Psychology; Motivation and Emotion
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is Motivation?
Motivation refers to the moving force that energizes behaviour
Direction or goal of motives
Strength of motives (circumstantial)
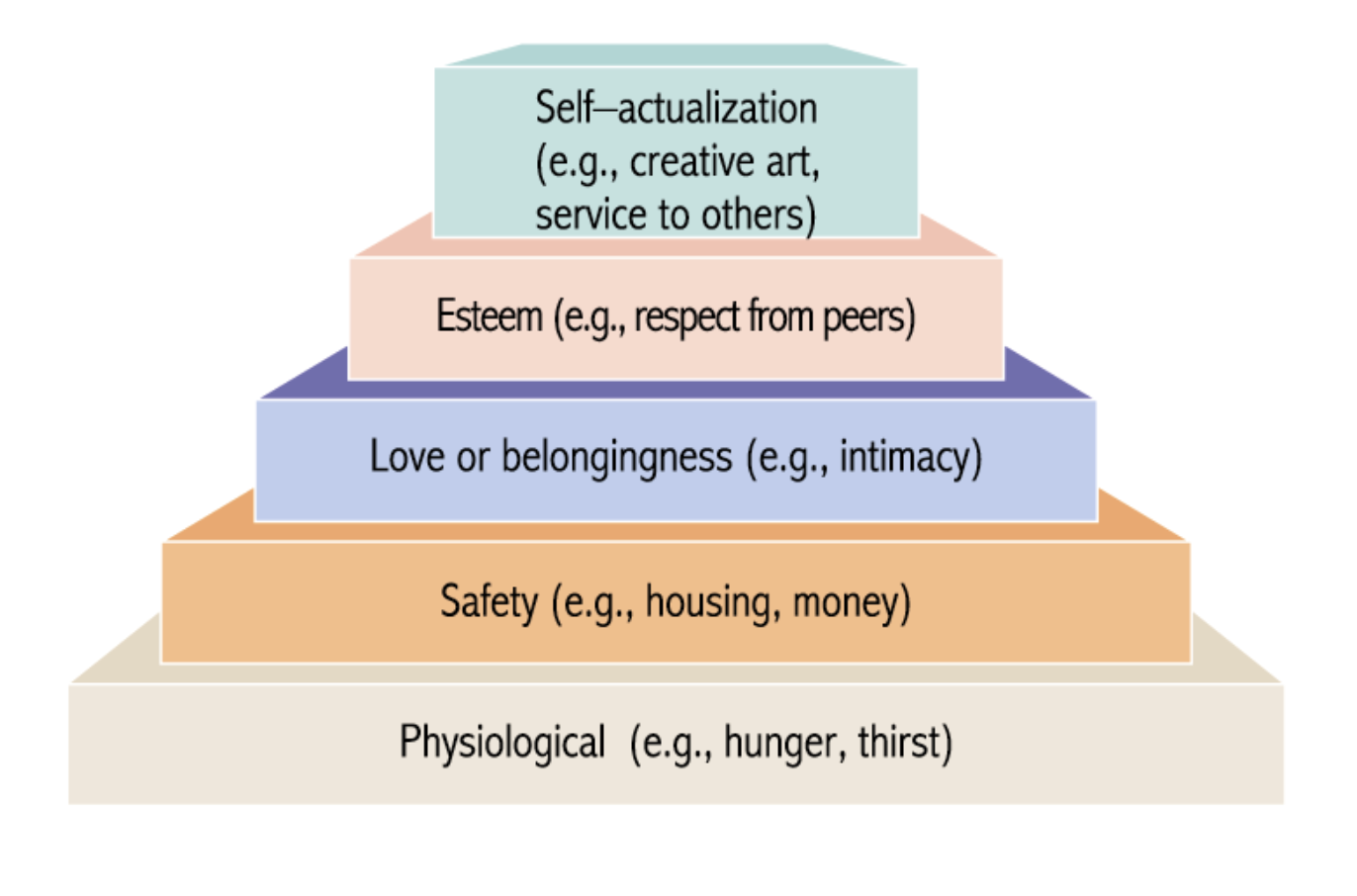
What are Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs?
Self actualization (e.g, creative art, service to others)
Context dependent; the idea of people who are self actualized are authentic and genuine, they are who they are if you like it that’s great if you don’t then that sucks.
Esteem (e.g, respect from peers)
Fear of failure, fear of being embarrassed and fear of what others think of me. Which relates back to anxiety which is the number one reason for the most common deaths which are due to stroke, heart attacks or general heart failure.
Love or belongingness (e.g, intimacy)
People was to belong with other people, feels of loneliness as a motivator for why people may do certain things such as building relationships or going to social outings so they would be able to build such relationships.
Safety (e.g, housing, money)
Physiological (e.g, hunger, thirst)
One note: Is that all these needs are reasons for why people commit crimes.
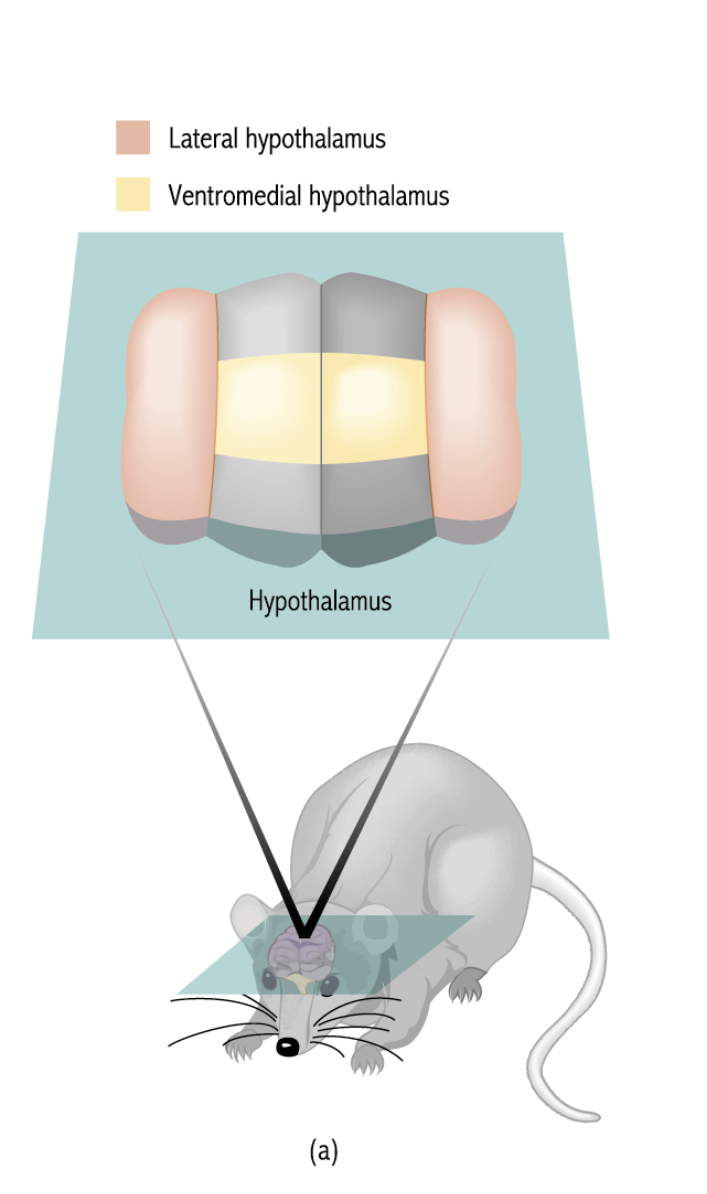
What is Hypothalamic Regulation of Eating
Hypothalamus receives information regarding nutrient levels in body. The two main regions of concern are;
Lateral region
Ventromedial region
What is the lateral region and its functions?
The lateral regionis an anatomical directional term meaninga location or structure situated to the side of a central point or the midline of the body or an organ. In specific contexts within anatomy, "lateral region" can refer to distinct areas with specialized functions.
Stimulation induces eating
Lesions of the lateral region produce starvation
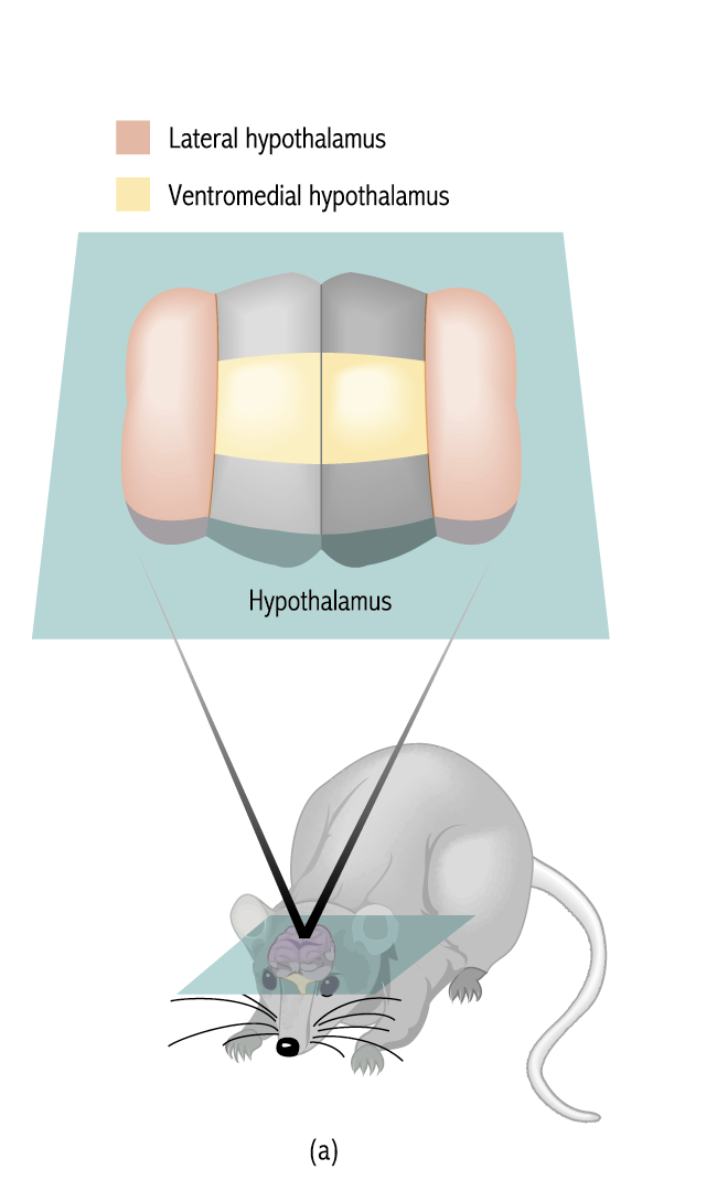
What is the ventromedial region and its functions?
The ventromedial (VM) regiongenerally refers to theventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC), a part of the brain located at the bottom of the frontal lobes, near the midline. This region isa crucial integrative hub for emotion, decision-making, social cognition, and memory.
Lesions induce overeating
Stimulation inhibits eating
What is Sexual Motivation?
It's an internal state that initiates and directs sexual interest, varying greatly between individuals and situations, and can manifest as seeking pleasure, reproduction, or connection
What do Motivations reflect?
Biological needs (need for procreation, sex, sleep, play (it’s about trust,, the importance of having a father in the home)
Psychosocial needs (Case study which tracked what women wore to clubs in Switzerland. The results of the study showed that women showed more cleavage when they were ovulating).
What are the 3 aspects of Sexual Motivation?
Hormones:
- Organizational effects: prenatal exposure to androgens alters the neural circuits in brain and spinal cord, Adult behaviour of androgenized subject is masculine. In the absence of androgens, “Nature’s impulse is to create a female…”
- Activational effects: alteration of adult levels of hormones can alter the intensity of a behaviour that is modulated by that hormone
Pheromones
Environmental cues
One note: If a male were to be androgenized, they would have more masculinized features that influence the appearance of their genitals and jawline. Whereas in females, they would have masculine features and a higher likelihood of being homosexual (30-40%).
What is the Evolutionary Analysis of Human Sexual Behaviour
Parental investment
Patterns of sexual activity
- People we asked how many sexual partners they would want in their life. Men said they would want 18, women would want 5. And these could be for a number of reasons on why women are less than men due to societal shame, chances of pregnancy and so on.
Differences in mate preferences
-Women’s wants in a man; Material resources, willing to invest, high income, high education.
-Men’s wants; Young and attractive.
Jealousy
What is Sexual Orientation?
Sexual orientation is the direction of attraction for a sexual partner
Homosexuality: attraction for a person of the same-sex
Twin studies document a biological basis for homosexuality
Hormonal responses differ between homosexual and heterosexual men
What are Affiliation Motives?
The need to associate with others and maintain social bonds.
Companionship, friendship, and love
Evolutionary bases
Safety, grooming, survival
Rejection, Loss of intimate, Loneliness
(anxiety, jealousy, and depression)
What are Achievement Motives?
Need for Achievement: refers to the need to do well, to succeed, and to avoid failure
Persons who have a high level of need for achievement tend to
Choose moderately difficult tasks
Enjoy being challenged
Avoid failure
Work more persistently
Enjoy success
What is Emotion?
Emotions reflect a “stirred up’ state
Emotions have valence: positive or negative
Emotions are thought to have 3 components:
Physiological arousal (Occurs before your brain can work; reflexive to stimuli (senses))
Subjective experience (Emotions can be measured, the basic emotions can be mimicked universally (smiling means you’re happy, frowning means your sad))
Behavioural expression
What is the Taxonomy of Emotions?
How many basic emotional states?
Between 5 and 9 basic states:
The common 5 include anger, fear, happiness, sadness, and disgust
Additional emotional states include surprise, contempt, shame, guilt, joy, and trust
Emotional valence may be related to activity in the nervous system:
Positive: activity of dopamine systems
Negative: activity of norepinephrine systems
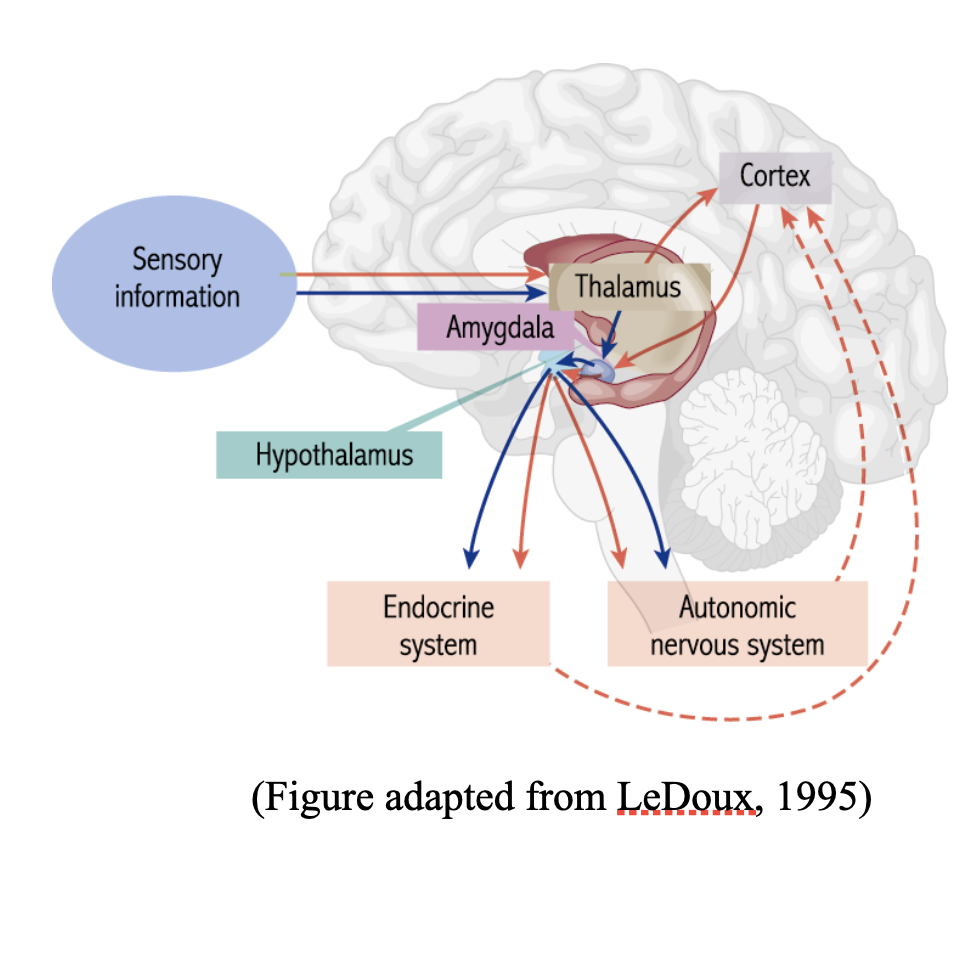
What is the Neuropsychology of Emotion?
Dual processing of emotions:
Activation of the amygdala produces visceral responses
Cortical activation allows for use of memory in understanding emotional stimuli
Limbic system
What are the 3 Theories of Emotion?
James-Lange Theory of Emotion
The James-Lange theory of emotion proposes that emotions are the result of perceiving our body's physiological responses to external stimuli, meaning we feel afraid because we tremble, or sad becausewe cry, rather than the other way around.
Cannon Bard Theory of Emotion
The Cannon-Bard theory of emotion, proposed by Walter Cannon and Philip Bard, suggests that emotional experiences and physiological responses happen simultaneously and independently after a stimulus,
Schachter-Singer Theory of Emotion
The Schachter-Singer theory, or two-factor theory of emotion, states that an emotion arises from a combination of physiological arousal(like a racing heart) and a cognitive label (interpreting that arousal based on the situation). Essentially, your body reacts physically, and your brain quickly analyzes the context to label that feeling as a specific emotion, like fear (snake) or excitement (roller coaster).
What are the Cognitive Perspectives on Emotion?
Plato: “reason must rein in the passions”
Schachter and Singer (1962): cognitive judgements are a critical part of emotional experience:
Subjects are aroused by an injection of adrenaline and then exposed to anger or happiness cues
The emotional cues played a prominent role in emotional experience
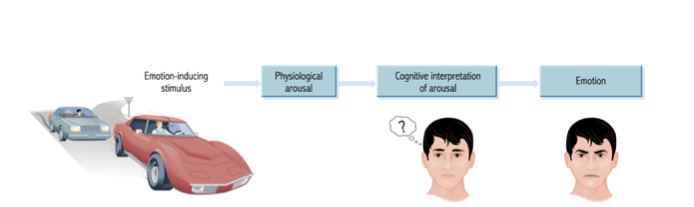
What Theory is this?
Schachter-Singer Theory of Emotion.
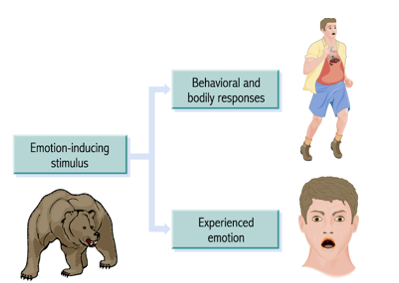
What Theory is this?
Cannon-Bard Theory.
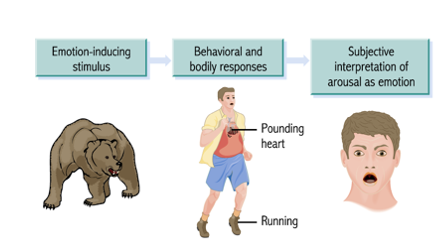
What Theory is this?
James-Lange Theory.
What is Happiness as an Emotion?
Happiness is an emotional state characterized by a positive valence
Research shows that happiness is
related to cultural values (highest in individualistic cultures, lowest in collectivist cultures)
Highly correlated with number of uninterrupted years of democracy in a country
Happiness is NOT related to:
Gender
Age
Wealth