelline layer of the egg.
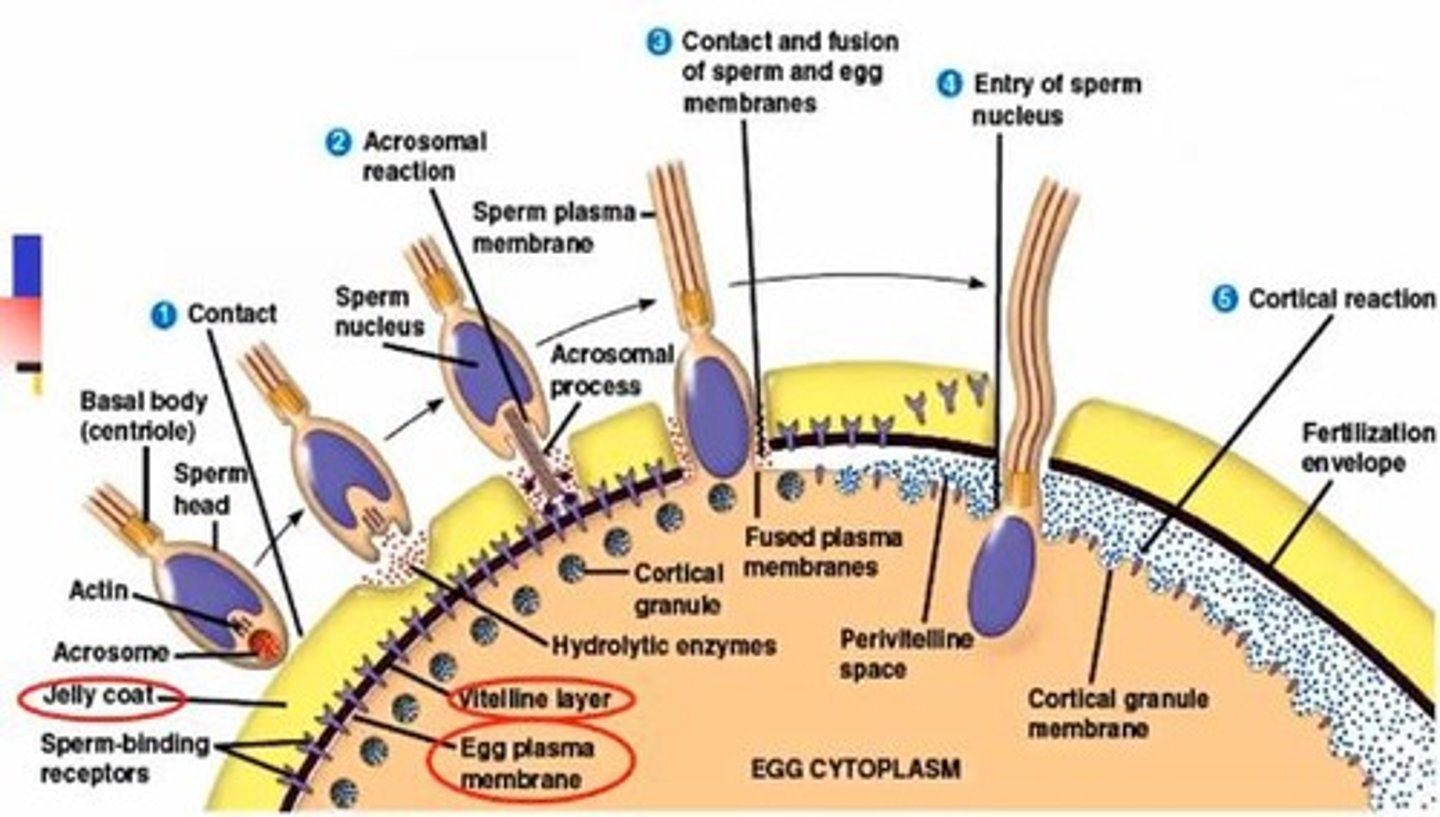
What is the fertilization cone?
A structure formed during the contact and fusion of sperm and egg membranes.
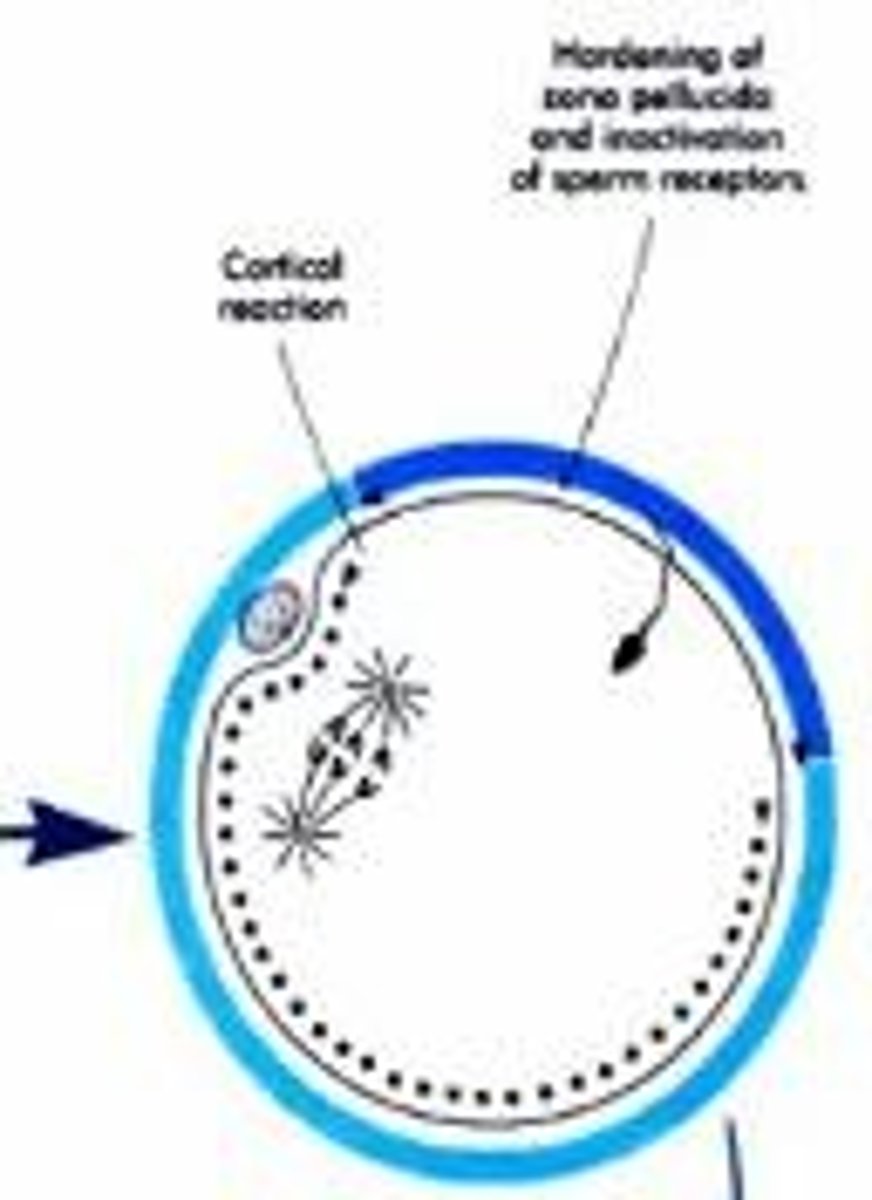
What is the cortical reaction?
The bursting of cortical granules that releases chemicals into the perivitelline space, contributing to the formation of the fertilization envelope.
What is the perivitelline space?
The space between the plasma membrane of the oocyte and the vitelline layer.
What is the fast block to polyspermy?
An electrical response that prevents additional sperm from entering the oocyte, occurring immediately after fertilization.
What is the slow block to polyspermy?
A chemical response that lasts longer and involves the formation of a fertilization membrane to prevent additional sperm entry.
What triggers the cortical reaction?
An increase in cytoplasmic calcium levels following sperm entry into the oocyte.
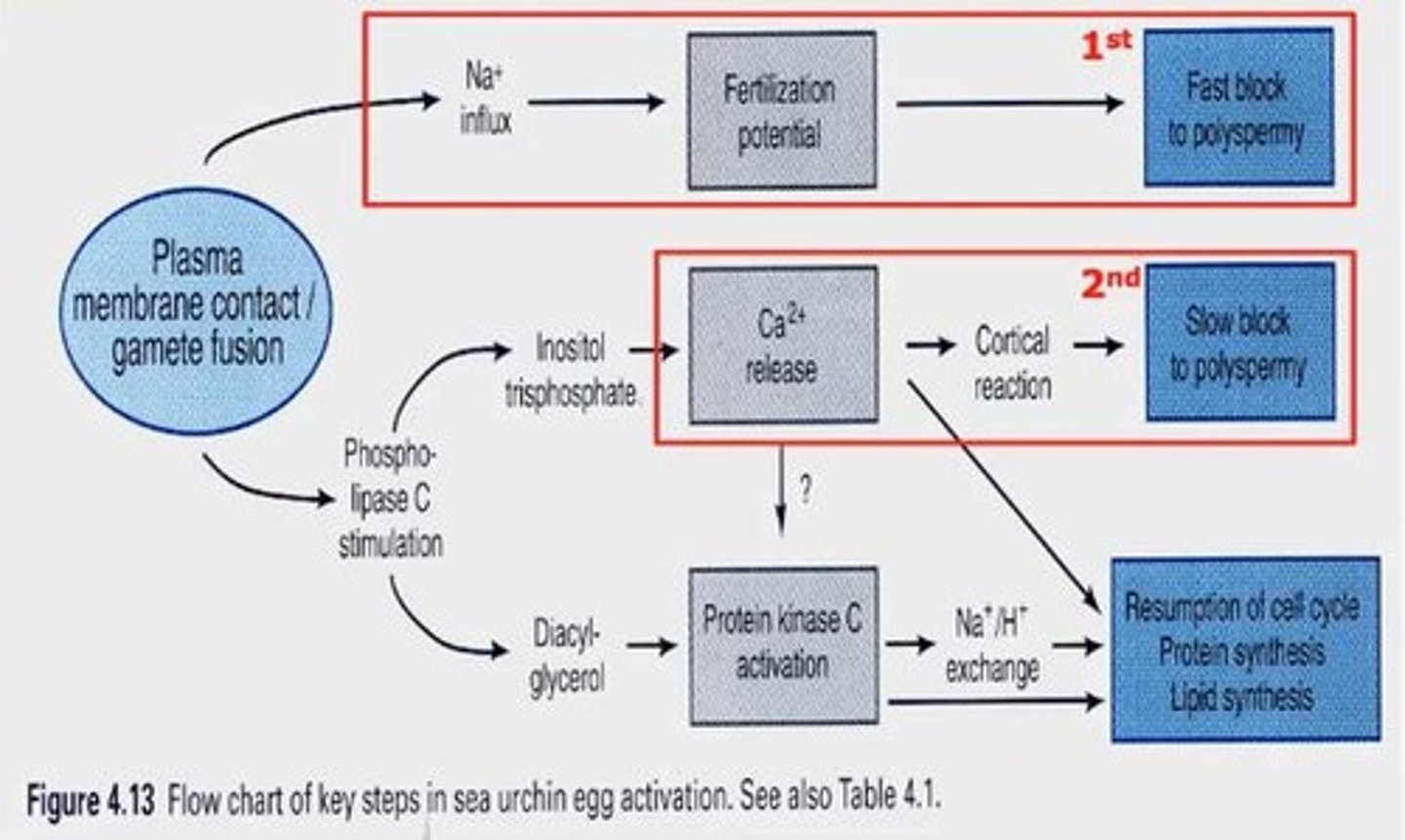
What happens during the regulation of sperm entry into the oocyte?
The first and second blocks to polyspermy occur, activating the oocyte and allowing for genetic material fusion.
What is the significance of the zona pellucida?
It is a glycoprotein layer surrounding the mammalian oocyte that plays a role in sperm binding and fertilization.
What is the role of proteases in fertilization?
They break down molecular bonds between the vitelline envelope and the plasma membrane during the cortical reaction.
What is the function of mucopolysaccharides in fertilization?
They create osmotic gradients that cause water to rush between the vitelline envelope and the plasma membrane.
What is the fertilization potential?
The rapid change in membrane potential from -70 mV to +10 mV following sperm activation.
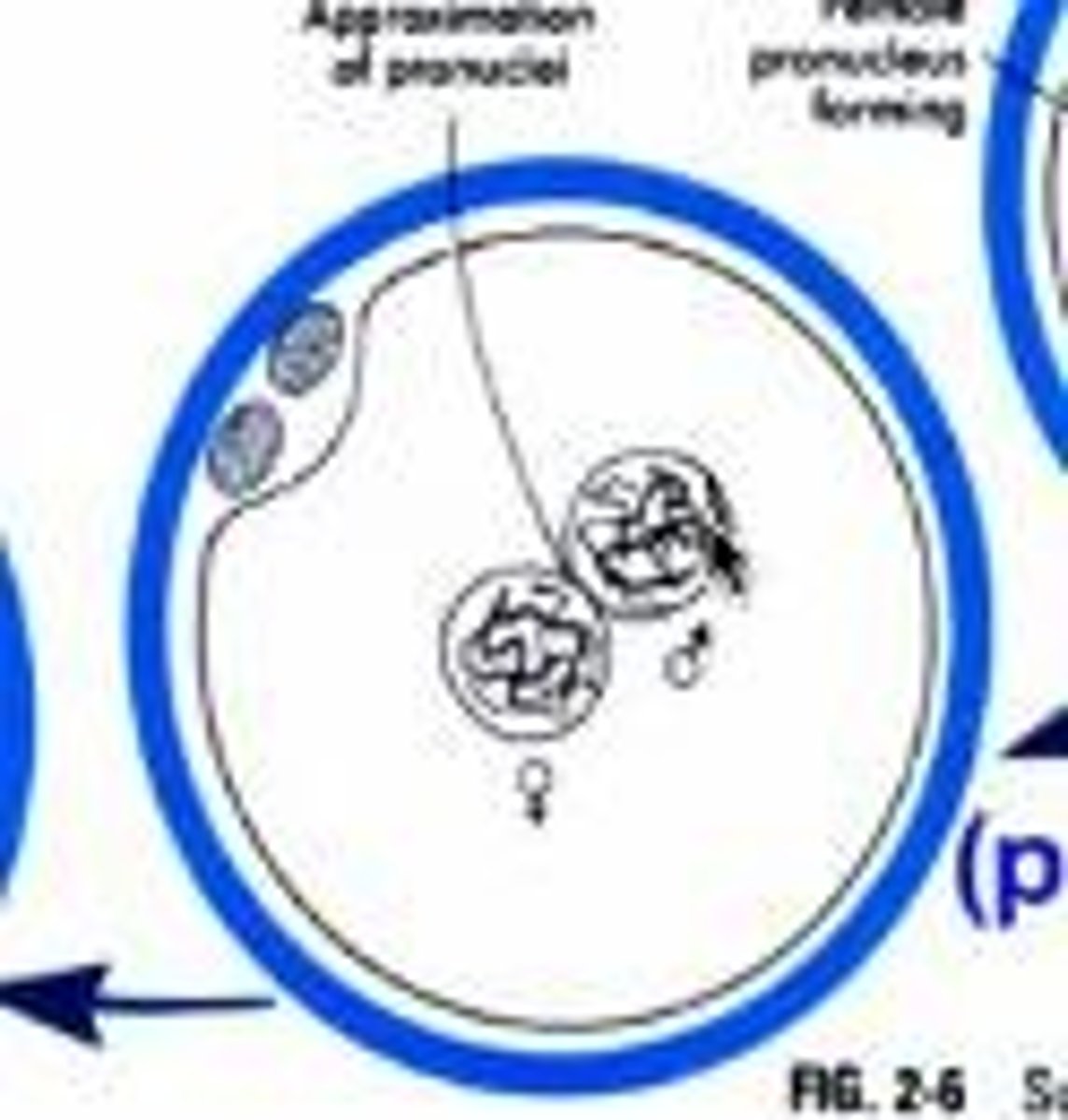
What occurs during the fusion of genetic materials?
The male and female pronuclei meet to form the zygote nucleus, completing fertilization.
What is the role of calcium ions in fertilization?
They trigger the cortical reaction and the activation of the oocyte, facilitating fertilization processes.
What is the significance of the studies by the Hertwig Brothers?
They were the first to observe fertilization using sea urchins as model organisms.
What happens to the oocyte during fertilization?
It becomes activated, lifting the metaphase II arrest and releasing the second polar body.
What is the function of peroxidases during fertilization?
They harden the fertilization membrane by cross-linking proteins, contributing to the slow block to polyspermy.
What is the cortical reaction in fertilization?
A mechanism that hardens the zona pellucida to prevent polyspermy, similar to the fertilization envelope in sea urchins.
What activates Phospholipase C during fertilization?
The fusion of the sex cells' plasma membranes.
What are the products of Phospholipase C activation?
Inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG).
What role does IP3 play in fertilization?
It causes the release of calcium ions, activating calcium-dependent kinases.
What is the function of NAD+ kinase activated by calcium?
It phosphorylates NAD+ to become NADP+.
What happens to the male sperm head after fertilization?
It undergoes decondensation and nuclear breakdown to form the new male pronucleus.
What is the significance of fertilization for the oocyte?
It triggers rapid processes like DNA replication and synthesis of proteins necessary for cell cycle regulation.
What is the role of lipids in fertilized oocytes?
They are necessary for the formation of plasma membranes of newly formed cells during cleavage division.
What is the fertilization site in mammals?
The ampulla of the fallopian tube.
What is insemination?
The process of depositing sperm into the female reproductive tract.
How does the female reproductive tract facilitate sperm transport?
Through changes in cervical mucus and the buffering capacity of semen that neutralizes vaginal acidity.
What is capacitation in sperm transport?
A conditioning period for sperm that involves the removal of the glycoprotein coat covering the acrosome.
What enzymes are released by the acrosomal cap during fertilization?
Hyaluronidase and proteolytic enzymes that help digest the zona pellucida.
What is the typical duration for sperm capacitation in humans?
5-8 hours.
What are the accomplishments of fertilization?
Completion of the second meiotic block, restoration of diploid chromosome number, determination of embryo sex, and metabolic activation of the fertilized oocyte.
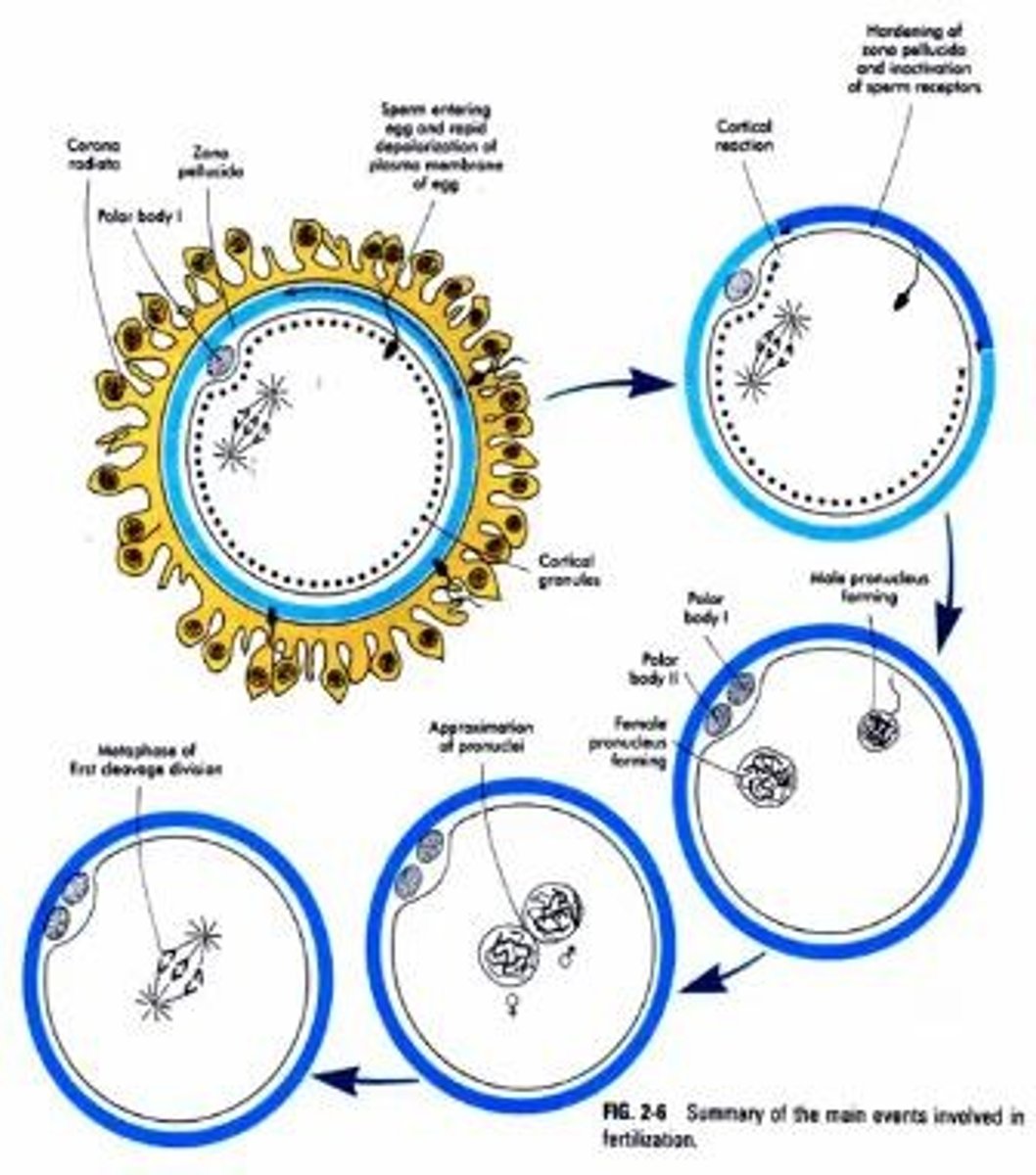
What initiates the fast-paced action of the fertilized oocyte?
Metabolic activation following fertilization.
What triggers the release of calcium ions in amphibian fertilization?
Fertilization lifts the metaphase II arrest, allowing calcium ions to bind with calmodulin.
What is the role of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in amphibians?
It activates processes that lead to the degradation of the cytostatic factor and completion of meiosis.
What happens to polar bodies during fertilization in amphibians?
They are released as part of the completion of fertilization.
What is the time frame for the fertilized oocyte to reach the uterus?
Approximately 6-7 days after fertilization.
What is the importance of the hyaline layer in fertilization?
It is a characteristic of some mammals that aids in the fertilization process.
What cellular responses are stimulated by DAG during fertilization?
Protein synthesis, DNA replication, and cytoplasmic movements of morphogenetic material.
What is the significance of the ampulla in fertilization?
It is the final site where sperm and oocyte meet for fertilization.
What is the role of cyclins and CDKs in fertilization?
They regulate the cell cycle and are synthesized rapidly after fertilization.
What happens to the oocyte during the cleavage stage?
It undergoes division and develops from a zygote to a multi-cell stage.