physio exam one
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
G-proteins
have an a, B, and y subunit that dissociate and “shuttle” between receptor and effector
semi-permeable
allowing some substances to pass
saltatory conduction
propagation of action potential along axons between myelin nodes
paracellular
movement of molecules between cells (only crosses the membrane once, where two cells touch)
peripheral proteins
proteins that are partially embedded on one side of the plasma membrane
catabolism
reactions that release energy from products, break down larger molecules into smaller ones
exocrine
secretes to ducts outside the body
skeletal muscle
tissue with a striped or striated appearance
transcellular
movement of molecules through a cell (by crossing membrane on both sides)
carrier
protein on cell membranes that helps transport substances across membrane
carbohydrates
organic molecule with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio
plasticity
ability to change over time; in reference to synaptic connection strength
endocrine
secretes to capillaries inside the body
symport
secondary active transport
lipid
organic molecule consisting of non polar hydrocarbon chains
anabolism
reactions that store energy by putting smaller products together into larger ones
dendrite
receiving end of a neuron
spatial summation
due to convergence of many signals onto one cell
convergence
when signals come together in a single location/on a single neuron
temporal summation
due to successive waves of neurotransmitter release through time
hormone
chemical released into the bloodstream
ribosome
organelle that builds proteins by “reading” mRNA
positive
blood platelets releasing chemical to recruit additional platelets to form a clot is an example of this type of feedback loop
potassium (K+)
under resting conditions, the ion in greatest concentration inside body cells
voltage-gated
term for a channel that will open or close depending on the charge of a cell’s membrane
homeostasis
tendency to maintain a dynamically constant internal environment; the goal of most physiological mechanisms
connective
blood, cartilage, and adipose tissue are all under this broad tissue type umbrella
sensor
part of a feedback loop responsible for detecting a change
enzymes
biological catalysts that reduce the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur d
diffusion
most basic path/term for movement of molecules down their electrochemical gradients
carrier
what type of membrane protein will only ever be open to one side of the plasma membrane at a time?
blood
what type of connective tissue is characterized by a liquid extracellular matrix?
compose genes
which of the following is NOT a function of proteins in the body?
carriers for membrane transport
enzymes
compose genes
receptors for regulator molecules
autonomic nervous system
which division of the nervous system innervates involuntary effectors?
valence of ion X
what does the z value stand for in the Nernst equation?
increased extra-cellular fluid osmolarity
dehydration might cause _____
increased water in extra-cellular fluid
decreased extra-cellular fluid osmolality
increased extra-cellular fluid osmolality
increase in cell volume
squamous
cells that are wider than they are tall have a ______ shape
specific receptor proteins within the cell or in the plasma membrane
regardless of solubility, a cell signaling molecule could not affect a target cell without_____
being attached to another cell
a second messenger in the plasma membrane
specific receptor proteins within the cell or in the plasma membrane
all of the choices are correct
occurs down a chemical gradient
which of the following characteristics would be shared by simple and facilitated diffusion of a molecule across a membrane?
requires a carrier molecule
requires metabolic energy
occurs down a chemical gradient
occurs with a Na+ gradient
the solution if hypotonic
what can you say FOR CERTAIN if 78% of the cells placed in a solution break open (lyse) from swelling due to water movement?
secondary active transport
which of the following processes is involved if transport of a molecule is inhibited by abolishing the usual Na+ gradient across the cell membrane?
simple diffusion
facilitated diffusion
primary active transport
secondary active transport
Ca+2 permeability
when an action potential reaches the axon terminal (end of pre-synaptic axon), it triggers an increase in _____ of the membrane to allow for neurotransmitter release
remain bound to the post-synaptic membrane
which of the following is NOT a potential fate of neurotransmitter after release into the synaptic cleft?
reuptake into the pre-synaptic cell
diffusion out of the synapse
remains bound to the post-synaptic membrane
degradation by enzymes in the cleft
hydrogen
the pH of a solution increases as the _____ ion concentration decreases
absolute refractory period
the period of time when Na+ channels are recovering from their inactive state and K+ channels are still open is the ______
intracellular fluid compartment
most of the water found in the body is in the ____
central and peripheral
what are the first two divisions of the nervous system?
brain and spinal cord
where does the central nervous system innervate?
efferent (motor) and afferent
what are the first two subdivisions of the peripheral nervous system?
autonomic (involuntary) and somatic (voluntary)
what are the divisions of the efferent nervous system?
parasympathetic, sympathetic, and enteric
what are the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
rest and digest
what is the phrase for the parasympathetic nervous system?
fight or flight
what is the phrase for the sympathetic nervous system?
the gut
what does the enteric nervous system focus on?
striations
histological distinction of skeletal muscle
striations and intercalated discs
histological distinction of cardiac muscle
very disorganized appearance, no striations or intercalated discs
histological distinction of smooth muscle
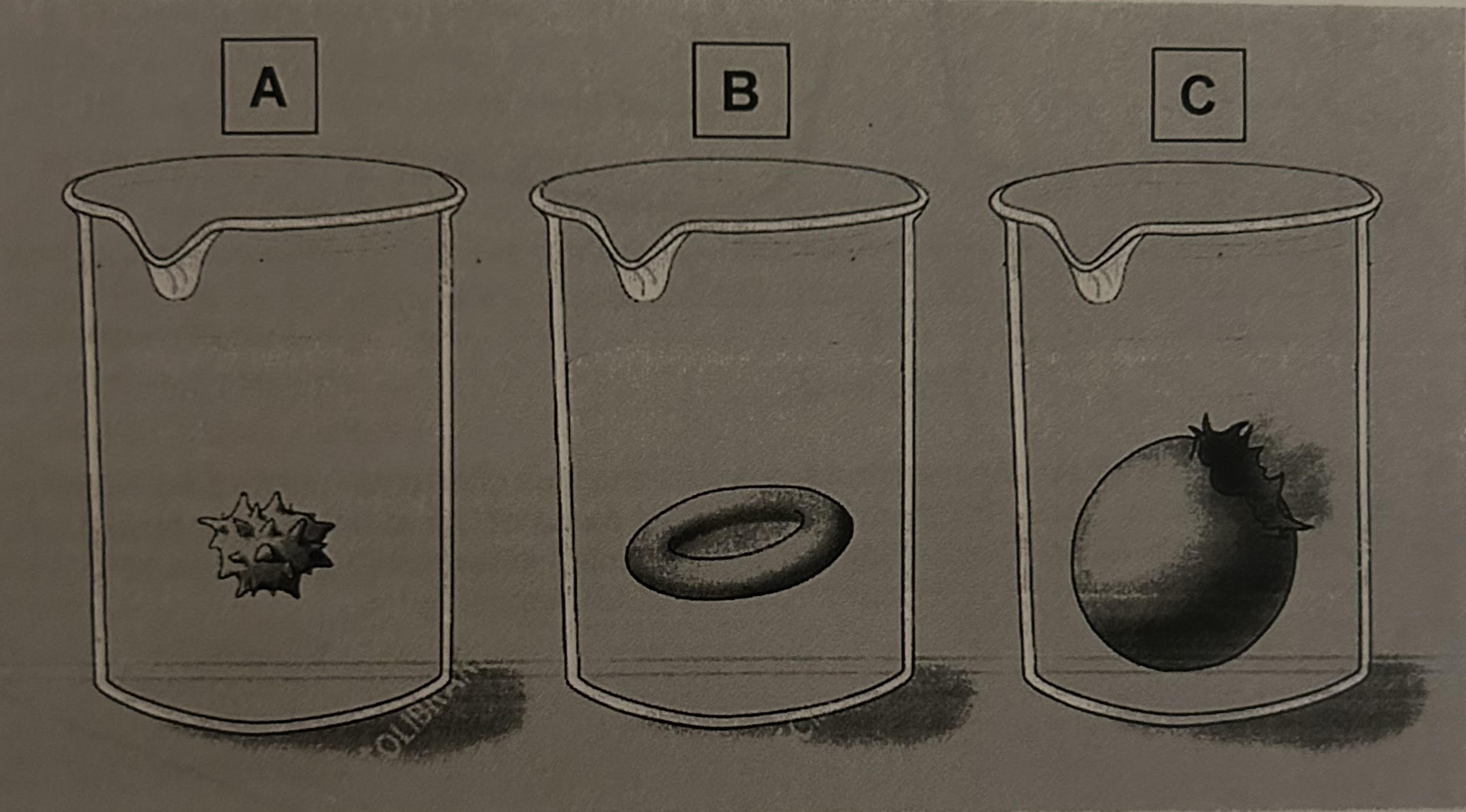
A) hypotonic
B) isotonic
C) hypertonic
Label which solution is isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic
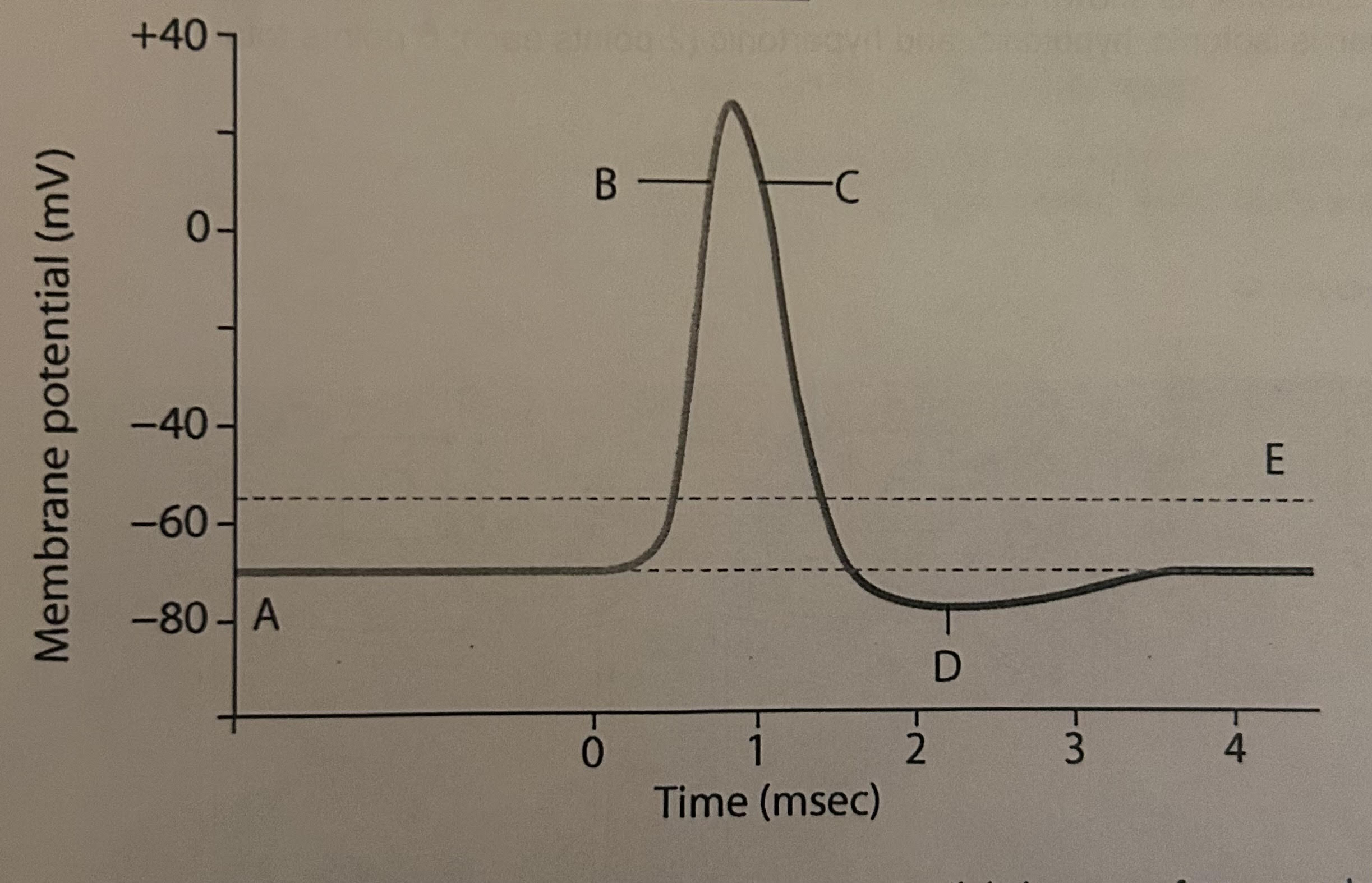
A) resting potential
B) depolarization
C) repolarization
D) hyperpolarization
E) threshold
label the graphs in terms of the name of the membrane potential value or the type of polarization that is occurring