unit 11 motivation and emotion
1/21
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
motivation
- a need or desire that energizes behavior and directs it toward a goal
- effects that influence the behavior is based on initiation, direction, intensity, and persistence
extrinsic motivation
- a desire to perform behavior because of promised rewards or threats of punishment
- behaviors will not be effectively sustained once the reward is removed
- ex: working for a salary
intrinsic motivation
- a desire to perform a behavior for its own sake because the act itself is rewarding or satisfying in some internal manner
- tends to result in higher achievement than extrinsic motivation
- ex: studying to improve knowledge
overjustification effect
when you're rewarded for things that you already enjoy doing, the intrinsic motivation goes away
instinct theory
- human behavior is guided by innate biological instincts
- ex: imprinting
instinct
a fixed pattern that occurs without learning
drive-reduction theory
- assumes behavior arises from physiological needs that cause internal tensions (drives) to push organism towards satisfying need, thus reducing tension and arousal
- physiological aim of drive reduction is homeostasis
- primary drives: food, water
- secondary drives: money
incentive theory
- positive or negative stimuli that push/pull us toward a goal
- behavior is guided by the lure of reward and/or threat of punishment
- ex: offering a donut, getting points
arousal theory
- people are said to have an optimal level of tension (arousal) they seek o maintain by increasing or decreasing stimulation
- yerkes-dodson law
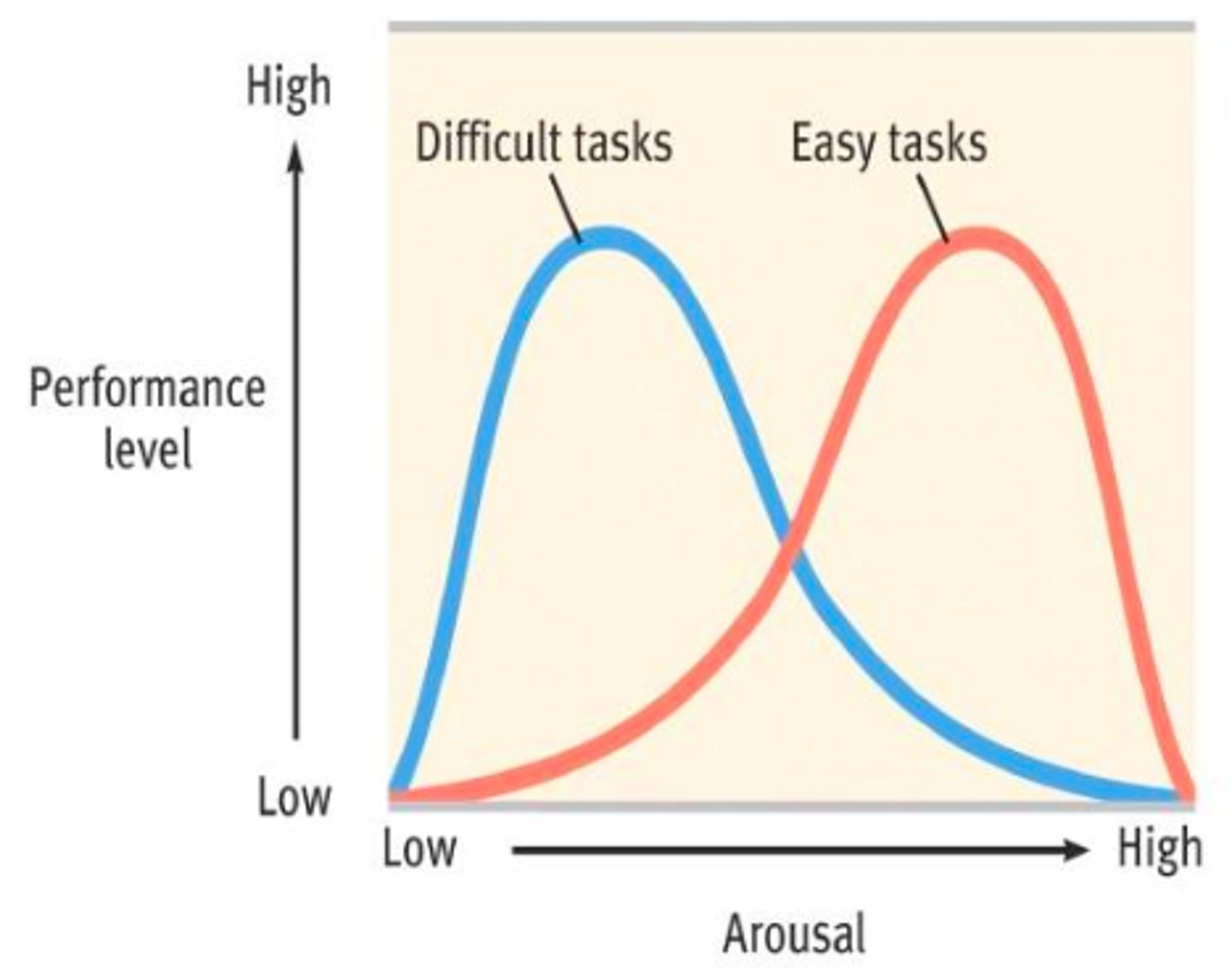
yerkes-dodson law
- psychological arousal helps performance, but only to a certain point
- optimum level of arousal depends on the difficulty of the task
- difficult tasks = low arousal
- easy tasks = high arousal
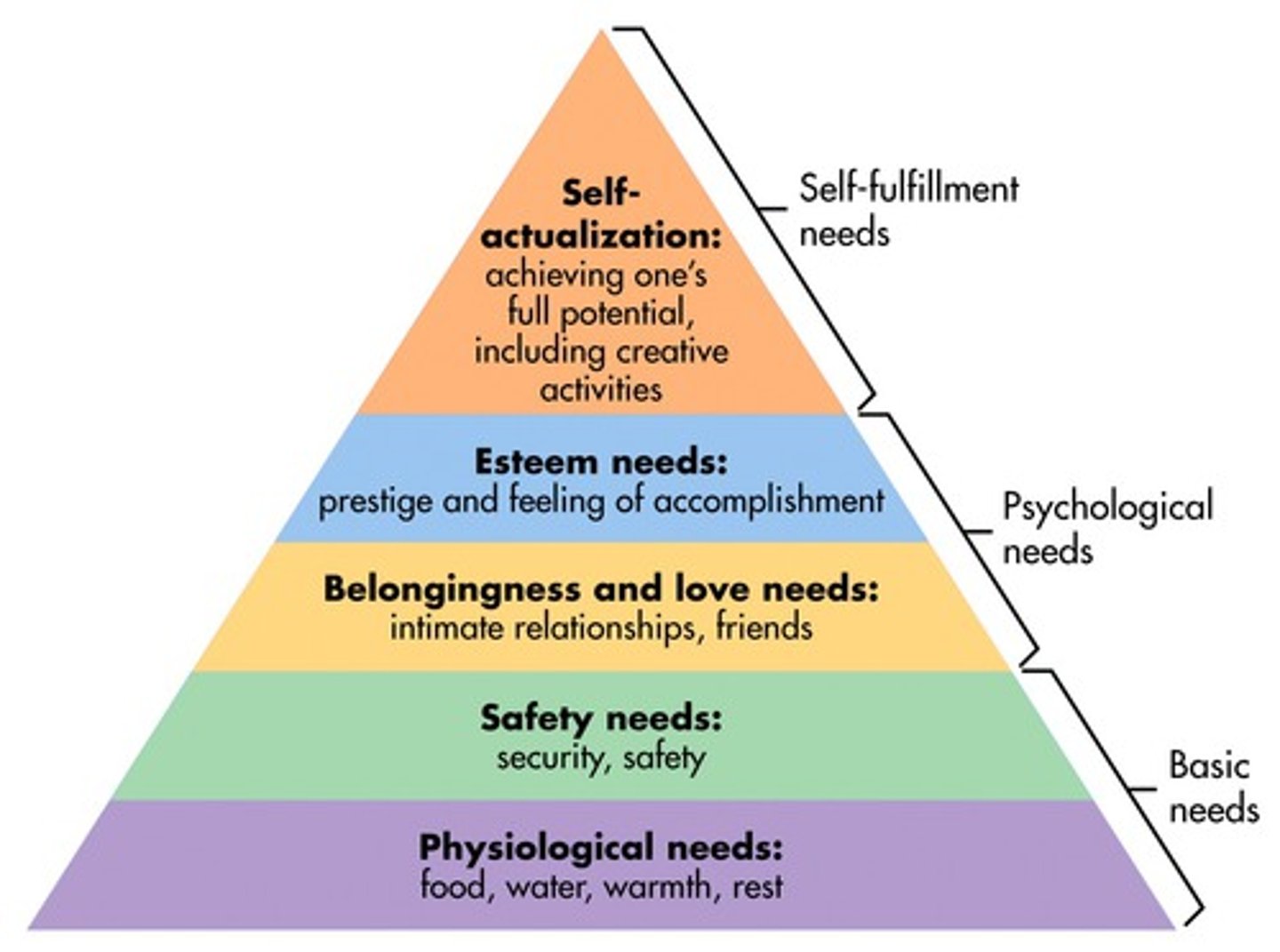
abraham maslow's hierarchy of needs
- humanistic psychologist who developed the hierarchy of needs, stating that some needs take priority over others
- higher-levels needs won't become priorities until lower-level needs have been satisfied
hunger motivation
STIM-LAT-FAT
theories of emotion
- james-lange
- cannon-bard
- schachter-singer two factor
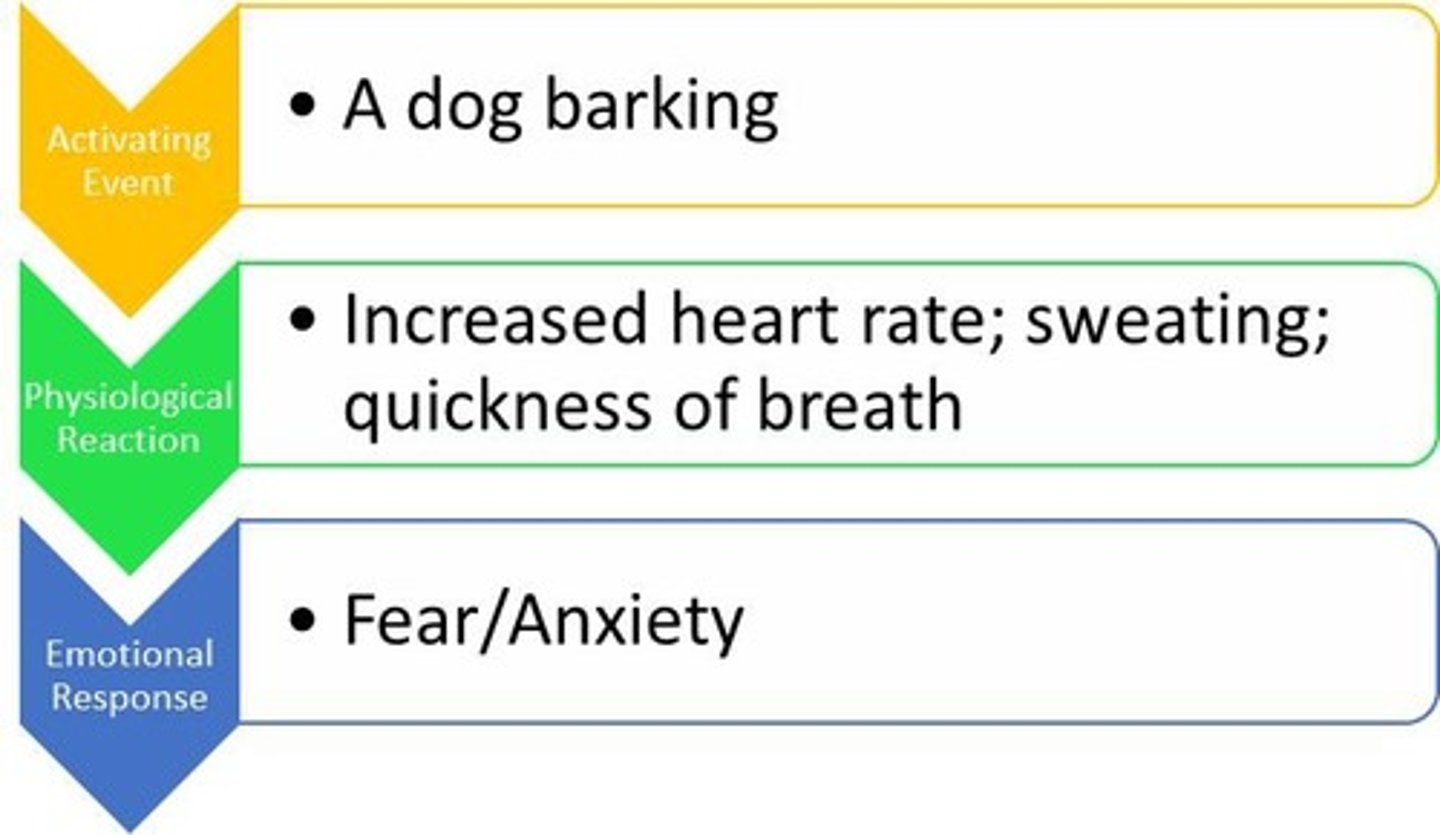
james-lang
- physiological activity precedes the emotional experience
- stimulus -> physical reaction -> emotion
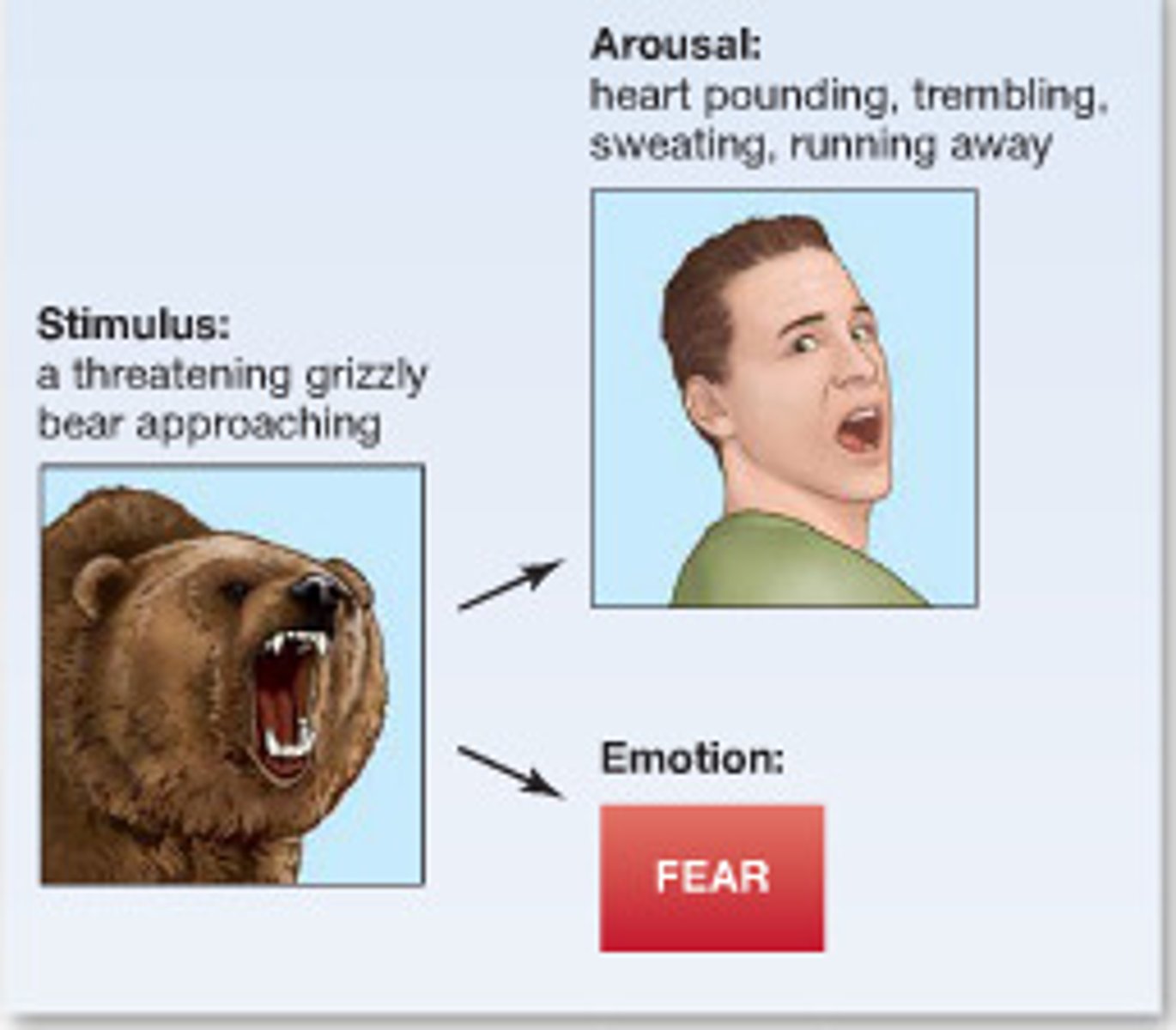
cannon-bard
emotion and physiological response simultaneously occurs
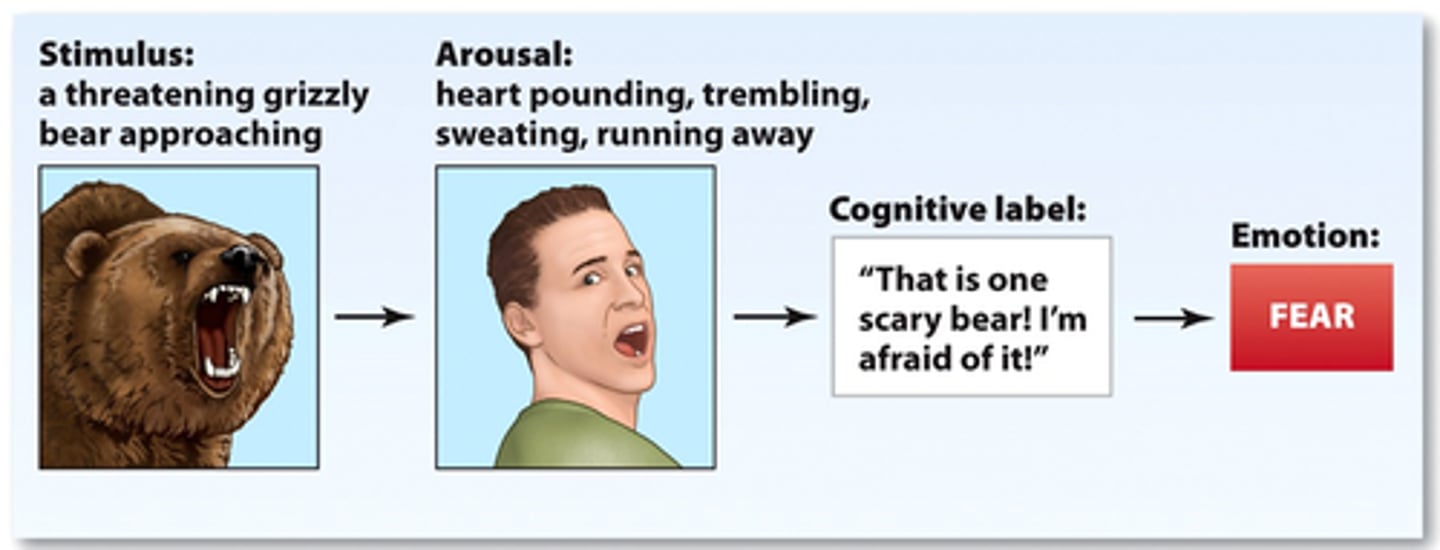
schachter-singer two factor
you feel physically aroused and able to cognitively label the arousal (appraisal)
joseph ledoux
- researcher believes that sensory information regarding emotion-evoking events moves along two separate pathways in the brain
- "fast" pathway: amygdala
- "slow" pathway: cortex
expressed emotion
- joy and sadness
- fear and anger
- surprise and anticipation
- acceptance and disgust
paul ekman
- studied facial expressions and emotions
- theorized that each basic emotion is associated with a unique facial expression
- these expressions are though to be innate and hard-wired; recognizable across cultures
- by 6 to 7 months of age, most babies exhibit facial expression for all basic emotions
facial feedback theory
emotional expressions can cause the emotional experiences they signify
type A personality
people who are more competitive, driven, hostile, and ambitious...and therefore, more prone to and impacted by stress
type B personality
relatively relaxed, patient, easygoing, amicable behavior...and therefore less impacted by stress