CHEM II Chapter 8, 9, 10
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Ionic Compound
Compound where a metal reacts with a nonmetal
Polar Covalent Bond
Unequal sharing of electrons
If Electronegativity = Zero
Bond is covalent
If Electronegativity = Intermediate
Bond is polar covalent
If Electronegativity = Large
Bond is ionic
Dipole Moment
When molecules have a center of positive charge and a center of negative charge
aka when, in a compound, one element has a higher electronegativity than the other
Ion size determines…
Electronegativity increases…
Right way
Electronegativity decreases…
Down way
Cation formation occurs…
On left of periodic table
electrons occupy high energy orbitals, so can lose electrons high energy electrons but not low —> limits size of positive charge on cations
Anion formation occurs…
On right of periodic table
electrons occupy low energy orbitals
To create cations…
For main group elements, take electron from highest energy orbital
For transition elements, take uppermost s subshell first before valence d electrons
Cations Size
Smaller than atom formed from
Anions Size
Larger than atom formed from
Bond breaking is a process of
Endothermic process
Bond formation is a process of
Exothermic process
Calculating ΔH for a given reaction
= energy required to break bonds – energy released when bonds form
Calculating Formal Charge
Atom’s group # - [Amount of lone pair electrons + ½ amount of bonding pair electrons]
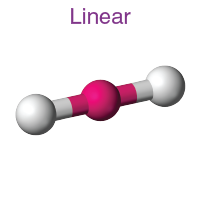
Electron-Pair Geometry: 2 groups around center
Linear
Bond angle: 180
Electron-Pair Geometry: 3 groups around center
Trigonal-planar
Bond angle: 120
Electron-Pair Geometry: 4 groups around center
Tetrahedral
Bond angle: 109.5
Electron-Pair Geometry: 5 groups around center
Trigonal-bipyramidal
Bond angle: 120 and 90
Electron-Pair Geometry: 6 groups around center
Octahedral
Bond angle: 90
If sum of lone pairs and atoms is 2, the hybridized orbital is…
Two sp orbitals
Unhybridized orbitals: Two p orbitals
If sum of lone pairs and atoms is 3, the hybridized orbital is…
Three sp² orbitals
Unhybridized orbitals: One p orbital
If sum of lone pairs and atoms is 4 the hybridized orbital is…
Four sp³ orbitals
Unhybridized orbitals: None
Geometry of sp hybrid orbital
Linear
Geometry of sp hybrid orbital sp² hybrid orbital
Planar-trigonal
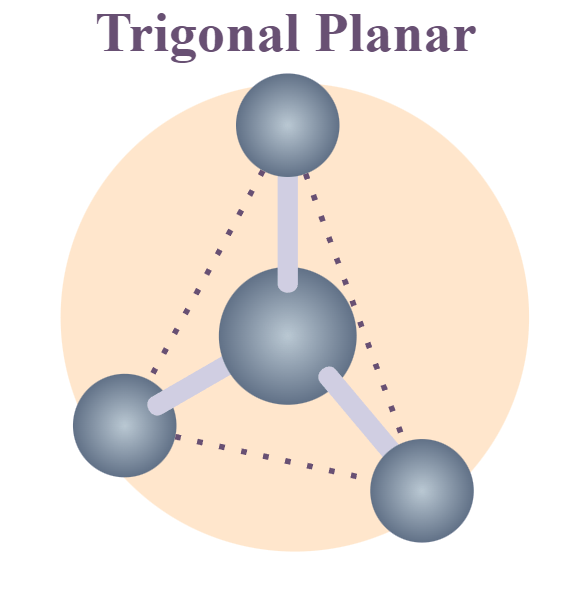
Geometry of sp hybrid orbital sp³ hybrid orbital
Tetrahedral
When 1s orbitals combine…
They form two sigma molecular orbitals
one bonding, one antibonding
When 2p orbitals combine…
They do
Direct head-to-head to form sigma and sigma+ molecular orbitals
Indirect, parellel to form pi and pi+ molecular orbitals
Molecular Geometry of 3 atoms + 0 lone pairs
Trigonal Planar
Molecular Geometry of 2 atoms + 1 lone pairs
Bent
Molecular Geometry of 4 atoms + 0 lone pairs
Tetrahedral
Molecular Geometry of 3 atoms + 1 lone pairs
Trigonal Pyramidal
Molecular Geometry of 2 atoms + 2 lone pairs
Bent
Molecular Geometry of 6 atoms + 0 lone pairs
Octahedral
Molecular Geometry of 5 atoms + 1 lone pairs
Square pyramidal
Molecular Geometry of 4 atoms + 2 lone pairs
Square planar
Molecular Geometry of 5 atoms + 0 lone pairs
Trigonal bipyramidal
Molecular Geometry of 4 atoms + 1 lone pairs
Seesaw
Molecular Geometry of 3 atoms + 2 lone pairs
T-shaped
Molecular Geometry of 2 atoms + 2 lone pairs
Linear
Most likely Resonance is…
The one with the smallest formal charge
Paramagnetism
Presence unpaired electrons
Diamagnetism
Presence of paired electrons
Bond order
(# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons) / 2
Larger bond order
Greater bond strength
Steps for Drawing MO Orbital Energy Diagram
Think of it as combining two atoms of the same element: AtomA and AtomB
Draw out left to right the amount of electrons in the 1s orbital for the element on both sides
Draw the bonding sigma 1s orbital and antibonding sigma 1s orbital
Transfer electrons from both sides into bonding sigma 1s orbital first, then antibonding if needed
Repeat for sigma 2s, pi 2p, etc
Hydrogen Bonding
When hydrogen reacts with N, O, F