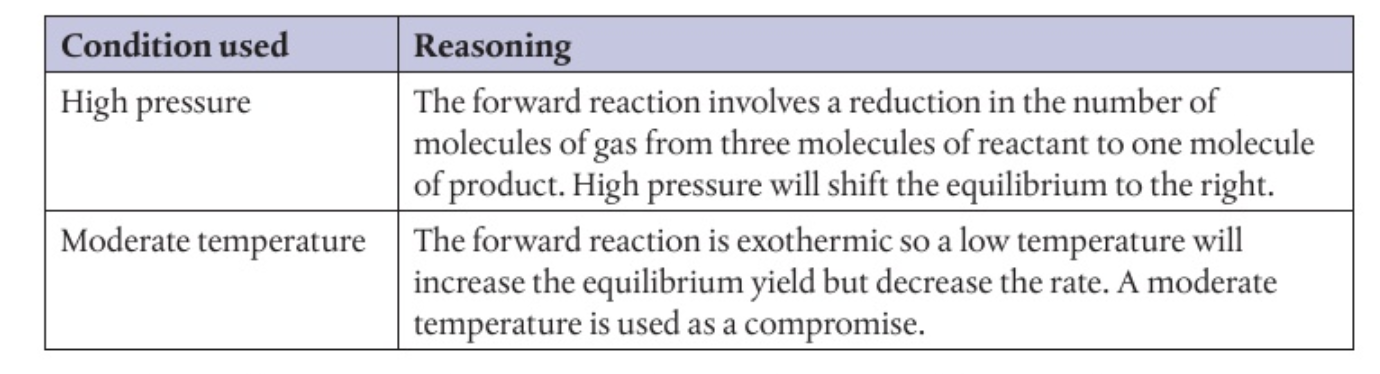
Dynamic Equilibrium
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What does rate of condensation equal to
Rate of evaporation
means system reached eq.
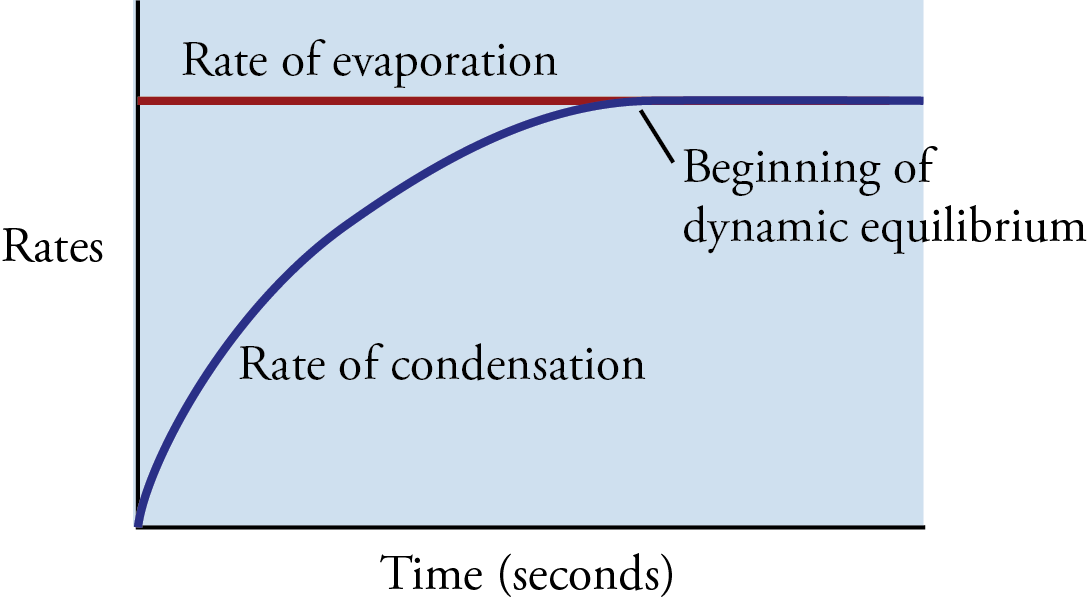
What remains constant at eq
concentrations
eq. reached
Why is it dynamic - chemical
Forwards and backwards reactions still occuring
Left to right
reactant to product
forward reaction
Right to left
Product to reactant
backwards reaction
Lies to left
more reactant
Lies to right
more product
Equilibrium constant expression
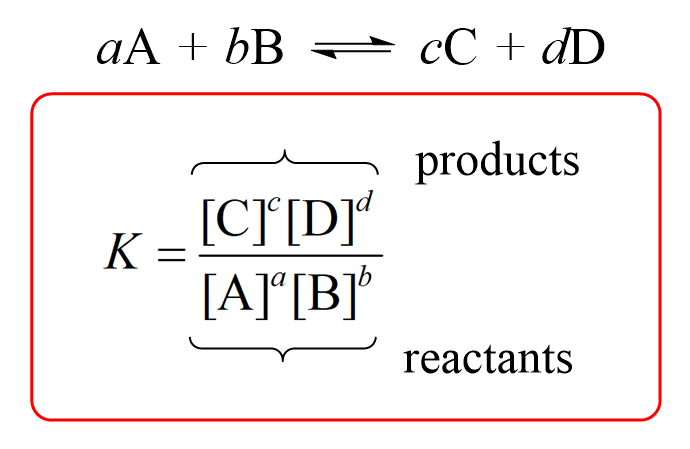
High value of K
more products than reactants
right
goes near completion
Low value of K
More reactants than products
left
barely taken place
reverse reaction
Backwards reaction
K’ or K-1
Le Châteliers principle
A system at equilibrium when subjected to a change will respond in such a way to minimise the effect of change
Changes in pressure
increase in P, favours side with smaller number of molecules
different eq. position, K stays the same
Changes in temperature
will change K, K depends on temp
Exothermic - releases energy (H negative)
endothermic - absorbs energy (h positive)
Increasing temp - increase K for endothermic
increasing temp - decrease K for exothermic
Adding catalyst
Lowers activation energy
speeds up achieving eq.
No effect on eq. position or K value
Used in industry
Summary - factors
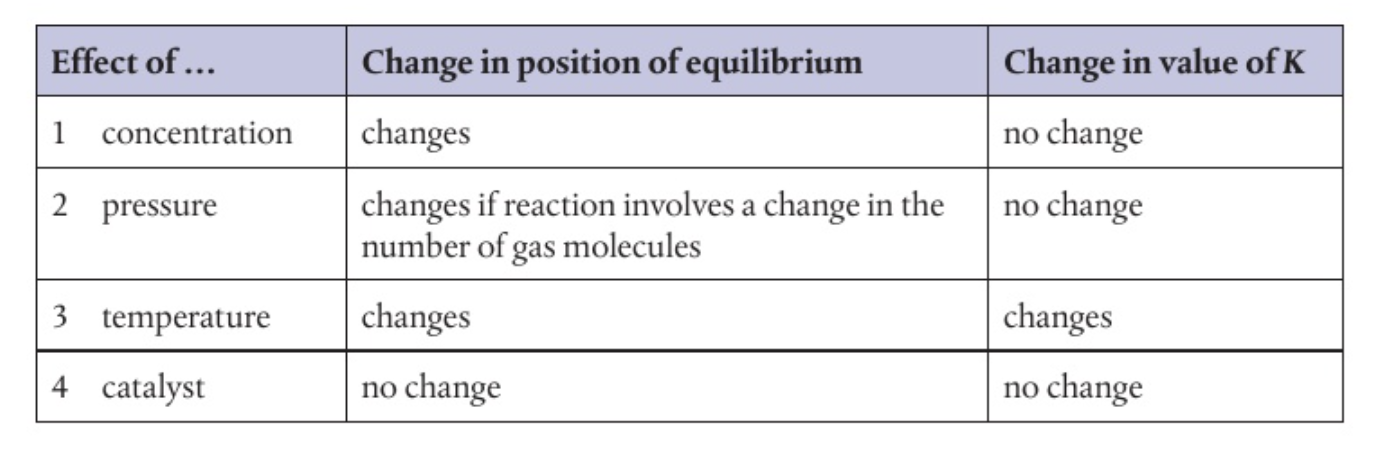
Production of ammonia
N2 + 3H2 = 2NH3