17. BIO110 LO17: Digestive System
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
List the sequence of organs of the digestive system
From the mouth to the anus
how else can we describe the digestive system
alimentary canal/GI tract
Bolus
Ball of food moved involuntarily from the mouth to stomach
Chyme
Food is mixed with gastric juices and broken down into semisolid form
Jaundice
Yellowish skin discoloration caused by bile buildup
Ulcer
Lesions that destroy stomach or intestine lining; can cause serious complications
Diarrhea
Stools or fecal material become more fluid
Constipation
Stools or fecal material become more solid
List and describe the four layers of the wall of the digestive tract from inside to outside.
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis
Serosa
Define motility. provide an example
A number of GI movements resulting from muscular contraction
ex. Peristalsis: Wavelike movement pushes food down the tract
Define secretion
Release of digestive juices and hormones that facilitate digestion
Define Regulation
Neural, hormonal, and other mechanisms that regulate digestive activity
Name three functions of the Mucosa layer.
Type varies depending on GI location (tough and stratified or delicate and simple epithelium)
Secretion of mucus, digestive enzymes and hormones
Absorbing the end products of digestion and Protection against pathogens
Describe the composition of the Submucosa layer.
Connective tissue layer that contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerves,
and lots of elastic fibres that allows the digestive tube to stretch and recoil.
What are the two main actions performed by the Muscularis layer?
Segmentation: Mixes & churns food
Peristalsis
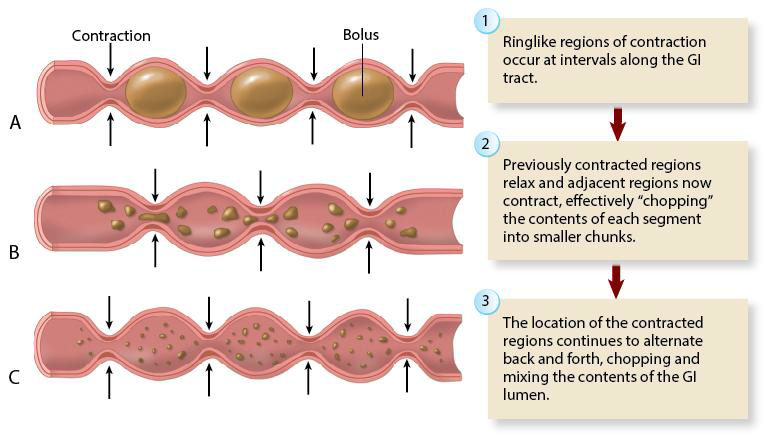
What are the typical layers of the Muscularis, dependent on the location in the GI tract?
Inner circular (lots at sphincters) and Outer longitudinal
Oblique layer sometimes present in addition to the circular and longitudinal layers
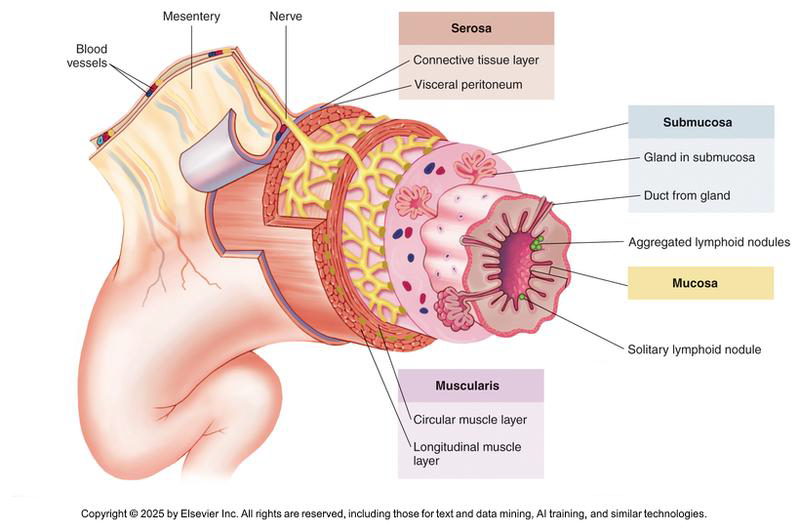
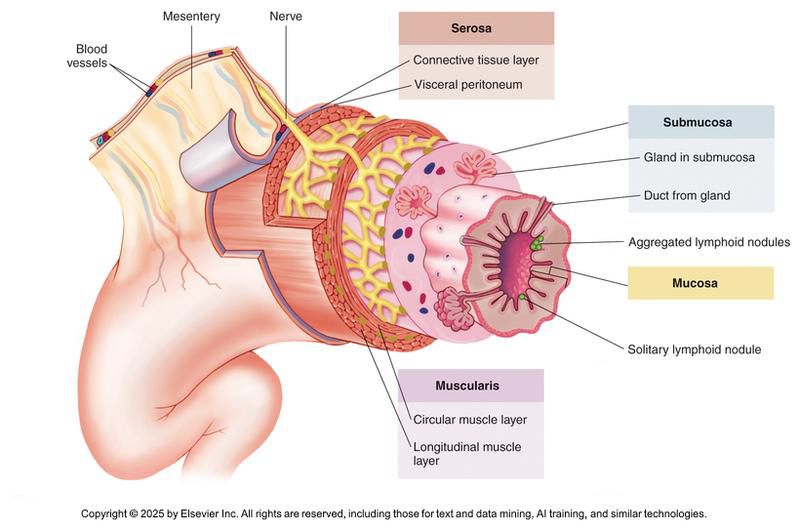
Describe the Serosa layer.++
Protective outermost layer that covers outside of abdominal organs
Attaches digestive tract to wall of abdominopelvic cavity by forming folds called mesenteries
composed of visceral and parietal peritoneum in the abdominal cavity?
What is the mouth also known as?
Hollow ‘chamber’ or ‘oral cavity’
Name the three parts of the mouth.
Roof, Floor, Walls
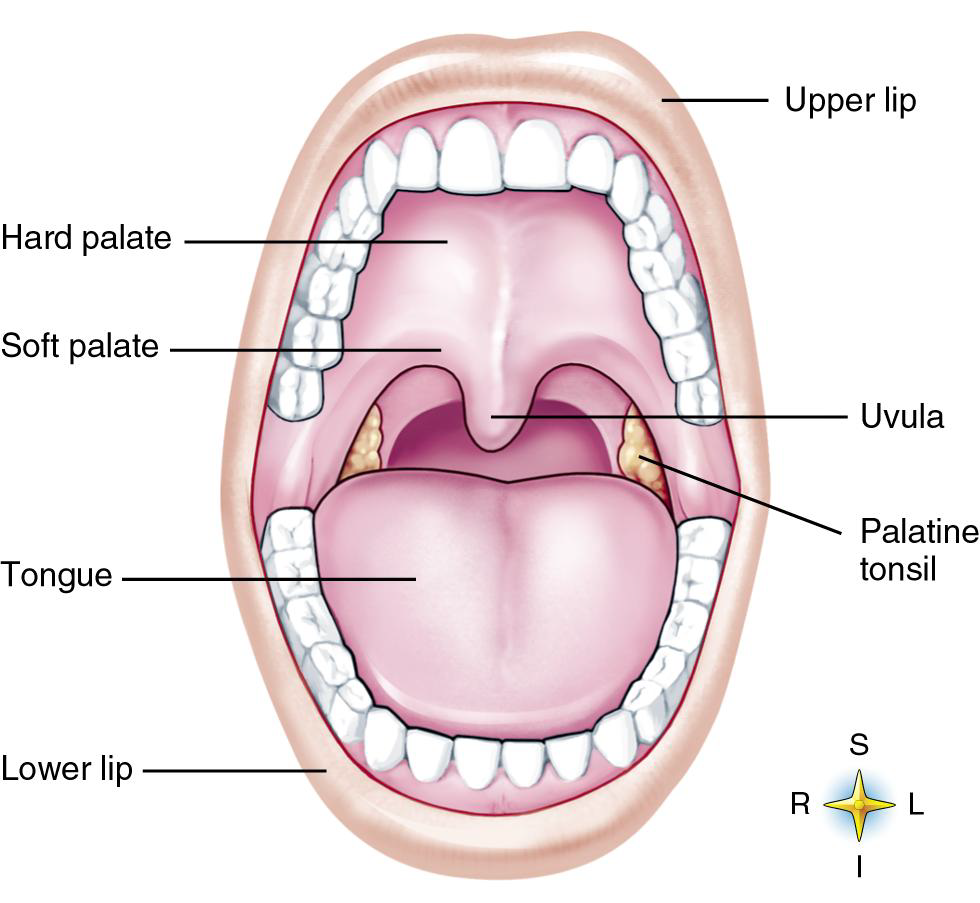
What structures form the Roof of the mouth?
Hard palate (maxillary & palatine bones) and Soft palate (arch-shaped muscle)
separates mouth from pharynx
Prevent food & liquid from entering nasal cavities
What is the name of the projection of the soft palate? What is its function
Uvula
Prevent food & liquid from entering nasal cavities
What forms the Floor of the mouth?
Tongue and its muscles
How is the tongue anchored to the floor of the mouth?
By the frenulum
What are the small nipple-like projections found on the tongue?
Papillae
Where are taste buds found?
In many papillae
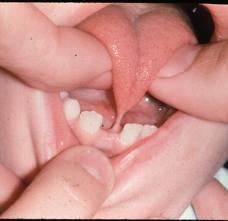
What is Ankyloglossia commonly called, and what causes it?
“Tongue tied”; The frenulum is unusually short and thick
May recede on its own; surgery is an option
What can Ankyloglossia affect?
Feeding/eating, swallowing, oral hygiene/structure, speech
What forms the lateral walls of the mouth?
The cheeks (buccinator muscle)
Define Gingivitis.
Inflammation of the gums, generally limited to superficial gum tissue
Define Periodontitis.
Inflammation of periodontal membrane & supporting tissues (including bone around teeth)
What condition can Periodontitis lead to?
Loose teeth/loss of teeth
Define Dental Caries and list its causes.
Disease of enamel, dentin and cementum, caused by food debris, bacteria & plaque
How many Incisors are there and what is their function?
8; Sharp edge; cutting function
What are the alternate names for Canines, how many are there, and what is their function?
Cuspids/eye teeth; 4; Pointy; piercing/tearing function
What are Premolars also known as, how many are there, and what is their function?
Bicuspids; 8; Flat surface; grinding/crushing function
How many Molars are there and what is their function?
12 (toughest, strong & wide); Function is grinding/crushing
How many Deciduous teeth (baby teeth) are there, and what is the average age for the first eruption?
20 teeth; 6 months
Which teeth are cut first among deciduous teeth?
8 incisors
Which type of teeth are absent in a complete set of deciduous teeth?
Premolars
How many Permanent teeth (adult teeth) are there?
32 teeth
What is the overall function of the Salivary Glands?
Secrete saliva (salivary amylase
List the three main Salivary Glands.
Parotid glands (largest), Submandibular glands, Sublingual glands
Where are the Parotid glands located?
Bottom of ear at jaw angle
Where are the Submandibular glands located?
Middle of mandible
Where are the Sublingual glands located?
Anterior to submandibular glands ('below tongue)
Describe the dual function of the Pharynx.
Digestion (food passes through on its way to the stomach) & respiration (air passes through on its way to the lungs)
What structure connects the pharynx with the stomach?
Esophagus
What is the length of the Esophagus, and how is food conducted through it?
25cm long; Via peristaltic action
Define Peristalsis.
Muscle contraction that squeezes food along the digestive tract
What is the location and function of the Stomach?
In the upper abdominal cavity (just under diaphragm); Temporary ‘storage’ sac for chewed food, and where chemical digestion of protein begins
What is the Cardiac Sphincter also known as, and what is its function?
Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES); Prevents stomach contents from refluxing back into the esophagus
What is a Hiatal Hernia caused by, and what can it lead to?
Weakening of the ‘hiatus’ (opening in the diaphragm for the esophagus); Can lead to GERD
List the three parts of the stomach.
Fundus (enlarged portion at top), Body (central part), Pylorus (lower part)
What muscle closes the opening of the pylorus into the duodenum?
Pyloric sphincter muscle
What are the three layers of smooth muscle found in the stomach wall?
Oblique (innermost, unique), Circular (middle), Longitudinal (outer)
What are the folds of the mucous membrane in an empty stomach called?
Rugae
How long does food typically stay in the stomach?
Anywhere from 30 minutes to 2 hours
What structure does food pass through before entering the small intestine?
Pyloric sphincter
What is considered the main digestive organ?
Small Intestine
What structure marks the end of the small intestine?
Ileocecal valve
List the three divisions of the Small Intestine.
Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum
What are the multiple circular folds in the small intestine lining called?
Plicae
What are the Plicae covered with, and what is their function?
Villi; Adapted for nutrient absorption
What structures do the Villi contain for nutrient absorption?
Blood capillaries and lymph lacteals
What covers the Villi?
Microvilli
What is the Liver described as, and where is it located?
Largest gland in the body; Fills the upper right section of the abdominal cavity and extends into the left side
What does the Liver secrete, and what is the function of this secretion?
Bile (cholesterol
What structure concentrates and stores bile?
Gallbladder
What ducts drain bile from the liver?
Hepatic ducts
What duct allows bile to enter and leave the Gallbladder?
Cystic duct
What duct drains bile into the duodenum, and what happens if it is blocked?
Common bile duct; Blockage (e.g. stone) leads to jaundice
What initiates the release of bile from the Gallbladder?
The presence of fat in chyme
What hormone stimulates the contraction of the Gallbladder?
Cholecystokinin (CCK), released from the duodenum’s intestinal mucosa
Where is the Pancreas located?
Behind the stomach, inside the ‘C’ of the duodenum
What is the Exocrine function of the Pancreas?
Secretes pancreatic juice into pancreatic ducts
Why is pancreatic juice considered the most important digestive juice?
It contains enzymes to digest all 3 macronutrients
What substance does the Pancreas secrete to buffer the acidic gastric juice entering the duodenum?
Alkaline sodium bicarbonate
What are the endocrine cells of the Pancreas called, and what hormones do they secrete?
Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans); Glucagon and Insulin
List the main functions of the Large Intestine lining.
Absorption of water, salts, vitamins
Does the Large Intestine have villi?
No
What enters the Large Intestine after passing through the ileo-cecal valve?
Undigested food material
What happens to semi-solid chyme in the Large Intestine to form feces?
Water and salts are reabsorbed, causing it to become more solid
Name two vitamins synthesized by bacteria in the Large Intestine.
Vitamin K and some of the B vitamins (e.g. B12)
How long does it take for fecal matter to pass through the Large Intestine?
3 to 5 days
Define Constipation.
Prolonged time in the L.I. leading to more water being absorbed, causing feces to become more solid and harder
Define Diarrhea.
Fecal matter rushes through the L.I. before the water is absorbed
List the main divisions of the Large Intestine.
Cecum, Colon (Ascending-transverse-descending colon → Sigmoid colon), Anus
What is the Cecum?
Pouch-like structure at the Ileocecal valve
What is the Appendix described as?
“Vermiform” (worm shaped) blind tube off the cecum
What kind of tissue is the Appendix composed of?
Lymphatic tissue
What is the Peritoneum?
Serous membrane lining the abdominal cavity and covering abdominal organs
What are the two extensions of the Peritoneum?
Mesentery and Greater omentum
Describe the Mesentery.
Shaped like a pleated fan; extension of parietal peritoneum; attaches most of the small intestine to the posterior abdominal wall
Describe the Greater omentum.
Referred to as the ‘lace apron’; pouch like extension of the visceral peritoneum; hangs down from the lower edge of the stomach and transverse colon over the intestines
Define Digestion.
Process by which foods are altered so that they can be absorbed and used by cells
Name three actions involved in Mechanical digestion.
Mastication, Deglutition (swallowing), Peristalsis/churning/movement
What agents are responsible for Chemical digestion?
Digestive enzymes to Breaks macronutrients down into the smallest compounds
What happens to digestive enzymes during the chemical digestion process?
They are not changed or used up
What suffix typically indicates an enzyme?
‘ase’