TFN MIDTERMS WEEK 5
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
LYDIA HALL
- She was born in New York City on September 21, 1906.
- She graduated from York Hospital School of Nursing in Pennsylvania.
- She took her BSN and Master of Arts from Teacher’s College, Columbia University.
- Died on February 27, 1969, of heart disease in Queens Hospital of New York.
CARE, CORE, AND CURE THEORY
- It was developed in the late 1960s is one of the well-known nursing theories that explains the roles of the nurse in patient care. It emphasizes that nursing is not just about treating disease, but also about caring for the whole person.
- The theory highlights that true healing requires balance between body, mind, and medical treatment.
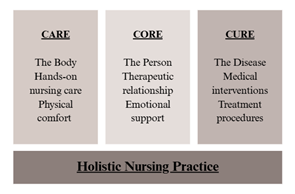
CARE
- The “nurturing” components of nursing.
- It involves hands-on bodily care of the patient, such as bathing, feeding, turning, and providing comfort.
- Nurse’s role in comfort and daily needs.
- Example:
o A nurse is caring for a post-stroke patient who has difficulty moving. The nurse assists with bathing, turning to prevent bedsores, and feeding to maintain nutrition.
o Meeting the patient’s basic needs.
CORE
- This is the “therapeutic use of self” in the nurse-patient relationship.
- It focuses on helping the patient explore feelings, set goals, and grow toward self-actualization.
- The nurse acts as a counselor or facilitator.
- Example:
o A patient recently diagnosed with cancer feels hopeless and anxious. The nurse sits down, listens actively, acknowledges the patient’s fears, and encourages them to express feelings.
o Emotional support & relationship.
CURE
- This relates to the medical and technical aspect of patient care, often carried out by physicians.
- It involves treatment of disease through interventions such as surgery, medication & therapies.
- Nurses participate by assisting and collaborating with the medical team.
- Example:
o A patient with pneumonia is prescribed IV antibiotics. The nurse administers, monitors for side effects, and check the patient’s oxygen saturation, collaborating with the physician if changes are needed.
o Medical treatment & procedures.
CARE
Hands-on care | Meets basic needs (bathing, feeding, comfort) | Assisting a post-stroke patient with hygiene & feeding |
CORE
Therapeutic relationship | Provides emotional support, counseling | Listening to and encouraging a cancer patient |
CURE
Medical/technical care | Administers treatment, collaborates with doctors | Giving IV antibiotics to a pneumonia patient |
FAYE GLENN ABDELLAH
- Born on March 13, 1919, in New York City.
- Graduated from Fitkin Memorial Hospital School of Nursing, New Jersey in 1942.
- She took her master’s degree in Physiology in 1947 and her doctorate degree in Education in 1955.
- Died on February 24, 2017.
21 NURSING PROBLEMS THEORY
- Abdellah’s model describes concerns of nursing rather than a theory describing relationships among phenomena. Her theory provides a foundation for determining and organizing nursing care (McEwen, 2007)
GOOD HYGIENE AND PHYSICAL COMFORT
Maintain good hygiene and physical comfort | Giving a bedridden patient a bed bath to prevent infections and keep them comfortable |
PROMOTE OPTIMAL ACTIVITY
Promote optimal activity (exercise, rest, sleep) | Encouraging a post-surgery patient to walk short distances to prevent blood clots |
PROMOTE SAFETY
Promote safety (prevent accidents, injuries, infections) | Raising bedside rails for an elderly patient at risk of falling |
MAINTAIN GOOD BODY MECHANICS
Maintain good body mechanics & prevent deformities | Repositioning a stroke patient every 2 hours to prevent bedsores and contractures |
MAINTAIN OXYGEN SUPPLY
Maintain oxygen supply to body cells | Administering oxygen therapy to a patient with pneumonia |
MAINTAIN NUTRITION
Maintain nutrition (adequate food & fluids) | Assisting a patient with swallowing difficulties to eat soft foods safely |
MAINTAIN ELIMINATION
Maintain elimination (bowel & bladder) | Assisting a patient with a catheter and monitoring urine output |
MAINTAIN FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE BALANCE
Maintain fluid & electrolyte balance | Starting IV fluids for a dehydrated patient (with doctor’s order) |
RECOGNIZE PHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSE
Recognize physiological responses to disease | Monitoring fever and vital signs in a patient with infection |
MAINTAINS REGULATORY MECHANISMS
Maintain regulatory mechanisms (temperature, circulation) | Using blankets for a hypothermic patient to maintain body temperature |
ACCEPT EXPRESSIONS OF FEELINGS
Identify & accept expressions of feelings (positive & negative) | Allowing a cancer patient to cry and express fear about chemotherapy |
INTERRELATEDNESS OF EMOTION AND ILLNESS
Identify interrelatedness of emotions & illness | Supporting a hypertensive patient who feels anxious, since stress worsens BP |
MAINTAIN GOOD COMMUNICATION
Maintain good communication (verbal & non-verbal) | Using pictures/gestures to communicate with a patient who has lost their voice |
PROMOTE INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIP
Promote interpersonal relationships | Encouraging family visits for a patient feeling lonely in the hospital |
FACILITATE SPIRITUAL GOALS
Facilitate spiritual goals | Allowing a patient to pray or arranging a chaplain visit before surgery |
MAINTAIN THERAPEUTIC ENVIRONMENT
Maintain therapeutic environment | Reducing noise in the ward so patients can rest properly |
FACILITATE SELF AWARENESS
Facilitate self-awareness | Helping a teenager with diabetes understand self-care responsibilities |
ACCEPT OPTIMUM GOALS
Accept optimum goals despite limitations | Teaching a spinal injury patient how to use a wheelchair for independence |
USE COMMUNITY RESOURCES
Use community resources | Referring a patient with TB to a local health center for continuous treatment |
UNDERSTAND SOCIAL PROBLEM IN ILLNESS
Understand social problems in illness | Identifying that a patient’s malnutrition is linked to poverty and lack of food access |
MARASMUS
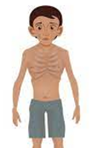 |
Total calorie deficiency (protein + energy) |
Infants <1 year (but can occur any age with severe starvation) |
Severe wasting, very thin, “skin and bones” |
Absent |
Severe muscle and fat wasting |
Dry, wrinkled skin |
Alert but hungry, growth failure |
KWASHIORKOR
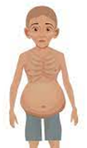 |
Protein deficiency (with adequate calories) |
Usually after weaning (1–3 years) |
Edematous, swollen belly, thin limbs |
Present (due to low albumin) |
Muscle wasting masked by edema |
Hair changes (sparse, reddish), skin lesions |
Irritability, enlarged fatty liver |
VIRGINIA HENDERSON
- City, Missouri.
- She is known as the “First Lady of Nursing” and the “Nightingale of Modern Nursing”
- She was the first chairman of the International Nursing Index Editorial Advisory Committee.
- Died on March 19, 1996, at a hospice in Branford, Connecticut.
NURSING NEED THEORY
- Nursing is primarily about assisting individuals— sick or well—in performing activities that contribute to health, recovery, or peaceful death, activities that they would do unaided if they had the necessary strength, will, or knowledge.
BREATHE NORMALLY
Monitor oxygen saturation, encourage deep-breathing exercises |
EAT AND DRINK ADEQUATELY
Maintain IV fluids (NPO), introduce clear fluids once bowel sounds return |
ELIMINATE WASTES
Monitor urine output (catheter), check for first bowel movement post-surgery |
MOVE AND MAINTAIN POSTURE
Assist to sit at bed’s edge, ambulate gradually to prevent blood clots |
SLEEP AND REST
Provide quiet environment, give pain medication for comfort |
SELECT SUITABLE CLOTHES
Help change into clean gown for comfort |
MAINTAIN BODY TEMPERATURE
Monitor for fever, provide light blanket, manage chills/sweats |
KEEP BODY CLEAN AND GROOMED
Give partial bed bath while incision heals |
AVOID ENVIRONMENTAL DANGERS
Keep side rails up, secure IV & catheter lines |
COMMUNICATE WITH OTHERS
Encourage expression of pain, fears, and recovery concerns |
WORSHIP ACCORDING TO FAITH
Provide privacy and quiet time for prayer |
WORK AND ACCOMPLISHMENT
Engage in simple self-care (e.g., brushing teeth) |
PLAY AND RECREATION
Allow use of phone, radio, or TV for relaxation |
LEARN AND DISCOVER
Educate on wound care, breathing exercises, ambulation importance |