K101 exam 4
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
transcription
DNA directed synthesis of RNA; happens inside the nucleus of the cell
RNA processing
introns are cut out of the strand and exons are spliced together and end caps are placed on the strand to create mRNA; this occurs inside the nucleus
amino acid activation
the initial stage of protein synthesis in which amino acids are attached to transfer RNA molecules; this occurs in the cytoplasm
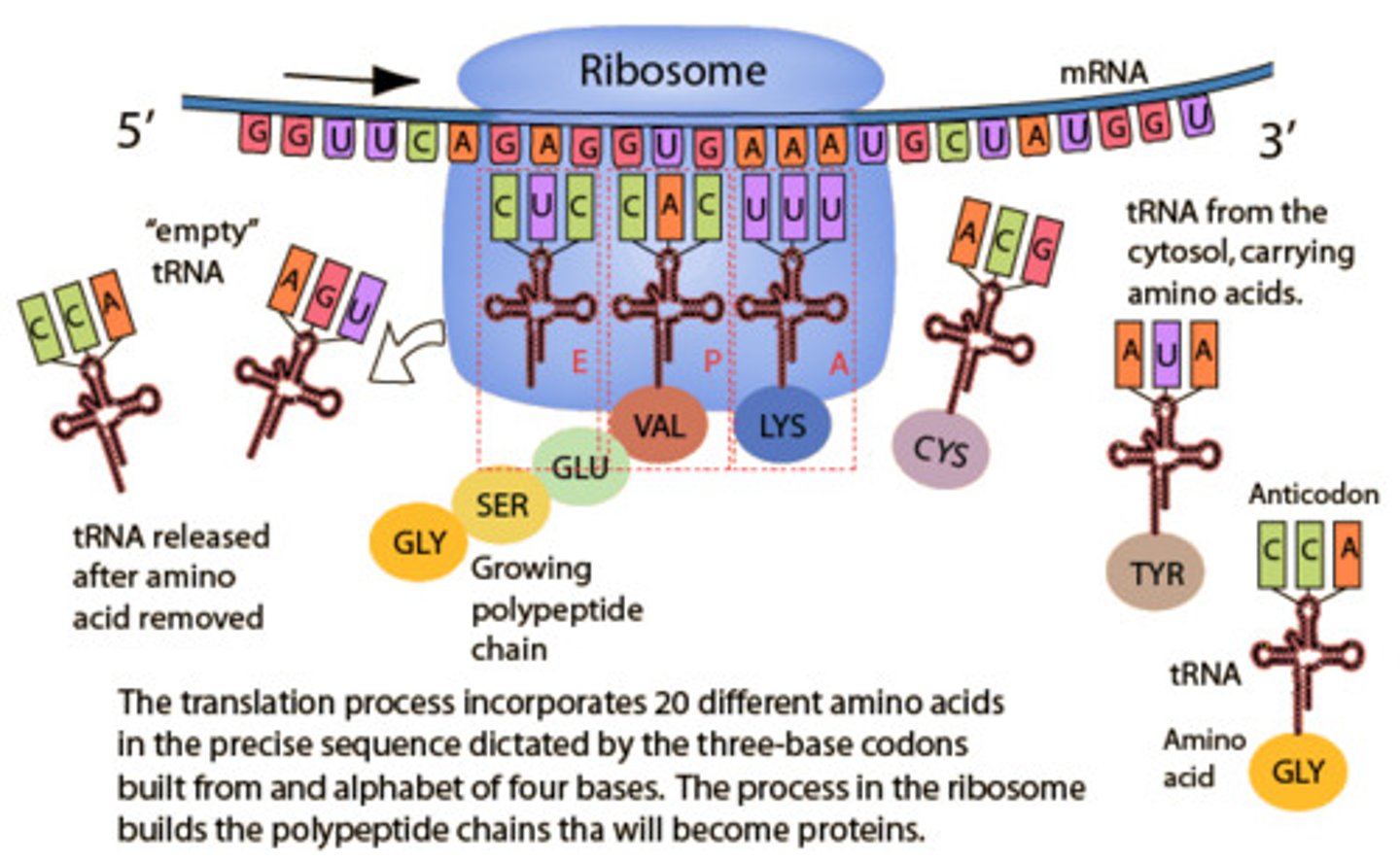
translation
RNA directed synthesis of a polypeptide (protein); occurs in the cytoplasm
RNA structure
1) ribose has two OH groups
2) phosphate at the 5' end
3) bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
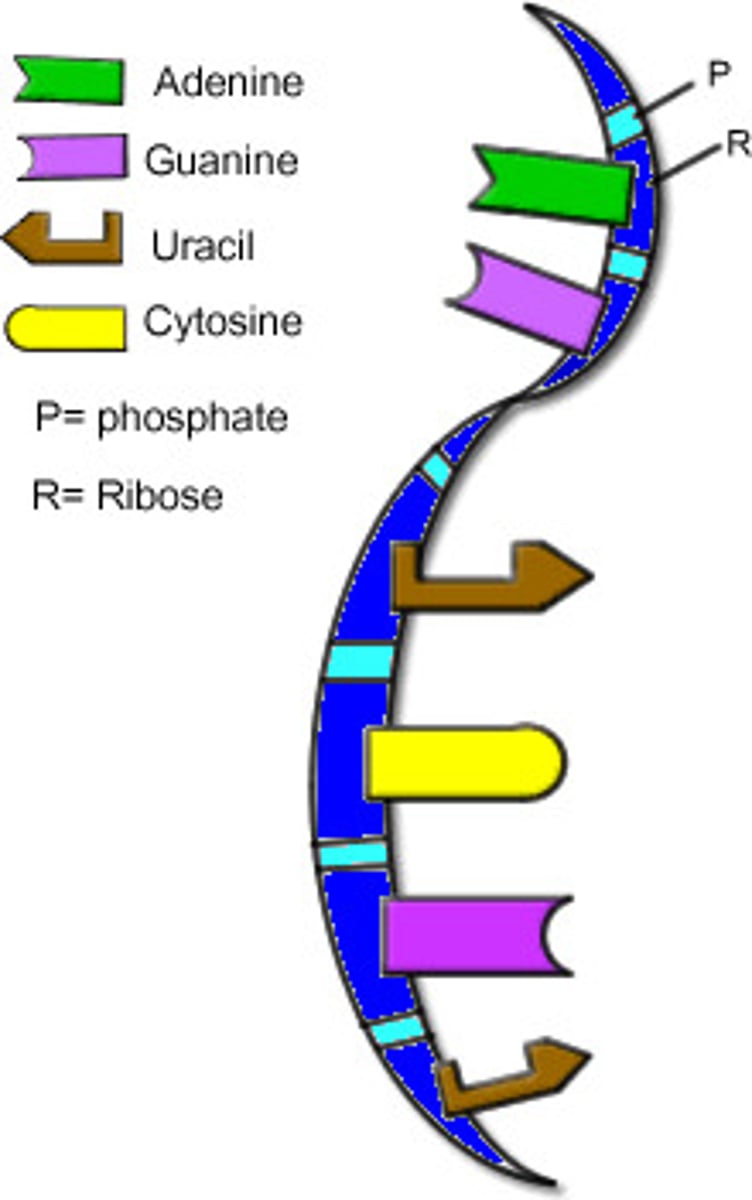
RNA typically...
functions as a single stranded polymer
which bases a pyrimidines
cytosine, uracil, thymine
which bases a purines
adenine, guanine
mRNA
provides genetic instructions to make 1 or more related proteins
tRNA
70-80 nt RNAs that carry amino acids at their attachment sites and carry an anticodon that binds to the mRNA strand during translation
rRNA
forms the body of a ribosome; this is the physical link between mRNA and tRNA
steps of transcription and translation
1) DNA of one gene unwinds
2) RNA polymerase transcribes a copy of DNA to RNA
3) RNA carries info in sets of 3 bases called a codon that specifies amino acids
4) codon gets read and translated to an amino acid and proteins in the ribosome
5) a protein is specified!
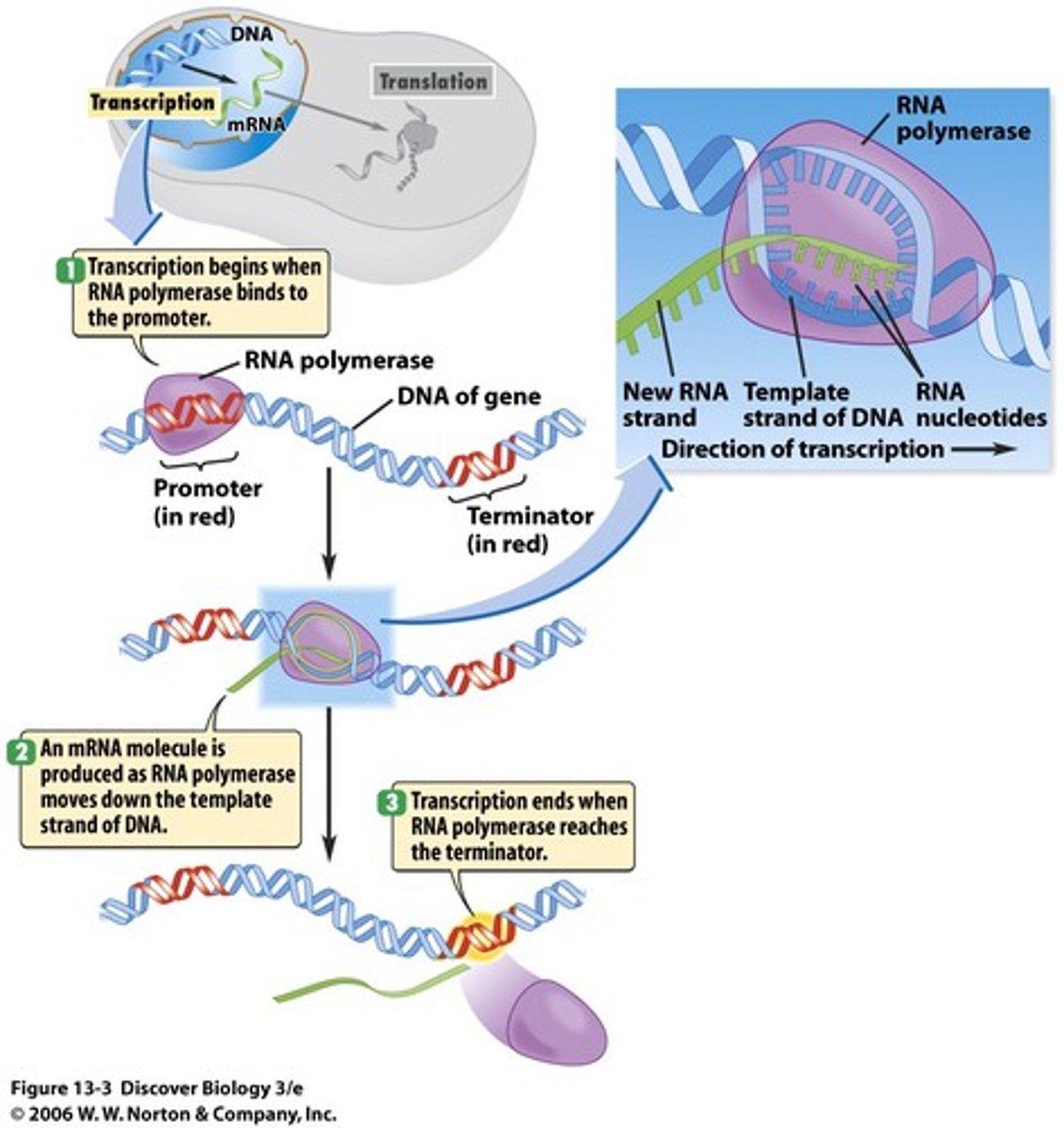
3 main steps of transcription
1) initiation
2) elongation
3) termination
initiation
RNA polymerase and other proteins bind to the promoter at the TATA box and unwind the DNA
elongation
RNA polymerase moves 5' to 3' elongating the RNA transcript
termenation
RNA polymerase hits a termination signal and and pops off; now there is a complete separate RNA strand called mRNA
transcription
translation
codon chart
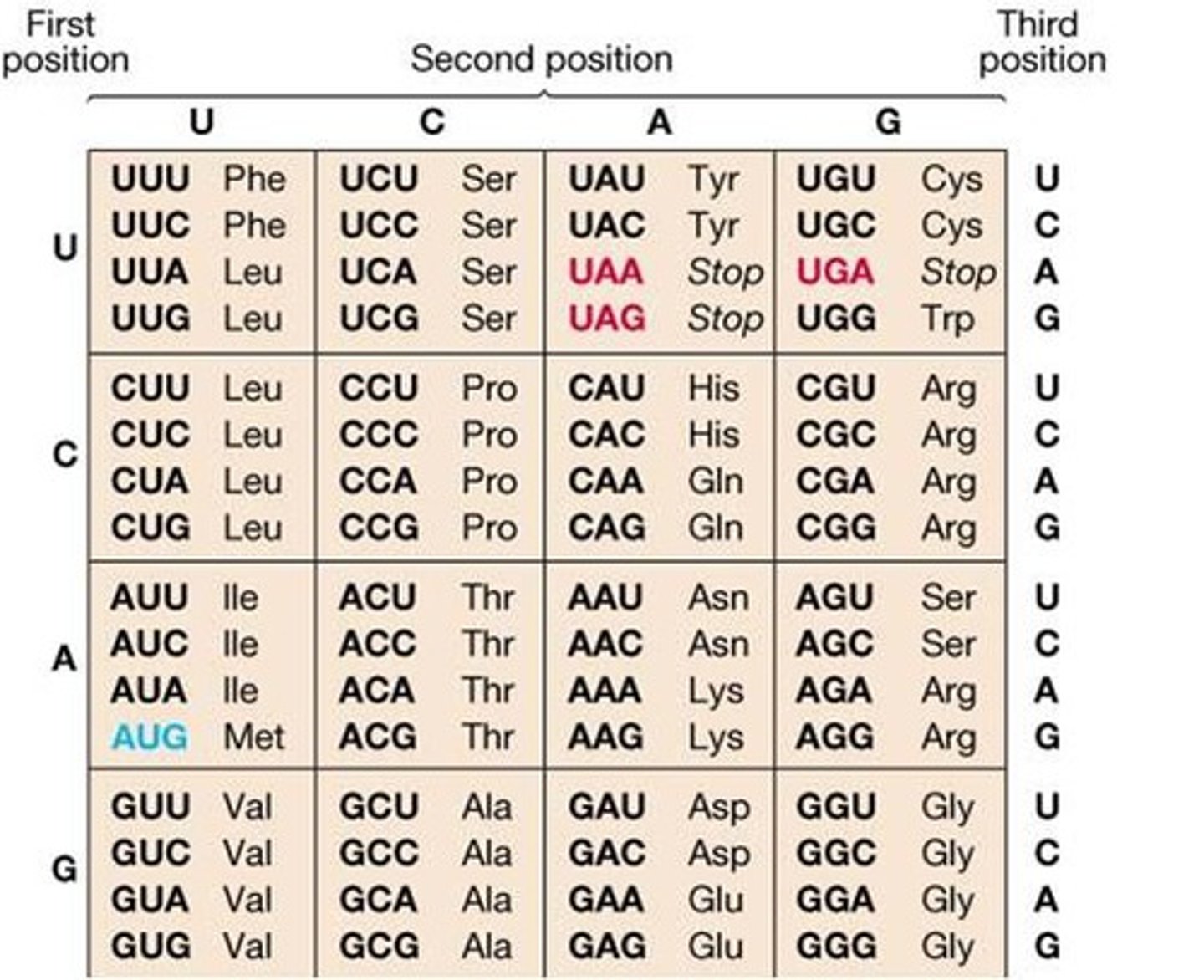
the genetic code is...
universal and redundant
start codon
AUG codes for methyl
tRNA looks like
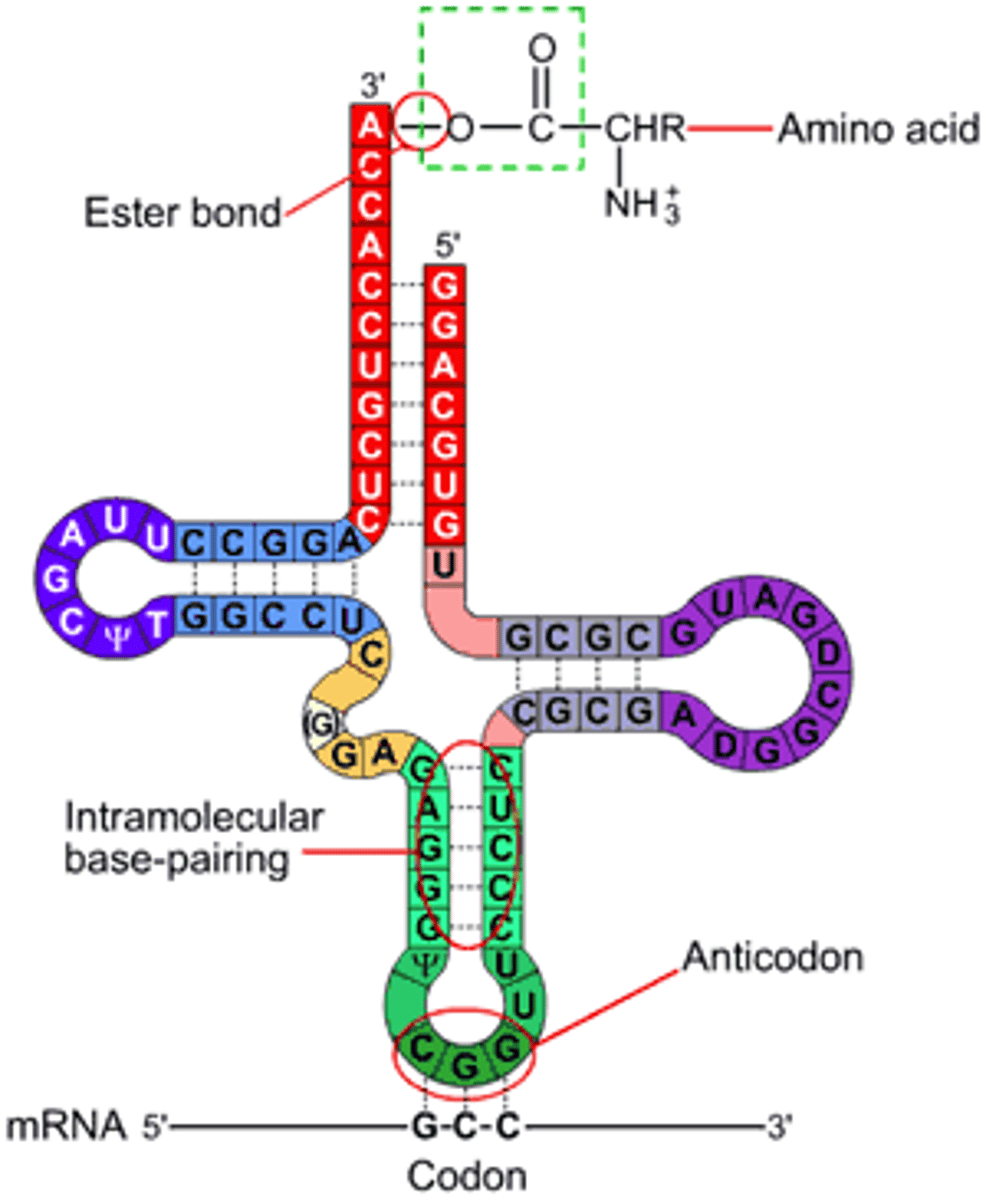
tRNA activation
1) active site binds to an amino acid and atp
2) atp loses 2 phosphate groups and joins amino acid amp
3) trna covalently bonds displaying amp
4) activated amino acid and trna are release by the enzyme aminoacyl synthase and trna is now activated for translation
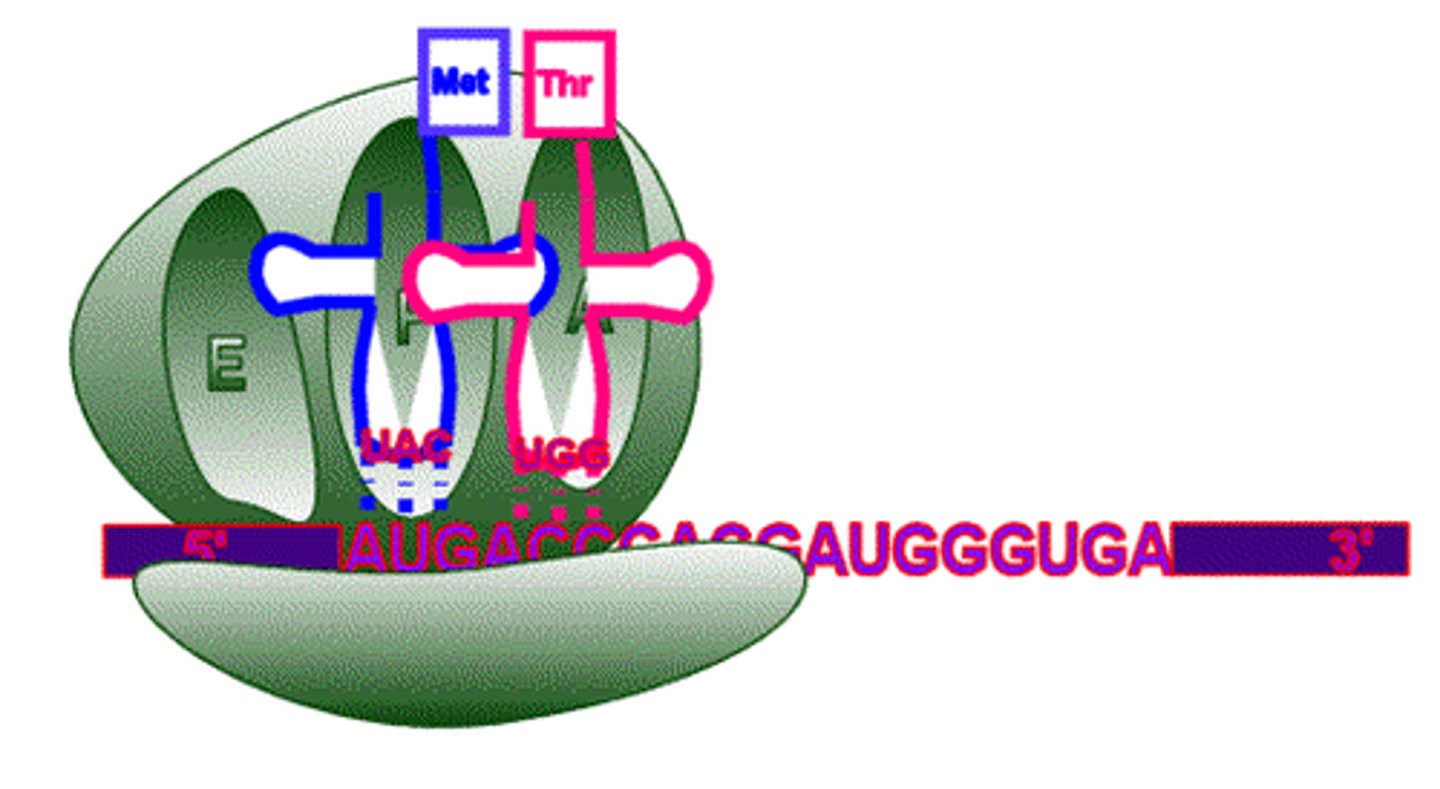
ribosome anatomy
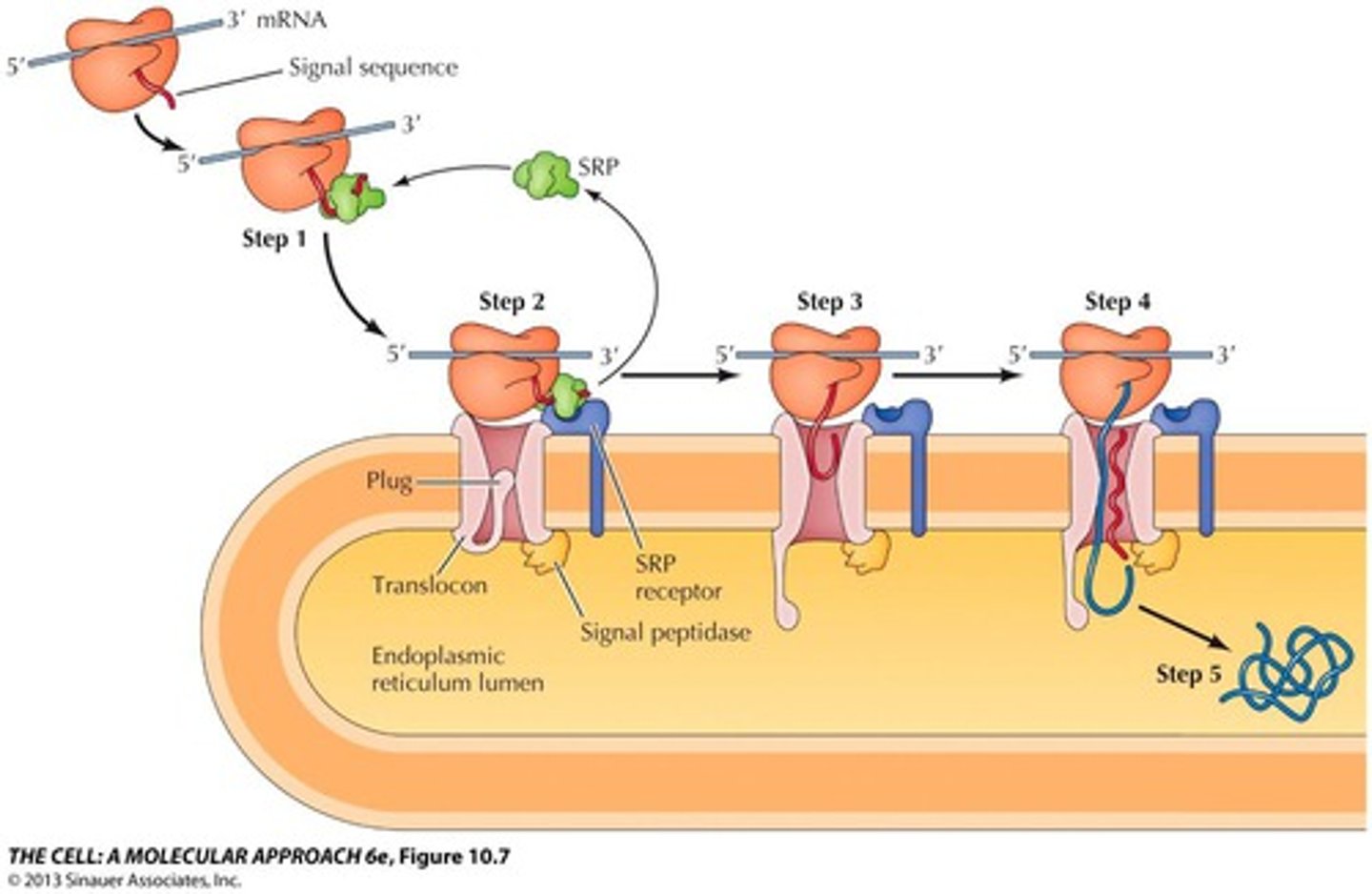
signal hypothesis
many proteins must be modified in the rER before secretion, so during translation the first few amino acids code for a signal peptide (KDEL) that is threaded into the ER lumen
how is bacteria's transcription and translation
it is done at the same time
point mutation
cause of sickle cell; one single base pair is wrong on the DNA template strand (has an adenine instead of a tyrosine so the copied mRNA has the wrong base as well)
silent mutation
the change in the nucleotide has no effect on the amino acid because of the wobble on aa
nonsense mutation
change in the nucleotide causes a premature stop codon, truncating the protein; example: phenylketonuria (PLK)
missense mutation
the change in the nucleotide codes for a new amino acid; examples: sickle cell and achondroplasia
frameshift (nonsense) mutation
the change in the nucleotide causes an immediate nonsense; example: BRAC1 tumor supressor gene not made
frameshift (missense) mutation
the change in the nucleotide causes and immediate missense; example: huntington's and fragile x
insertion mutation
there is an insertion of an extra nucleotide; example: cystic fibrosis or DMD
deletion mutation
there is a deletion on a certain nucleotide; example: also cystic fibrosis or DMD
Garrod propsed...
that babies were born with inherited metabolic errors
Beadle and Tatum proposed...
the one gene, one enzyme hypothesis with yeast cells
Linus Pauling proposed...
that there was a genetic connection between the sickle cell hemoglobin and the sickle cell trait
one of the mRNA codons specifying for the amino acid leucine is 5'-CAU-3'... it's corresponding anticodon is:
3'-GAU-5'
which of the following is a characteristic of uracil:
a. the ability to bond with adenine
b. the ability to bond with guanine
c. it is a purine
d. the ability to bond with cytosine
e. it contains two nitrogenous rings
a. the ability to bond with adenine
what is the attachment site for RNA polymerase
the TATAAA box
tRNAs:
enter the ribosome via complementary base pairing with the mRNA codons, they have an anti codon, they have an attachment site for an amino acid, and they are recognized by aminoacyl-RNA synthases that adds the correct amnio acid
a polyribosome is...
a complex of many ribosomes and and mRNA
a frameshift mutation results from...
the insertion or deletion of one or more base pairs
transcription begins...
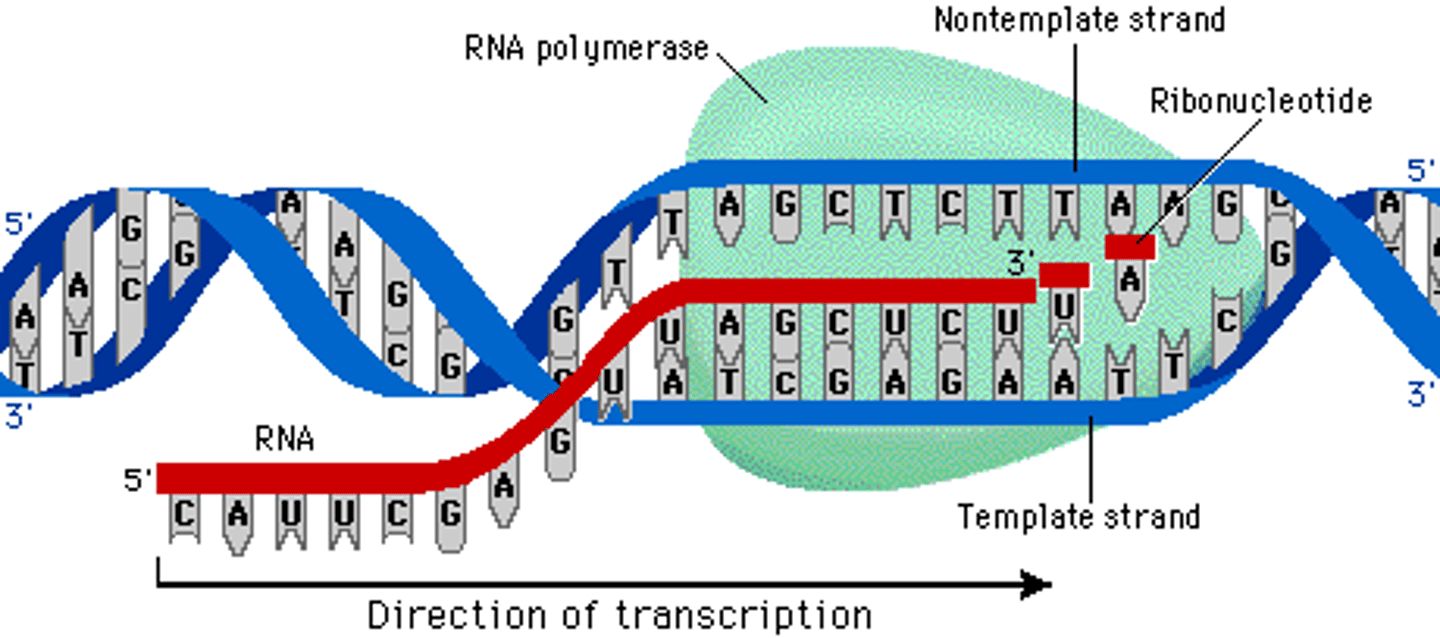
anticodon anatomy

achondroplasia
is caused by a change of the mRNA codon from GGA to AGA and is a missense mutation and changes the amino acid from gly to arg
a gene that is 8,000 nucelotides long may use 1,200 nucleotides to make a protein consisting of approximately 400 amino acids..this is best explained because...
many noncoding stretches of nucleotides will be spliced out of DNA
promoter "tata box"
initiates transcription and decides what genes will be expressed
enhancers
increases/decreases/silences the rate of transcription; brings an enzyme to the tata box, enhances the likelyhood that transcription will occur
histone methylation
makes dna tightly wound "heterochromatin" and not available for transcription
histone acylation
loosens the dna "euchromatin" and makes it available for transcription
ubiquination
effects the expression of proteins because it tags the cell for the kiss of death by proteasomes
miRNAs
effects translation because it binds the the complementary mRNA and silences parts of it or degrades it
linked genes
the closer genes are, the more likely they will be to share genetic information and travel together; we can use these to make gene maps
spliceosome
cuts out the introns in RNA
dicer
moves along the double stranded RNA and cuts it into smaller segments of 10 base pairs
proteasome
involved in unfolding protein and putting it in its central cavity for degradation
how to make a gene map
(total recombinants/total offspring) x100
hardy-weinburg ideal conditions for equation to work
1. mutation does not occur
2. natural selection does not occur
3. population is infinitely large
4. all members of the population breed
5. all mating is random
6. everyone produces the same number of offspring
7. no migration occurs
hardy-weinburg equations
allele frequency:
dominant + recessive = 1
(p+q)=1
genotype frequency:
p^2+2pq+q^2
chi squared table

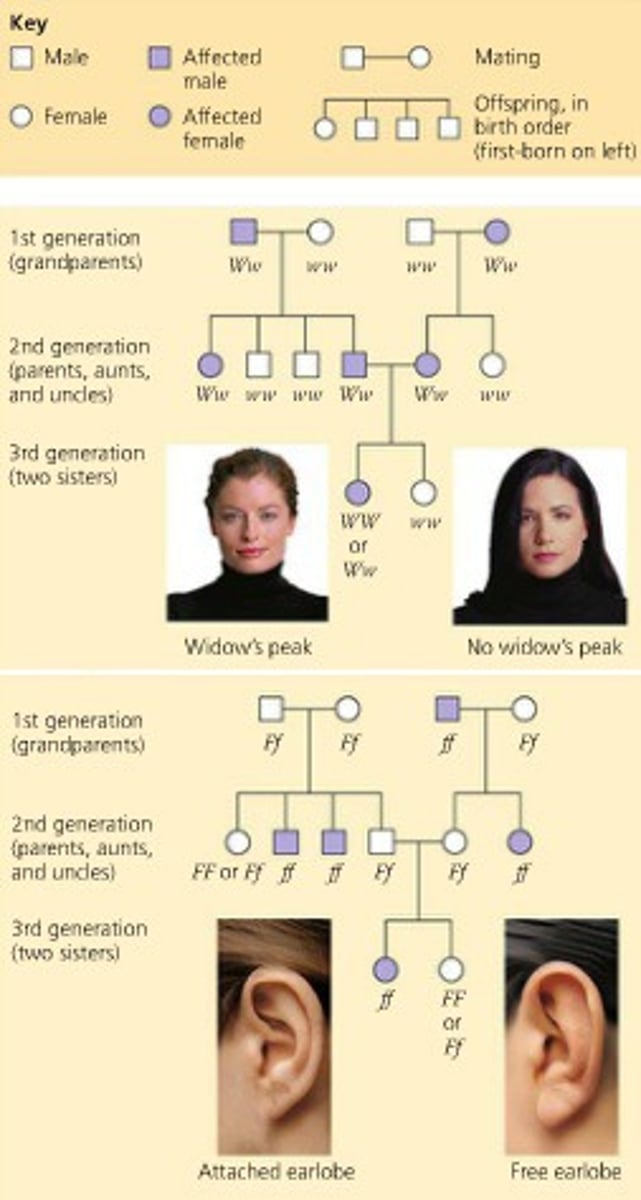
pedigree analysis
virus
small infectious particles consisting of nucleic acids enclosed in a protein coat or sometimes membranous envelopes
they are small obligate intracellular parasites that self assemble and reproduce with the use of the host
may consist of RNA or DNA and be single or double stranded
capsid
protein shell encloses viral genome
viral envelopes
come from membranous host cells and surround capsids
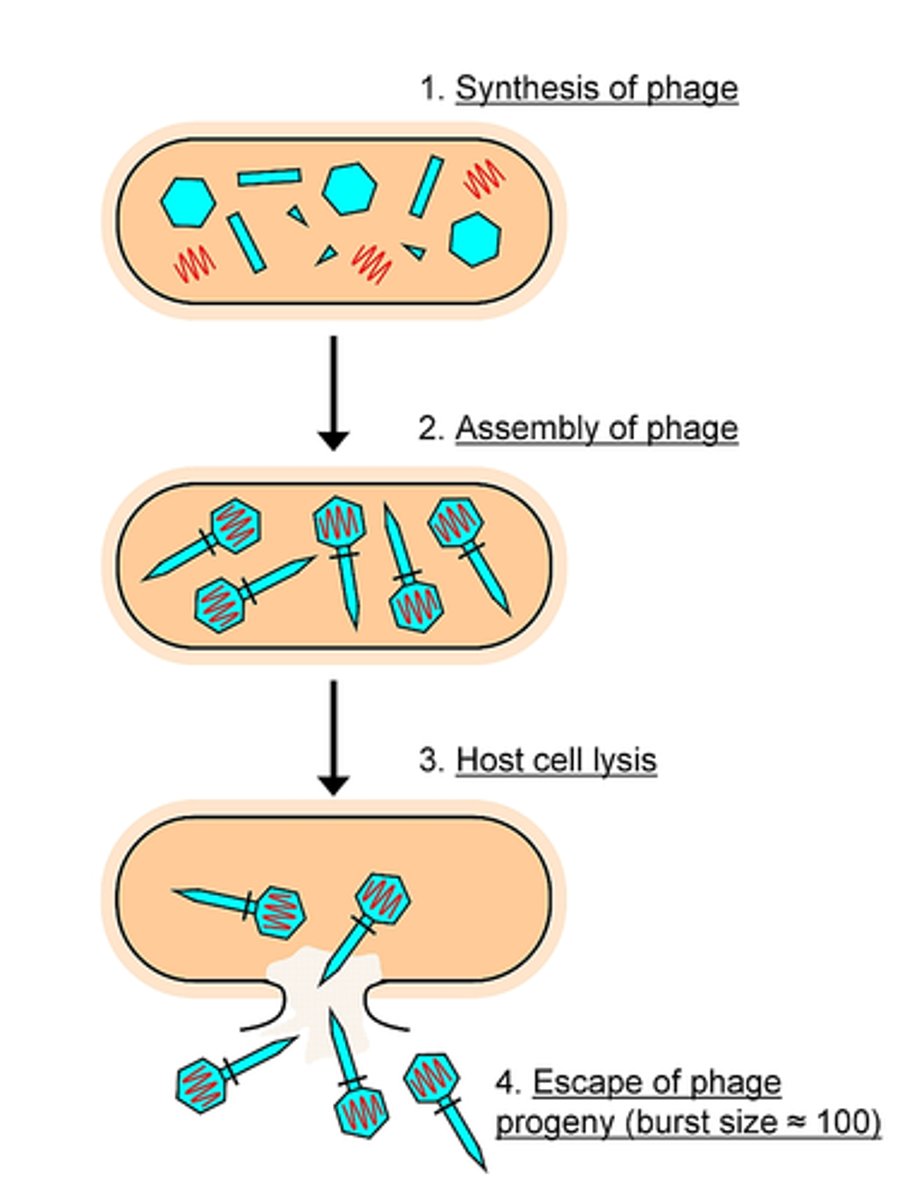
bacteriophage
virus that infects bacteria
lytic cycle
1. attachment to host cell
2. insert into host cell
3. self assemble
4. burst cell and spread
lysogenic cycle
1. attach to host cell
2. insert dna in to host cells genome
3. dna is replicated
4. cell divides into new cells that are now infected also
5. lytic cycle my also occur

RNA viruses
use reverse transcriptase to create its own dna from transcription and translation from its beginning RNA
the RNA is the template strand used
single and double stranded RNA examples
picornavirus: polio
coronavirus: SARS
flavivirus: hepatitis c
paramyxoviruses: measles/mumps
filovirus: ebola/zika
influenza viruses: flu
retroviruses? HIV
single and double stranded DNA examples
adenovirus: common cold
papillomavirus: HPV
herpes virus: cold sores or genital warts
pox viruses: small pox
steps hiv takes for replication
1. virus binds to host cell with glycoproteins
2. hiv enters host cell
3. reverse transcriptase creates a dna-rna hybrid
4. dna is now replicated with viral piece
5. rna piece of genome is released and is sent out in a vesicle to infect more cells
prions
slow acting, indestructible, infectous proteins that cause transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs)
propagate by converting normal prp proteins to prions
causes neurodegenerative diseases
neurodegenerative diseases
scrapie in sheep
mad cow disease in bovines
CWD in deer
FSE in cats
creutzfeldt-jakob and kuru in humans
enhancers:
a. increase the rate of eukaryotic gene transcription
b. are binding sites for cell-specific transcription factors
c. may be located upstream or downstream from genes they regulate
d. may be located thousands of base pairs away from the promoter
e. all of the above
e. all of the above
the human crystalline gene is contained in the genome of every cell of a human, but is only expressed in the lens of the eye, this is because:
activator proteins (transcription factors) that bind to regulatory regions of the crystalline gene only found in the lens cell
regulation of gene expression can be accomplished by controlling:
1. the amount of chromatin packing
2. the amount of mRNA that is transcribed
3. the rate of translation of mRNA
4. the rate of mRNA degradation
in human females the barr body caused by inactive x chromosome
forms heterochromatin
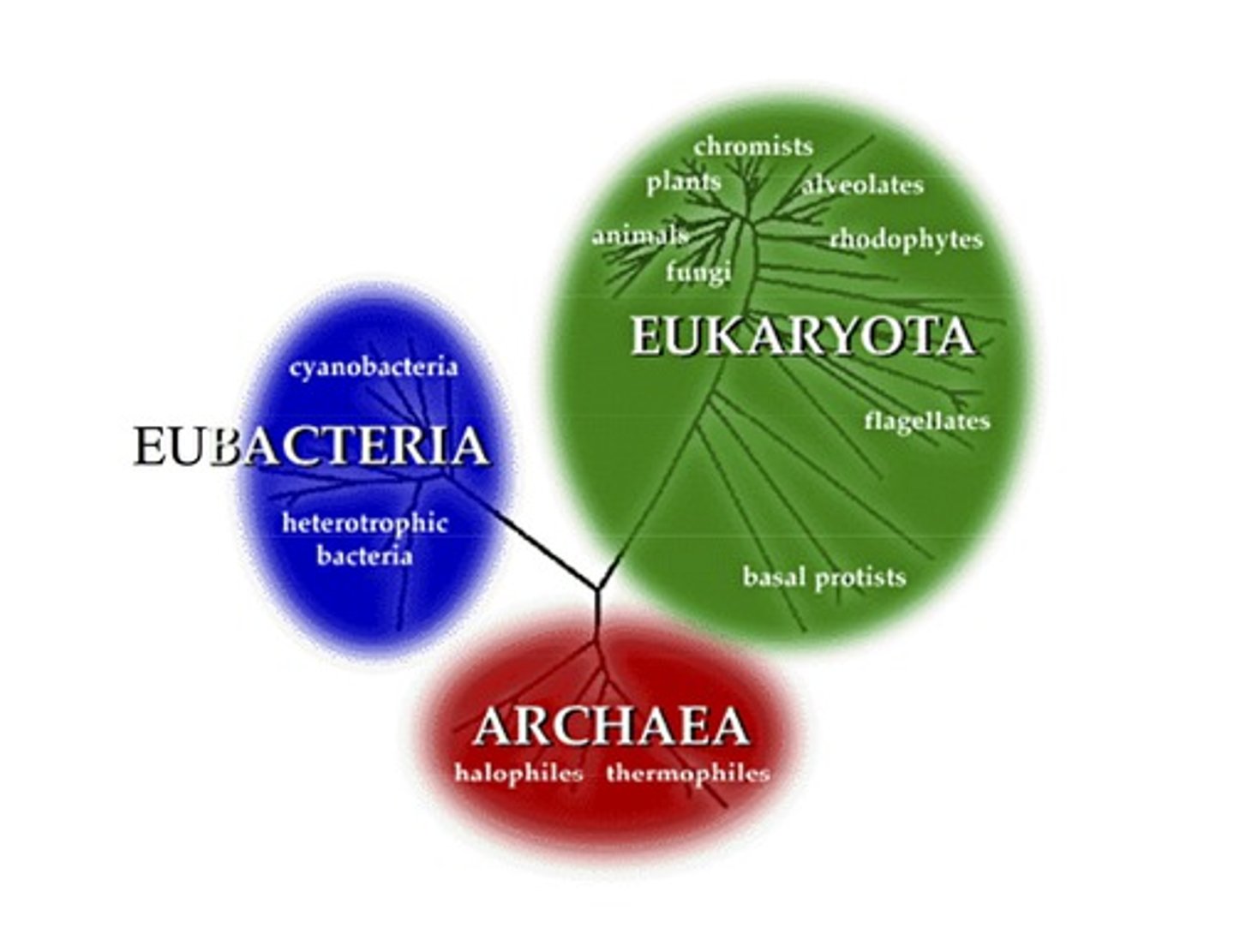
3 domains of life
1. eukaryota
2. archaea
3. bacteria
carl woese
created 3 domains phylogentic tree/cladogram using dna homology from rna
why RNA works as a good chronometer
1. all organisms have rRNA
2. it functions the same in all organisms
3. its sequence changes slowly
4. rRNA
bacteria clades
1. proteobacteria
2. chlamydias
3. spirochetes
4. cyanobacteria
5. gram (+) bacteria
archaea clades
1. methanogens
2. thermophiles
3. psychrophiles
4. halophiles
oldest known organism on earth *3.6 bya
eukaryote clades
1. protists
2. fungi
3. plants
4. animals
we are more closely related to archaea than bacteria is
methanogens
decomposers, make methane

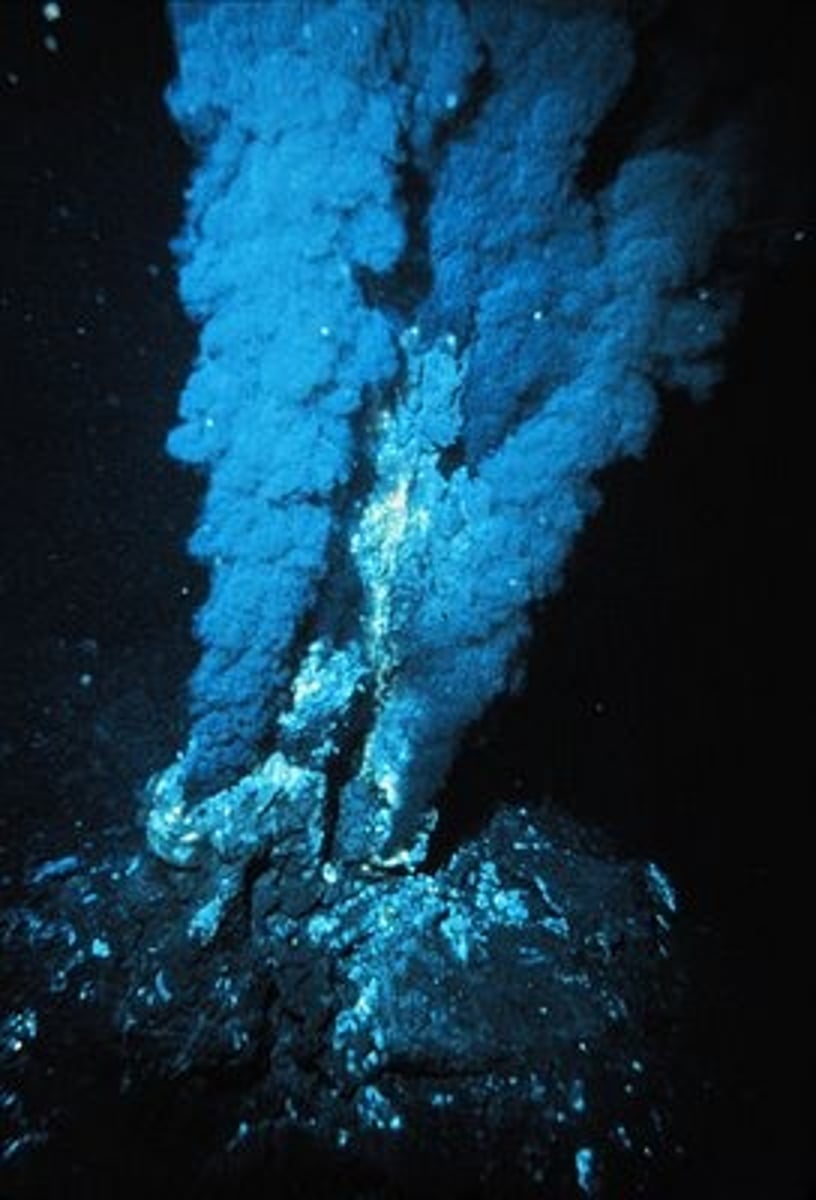
thermophiles
love heat 6-110 degrees celcius, in yellowstone hot springs, or deep sea black smokers

psychrophiles
love cold below or near 30 degrees celcius, polar ice caps, antarctica
halophiles
salt lovers, need environment 10x saltier = (rhodopsins) found in dead sea, red sea, cause bright colors

rod shape bacteria
Lactobacillus (probacteria in yogurt)
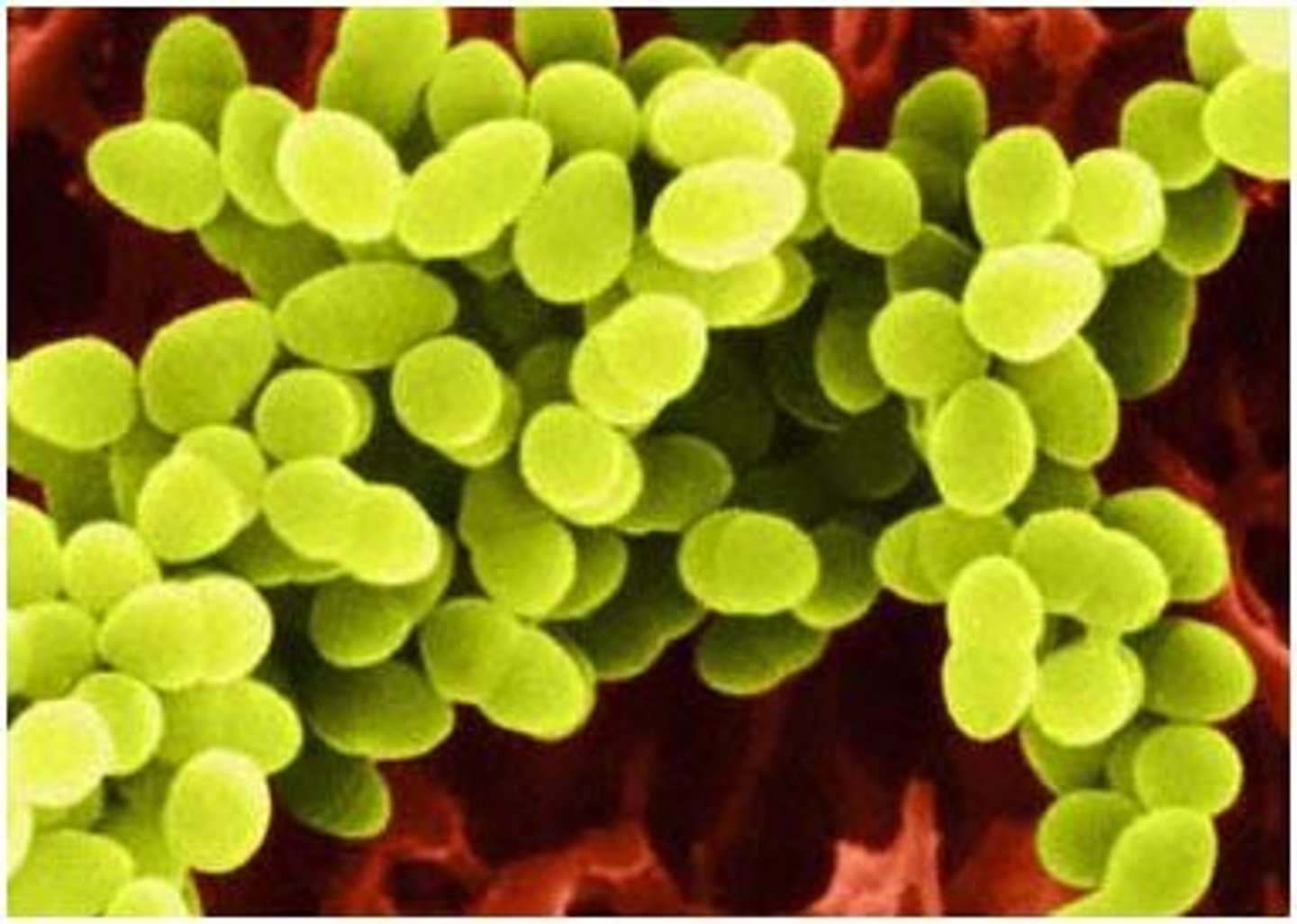
cocci shape bacteria
Staph aureus (MRSA)
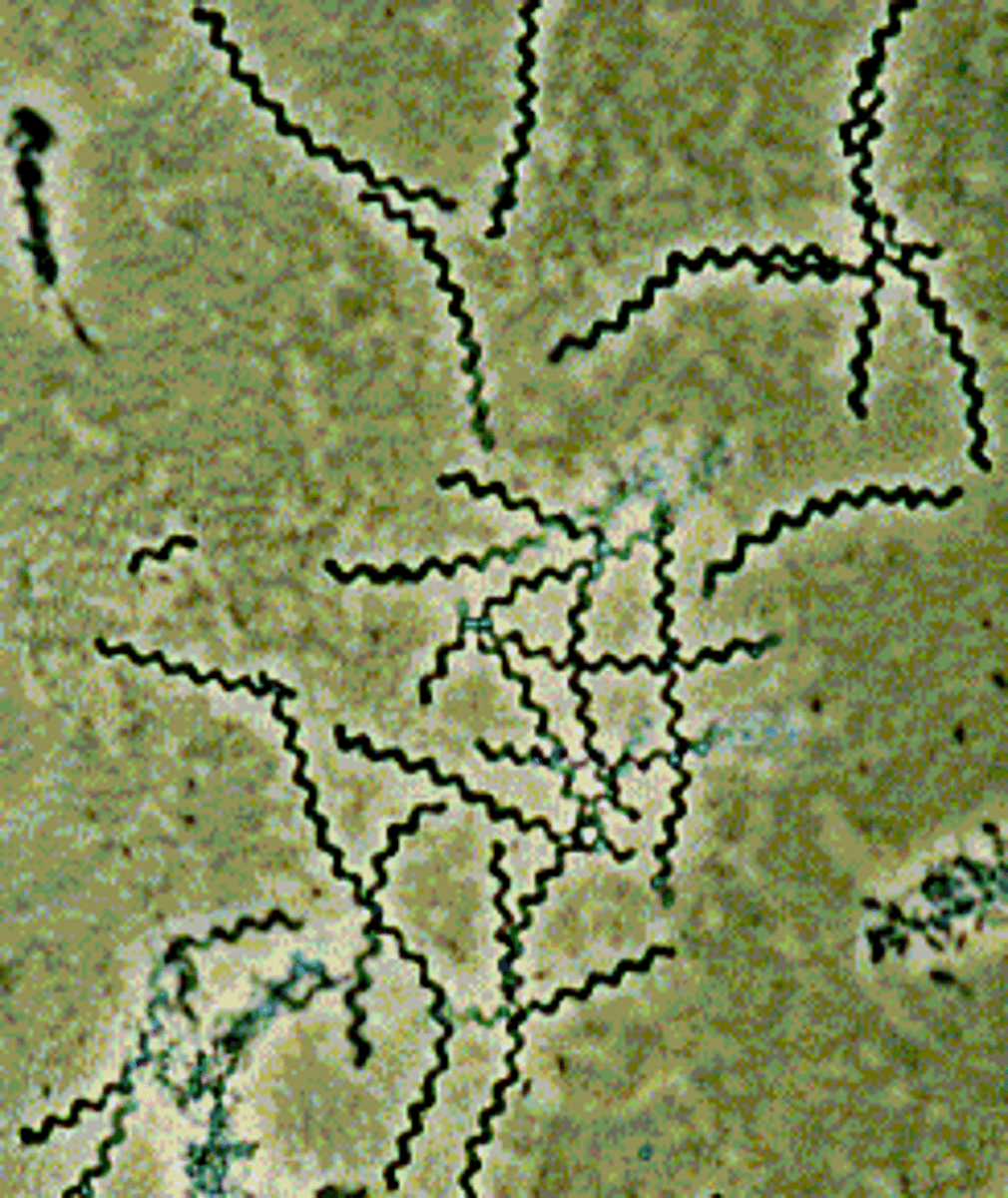
spiral shape bacteria
Triponema pallidum (syphillis)
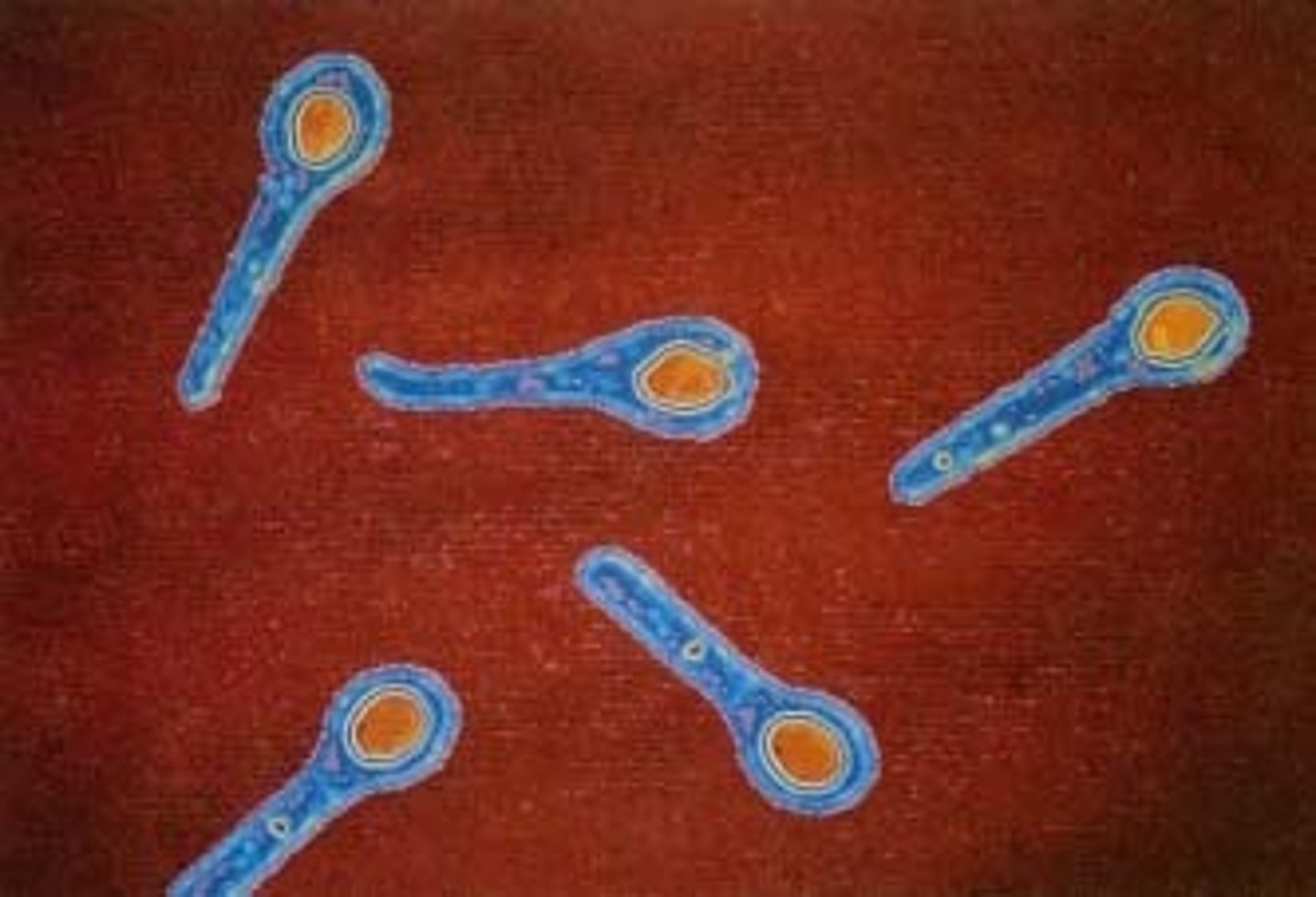
Clostridium tetani
tetanus "lockjaw"
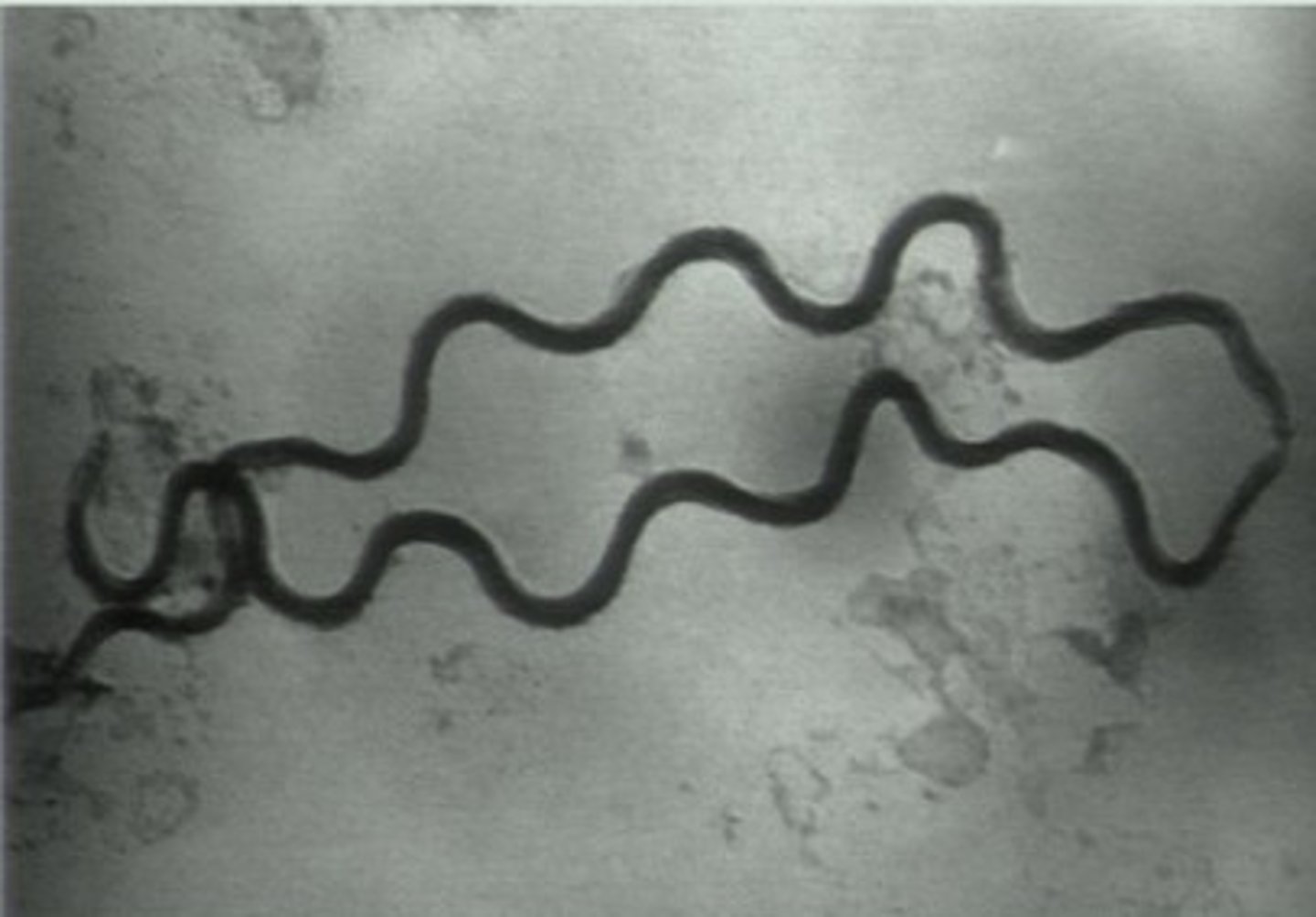
Treponema pallidum
syphillis
spirochaetes
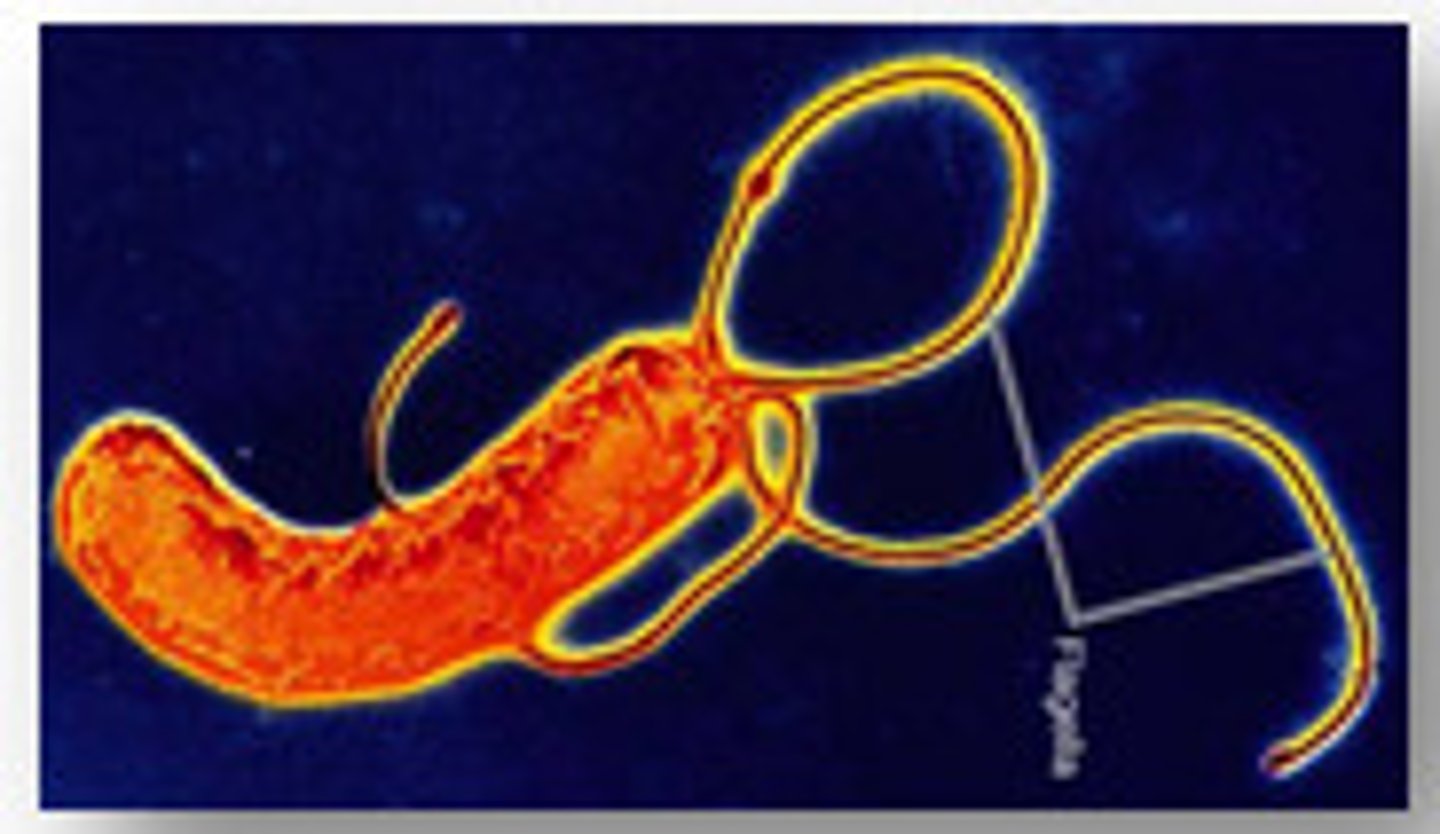
Helicobacter pylori
stomach ulcers
gram (-) proteobacteria
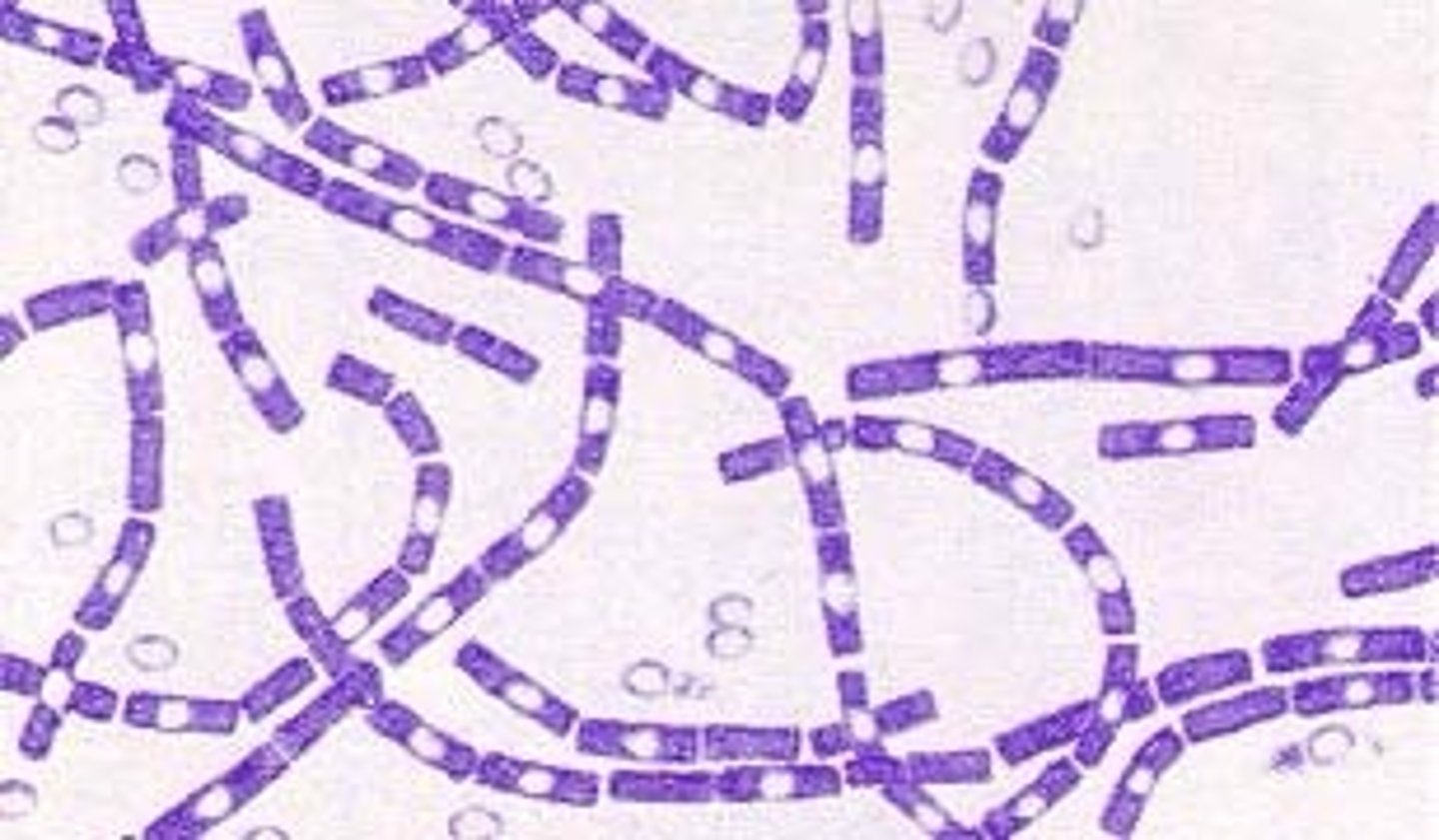
Bacillus anthraxis
anthrax
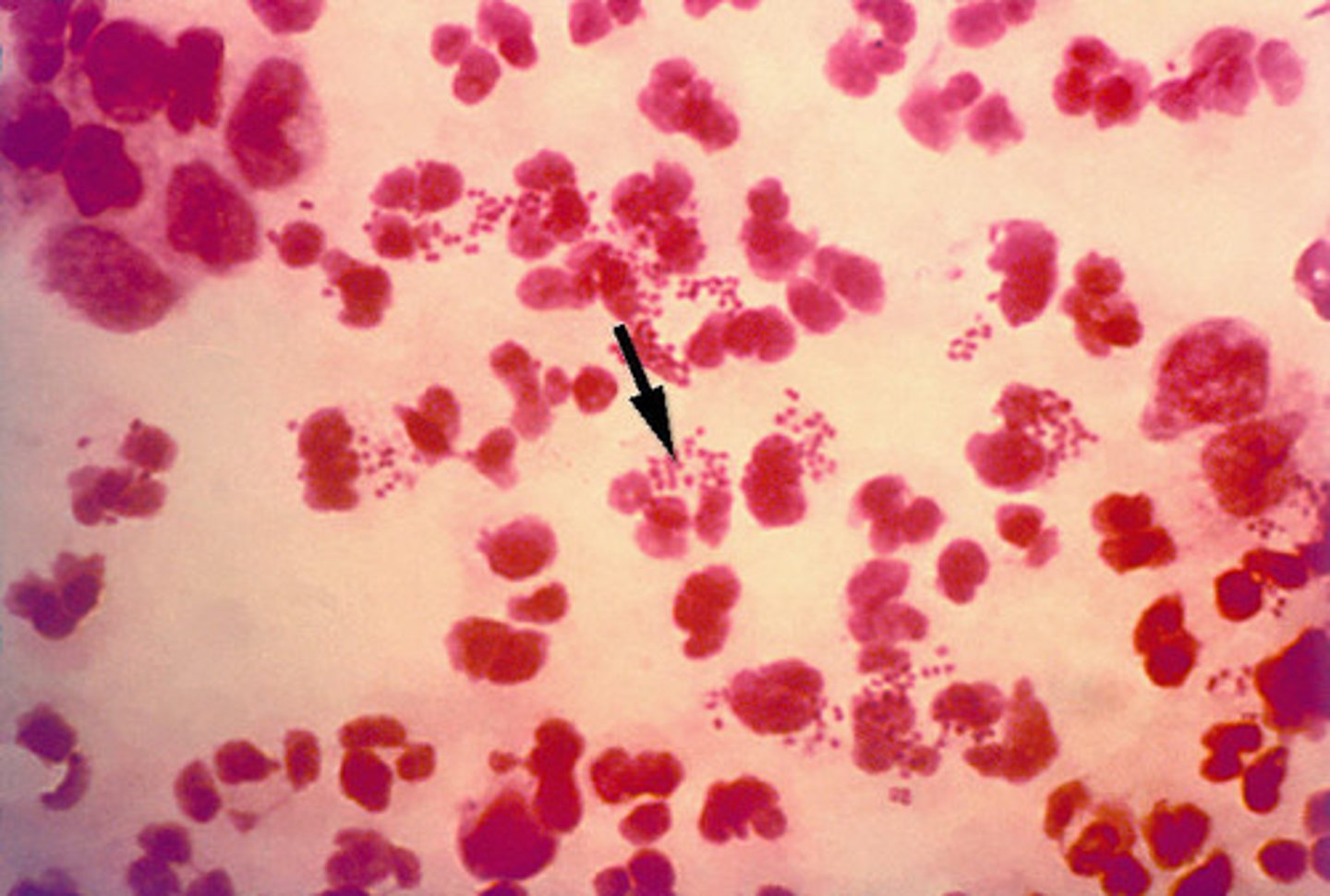
Neisseria gonorrhea
gonorrhea
Clostridium difficile
gram (+) eubacteria
Anabaena
cyanobacteria

gram (-) proteobacteria
closely related to the eukaryotic mitochondria
E. coli
Salmonella typhus
Legionella
Heliobacter pylorii
Neisseria gonerrhea
Rickettsia