Brain and Behaviour (3): Neurotransmission
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Structure of a Neuron
Dendrites: Recipients of information from other neurons
Soma (Cell Body): Contains machinery that controls processing in the cell and integrates information
Axon: Carries information (action potentials) from the soma → Axon terminals. They branch to connect multiple neurones.
Axon Terminals: Communication point with other neurons found at the end of axons (where synapses are found)
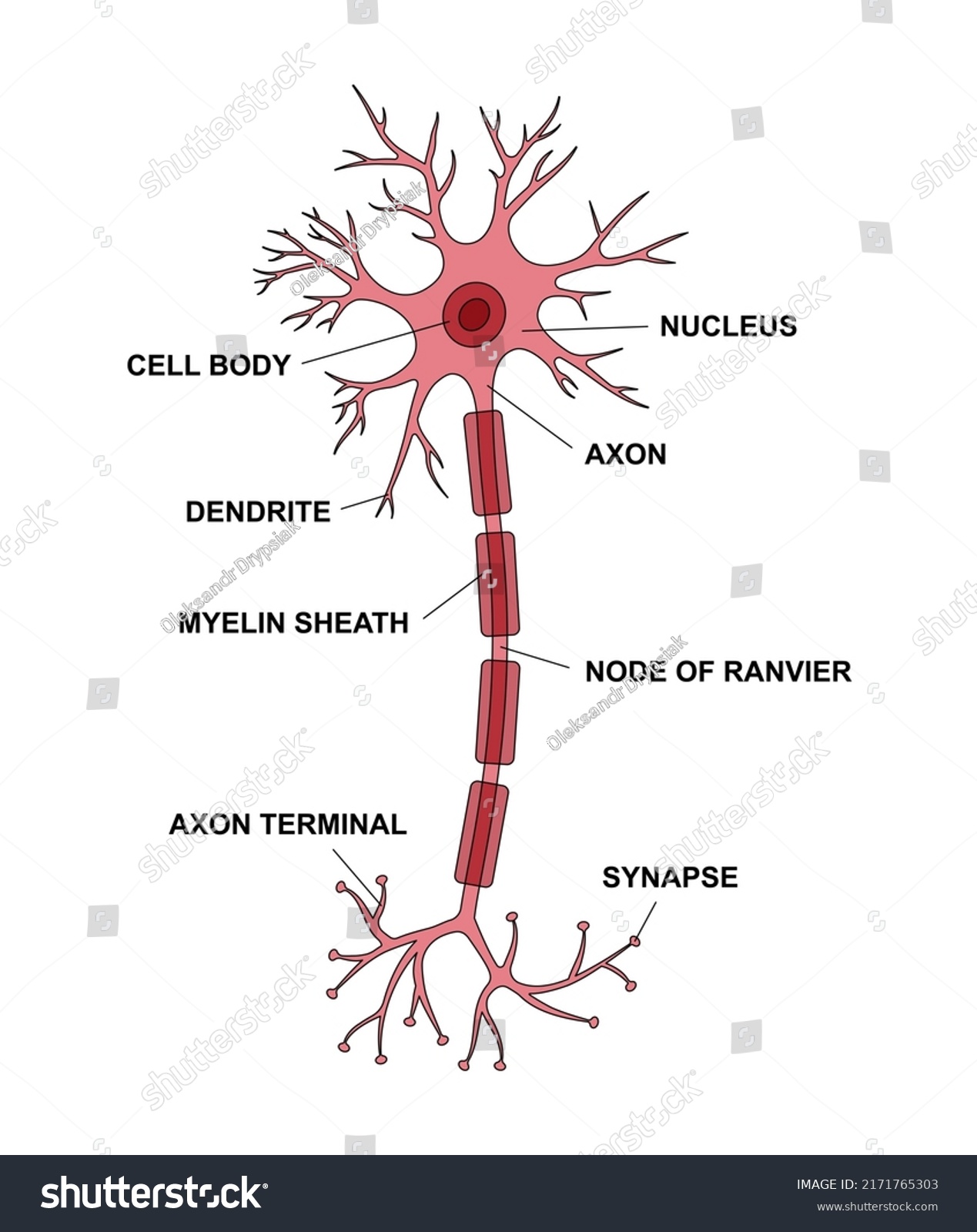
Neuronal Membrane
5nm thick lipid bilayer that separates the extracellular and intracellular environment.
It acts as the boundary of soma, dendrites and axons and their terminals.
Contains protein structures that detect substances outside the cell and allows access of certain substances into the cell
Types of Synapse
Electric Synapse:
Rare in adult mammals (e.g. in retina)
Small junctions between neurons (3nm) which is spanned by proteins that communicate between neurons through ion flow
Chemical Synapse
Common in adult mammals
Junction between neurons (20-50nm)
Chemicals are released from the presynaptic neuron → postsynaptic neuron
Evidence for Chemical Transmission
Loewi: Fluid collected after vagus nerve stimulation of one frog heart could slow heart rate when applied to a different frog heart, proving chemical transmission of nerve impulses.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit information from the presynaptic → postsynaptic neuron
4 Properties of Neurotransmitters
Pharmacology – What binds and how drugs interact (agonists/antagonists)
Kinetics – Rate of binding and channel gating
Selectivity – Which ions are fluxed
Conductance – Rate of ion movement
Steps of Chemical Transmission
Depolarisation - Impulse (Action Potential) travels down axon →
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open and calcium ions enter the neuron
Vesicles move to the presynaptic membrane
Exocytosis - the vesicle fuses with the membrane and the neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft (diffusion)
Neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron →
Ion channels in the postsynaptic neuron open →
Positive Ions flow in: Excitatory effects OR
Negative Ions flow in: inhibitory effects
Remaining neurotransmitters are removed through reuptake or deactivating enzymes
GABA
Main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain, which reduces neuronal excitability. It is synthesised from Glutamine.
Glutamate
Main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. It binds to NMDA & AMPA receptors, allowing synaptic transmission. It is synthesised from Glutamine.
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter that plays a role in the nervous system. It binds to nicotinic & muscarinic receptors which influence neuronal excitability.
Differences between Ionotropic & Metabotropic receptors
Ionotropic (e.g. GABA):
Fast
Direct ion channel opening
Immediate effect
Metabotropic (Dopamine/Serotonin):
Slow
Indirect ion channel opening via G-protein activation, activating molecules → reactions → signal amplification
Amplified, lasting effect
Autoreceptors
(Typically) G-coupled metabotropic protein receptors located on the presynaptic terminal that regulate neurotransmitter release via a negative feedback mechanism.