Y11 Geography Changing Climate
1/30
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
climate change definition
the long-term change in global/regional climate due largely to increased levels of CO2 in the atmosphere
the quaternary period + its epochs
a subdivision of geological time covering the last 2.6 mil years up to the present day.
pleistocene epoch: start of period - 11,700 years ago
holocene epoch: 11,700 years ago - now
ice ages
any period of time when the earth has permanent ice sheets
5 major ice ages in earth’s history. outside these the earth was ice free even at high latitudes. these were warm periods known as greenhouse periods
within ice ages are glacial periods (cold) and interglacial periods (warm)
we are in an ice age but in an interglacial period
greenhouse periods
ice ages
glacial periods (colder)
interglacial periods (warmer)
climate proxies
reserved physical characteristics of the past that stand in for direct meteorological measurements and enable scientists to reconstruct the climactic conditions over a long fraction of the earth’s history
climate proxies: tree rings
trees add a new layer of material each year. wide thick rings indicate a fertile well-watered growing period, thin narrow rings indicate lower rainfall & less than idea growing conditions
climate proxies: ice cores
each year more snow/ice is added to the sheets of ice in the arctic & antarctic. scientists can drill down into ice and remove tubes of ice (ice cores)
ice cores can be used to study ice laid down 800,000 years ago
they contain bubbles of gas that tell us what the air was like thousands of years ago. these contain different isotopes of oxygen and this can tell us whether the climate was warmer/colder
climate proxies: global temperature data
records of temps across the world began being kept from ~1880. today there are over 1,000 weather stations recording temps
scientists use records to study the earth’s temp and compare it to different time periods, work out global average temps, develop lists of hottest/coldest years
climate proxies: sea ice extent
arctic sea ice is shrinking quickly - photos from earliest 1900s can be compared with current ones e.g. satellite images / images from specific locations
comparing photos can show how much ice levels have reduced
but these aren’t very reliable as photos provide comparison not quantitative data. photos can be edited too
qualitative data
data about images, words, experiences (not numbers)
quantitative data
data about numbers (tends to be more useful as is more precise)
climate proxies: paintings & diaries
people made paintings/wrote diaries before cameras were invented or temps were recorded. so they can be used to gauge climate events further in the past
e.g. paintings & diary entries show that the river thames froze a bunch of times between 1300s - 1800s and this shows a colder time period (known as the ‘little ice age’)
natural causes of climate change: milankovitch cycles
in the 1930s milankovitch argued that climate change was linked to the way the earth orbits the sun, how it wobbles, how it tilts. these three ideas are the milankovitch cycles
obliquity - how the earth tilts on its axis
precession - how the earth wobbles on its axis
eccentricity - changes in the shape of the earth’s orbit
(obliquity = tilt, precession = wobbles, eccentricity = shape of orbit)
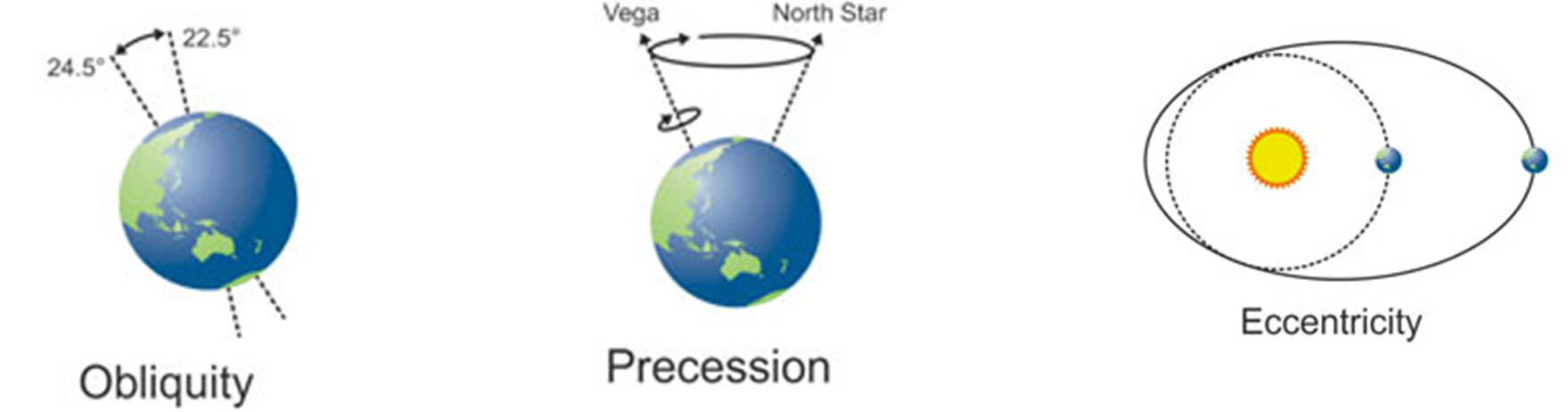
milankovitch cycles: eccentricity
the path of the earth as it orbits the sun, which isn’t fixed and changes over time from being almost circular to almost elliptical
one cycle (circular - elliptical - circular) takes 100,000 years
eccentricity may have caused the glacial & interglacial cycles of the quaternary period
orbit is more circular = colder periods (as sun is never close to earth)
orbit is more elliptical = warmer periods (as sun is sometimes really close to earth and when it’s far there isn’t enough time to freeze up again)

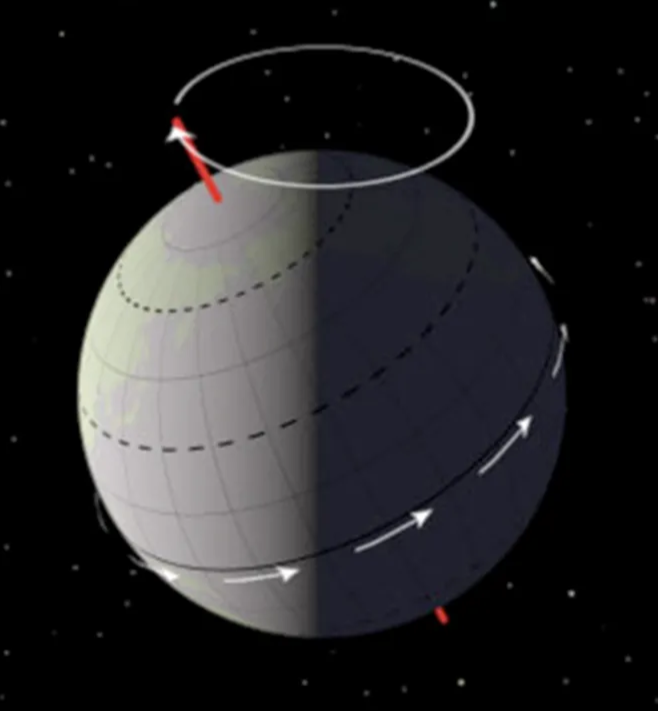
milankovitch cycles: precession
the earth wobbles as it spins on its axis (wierdo)
the wobble is caused by the force of gravity from the sun & moon
as the axis turns it slowly changes the direction it points in, tracing a circular shape (see picture)
it takes 23,000 years to go from one extreme to the other
this can change severity of seasons, which hemisphere is closer to the sun at different times, meaning some regions of the world have very long days & nights (eg northern norway)
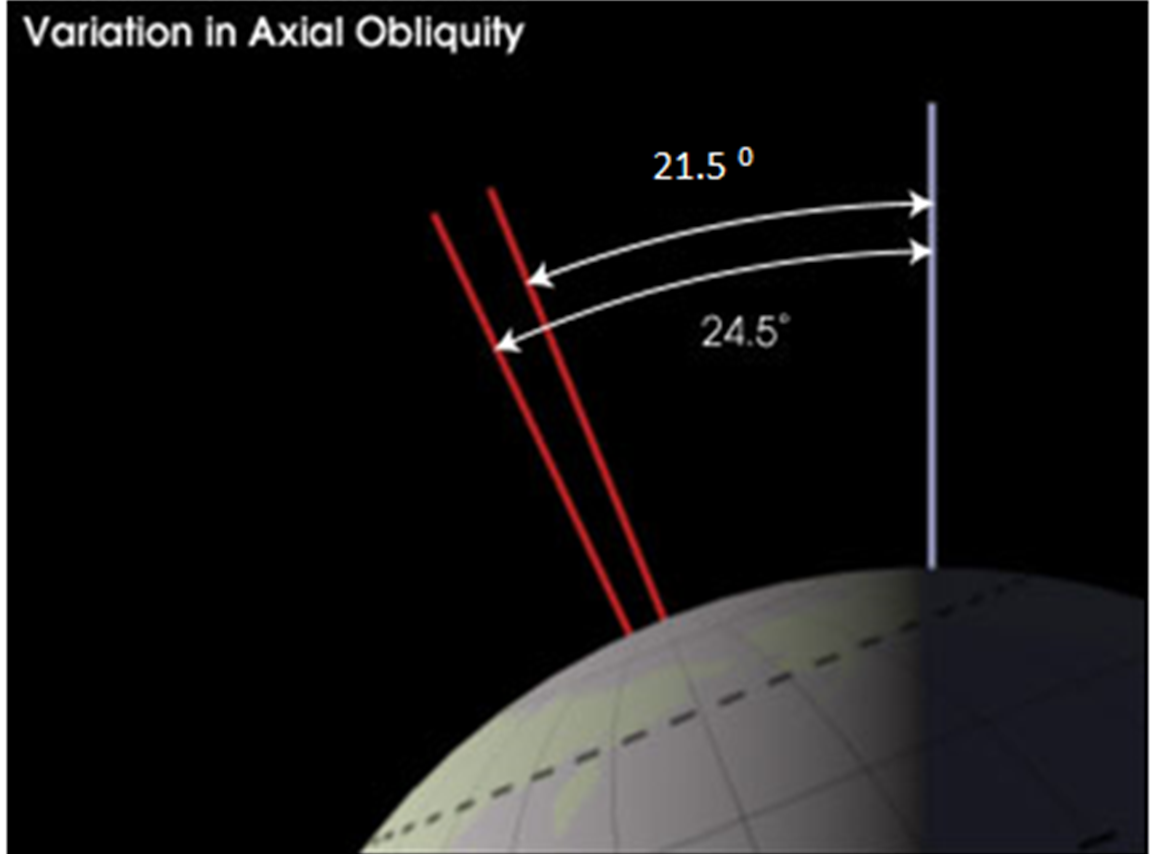
milankovitch cycles: obliquity
the earth is tilted on its axis (wierdo)
over 400,000 years the angle changes from 21.5° to 24.5°. rn we are at an angle of 23.5°
less tilt = less extreme seasons (cool summers, warm winters)
more tilt = more extreme seasons (hot summers, cold winters)
natural causes of climate change: sunspots
the dark spots on the sun’s surface - temporary and caused by magnetic storms
more sunspots = more radiation earth recieves from the sun = higher temps
there is an 11 year cycle of sunspot activity (although some are longer)
the little ice age (1300-1870) is linked to a time when there were fewer sunspots, the medieval warm period is linked to more sunspots
natural causes of climate change: volcanoes
supervolcano = one that erupts more than 1000km³ of material at once
when volcanoes erupt they release lots of dust into the atmostphere, which blocks sunlight resulting in cooler temps
dust can be carried by winds across the globe, meaning cool temps everywhere
mount pinatubo in the philippines erupted on 15th june 1991 (charlie’s birthday) putting 20mil tones of sulphur dioxide & ash 20 miles into the atmosphere. this reduced global sunlight by 10% and cooled the planet by 1.3o for 2yrs
greenhouse effect vs enhanced greenhouse effect
the greenhouse effect is natural and has been occurring for millions of years
the enhanced greenhouse effect is caused by humans and is causing global warming
the natural greenhouse effect
a natural process that keeps the earth warm enough to support life. greenhouse gasses trap the sun’s energy to keep the earth warm
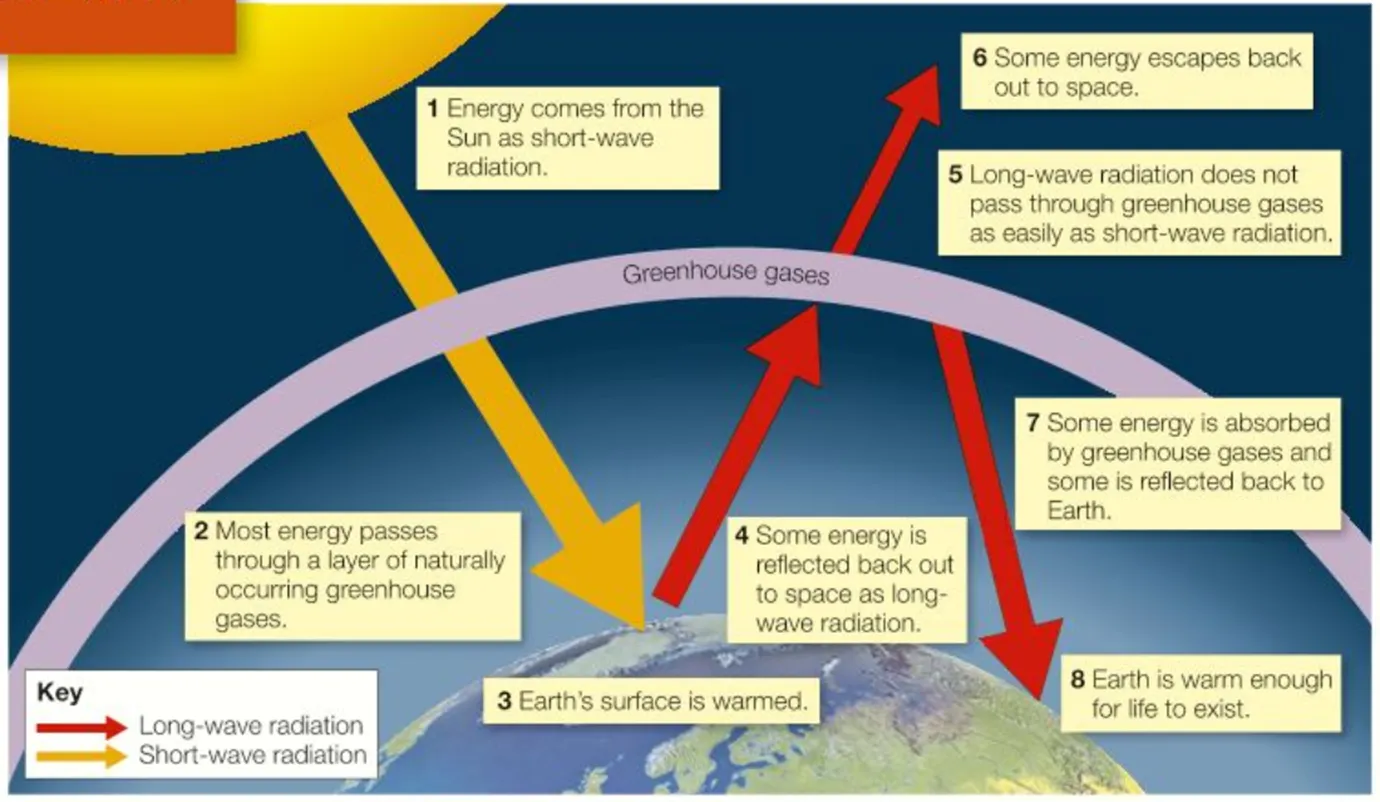
greenhouse gasses
gasses in the atmosphere e.g. CO2 and water vapour that act like the glass roof of a greenhouse - allow the sun’s radiation in and trap the energy that’s reflected back out to keep the earth warm
the enhanced greenhouse effect
only started happening after human intervention - not a natural process
occurs thanks to human processes putting more greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere than occur naturally. this makes the layer of greenhouse gasses thicker meaning more of the sun’s energy is trapped by them and the earth’s temperature increases, causing climate change
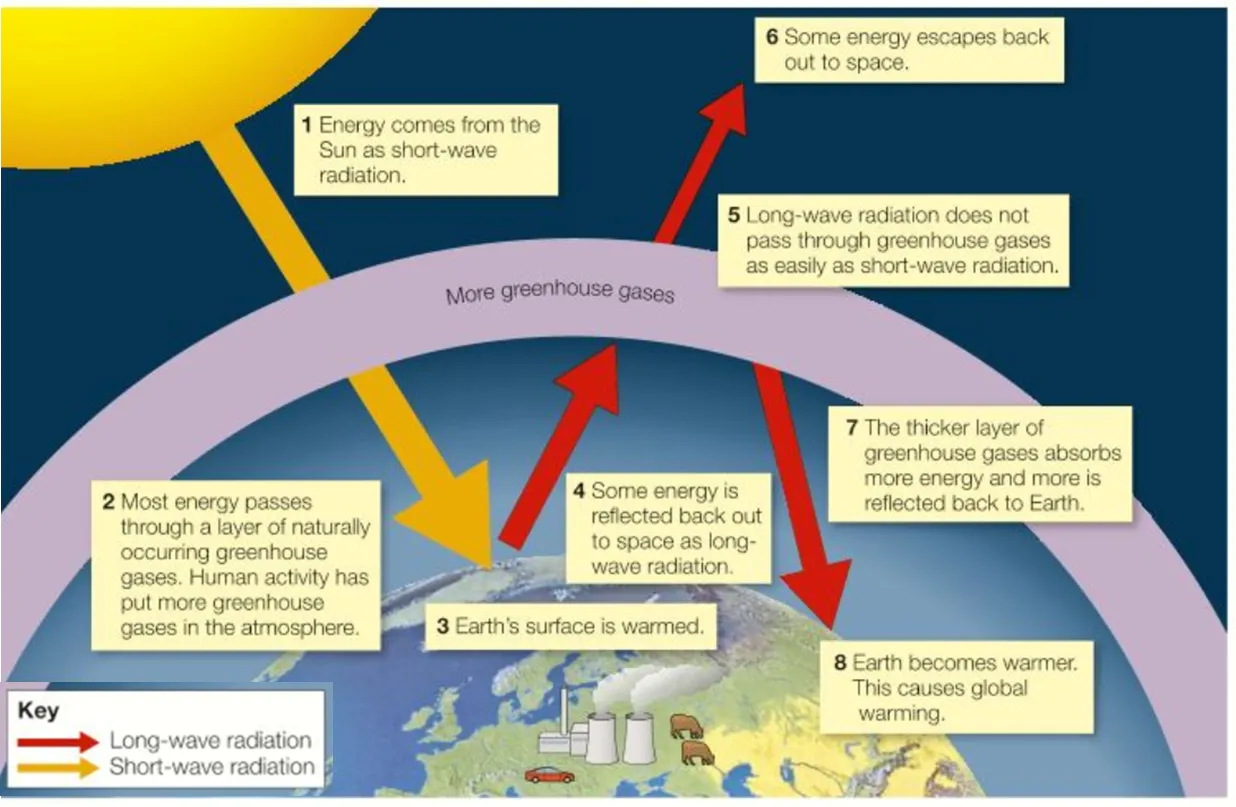
reasons for the enhanced greenhouse effect
97% of climatologists agree that the enhanced greenhouse effect is caused by human activity emitting greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere
the lifestyle of people in ACs uses lots of fuel & energy (cars, aeroplanes, food, phones, electrical products) and is the reasons that so much CO2 is being put into the atmosphere
not all countries emit the same amount of Co2. LIDCs emit very low levels but ACs & EDCs emit much more e.g. china & india emitting CO2 as they develop industry & people start wanting a lifestyle similar to ACs
greenhouse gasses: carbon dioxide (CO2)
causes
burning of fossil fuels
deforestation - plants remove CO2 from the atmosphere during photosynthesis, so when they are felled they stop taking in CO2 and it’s released into the atmosphere when trees are burnt
industrial processes e.g. making cement releases CO2
global emissions: 77%
greenhouse gasses: methane (CH4)
causes
vehicle exhausts
agricultural & industrial processes - livestock farming produces lots of methane, flooded rice paddies emit methane
burning of fossil fuels
waste management - decomposing organic waste in landfill releases methane
global emissions: 14%
greenhouse gasses: nitrous oxide (N20)
causes
industrial processes e.g. production of nitric acid & adipic acid
agricultural practises - fertilised soil & animal waste emit nitrous oxide
burning of fossil fuels
global emissions: 9%
global impacts of climate change: extreme weather in australia (social)
extreme weather events damage homes and infrastructure in australia
for example there have been 4,000+ heat related deaths each year
this means people are displaced and lose their homes
displacement, increase in homelessness, insurance prices rise, housing prices rise due to demand
global impacts of climate change: warming temps in the arctic (econonomic positive)
warming temps cause more hospitable weather and melting of sea ice
since the 1980s sea ice volume has decreased by 75%
this makes it easier to venture into the arctic & collect resources as new shipping routes are opened
e.g. canada’s northwest passage
this brings more money to the area to help improve it
global impacts of climate change: changes to the sea in east asia (environmental)
warming waters, ocean acidification and rising sea levels are becoming more severe
ocean acidity has increased by 30% since pre industrial levels
this can alter and/or destroy vulnerable ecosystems
e.g. coral reefs and mangroves
this leads to loss of biodiversity & extinction as animals can’t survive
impacts of climate change on the uk: increased flood risk (social)
rising sea levels create an increased flood risk in the eastern lowlands of england
flooding can cause destruction of houses, land, infrastructure etc
6.3 million properties in england are at risk of flooding
this causes loss of homes, displacement, homelessness, loss of life
bonus: economic impact too because repairs cost lots of money
impacts of climate change on the uk: increase in tourism (economic)
climate change creates warmer temps in the uk (especially in summer)
this increases tourism thanks to more hospitable weather e.g. in the lake district
there were 38 mil visits to the uk in 2023, 7 mil more than the year before
this brings in more money to the uk which can be used for education, infrastructure, healthcare etc
impacts of climate change on the uk: rising sea temps (environmental)
as a result of climate change the temp of the sea around the uk is rising
this means that sea life struggles to survive as their habitat changes
this leads to loss of species, extinction, and loss of biodiversity
vulnerable species could lose 40% of their habitat by the end of the century