8.2 introduction to software development
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:14 AM on 8/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
1
New cards
how do you ==understand a problem== (understanding the problem)
1. ==identify== __**requirements**__ and __**parameters**__ of the __**problem**__
2. ==determine== the __**steps**__ that will __**solve**__ the problem
3. ==check== and ==test== the solution
2
New cards
what is an ==IPO== diagram (understanding the problem)
used to ==describe data elements== that __**enter**__ a __**system**__/__**subsystem**__, ==processors== that will ==occur==, and the ==data elements== that will then __**leave**__ the __**system**__
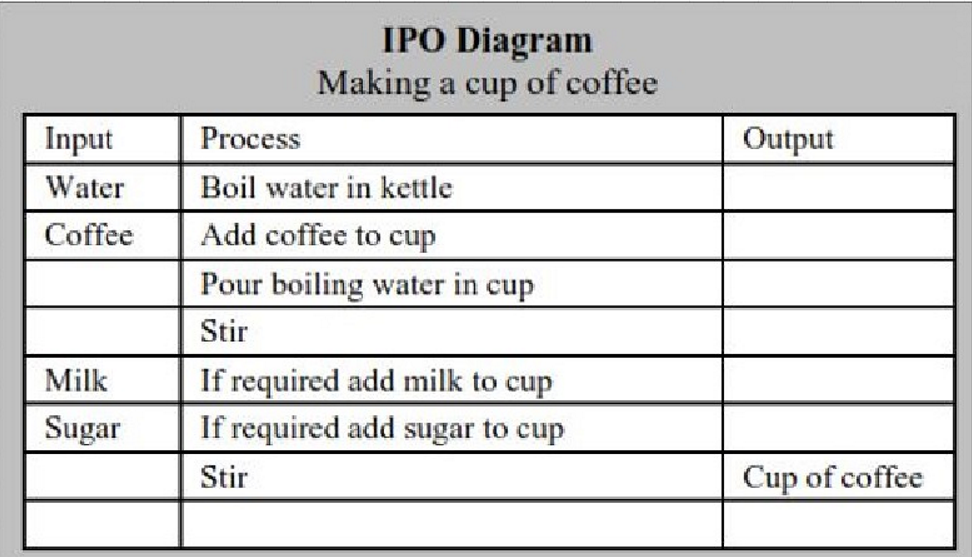
3
New cards
what is the @@top down@@ approach (abstraction/refinement)
@@breaking@@ down @@large@@ __**complicated**__ @@problems@@ into @@smaller problems@@ that are __**easier to solve**__
4
New cards
what is a @@program made of@@ (abstraction/refinement)
@@modules@@ and @@subprograms@@
5
New cards
what are @@modules@@ (abstraction/refinement)
written @@separately@@ and brought @@together@@ to form a @@whole@@
6
New cards
what is @@algorithm/main program@@ known as
the @@driver module@@
7
New cards
what are @@subprograms@@ (abstraction/refinement)
used within the @@main program section@@, used often in @@__**top-down**__@@ method
8
New cards
what are @@data flow diagrams@@ and @@when@@ are they @@used@@ (abstraction/refinement)
describes the @@path@@ of @@data in system@@, __**initial DFD**__ represents @@one whole system@@ as a @@__**single**__ **process**@@ (known as a __**CONTEXT DIAGRAM/LEVEL 0 DFD**__)
1. used during design processes
1. used during design processes
9
New cards
what are @@structure charts@@ (abstraction/refinement)
represents a @@system@@ by showing the @@separate modules/subroutines@@
10
New cards
what do the @@shapes in structure charts@@ mean (abstraction/refinement)
1. rectangle
2. empty circle arrow
3. filled circle arrow
4. diamond
5. curved arrow
1. rectangle
2. empty circle arrow
3. filled circle arrow
4. diamond
5. curved arrow
1. module
2. flow of data
3. flag to show processing being doing
4. decision
5. loop
11
New cards
what are @@system flowcharts@@ (abstraction/refinement)
representing a system to show the flow of data
12
New cards
what do the shapes of @@system flowcharts@@ mean (abstraction/refinement)
1. parallelogram
2. rectangle with a chomp
3. pencil looking shape
4. slanted roof
5. rectangle with a fold on the top left
6. rectangle
7. rhombus
8. tape
9. cylinder
10. diamond
11. line
1. parallelogram
2. rectangle with a chomp
3. pencil looking shape
4. slanted roof
5. rectangle with a fold on the top left
6. rectangle
7. rhombus
8. tape
9. cylinder
10. diamond
11. line
1. input/output
2. paper document
3. online display
4. online input
5. punched card
6. process
7. manual operation
8. magnetic tape
9. disk drive
10. decision
11. telecommunication link
13
New cards
what is the @@difference@@ between a @@system flowchart@@ and a %%program flowchart%%
@@system flowcharts@@ __**do not use a start/end**__ system and dont represent complex logic
%%program flowcharts%% are used to represent the %%logic%% in an algorithm
%%program flowcharts%% are used to represent the %%logic%% in an algorithm
14
New cards
what are the different data types (data types)
integer, string, floating point, boolean, date, array, record, file
15
New cards
what is an integer (data types)
whole numerical data stored as 2 bytes
16
New cards
what is a string (data types)
a sequence of characters
17
New cards
what is a floating point (data types)
numbers with decimal places and __**requires**__ more data than an integer
18
New cards
what is a boolean (data types)
simplest data type with only two possible values, __**true or false**__
19
New cards
what is a data structure (data types)
literally top-down
20
New cards
what is a one-dimensional array (data types)
allows a variable to store a number of related data items, that are the __**same type**__, __**rather than just one item**__
21
New cards
what is a record (data types)
used to link data items that are related but are __**DIFFERENT types**__
22
New cards
how are records use in sequential files (data types)
records being stored in a way that only __**allows access**__ to a record __**if all previous records have been processed**__
usually end-of-file (EOF) marker used at the end of a file
usually end-of-file (EOF) marker used at the end of a file
23
New cards
what is a data dictionary (data types)
information of variables including *name, data type, size, description and examples*
24
New cards
what are %%structured algorithms%%
a series of %%steps%% or %%instructions%% __**designed to solve a problem**__
25
New cards
what is a %%control structure%% (structured algorithms)
literally a %%flowchart%%
26
New cards
what is a %%sequence%% (structured algorithms)
a __**simple**__ %%sequence of instructions%%
27
New cards
what is a %%selection%% and examples (structured algorithms)
a __**selection**__ between %%two%% or %%more%% %%different%% courses of %%actions%%
eg. *binary selection* (if, then, else) *and multiway selection* (casewhere)
eg. *binary selection* (if, then, else) *and multiway selection* (casewhere)
28
New cards
what is %%repetition%% and examples (structured algorithms)
the __**repetition**__ of a set of %%instructions%% a %%number of times%%
eg. *pre-test* (while, endwhile) *and post-test* (repeat, until) *loops*
eg. *pre-test* (while, endwhile) *and post-test* (repeat, until) *loops*
29
New cards
what is %%pseudocode%% (structured algorithms)
relies on %%indented%% words and use of keywords (in caps) to highlight structure of an algorithm
BEGIN
END
BEGIN
END
30
New cards
what are %%program flowcharts%% (structured algorithms)
a pictoral or graphical method of describing an algorithm
31
New cards
what do the %%shapes of flowcharts%% mean
1. rounded rectangle
2. rectangle
3. diamond
4. parallelogram
5. weird chomped rectangle
6. rectangle with lines
7. arrow
1. rounded rectangle
2. rectangle
3. diamond
4. parallelogram
5. weird chomped rectangle
6. rectangle with lines
7. arrow
1. start and end of a flowchart
2. process
3. decision
4. input/output
5. paper document
6. subroutine
7. flow of logic
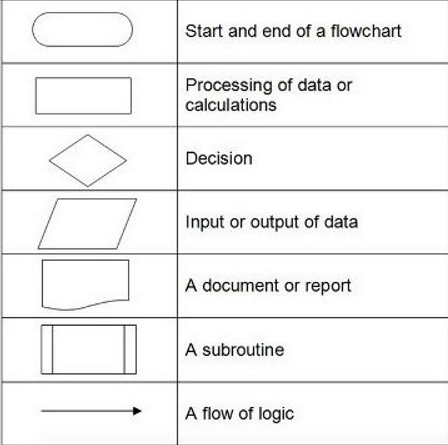
32
New cards
how do you %%load an array%% and %%print%% its %%contents%% (structured algorithms)
BEGIN
→ %%OPEN%% …………. %%FOR INPUT/OUTPUT%%
→ %%READ%% …… %%FROM%% …………..
→ → WHILE NOT %%EOF%%
%%CLOSE%% …………..
END
→ %%OPEN%% …………. %%FOR INPUT/OUTPUT%%
→ %%READ%% …… %%FROM%% …………..
→ → WHILE NOT %%EOF%%
%%CLOSE%% …………..
END
33
New cards
%%what%% and %%how%% do you %%use stubs%% (structured algorithms)
%%temporary section of code%% used to %%__**reduce**__%% __**the places**__ that you need to look to __**find an error**__, used to represent %%incomplete modules%%
34
New cards
what are %%structured algorithms good for%% (structured algorithms)
to %%improve%% the __**clarity, quality**__, and __**development time**__ of a %%computer program%%
35
New cards
what are ^^meta-languages^^ (implementing software solutions)
^^describing^^ the ^^syntax^^ of a programming language
* made by **john backus** in __**mid to late 1950s**__
* made by **john backus** in __**mid to late 1950s**__
36
New cards
what do ^^EBNF^^ diagrams look like (implementing software solutions)
1. {}
2. \[\]
3. ()
4. |
5. =
6. <>
1. {}
2. \[\]
3. ()
4. |
5. =
6. <>
1. ^^repetition^^, DOESNT have to be carried out
2. ^^optional^^
3. ^^grouped^^ elements
4. ^^or^^
5. is ^^defined^^ as
6. ^^needs^^ to be ^^defined^^
37
New cards
what do ^^railroad^^ diagrams look like (implementing software solutions)
1. lines
2. rectangles
3. circles/rounded rectangles
1. lines
2. rectangles
3. circles/rounded rectangles
1. __**lines**__: ^^branches^^ (can be loops/optionals)
2. __**rectangles**__: ^^pre-defined^^ element
__**circles/rounded rectangles**__: ^^fixed^^ element
38
New cards
what are ^^syntax^^ errors (implementing software solutions)
1. **occurs** __**how**__
2. when is it __**discovered**__
3. ways to __**avoid**__
1. **occurs** __**how**__
2. when is it __**discovered**__
3. ways to __**avoid**__
1. ^^occurs^^ when programmers ^^fails to follow grammar rules^^
2. during ^^translation^^ process it will ^^stop^^ and an ^^error message^^ will appear
3. take ^^care^^ when typing code and ^^desk check^^
39
New cards
what are ^^runtime^^ errors (implementing software solutions)
1. **occurs** __**how**__
2. when is it __**discovered**__
3. ways to __**avoid**__
1. **occurs** __**how**__
2. when is it __**discovered**__
3. ways to __**avoid**__
1. __**trying to** ^^**divide by 0**^^**,**__ reading ^^data^^ from a ^^non-existent^^ file, finding the square ^^root^^ with ^^negative^^ numbers, outside of a boundary
2. whilst a __**program is** ^^**running**^^__ it will ^^randomly quit^^
3. be ^^aware^^ of ^^where^^ these types of errors may occur
40
New cards
what are ^^logic^^ errors (implementing software solutions)
1. **occurs** __**how**__
2. when is it __**discovered**__
3. ways to __**avoid**__
1. **occurs** __**how**__
2. when is it __**discovered**__
3. ways to __**avoid**__
1. ^^condition^^ __**does not check**__ ^^boundary values^^, ^^reusing variable names^^ which still contain __**old values**__
2. when ^^operations^^ are performed invalid
3. ^^desk check^^ the algorithm
41
New cards
what are ^^flags^^ used for (implementing software solutions)
used to ^^check^^ if a ^^section^^ of ^^code^^ has been ^^processed^^, __**boolean**__, *set to false and set to true if code is executed*
42
New cards
what are some ^^reasons^^ for ^^maintaining^^ code (maintaining software solutions)
1. changing ^^user requirements^^
2. ^^upgrading^^ the user interface
3. changes in the data to be ^^processed^^
4. introduction of ^^new^^ hardware or software
5. changing organisational ^^focus^^
6. changes in ^^government requirements^^
7. ^^poorly^^ implemented ^^code^^
43
New cards
how do you ^^create solutions^^ that are ^^easy^^ to ^^maintain^^ (maintaining software solutions)
1. use of ^^variables^^ instead of ^^literal constants^^
2. use of ^^meaningful^^ __**variable names**__
3. ^^explanatory comments^^ in the code
4. use of ^^standard control structures^^ with appropriate ^^indentation^^
5. appropriate use of ^^white space^^ to improve ^^legibility^^ of the source code
6. a ^^clear^^ and ^^uncluttered mainline^^
7. ^^one^^ logical ^^task^^ per ^^subroutine^^
8. ^^meaningful names^^ for __**subroutines and modules**__