igneous rocks🌋🔥🌄
1/63
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
igneous rocks
the products of the cooling + solidification of magma/lava.
composition → silicic, intermediate, mafic + ultramafic
crystal grain size → coarse (>5mm) medium (1-5mm) fine (<1mm)
evidence for depth of formation, rate of cooling + cooling history of igneous rocks
crystal grain size, crystal shape + texture

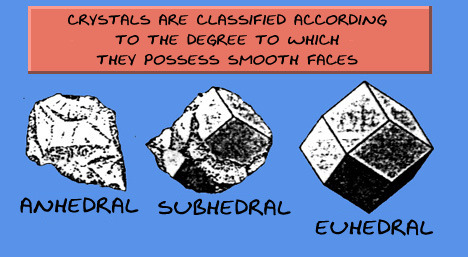
some crystal shapes
euhedral → flat faces with sharp angles.
subhedral → incompletely bounded by crystal planes: partly faced.
anhedral → a mineral that shows no crystal habit.

some crystal textures
equicrystalline
porphyritic
vesicular
glassy
fragmental (tuff)
amygdaloidal
flow banding

some crystal surfaces
pillow structure
aa
pahoehoe
columnar joints

evidence for the earth’s internal heat
increased temperatures in mines & boreholes
hot springs
volcanoes
satellite imagery + remote sensing to measure surface temperatures → measuring the change in surface temperature is one way of predicting volcanic events
at the base of some glaciers, the ice melts due to heat coming up from the crust = easier to move
mines + boreholes
Kola Superdeep Borehole in Russia → at a depth of over 12 000 metres, the rock became too plastic to drill through, at a higher than expected temperature of 300C
hot springs
where magma lies close to the surface, percolating groundwater becomes heated + rises to the surface by hot natural