MSSC - Quality Practices & Measurement
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/277
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
278 Terms
1
New cards
Which type of feature is parallel to the surface being dimensioned?
Dimension line
2
New cards
The three standard views of an object are \__________.
Top, front, right side
3
New cards
Which type of lines are used to show the counterbored hole in the part?
Hidden lines
4
New cards
The number of views in a drawing \__________.
Is the fewest number that shows all of the features and dimensions
5
New cards
Which of the following steps is NOT used in the glass box method?
Rotate object in glass box.
6
New cards
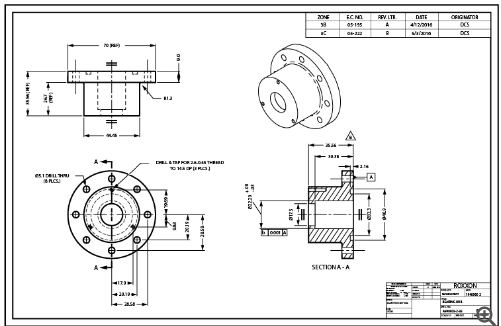
What type of drawing is shown?
Multiview
7
New cards
The dimensions of raw material supplied by metal suppliers are described by the \__________.
Stock size
8
New cards
Which of these requires a computer?
CAD
9
New cards
An isometric drawing is a type of \__________.
Pictorial drawing
10
New cards
Dimensions are used to specify the \__________ and location of the features of an object.
Size
11
New cards
What feature in the figure shown is a Chamfer?
D
12
New cards
A \__________ dimension is described in inches per foot.
Shaft taper
13
New cards
What is the order of precedence of lines in a drawing?
Object, Hidden, Center
14
New cards
Which of the following is not one of the six rules for dimensioning an object?
Dimension hidden lines
15
New cards
Engineers sometimes use a \__________ to measure angles on a drawing.
Protractor
16
New cards
There are 60 minutes of arc in one \__________.
Degree
17
New cards
In manufacturing, a blueprint is also called what?
A technical drawing
18
New cards
The distance across the flats of the hex head shown in the part drawing is \__________ inches.
2 ¼
19
New cards
The length of the part shown in the drawing is \__________ inches.
9 ¾
20
New cards
Which type best describes the line indicated in the graphic?
Object Line
21
New cards
Which of the following bolts is a grade 2?
A
22
New cards
The hole shown in the graphic is a \__________ hole.
Counterbore
23
New cards
What are the two types of assembly drawings?
Exploded and basic
24
New cards
A sectional view \__________.
All of the above
25
New cards
Which of the following is not used to specify a threaded fastener?
Minor diameter
26
New cards
Two types of threads are \__________.
Internal and external
27
New cards
In the assembly drawing shown, part 3 screws into part \__________.
4
28
New cards
The material that will be used to create the gear is indicated in the part drawing's title block to be \__________.
Cast iron
29
New cards
In a threaded fastener assembly what is designed to protect the threads?
Shank
30
New cards
Manufacturing workers can use a calibrated torque wrench to \__________.
Measure the proper amount of torque
31
New cards
The part of a drawing that indicates that the drawing has the most up to date information on it is \__________.
Drawing revision level
32
New cards
What type hole is shown in the figure?
Counterbored
33
New cards
The minor diameter of a screw thread is measured at the \__________.
Root of screw thread
34
New cards
Section lines in a sectional view are \__________.
All of the above
35
New cards
To establish on a drawing that 1/4 inch equals 1 inch, the designer would write \__________.
1/4\=1
36
New cards
Metals treated by \__________ processes become soft.
Annealing
37
New cards
Where would you look in a title block to see if there has been changes?
Revision number
38
New cards
Section lines on a blueprint indicate \__________.
A surface that has been cut
39
New cards
A screw with fine thread is represented on a drawing with what designation?
UNF
40
New cards
What is the depth of the countersink in the image?
0.12 inches
41
New cards
What is placed at the arrowheads of the cutting plane line to identify the cutting plane with the proper sectional view?
Capital letter
42
New cards
Assembly drawings rely on reference letters or numbers to \__________.
Identify the individual parts
43
New cards
If a feature on a drawing is drawn 3 inches long and the scale is 1:4, what is the actual dimension on the object?
12"
44
New cards
The specifications for the length of produced parts is 5.146 inches with a tolerance of ± 0.005. Is a part that has been produced at 5.140 inches out of spec?
Yes, it is out of spec
45
New cards
Which dimension on a production drawing has the most accuracy?
The one with the most "tolerance" decimal places
46
New cards
A datum feature symbol can be connected to \__________.
Any of the above
47
New cards
The graphic shown is an example of \__________ dimensioning.
Baseline
48
New cards
If 4 percent of 1200 production pieces are out of spec, how many are out of spec?
48
49
New cards
A part measuring 2.54 inches is out of spec if the specification is \__________.
2.00 ± .53
50
New cards
A running fit is also called a(n) \__________.
Sliding fit
51
New cards
Form, profile, orientation, location and runout are shown by \__________.
GD&T
52
New cards
If a drawing shows a part with a diameter of 1.275 ± .003, what is the minimum and maximum size allowed?
1.272, 1.278
53
New cards
The equipment at a workstation is supposed to produce parts at 2.593, per the part drawing, and has a spec limit of ± 0.004. Is a part that has been produced at 2.590 out of spec?
No, it is within spec
54
New cards
A part measuring 44.85 mm in a process with a tolerance of 45mm ± .28 is considered \__________.
**In spec (within the tolerance range)**
55
New cards
Datums are a point of reference to establish \__________.
Job tasks
56
New cards
The maximum material condition for the part shown is \__________.
15.75
57
New cards
The least material condition for the part shown is \__________.
0.75
58
New cards
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing uses \__________ to represent features and tolerances.
Symbols
59
New cards
Examples of \__________ tolerance describe the form and orientation of a part.
Profile
60
New cards
Which of the following part lengths is out of spec if the specification calls for a part length of 3.202 (± 0.003)?
3.197
61
New cards
Length, width, height, diameter, and hole diameter are all examples of \__________.
Features of size
62
New cards
The tolerance for a geometric feature can be easily identified by reading the \__________.
Feature control frame
63
New cards
The term \__________ refers to a physical portion of a part.
Feature
64
New cards
A letter with a box around it is a standard notation symbol used to indicate a(n) \__________.
Datum feature
65
New cards
GD&T \__________.
Allows certain tolerances on part features to be increased
66
New cards
Which of the following is a feature control frame typically used to identify?
Extension lines
67
New cards
A \__________ is a theoretically perfect line, point or plane that is located by a similar feature of the part.
Datum
68
New cards
Dimensional measurement determines physical dimensions such as \__________.
Width, height, and depth
69
New cards
The measurement of a 5.000 inch part, with an instrument having \__________ accuracy, should range from 4.998
5.002 inches.
70
New cards
Convert 650 millimeters to inches (1mm \= 0.0394 inches).
25.61
71
New cards
One inch is equal to \__________.
25.4 mm
72
New cards
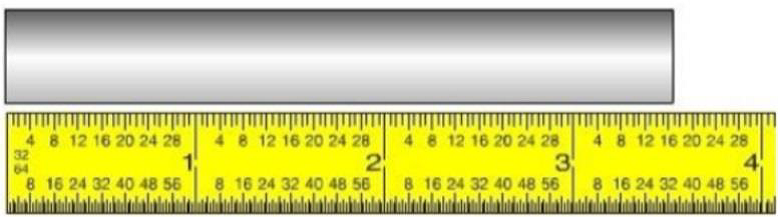
What is the measurement shown on the rule?
3 17/32 inch
73
New cards
10 inches is the same length as \__________ mm.
254
74
New cards
The first step in dimensional measuring is to align the end of the rule where the zero is located with one edge of the dimension you want to measure. This edge is called the \__________.
Reference point
75
New cards
A common decimal inch rule graduation is in \__________.
50ths
76
New cards
Two systems of dimensional measurement used in manufacturing are the SI Metric System and the \__________.
US customary system
77
New cards
Flatness is an important geometric feature of what measurement component?
Reference plane
78
New cards
What value is shown on the gauge?
56 psi
79
New cards
Resolution is sometimes called \__________.
Discrimination
80
New cards
A tape measure is flexible so that \__________.
It can be easily stored
81
New cards
A \__________ has its graduations engraved so that they can not be rubbed off.
Machinist's rule
82
New cards
The conversion of 3
3/8 inches to decimal inches is \__________.
83
New cards
A common fractional inch rule graduation is in \__________.
32nds
84
New cards
You have designed a part that has a length of 1.125 inches. Your supervisor requests that you reduce its length by 1/16 of an inch, what will be its final length?
1.0625 inches
85
New cards
\__________ error comes from either built
in sources or calibration.
86
New cards
From a 2 ft x 3 ft piece of stock, theoretically how many 1 ft x 1.5 ft pieces can be cut?
4
87
New cards
The work measured with a tape measure requires \__________ than that of work measured with a machinist's rule.
Less precise graduations
88
New cards
A scale typically found on a machinist rule is \__________.
1/16
89
New cards
The typical accuracy of a modern dial caliper is about \__________.
0.001 inches
90
New cards
The reading on the 3
4 inch micrometer indicates a measurement of \__________ inches.
91
New cards
The width of the plate being measured in the image using a metric micrometer is \__________.
6.89 mm
92
New cards
The digital caliper's \__________ houses the digital display.
Carriage
93
New cards
What is 1 /1000 inches in decimal?
0.001
94
New cards
A typical dial caliper can be used to measure dimensions to the nearest \__________ inches.
0.001
95
New cards
Calibration means to \__________.
Adjust a device to a standard
96
New cards
A micrometer increments how far for each complete rotation of its thimble?
0.025
97
New cards
The two outside jaws of a \__________ are only used to measure the outside dimensions of parts.
Digital and dial caliper
98
New cards
The measuring tool shown is a \__________.
Depth micrometer
99
New cards
A vernier micrometer is \__________ as accurate as a caliper.
10 times
100
New cards
A measurement made with a precision measurement tool can be as precise as \__________.
0.001 inches