NROB60 Lec 1-2
1/263
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
264 Terms
ectoderm
the top plate of the embryo that becomes the neural plate
What happens at 18 days of neural tube development?
Notochord forms and the ectoderm becomes the neural plate
What happens at day 20 of neural tube development?
Floorplate comes up form the neural plate above the notochord and the neural crest emerges in the lateral margins of the neural plate
What happens at day 22 of neural tube development?
Neural tube completes when the edges of the neural plate meet in the midline and somites begin to form in the mesoderm which becomes the skeleton
somites
form in the mesoderm around the neural tube and develop into the skeleton
What does the Prosencephalon divide into?
Telencephalon and diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus)
Neurulation
the process of developing the neural tube from the ectoderm of the embryo, leads to brain and spinal cord development
Notochord
A long rod structure that develops into ventral (beneath) the neural tube
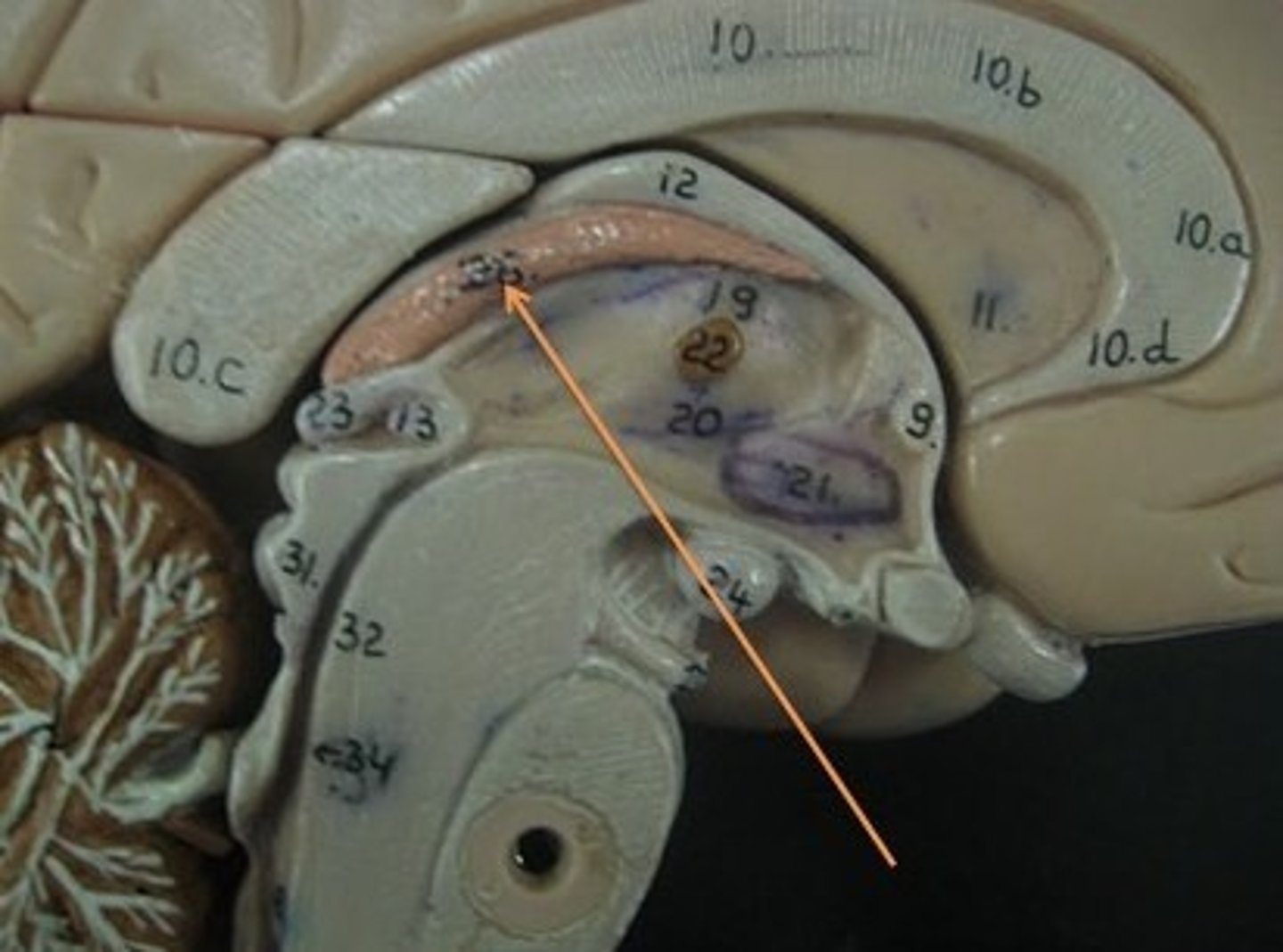
Olfactory nerve (CN I)
Carries information about smell
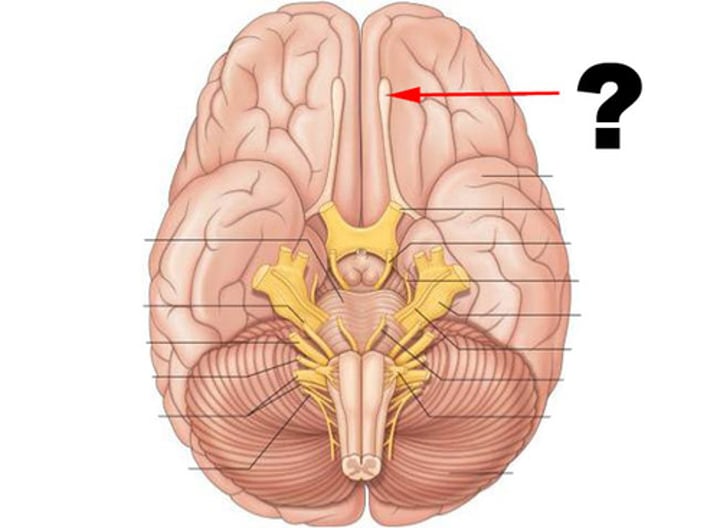
Optic nerve (CN II)
Carries vision
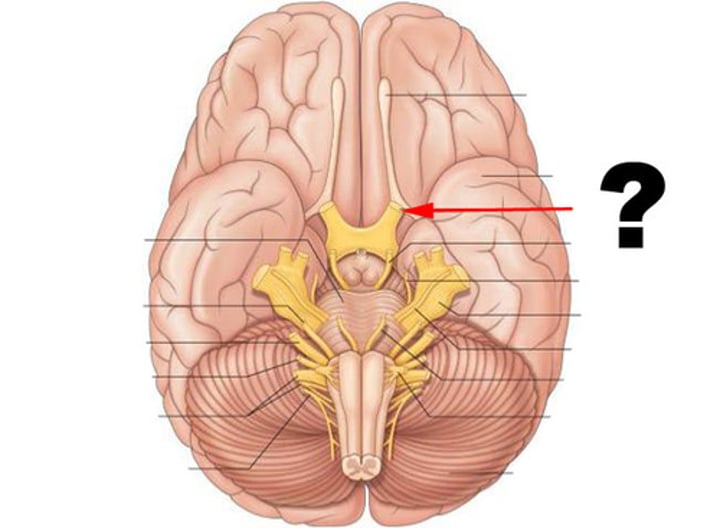
Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
Carries information about hearing and balance
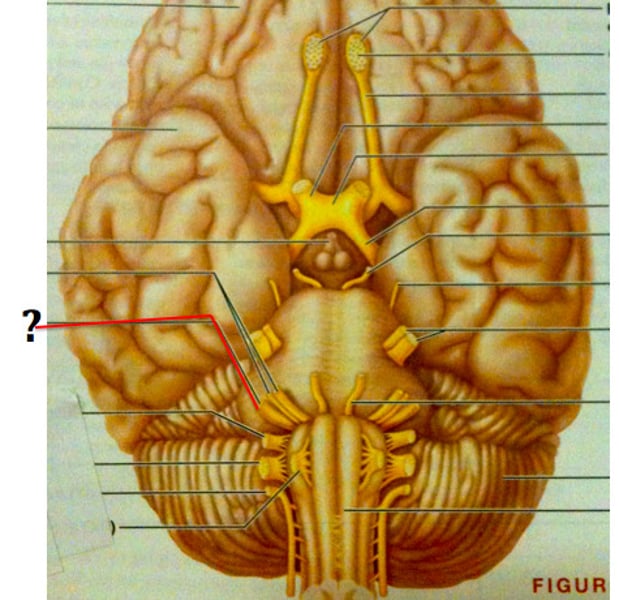
Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Controls eye movement
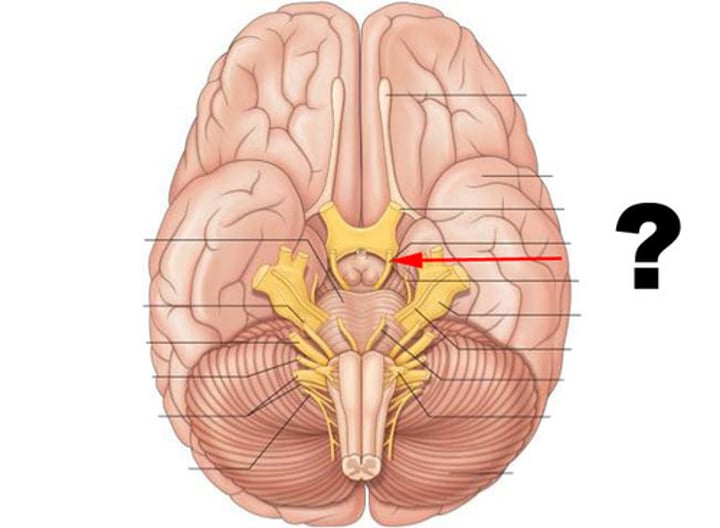
Trochlear nerve (CN IV)
Controls eye movement
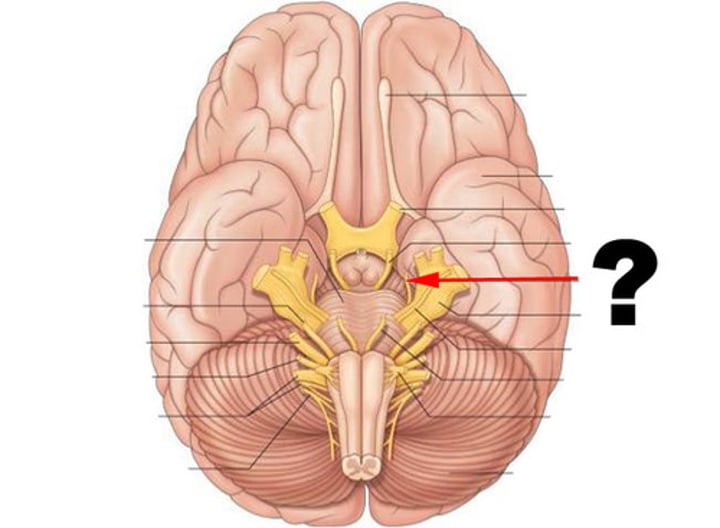
Abducens nerve (CN VI)
Controls eye movement
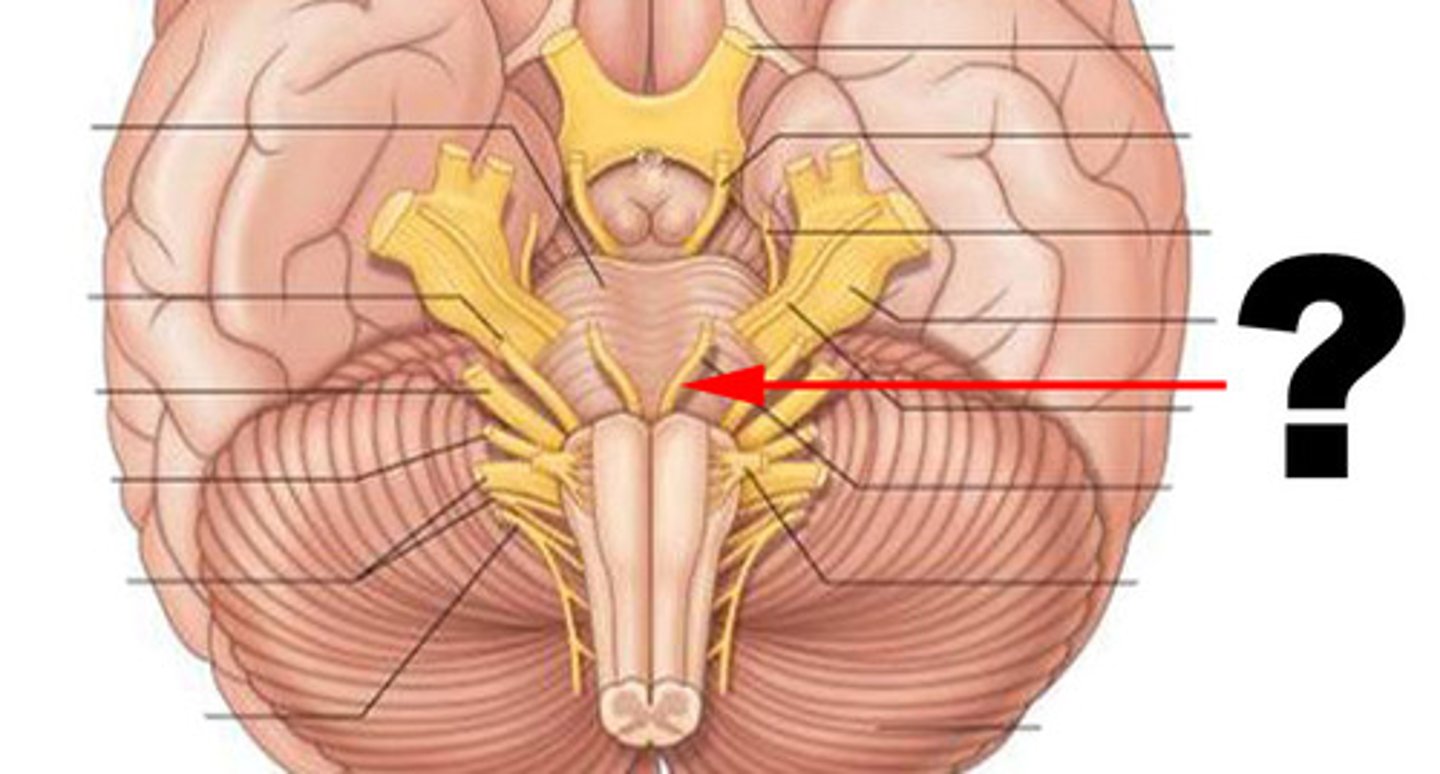
Spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
Controls neck muscles
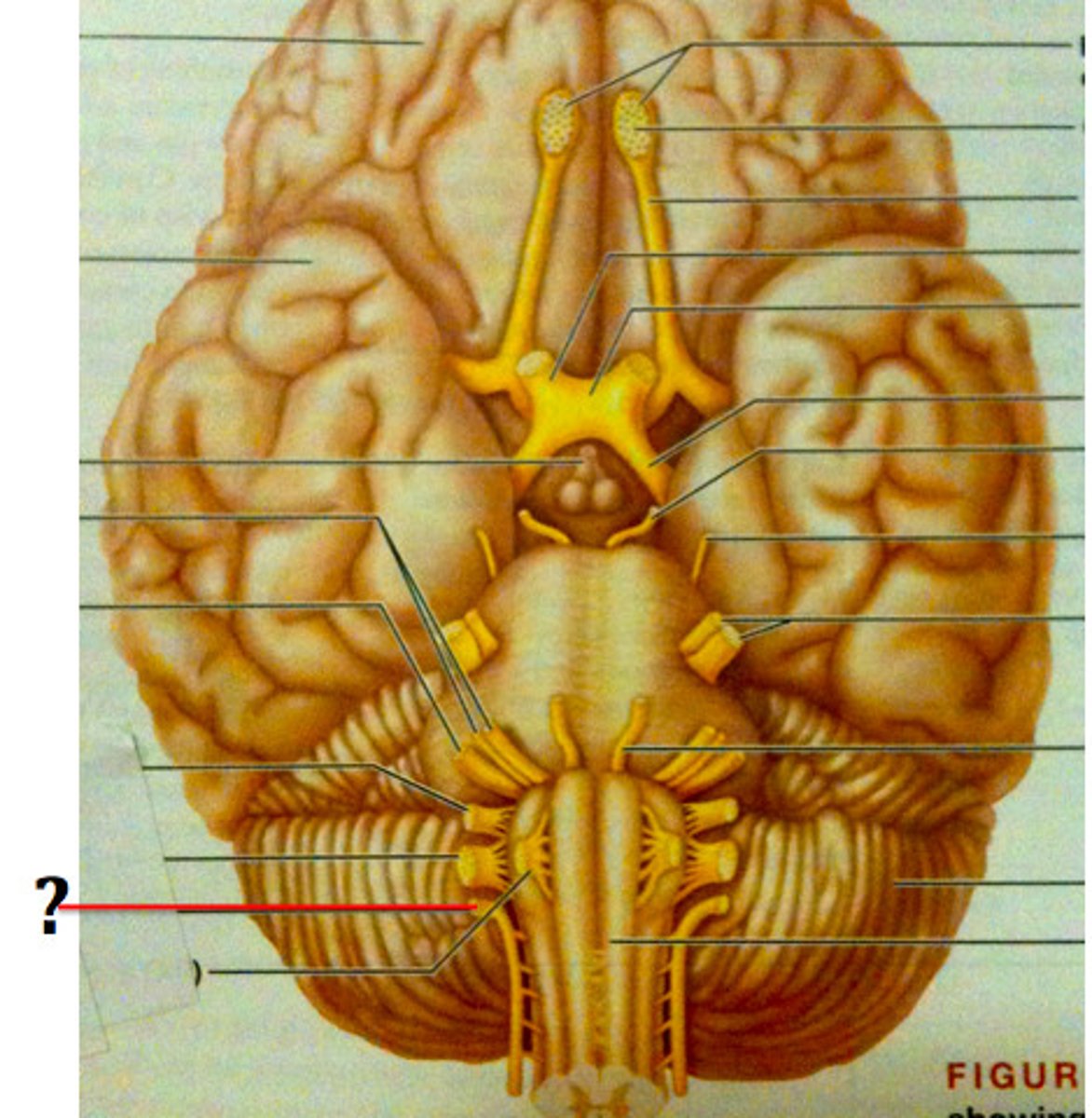
Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
Controls the tongue
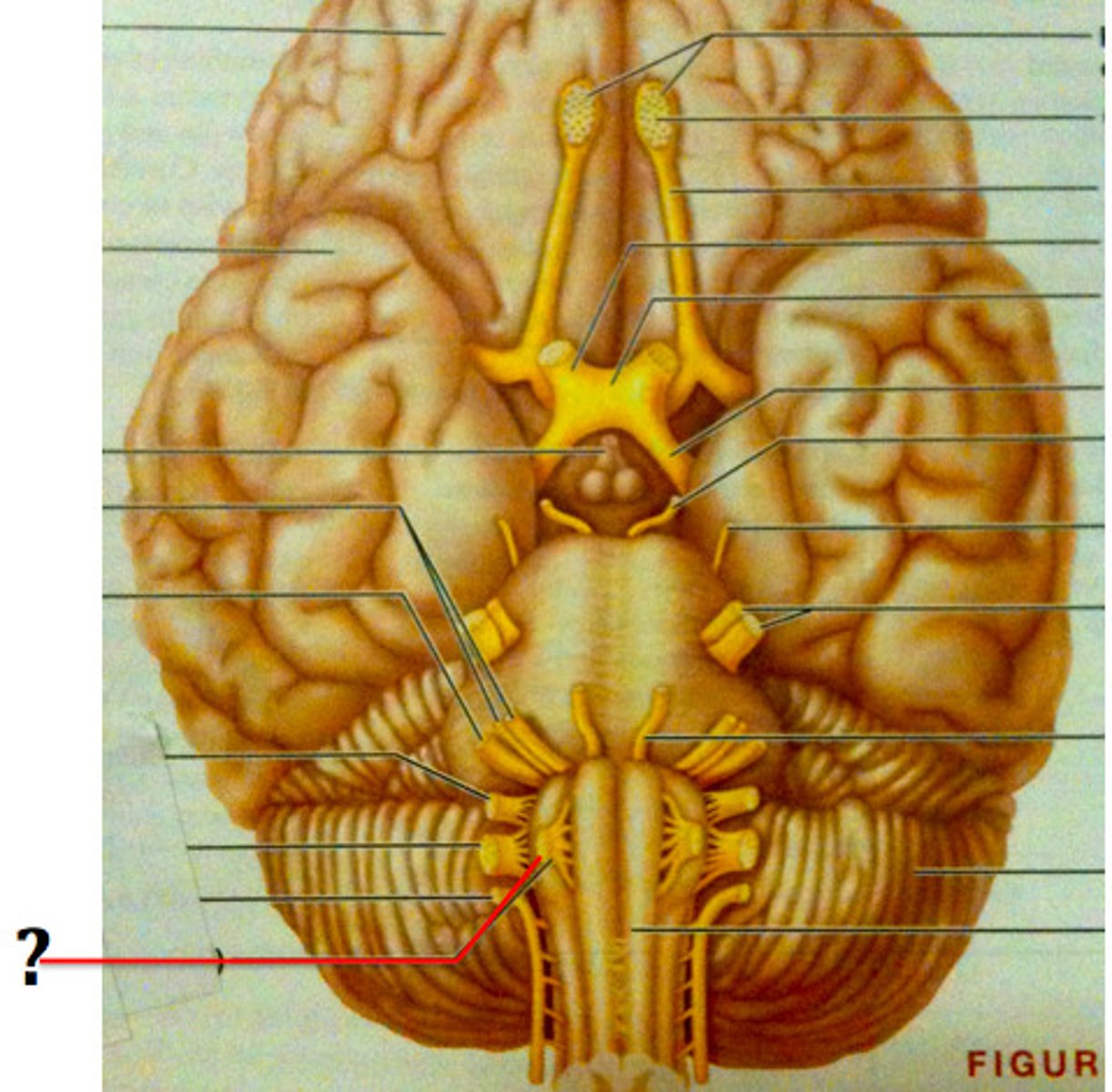
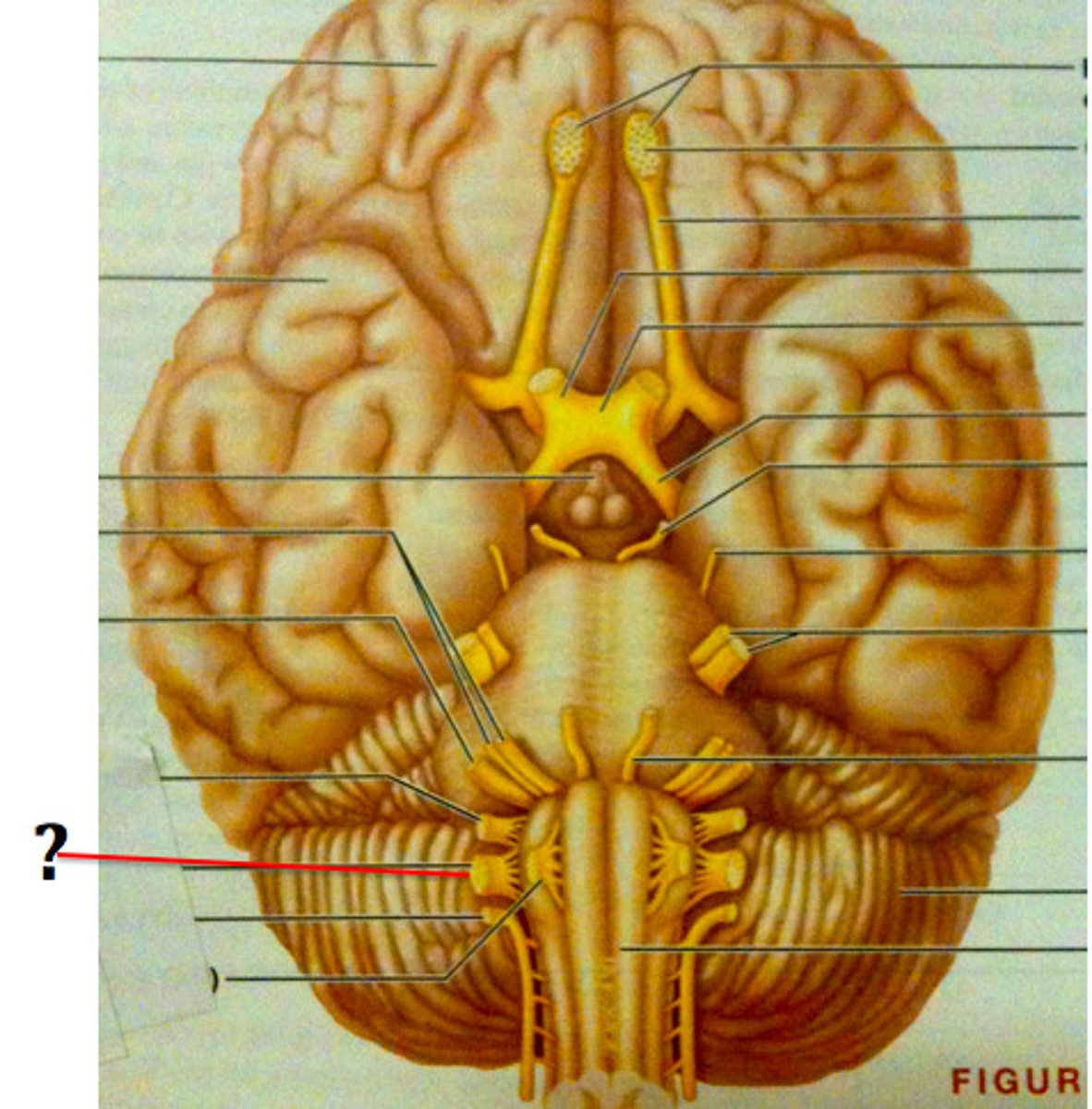
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
Transmits facial sensation and controls chewing
Facial Nerve (CN VII)
Controls facial muscles and receives taste sensation
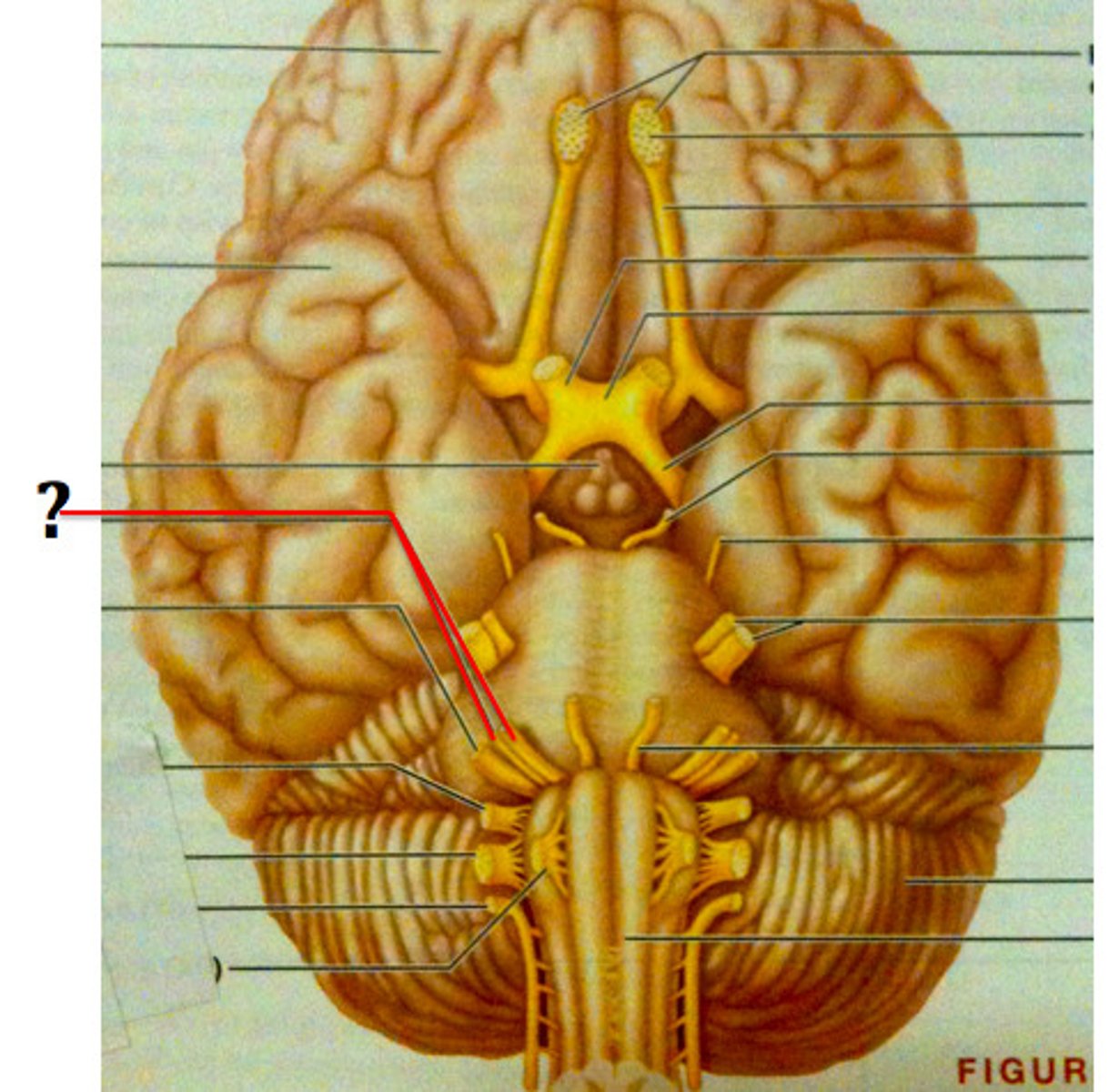
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Receives taste sensation and sensation from posterior end of throat/tongue, and also controls muscles of the throat
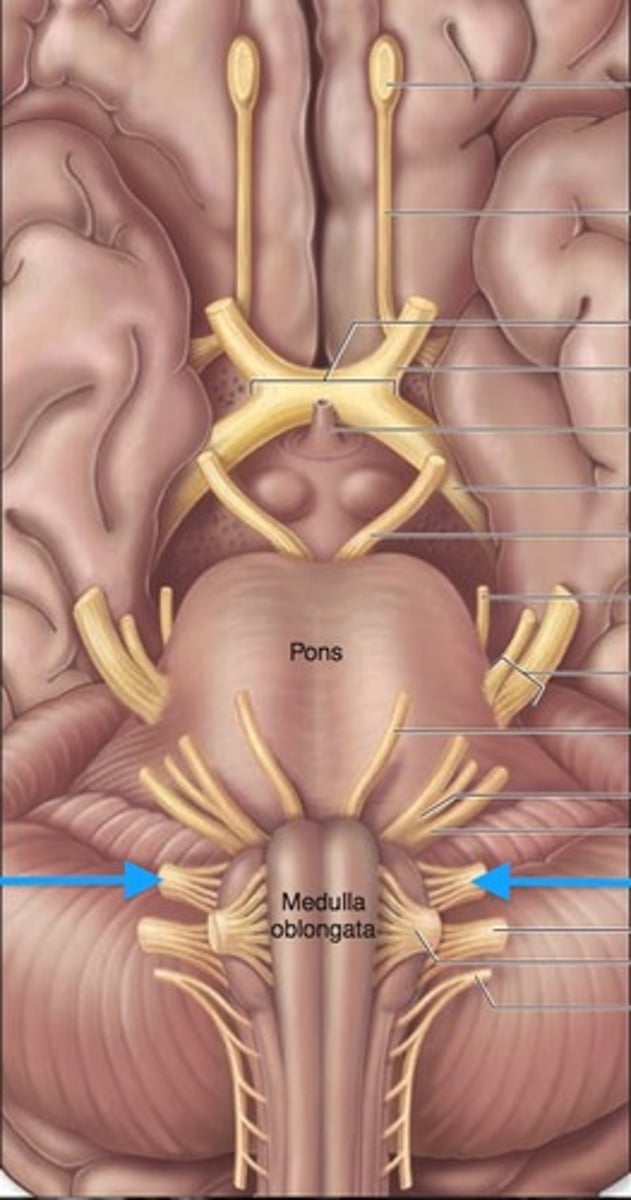
Vagus nerve (CN X)
Receives sensation and controls many visceral organs
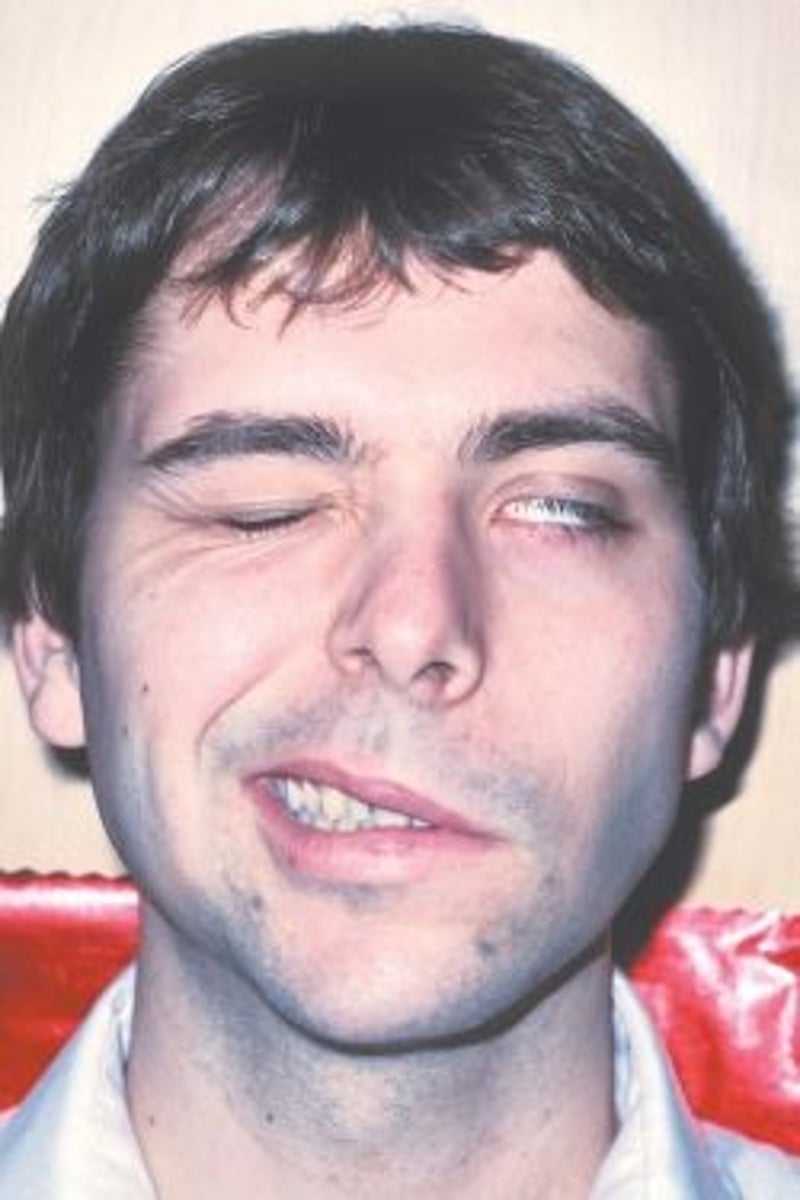
Bell's palsy
Sudden weakness or paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face
Vestibular neuritis
Inflammation of the vestibular portion of CN VIII
Vestibular schwannomas
Slow-growing benign tumor arising from Schwann cells of the vestibular nerve
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy
Degenerative brain disease associated with repeated hits to the head
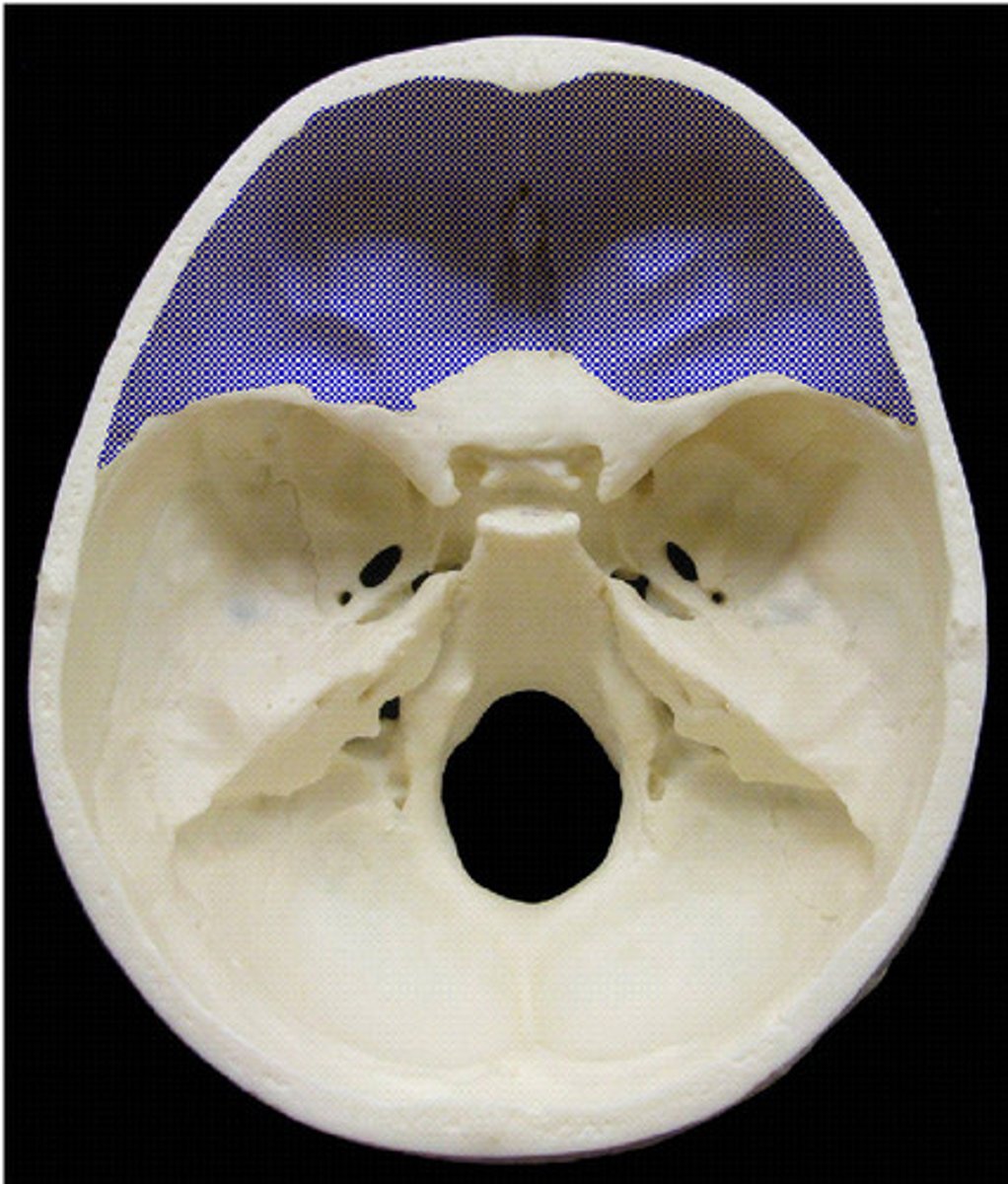
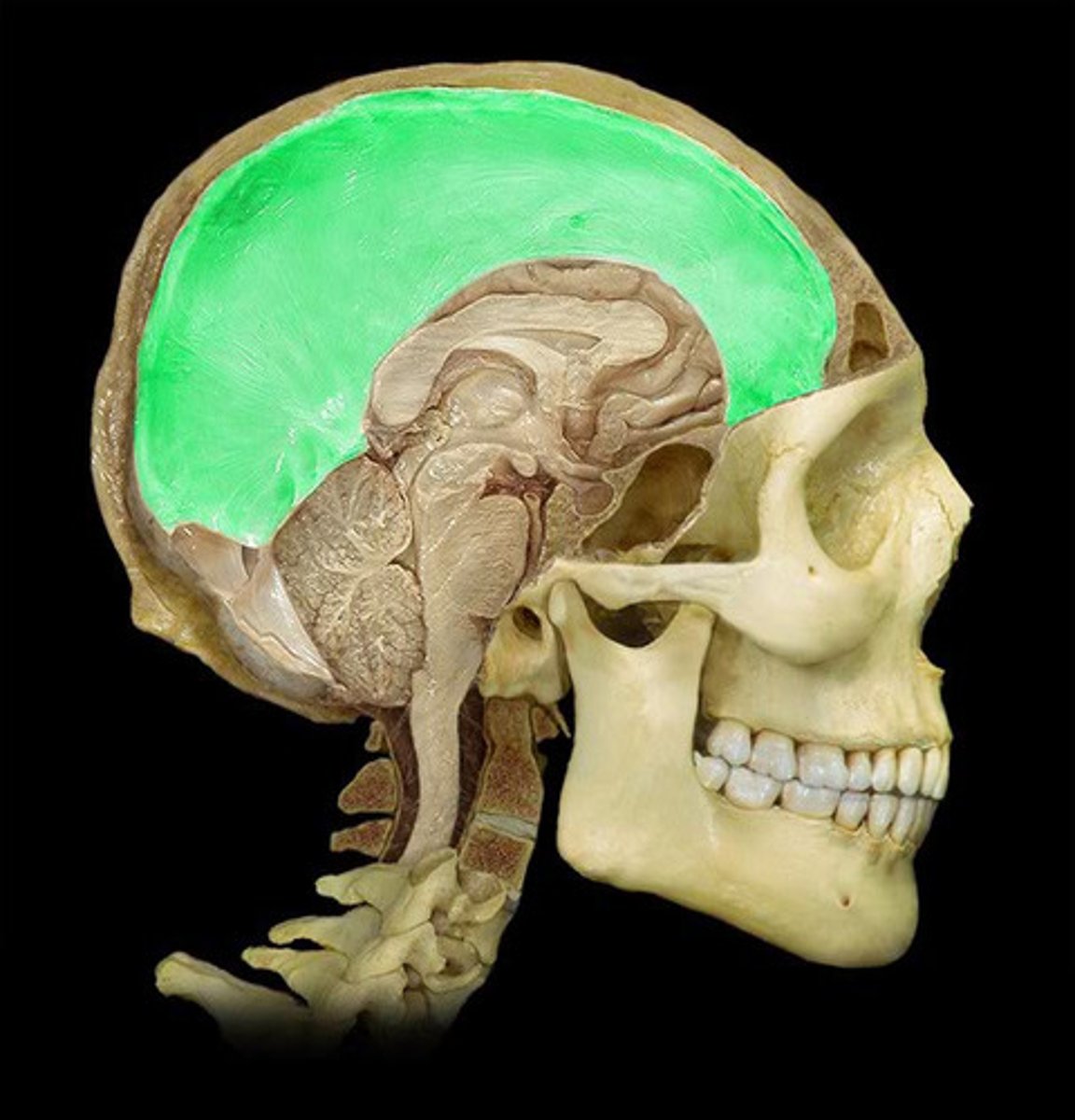
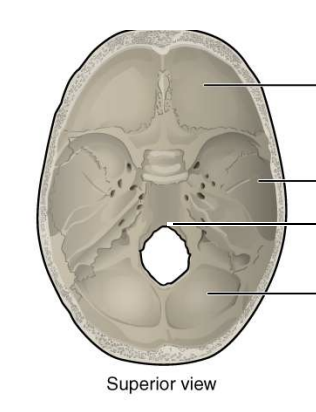
Anterior fossa
Ventral aspect of the frontal lobe
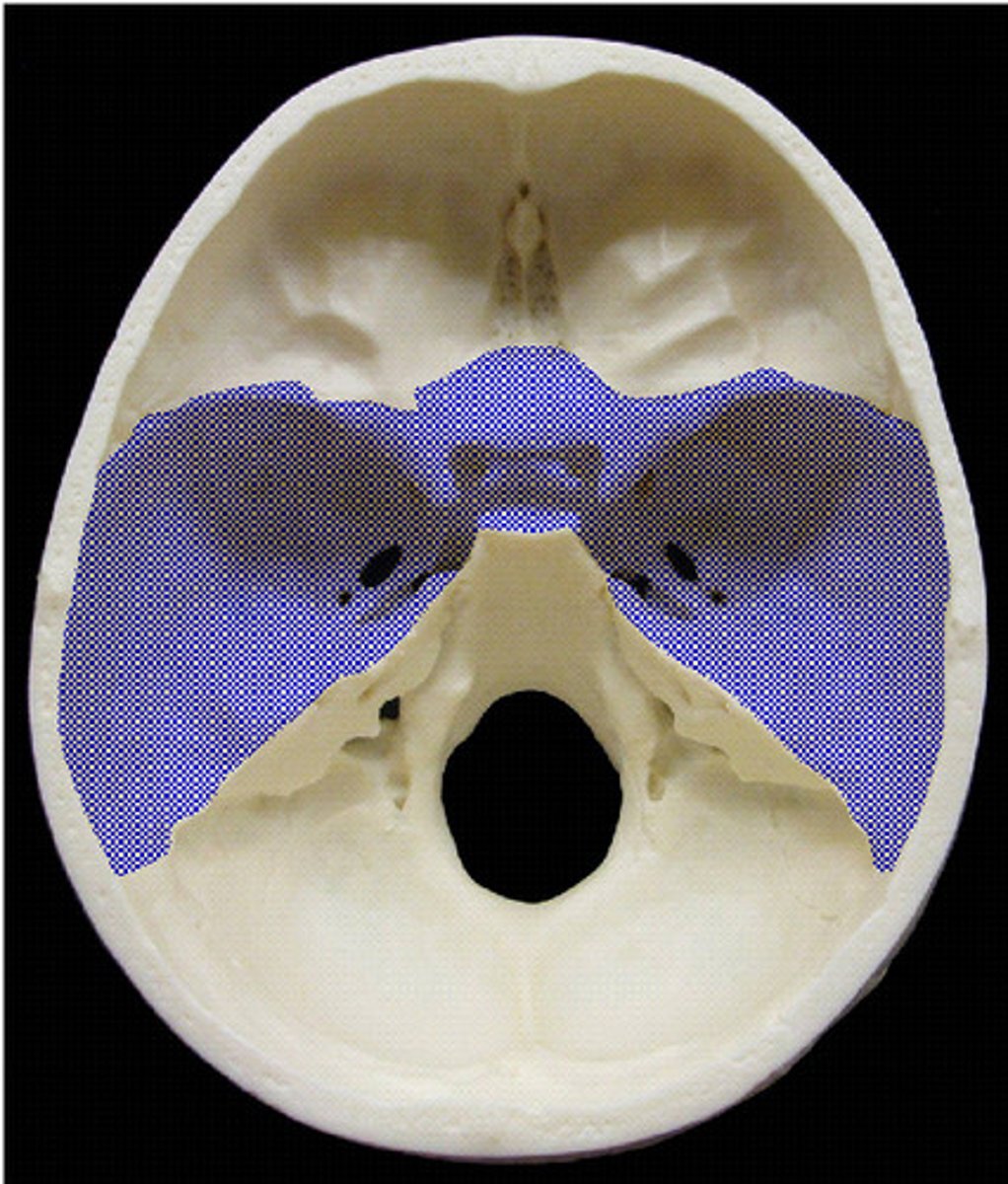
Middle fossa
Much of the temporal lobe
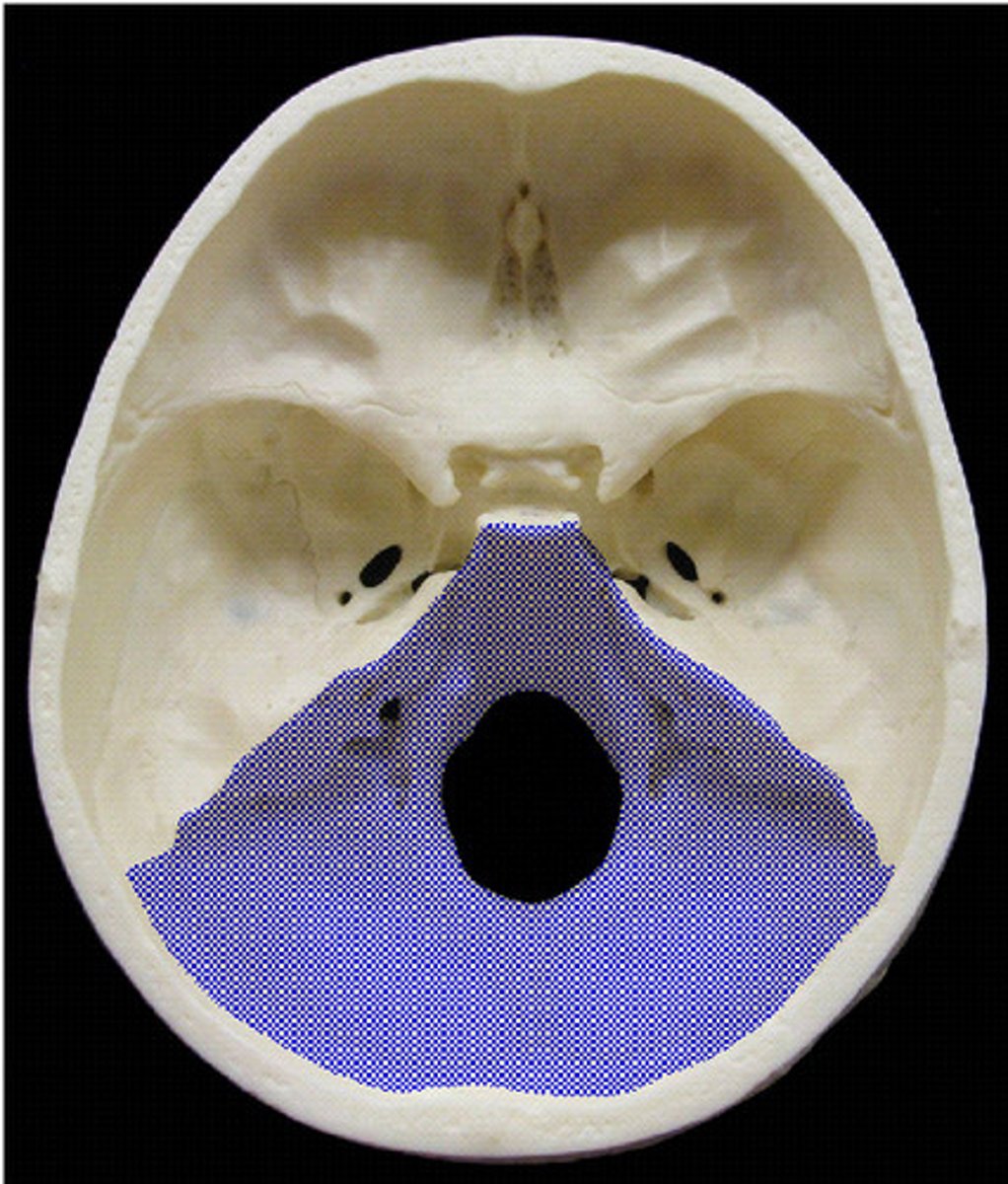
Posterior fossa
Brainstem and cerebellum
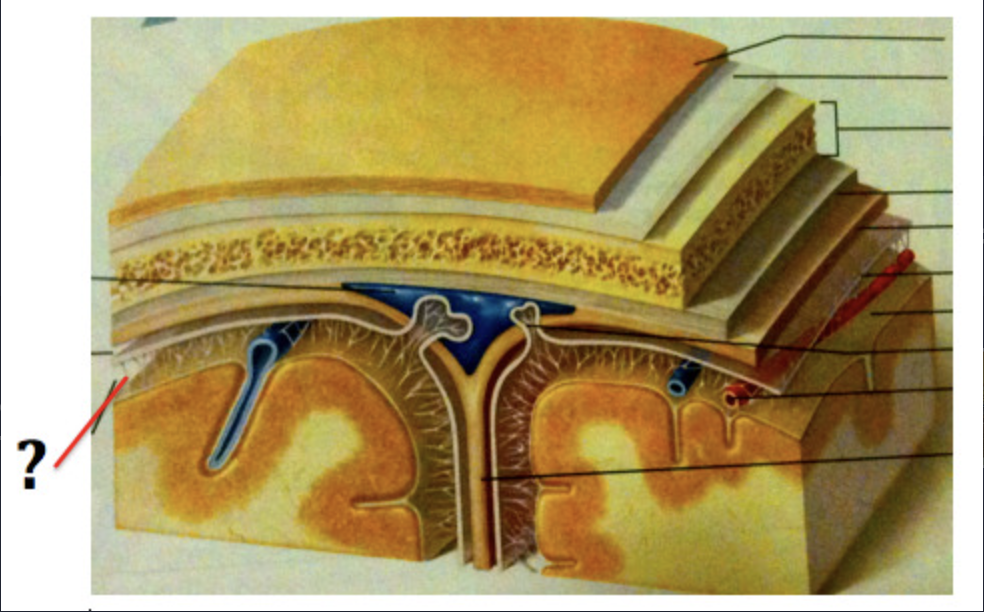
Dura mater
Outermost protective membrane of the brain and spinal cord
Arachnoid mater
Middle protective membrane of the brain and spinal cord
Pia mater
Innermost protective membrane of the brain and spinal cord
Falx cerebri
Crescent-shaped fold that separates the two hemispheres of the brain
Major venous sinuses
Formed by a separation of the inner and outer layers of the dura mater
Subarachnoid space
Space filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and major cerebral arteries, and space where CSF flows after exiting the fourth ventricle
Brain hemorrhage
Localized bleeding in the brain
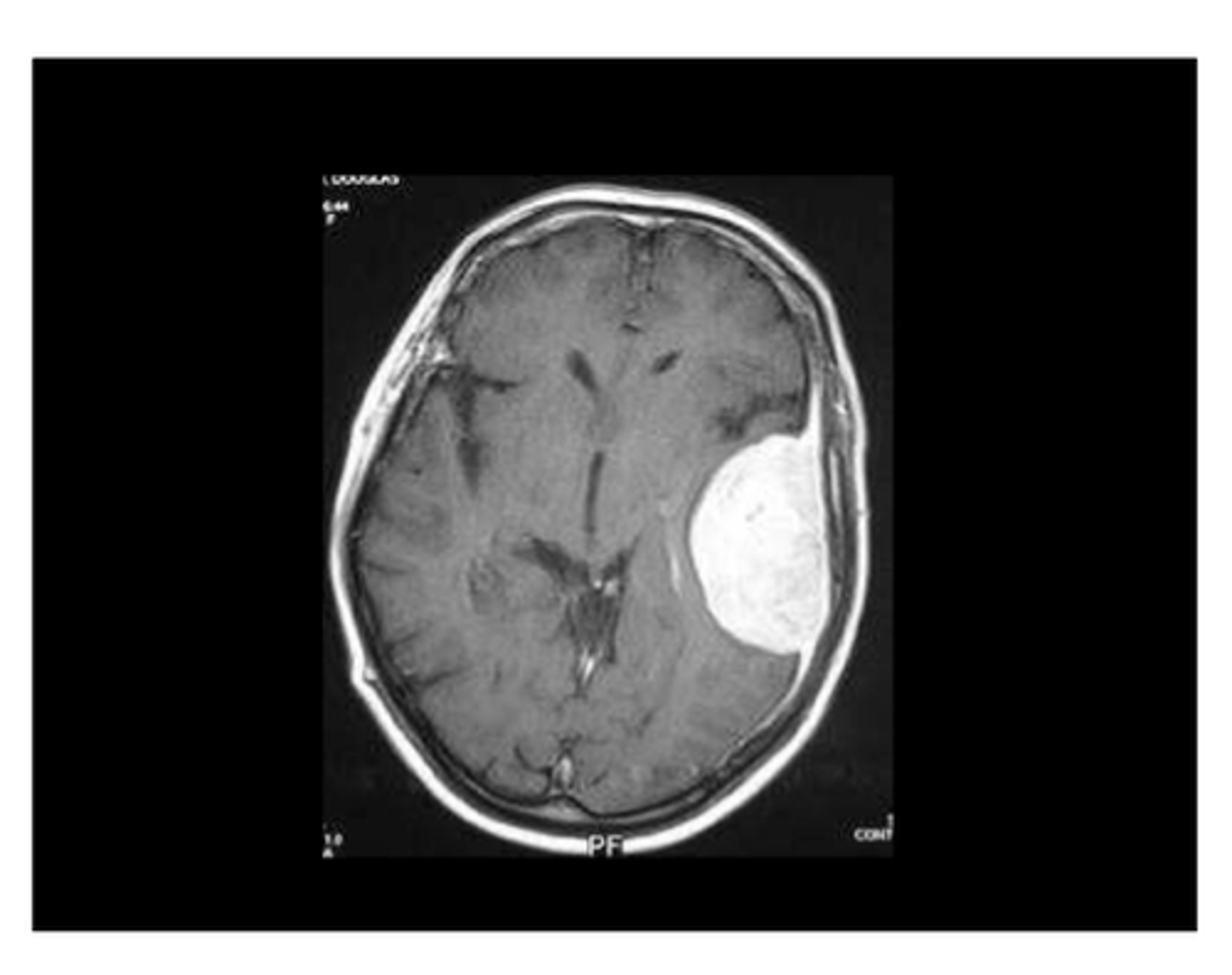
Meningiomas
Benign tumors arising from the dura mater
Meningitis
Infection and inflammation of the meninges
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Clear, colorless fluid that flows in and around the brain and spinal cord
Ependymal cells
Specialized cells in the choroid plexus that produce CSF
Ventricles
Cavities in the brain that contain CSF
Fourth ventricle
Space between the dorsal brainstem and cerebellum
Ventriculoperitoneal shunt
Surgical procedure to relieve buildup of CSF by draining it into the peritoneal cavity
Alzheimer's Disease (AD)
Neurodegenerative disease that causes shrinkage of the brain and ventricles
Blood supply
Elaborate vascular system crucial for neurological diagnoses
Embolic Stroke
Blockage due to blood clots formed elsewhere in the body
Internal Carotid Arteries
Arteries ascending up the sides of the neck, branching into external and internal carotid arteries
Neurodegenerative Diseases
Diseases causing neuron death and shrinkage
Thrombotic Stroke
Blockage due to fatty plaque build-up on cerebral vessels
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
Temporary blockage of blood supply to the brain
Stroke Risk Factors
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, age, race, sex, sleep apnea, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, high alcohol or drug use
Stroke Symptoms
Numbness or weakness of face, arm, or leg; confusion, trouble speaking, or understanding speech; blurred vision; dizziness, loss of balance or coordination, difficulty walking; severe headache with no known cause
Blood Supply of Brain
Internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries supplying oxygenated blood
Brain Atrophy
Shrinking of brain size due to neuron loss
Prediction of AD Ventricles
Larger ventricles due to atrophy of neurons
Stroke
Blockage or bleeding in the brain resulting in functional deficits
Ischemic Strokes
Blocked blood vessels in the brain
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Ruptured blood vessel causing bleeding in or around the brain
Vertebral Arteries
Arteries ascending up each side of the cervical vertebrae, fusing together to form the basilar artery
Anterior Circulation
Supplies forebrain (cerebral hemispheres and diencephalon)
Posterior Circulation
Supplies brainstem, cerebellum, and upper portion of the spinal cord
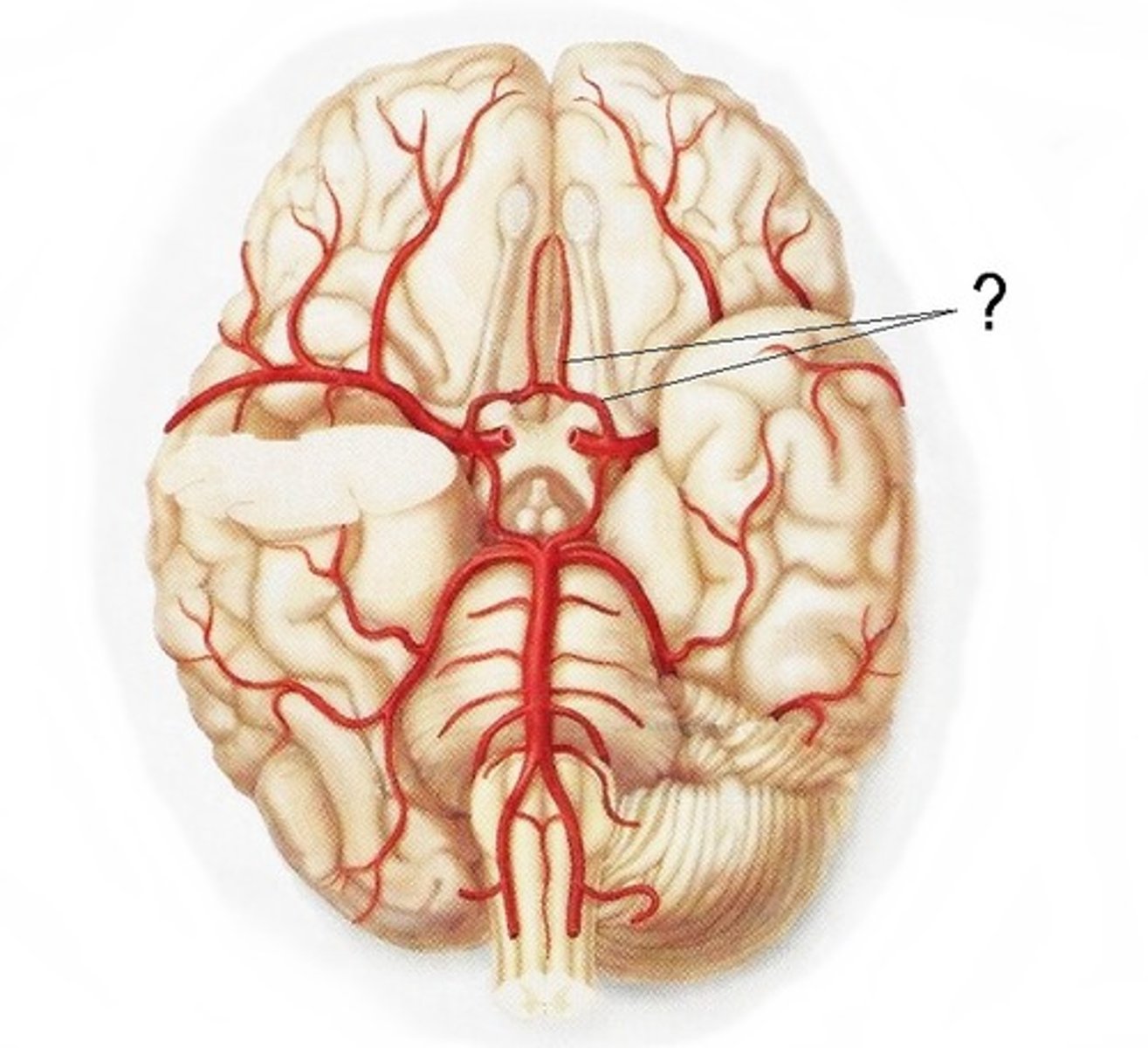
Circle of Willis
Ring formed by major cerebral arteries at the base of the brain, providing an alternate route if a main artery is damaged or blocked
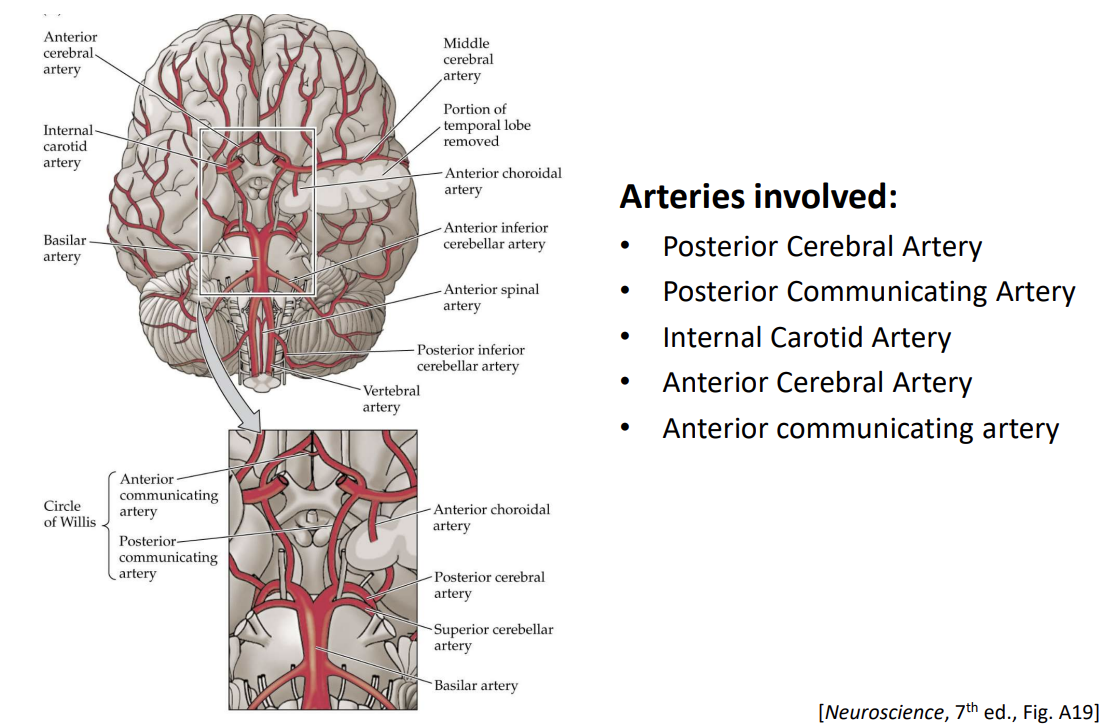
Major Cerebral Arteries
Internal carotid artery, posterior cerebral artery, anterior cerebral artery
Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA)
Artery supplying anterior regions of basal ganglia and internal capsule
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)
The artery that supplies an extensive region of the central and lateral cerebral hemispheres; supplies the internal capsule, anterior hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, and basal ganglia
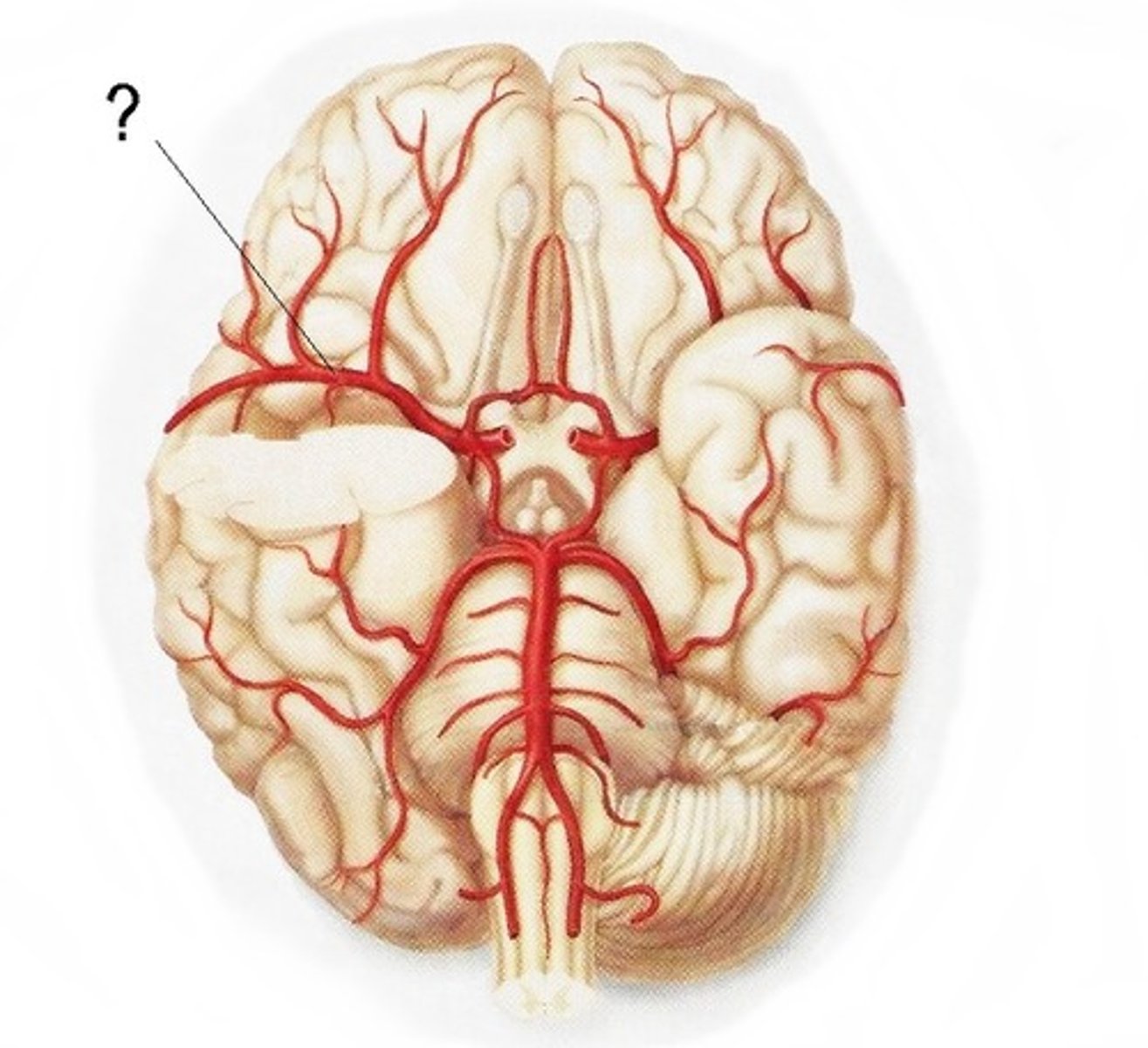
Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA)
Artery supplying posterior hypothalamus, thalamus, and regions in the parietal and occipital lobes
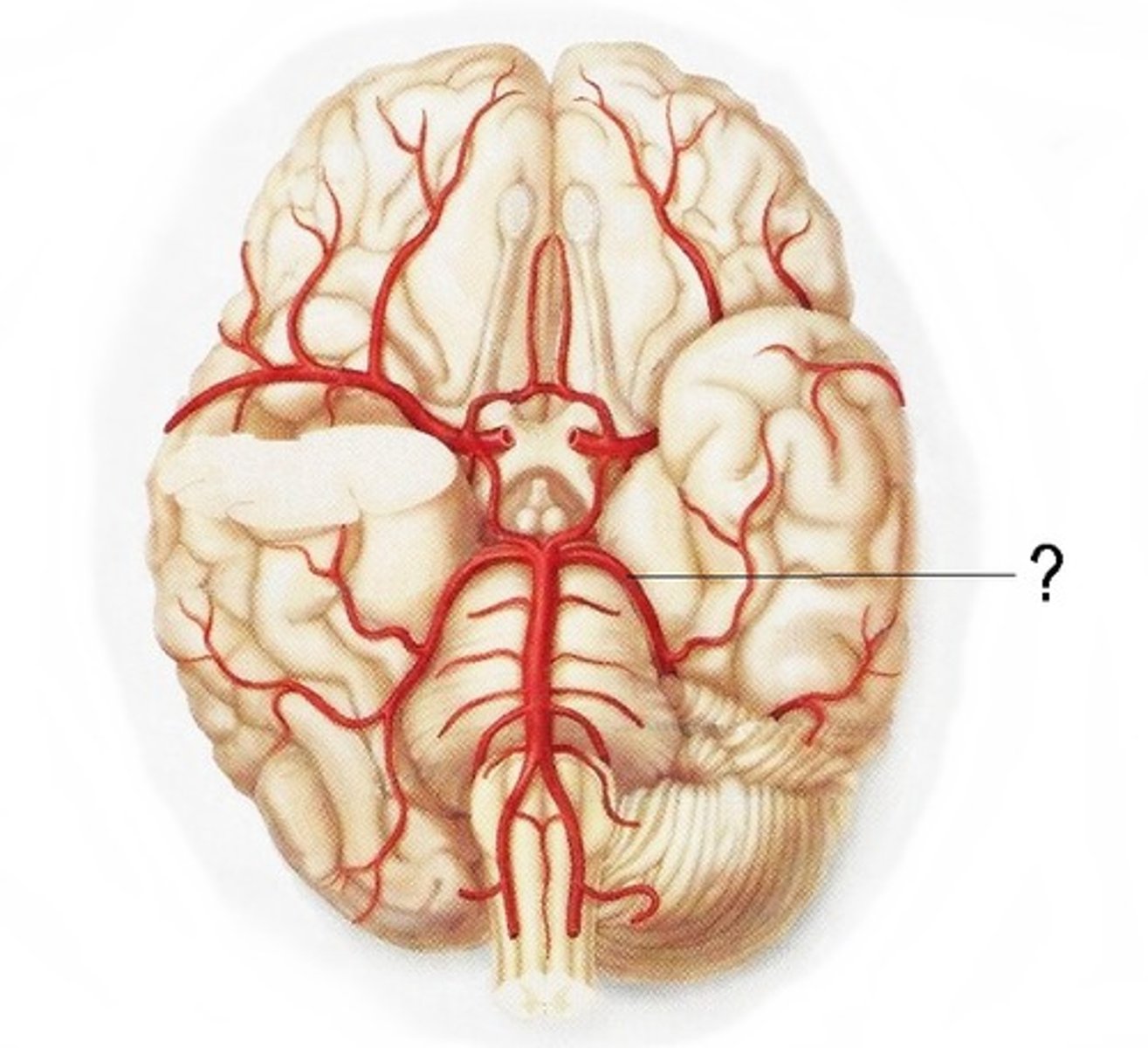
Lenticulostriate Arteries
supplies most of basal ganglia, main body of the internal capsule, anterior hypothalamus
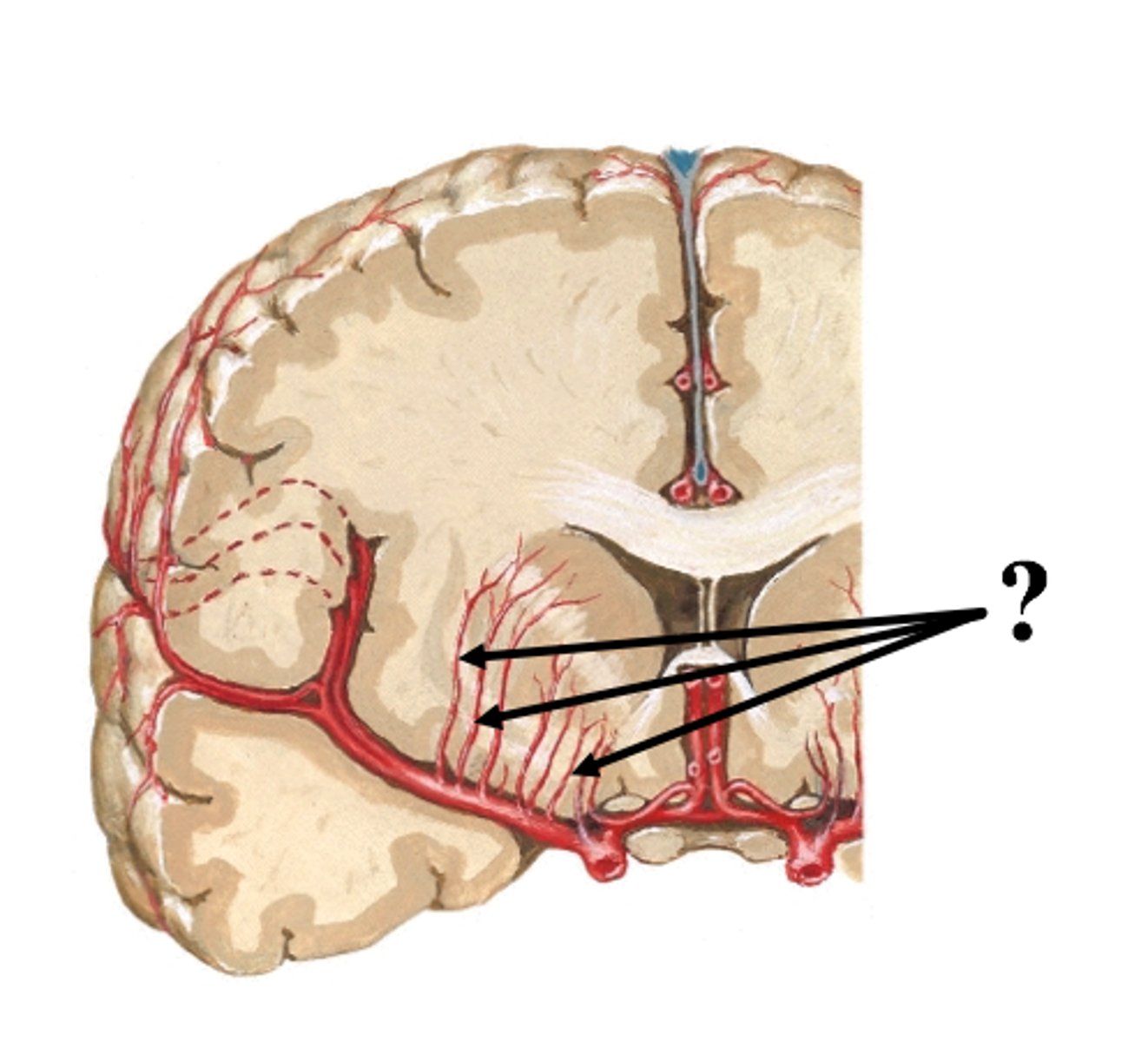
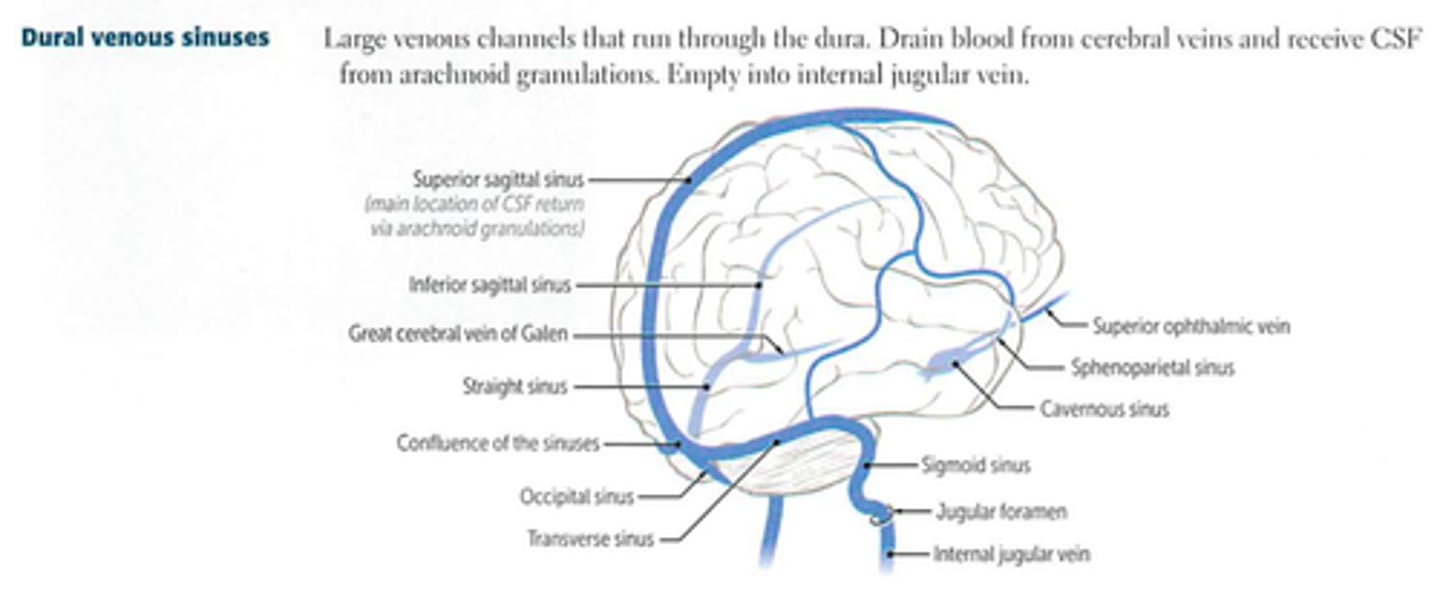
Dural Venous Sinuses
Sinuses formed between the inner and outer layers of dura mater, draining venous blood from the brain and returns blood from the brain back to the heart via the internal jugular veins
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
Barrier that restricts movement of substances from blood vessels into brain cells
Endothelial Cells
Cells forming tight junctions in the BBB
Astrocyte End Feet
Surrounding structures that contribute to the BBB
BBB Permeability
Only allows substances soluble in lipids or transported via specific transporters
Importance of BBB
Maintains stable ionic milieu, prevents infections and blood-borne toxins from reaching the brain
Challenges of BBB
Hurdle for developing drug therapeutics to treat CNS disorders
Drug Delivery Strategies
Mimic natural substances, temporarily disrupt BBB, intranasal administration, use of nanoparticles
Glymphatic System and Sleep
During sleep, glymphatic flow increases, aiding waste removal
Glymphatic System and Alzheimer's
Disruption of glymphatic system may contribute to AD onset/progression
Bilateral anosmia
(loss of smell) can occur following head trauma that causes shearing forces on olfactory nerves
Bell's palsy
a condition that causes sudden weakness or paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face
Vestibular neuritis
results from inflammation of just the vestibular portion of CN VIII
Vestibular schwannomas
a slow-growing benign tumor that arises from Schwann cells of the vestibular nerve
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy
a degenerative brain disease associated with repeated hits to the head
Foramen magnum
a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull that the spinal cord passes through when exiting the cranial cavity
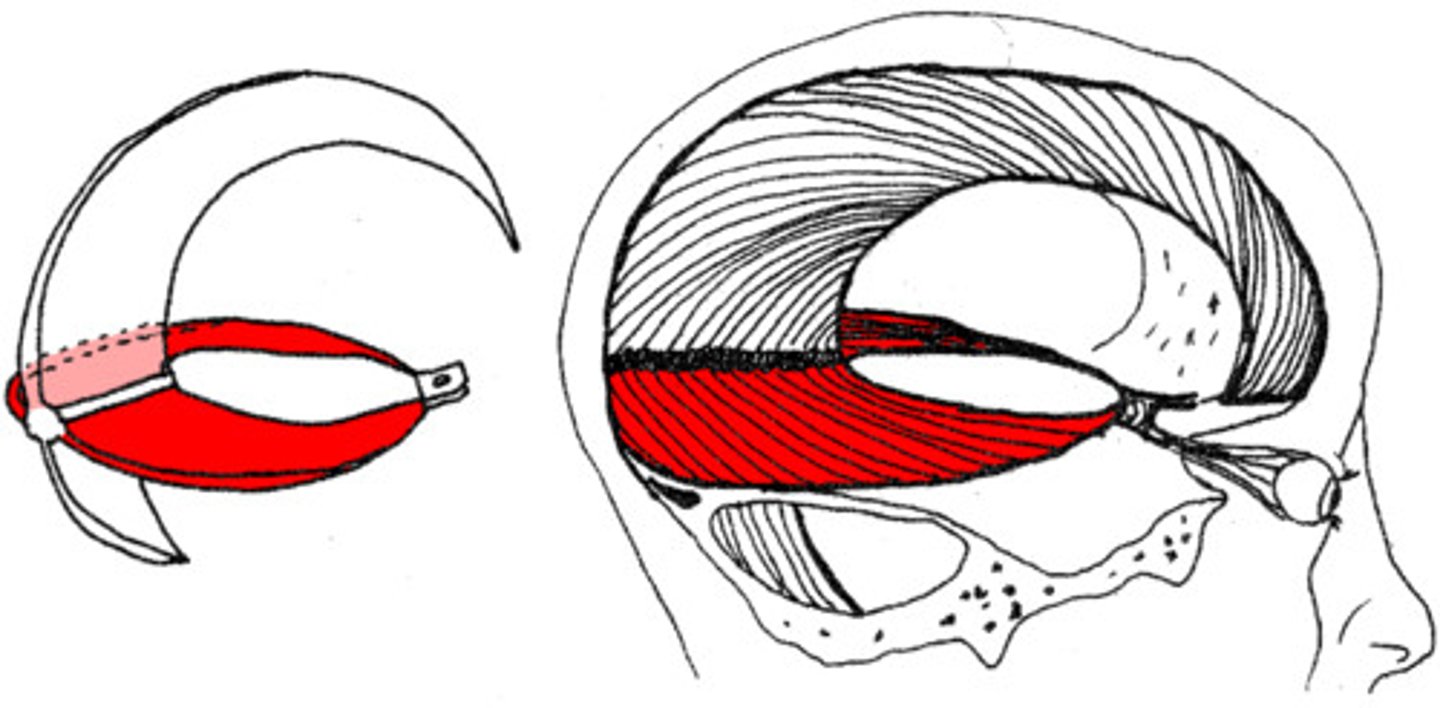
meninges
three protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
Dura mater
Outermost layer of the meninges
Tentorium cerebelli
a U-shaped which that runs between the occipital lobe and the cerebellum, separate the cerebrum from the cerebellum
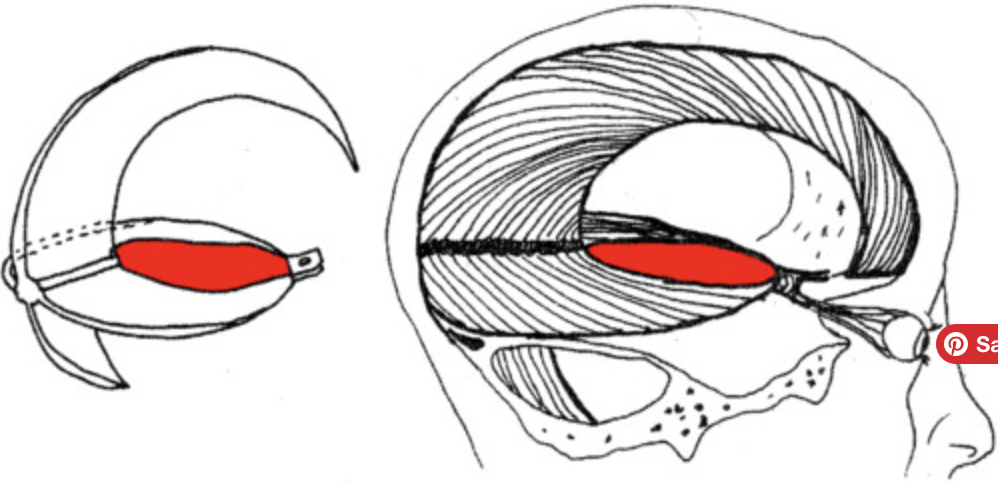
tentorial notch
provides space for the brainstem to pass
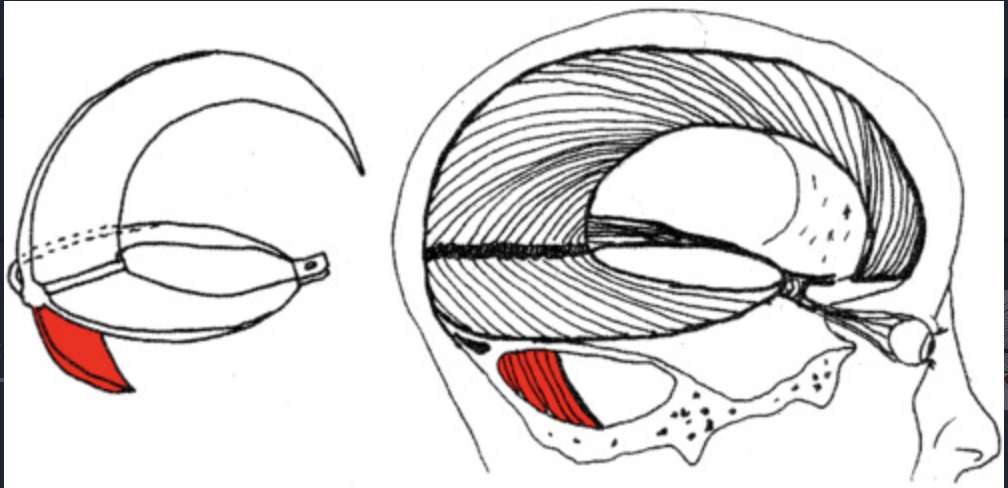
Falx cerebelli
a small midline fold that runs in the space between the two cerebellar hemispheres
How the venous sinuses is formed
a separation of the inner and outer layers of the dura mater
Epidural hemorrhage
collection of blood between the dura mater and the skull
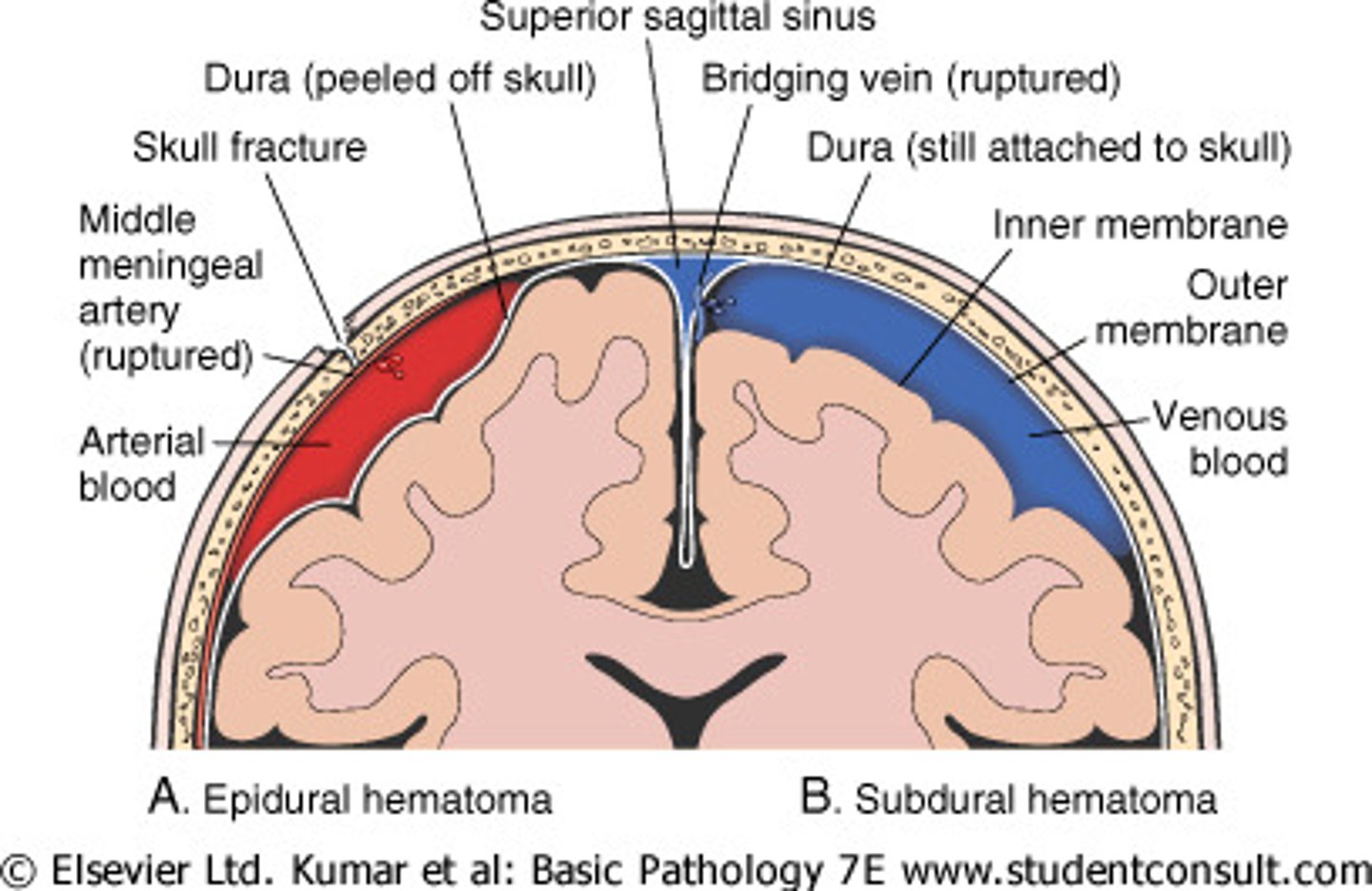
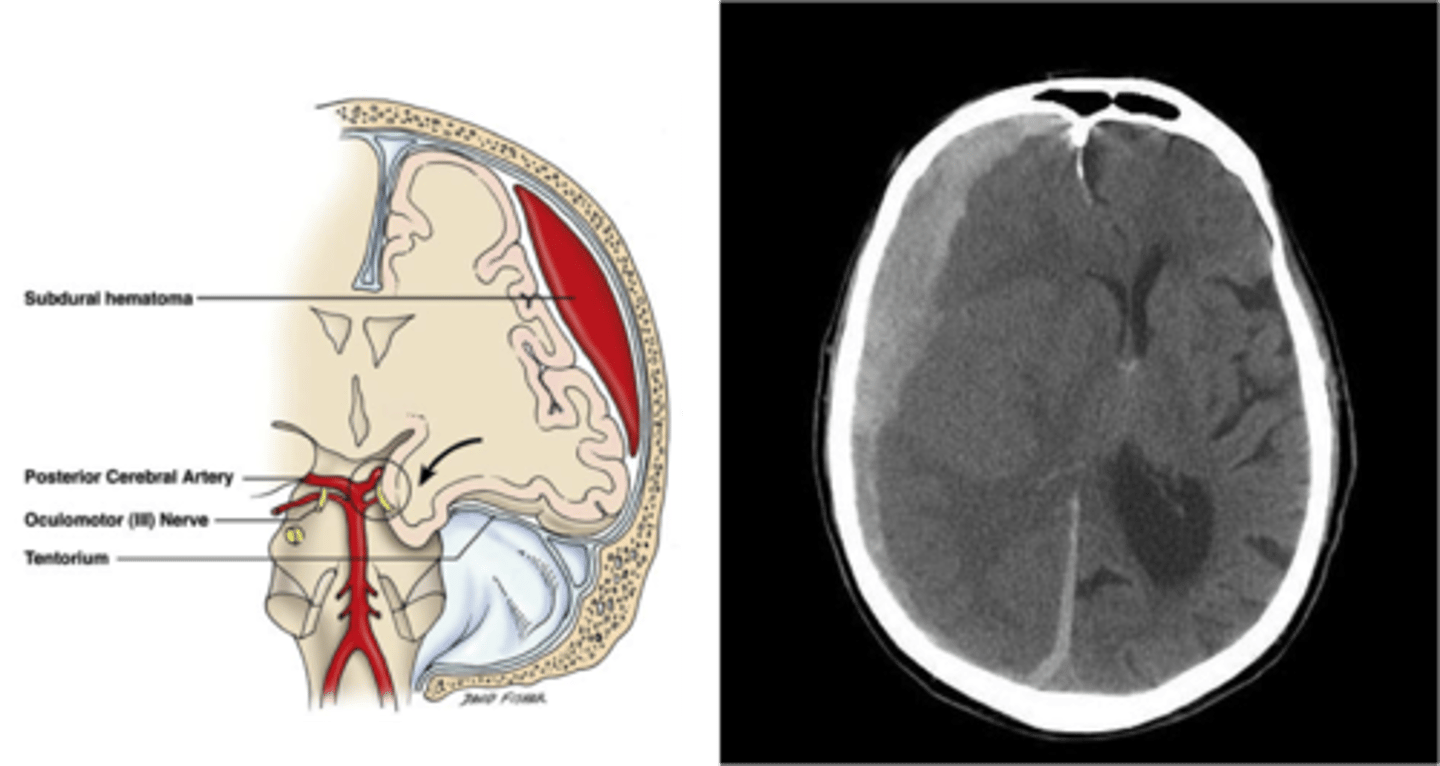
Subdural hemorrhage
a collection of blood between the dura mater and arachnoid mater
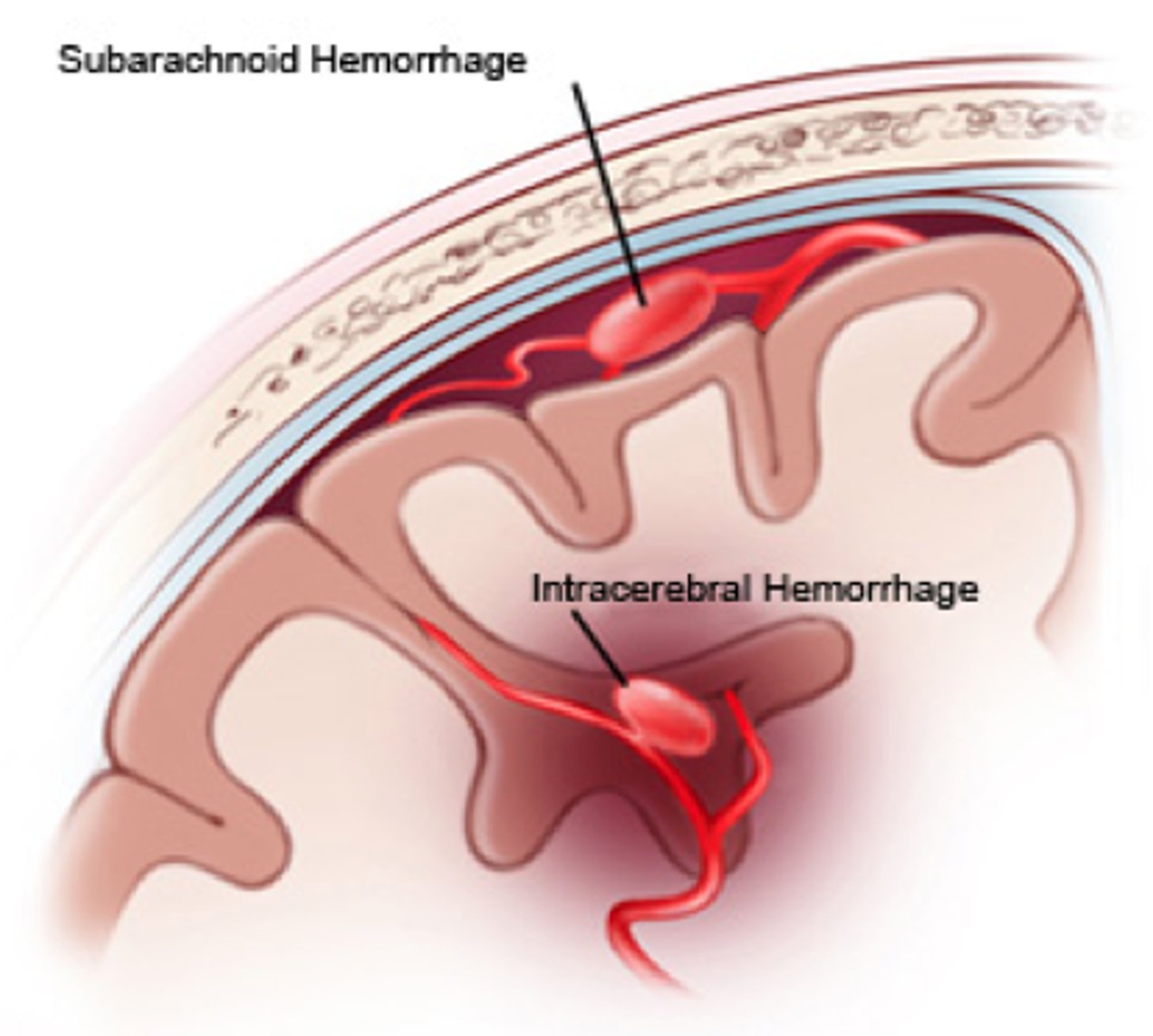
subarachnoid hemorrhage
Bleeding into the subarachnoid space, where the cerebrospinal fluid circulates.
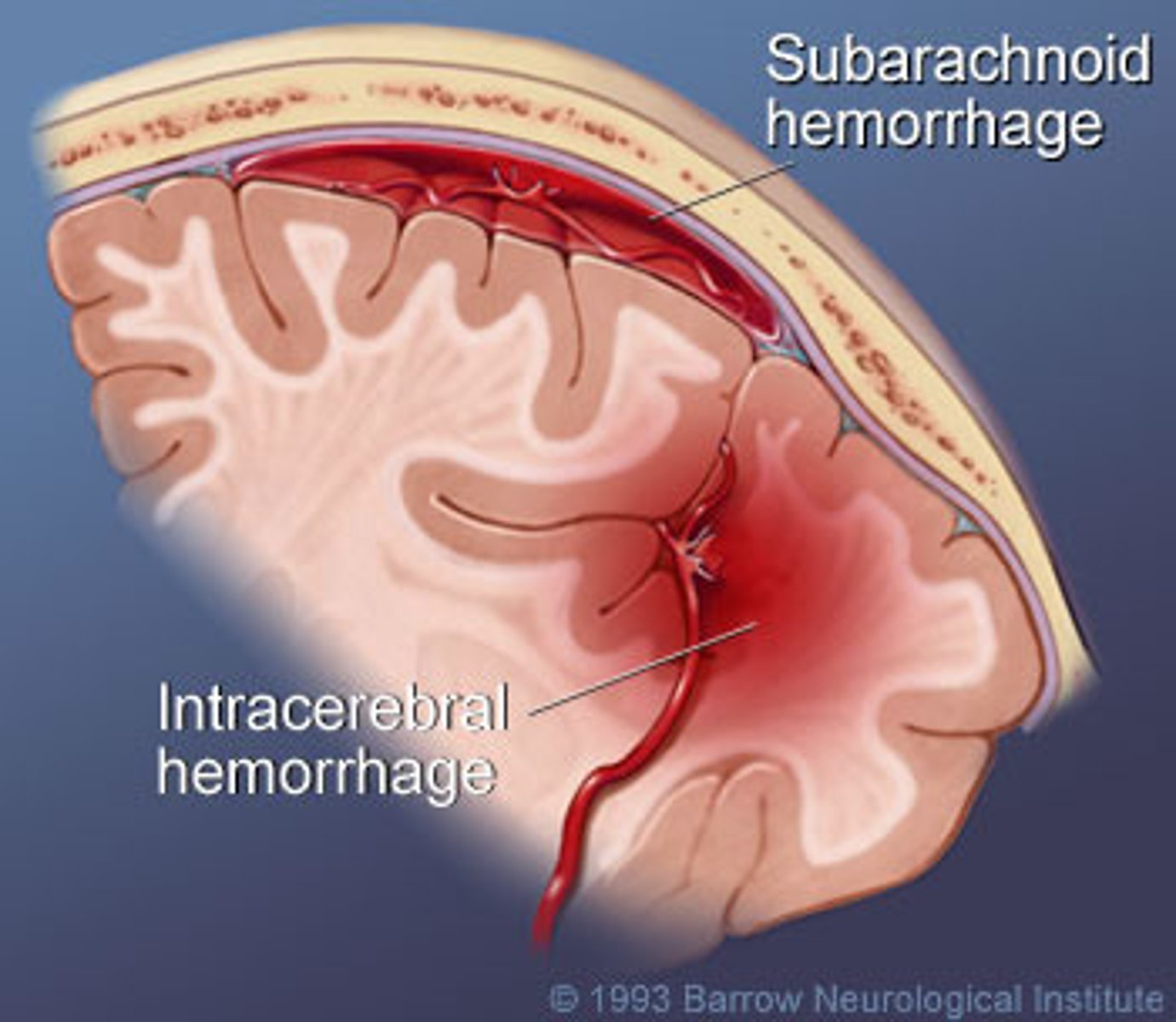
Intracerebral hemorrhage
bleeding within the brain tissue itself
Meningiomas
typically benign tumors arising from the dura mater
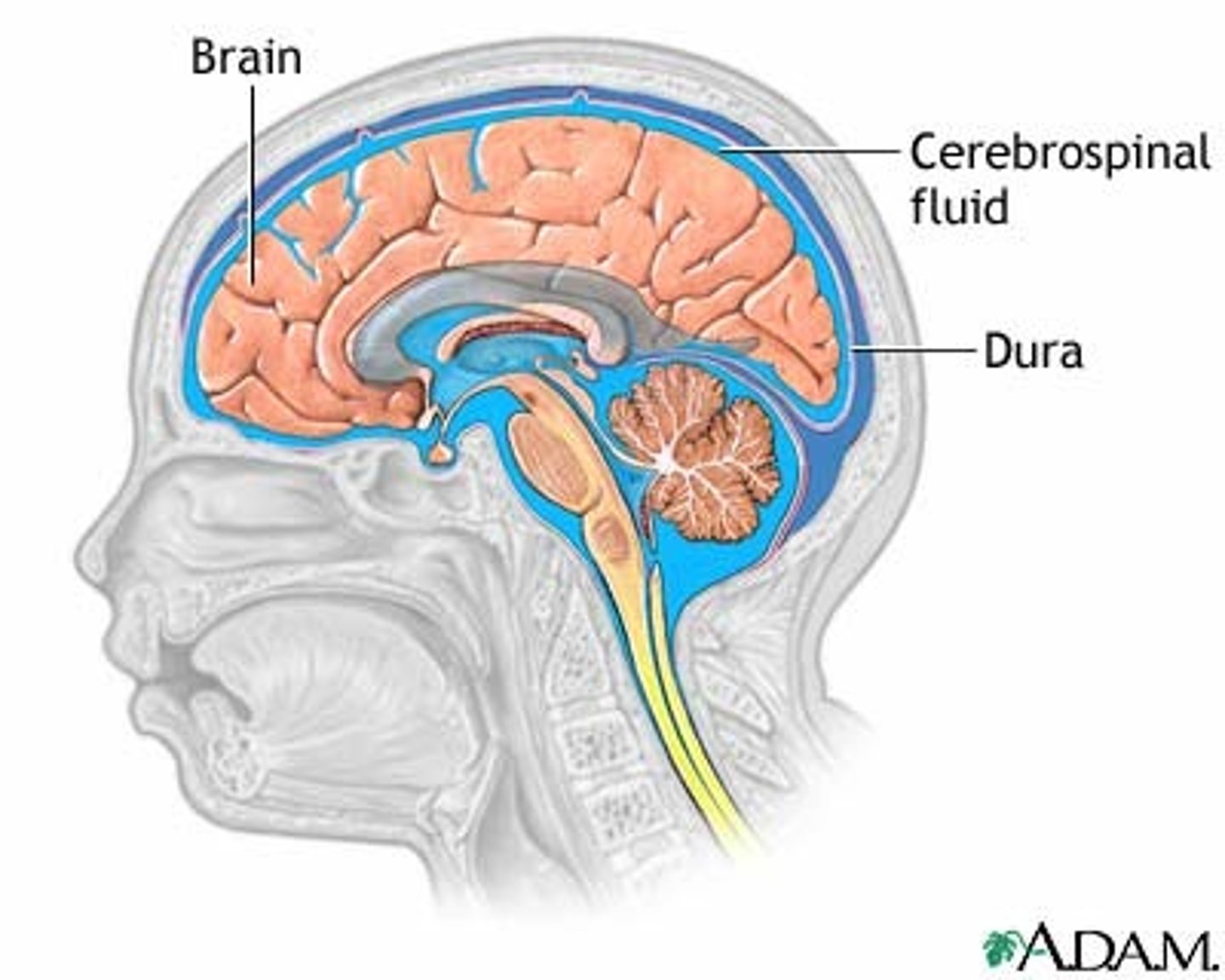
Functions of the ventricular system
Protects brain, Provides buoyancy, and Provides a medium for the exchange of materials between blood vessels and brain tissue
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
produced by specialized ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles
Lateral Ventricles
Large, C-shaped spaces in each cerebral hemisphere
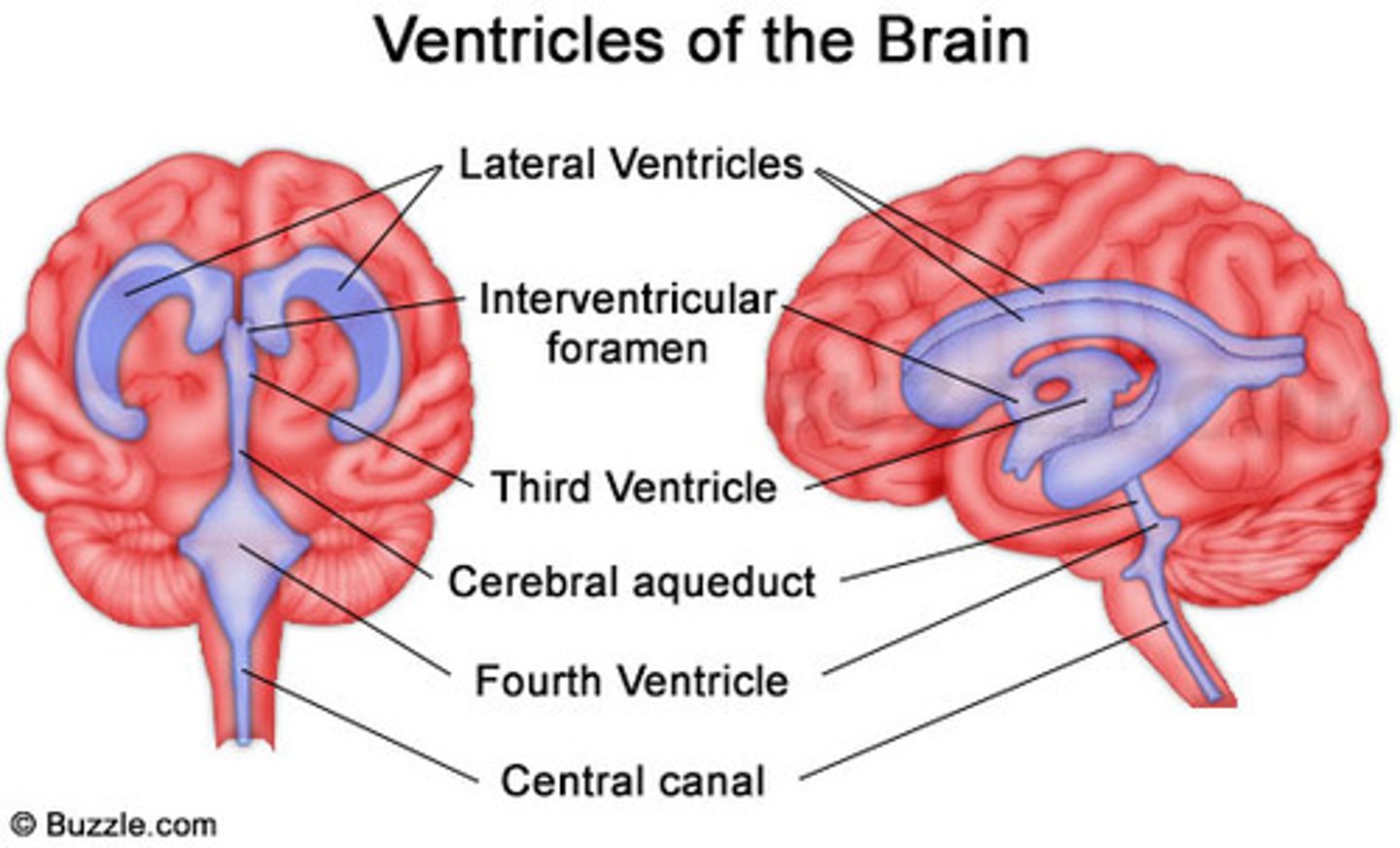
Interventricular foramen of Monro
a short conduit that connects the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle
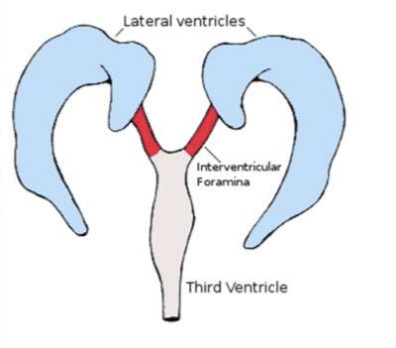
Third Ventricle
a narrow midline space between the right and left diencephalon (thalamus + hypothalamus)
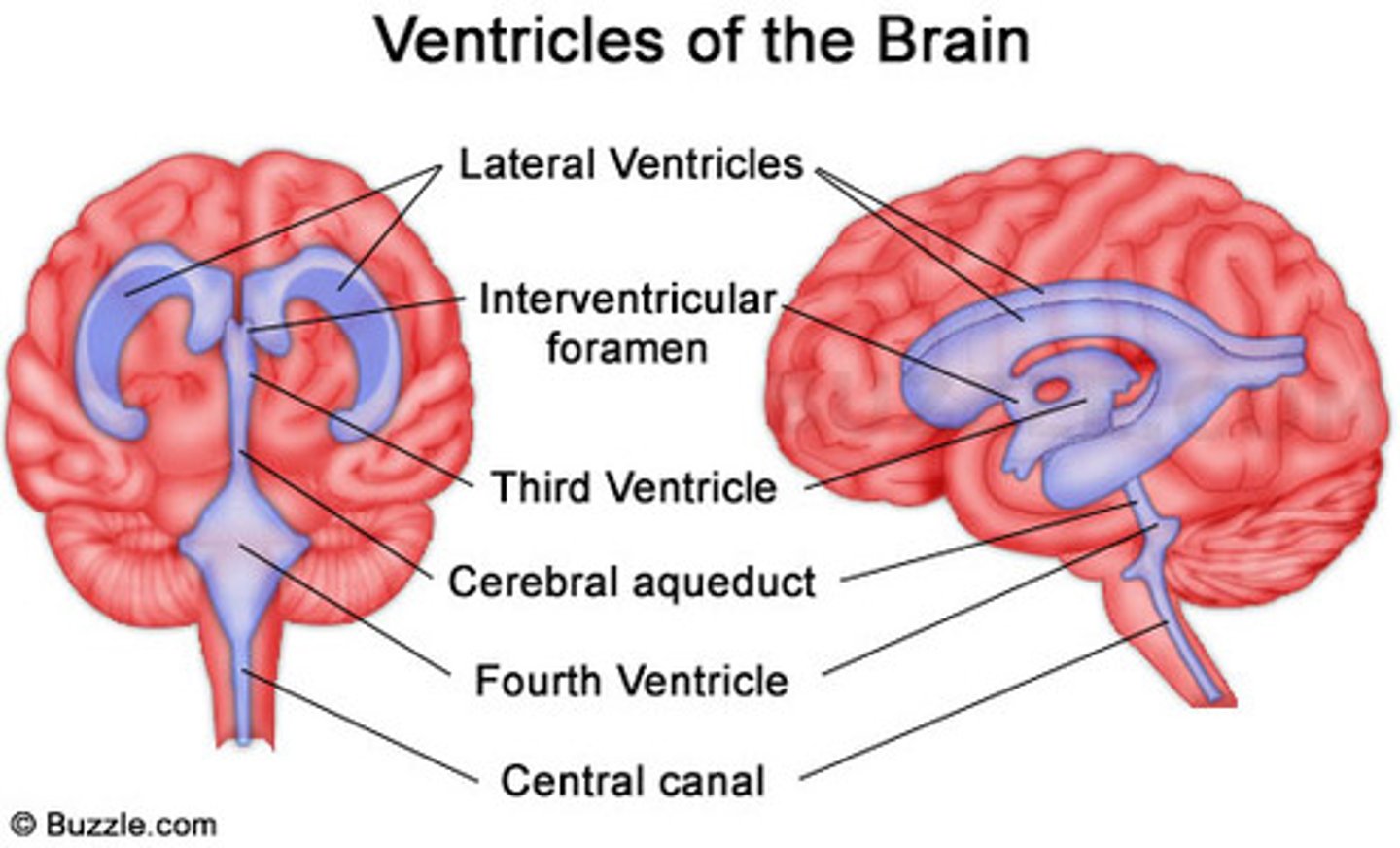
cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
Fourth Ventricle
found between the dorsal brainstem and cerebellum
choroid plexus
Modified vascular structure lining the ventricles that produces CSF by filtering blood