Antibiotic Resistance
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
bactericidal vs bacteriostatic
kill (bactericidal)
inhibit growth (bacteriostatic)
what are different sources of antibiotics?
Natural metabolites produced by microorganisms (usually bacteria or fungi) (e.g., Penicillin)
Synthetic or semi-synthetic made by pharmaceutical companies (e.g., Ciprofloxacin)
how was penicillin discovered?
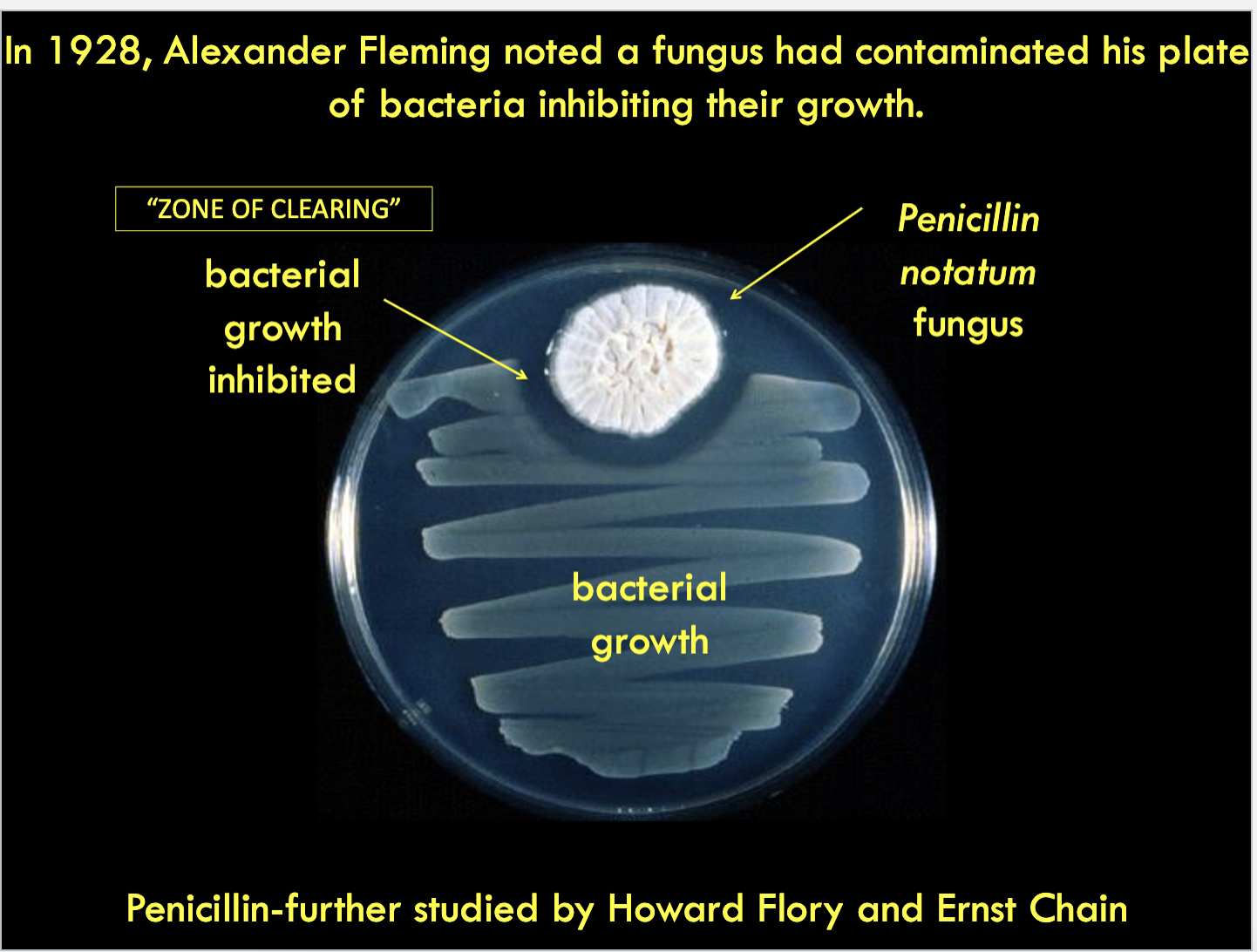
what are the 6 key main antibiotic targets/
DNA replication
Transcription-RNA synthesis
Translation-Protein synthesis
Folic acid synthesis
Membrane disruption
Cell wall synthesis
how do antibiotics target DNA replicaiton?
DNA gyrase relieves supercoiling tension of dsDNA during replication. Fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin) inhibits gyrase activity. Without gyrase activity, replication cannot occur.
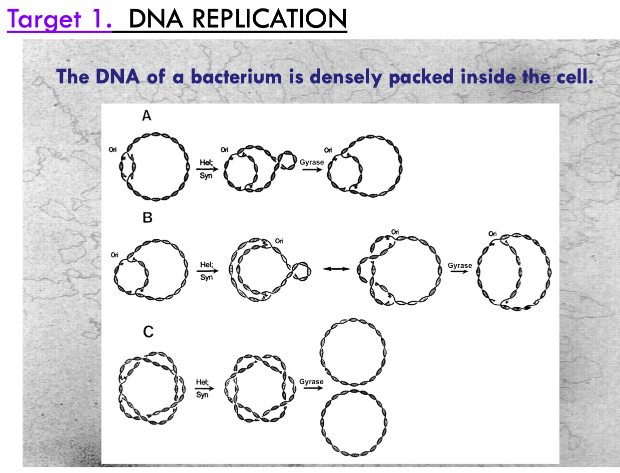
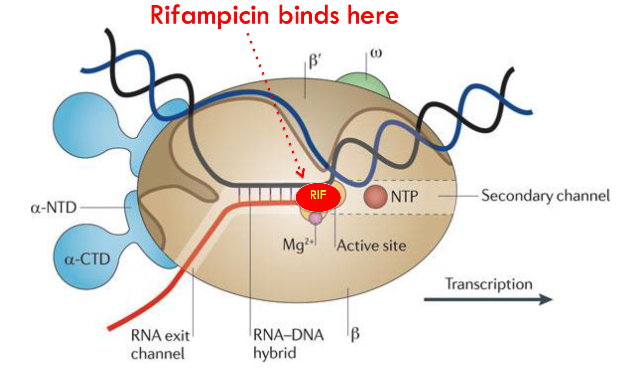
how do antibiotics target RNA synthesis (transcription)?
Rifampicin binds to RNA Polymerase and blocks transcription.
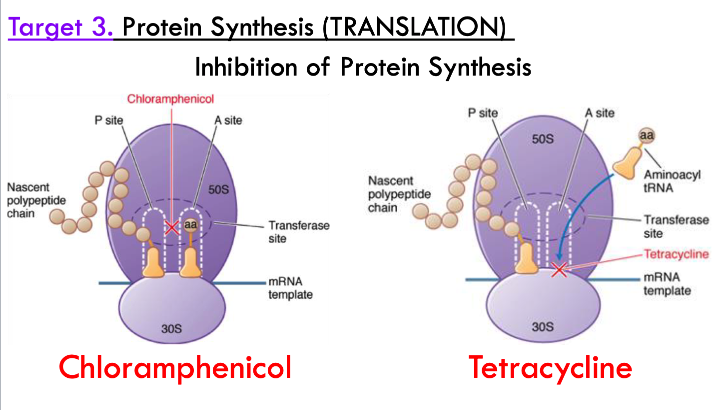
how do antibiotics target protein synthesis (translation)?
chloramphenicol blocks peptide linkages
tetracycline sits in the tRNA pocket to block peptide lengthening
Tetracycline treatments can cause …? (side effects)
tooth discoloration
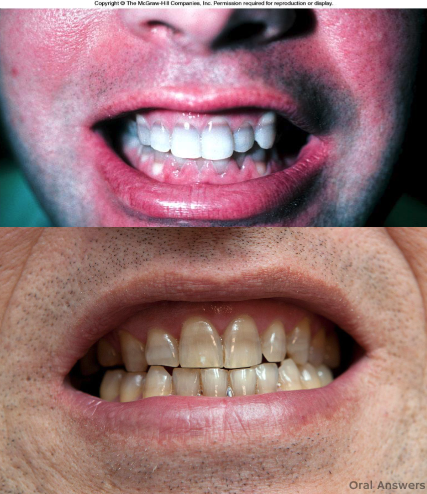
Don’t prescribe tetracycline to …?
pregnant women and young children (due to tooth discoloration)
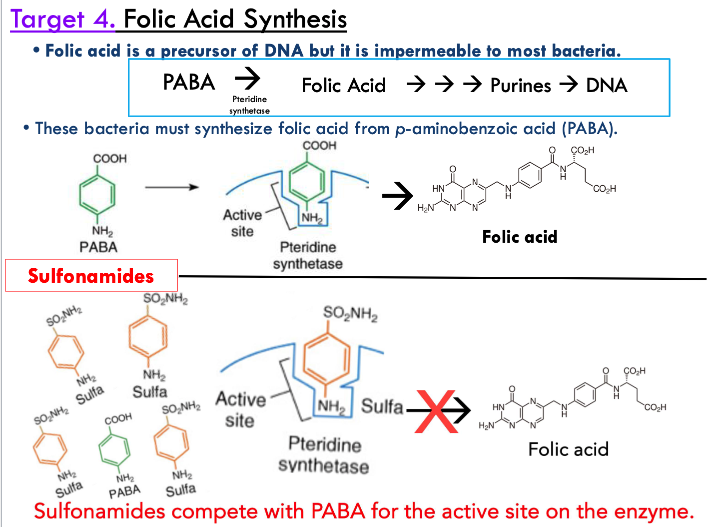
how do antibiotics target folic acid synthesis?
folic acid is precursor of DNA but it is impermeable to most bacteria so they must synthesize it on their own from PABA
sulfonamides compete with PABA for the active site on the enzyme to inhibit folic acid synthesis
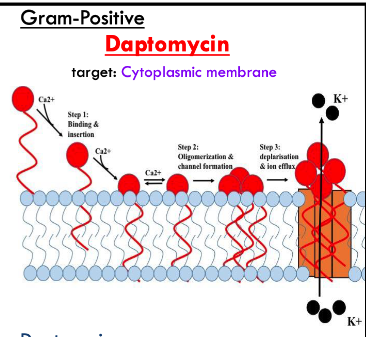
how do antibiotics target gram-positive membrane disruption?
daptomycin binds/inserts into cell membrane
aggregates in cell membrane
forms a hole allowing ions in and out of cells
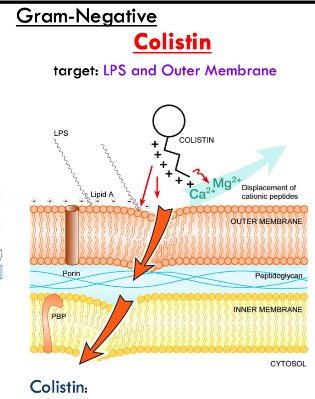
how do antibiotics target gram-negative membrane disruption?
colistin is a polycationic peptide that binds to LPS in outer membrane
disrupts and solubilizes membranes
daptomycin target is?
cytoplasmic membrane on gram positive bacteria
colistin target is?
LPS and outer membrane of gram negative bacteria
how do antibiotics target cell wall synthesis?
normally, transpeptidase binds to D-Ala-D-Ala and performs cross-links
penicillin is a chemical mimic of D-Ala-D-Ala that blocks cell wall crosslink formation
transpeptidase instead binds to beta-lactam antibiotics, preventing it from binding to D-Ala-D-Ala
growing bacteria unable to crosslink the cell wall will lyse due to osmotic pressure
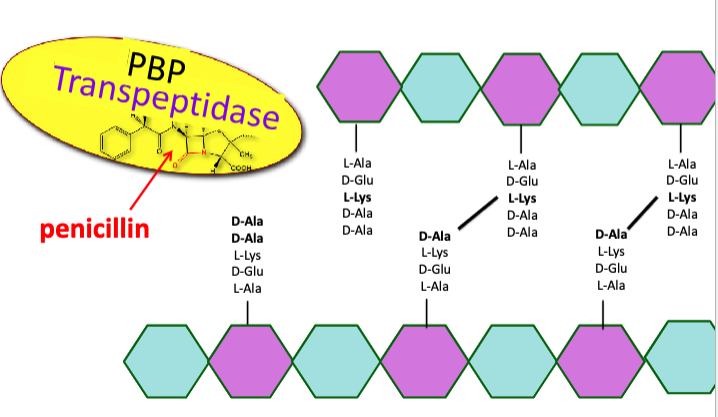
what are some antibiotics that block cell wall crosslink formation?
penicillin
vancomycin
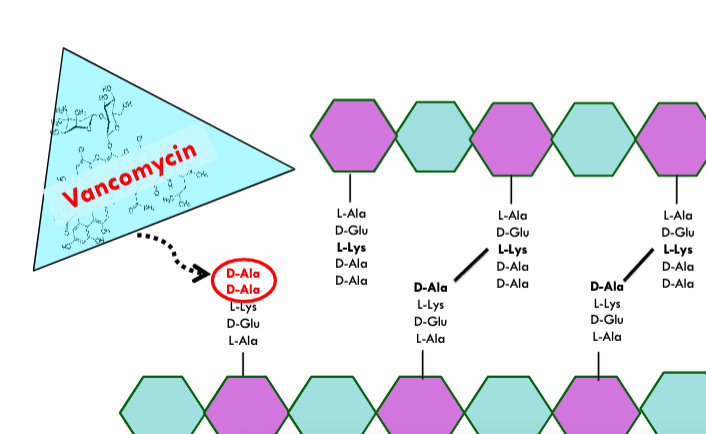
how does vancomycin target cell wall synthesis?
binds directly to D-Ala-D-Ala so transpeptidase can’t bind
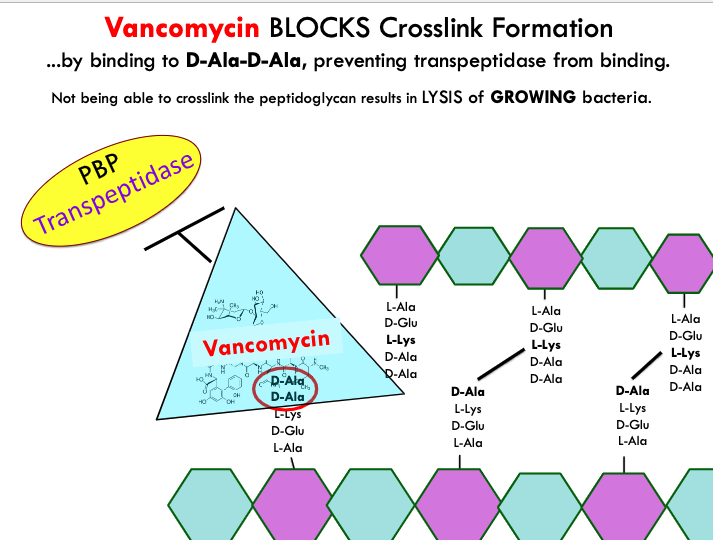
how does penicillin target cell wall synthesis?
penicillin binds to transpeptidase which blocks it from being able to link the D-Ala-D-Alas
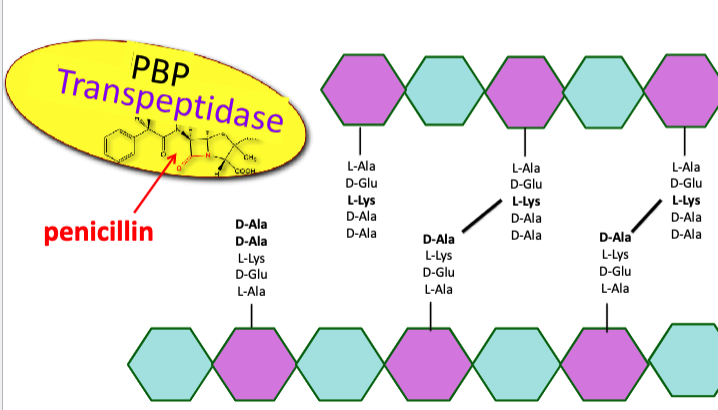
how do bacteria resist actions of antibiotics?
inactivate antibiotics (degradation/modification)
modify target
remove antibiotic from cell
prevent uptake of antibiotic
develop persister cells
what is the mechanism used by bacteria to inactivate antibiotics by degradation or modification?
beta-lactamase gene is often encoded on a plasmid
beta-lactamase is secreted from cytoplasm to cleave beta-lactam ring on antibiotic like ampicillin to inactivate
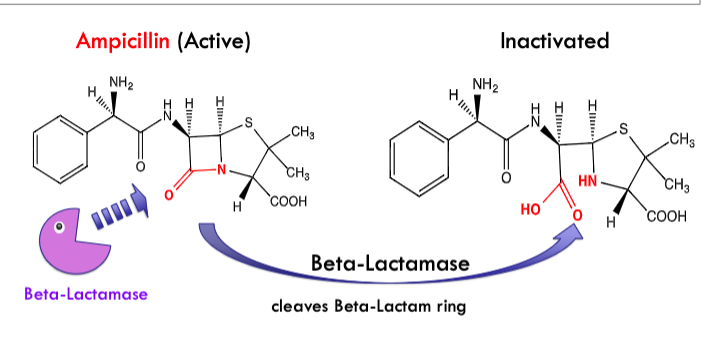
what antibiotics can be inactivated by degradation or modification?
beta-lactam antibiotics (penicillin, ampicillin, etc.)
what is the mechanism used by bacteria to modify the target?
normal → vancomycin impedes cell wall synthesis by binding to D-Ala D-Ala and thus blocking transpeptidase
resistance → bacteria make D-Ala-D-Lactate which vancomycin cannot bind to
transpeptidase can bind to D-Ala-D-Lactate and make crosslink
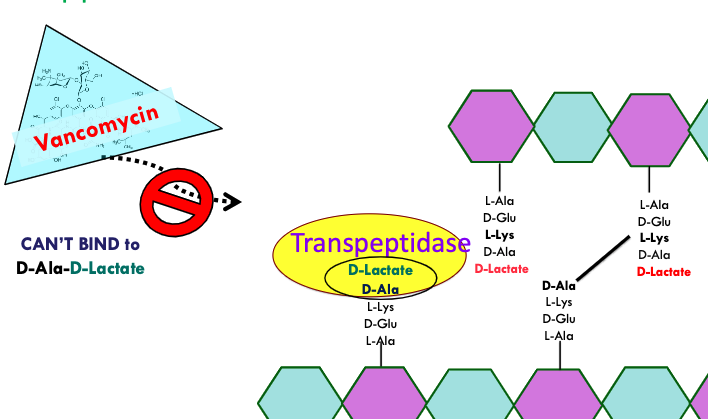
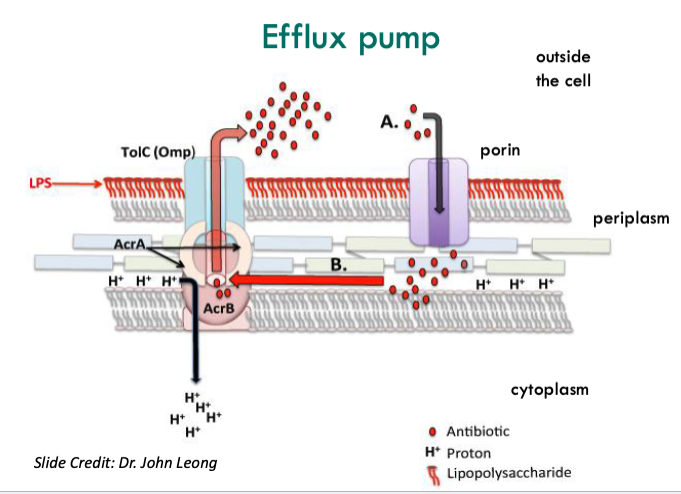
what is the mechanism used by bacteria to remove the antibiotics from the cell?
efflux pumps kick out antibiotics that came in through porins from within
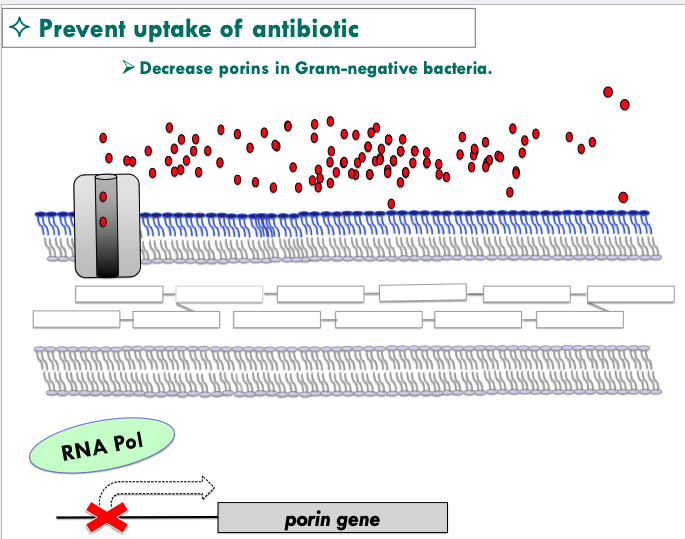
what are some ways to prevent uptake of antibiotics?
Decrease porins in Gram-negative bacteria
Increase thickness of the peptidoglycan cell wall in Gram-positive bacteria
Capsule formation
Biofilm production
how can we decrease porins in gram-negative bacteria?
mutation in RNA polymerase that transcribes porin genes
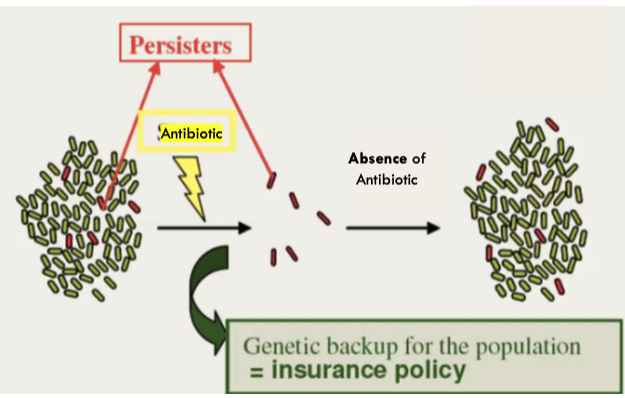
what are persister cells?
cells that contain genetic backup for the population that are resistant to antibiotics
what is intrinsic resistance?
organism is innately resistant to the antibiotic
what is acquired resistance?
organism develops the ability to resist the antibiotic
what are examples of intrinsic resistance?
Gram-negative resistance to Vancomycin (The drug is too big to pass through the porins.)
Gram-positive resistance to Colistin (lack of outer membrane)
what are examples of acquired resistance?
New mutations
Acquire new genes via horizontal gene transfer (HGT)
what are DNA transfer mechanisms that can spread antibiotic resistance?
horizontal gene transfer
Transformation (naked DNA taken up from the environment)
Transduction (bacterial DNA delivered by phages)
Conjugation (DNA transfer between bacteria involving a sex pilus)
what can carry antibiotic resistance genes?
Plasmids
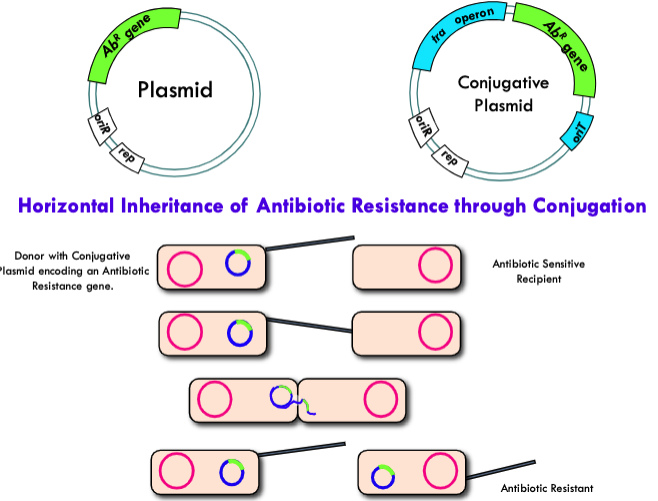
Drug resistance genes on plasmids are often on
“TRANSPOSONS”
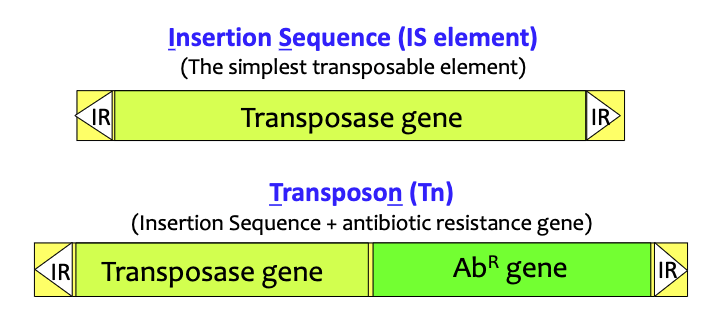
what are transposons?
mobile DNA elements that can move (transpose) within and between DNA molecules
cannot self-replicate (need to insert into other replicons for propagation)
t/f: transposons insert randomly into plasmids, chromosomes and viral genomes independent of homologous recombination
Transposition is mediated by the enzyme _______, which is encoded on the transposable element.
transposase
Transposases recognize DNA sequences that are __________ located at both ends of the transposable element
inverted repeats (IR)
insertion sequence (IS element) vs transposon (Tn)
Everything between the inverted repeats (IR) on the ends can be transposed.
The transposase enzyme only “looks at” the repeats, so it doesn’t matter what lies between
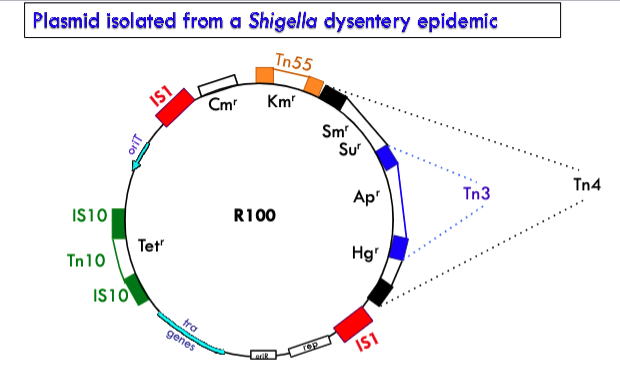
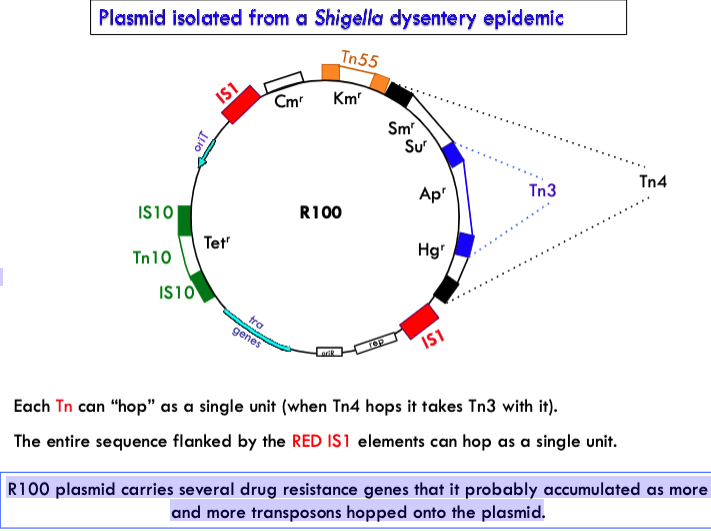
how did all the drug resistance genes on a plasmid isolated from a shigella dysentery epidemic form?
R100 plasmid carries several drug resistance genes that it probably accumulated as more and more transposons hopped onto the plasmid.
Transposition provides a means to:
Assemble cassettes of genes that confer a variety of properties to a bacterial cell including virulence factors and antibiotic resistance.
Place those cassettes of genes onto mobile elements such as conjugative plasmids or virus genomes resulting in rapid spread of antibiotic resistance and virulence genes through bacterial populations
what are some Key Factors contributing to the spread of resistance?
widespread antibiotic use in agriculture
overuse/misprescribed antibiotics
what are some examples of overuse/misprescribed antibiotics?
Prescribing antibiotics for non-bacterial diseases
Prescribing the wrong antibiotic for a given infection
Over the counter availability in some countries
% of the antibiotic usage is in the animal husbandry industry
70-80%
why are antibiotics used in food animals?
promote weight gain
prevent infections in crowded pens
treat infections
% of all Antibiotic Prescriptions are UNNECESSARY
30%
what are ways to combat antibiotic resistance?
increase awareness/monitoring for ABR organisms in clinical/agricultural settings
modify antibiotics used in agriculture
reduce/eliminate unnecessary prescriptions
design better diagnostic methods
develop new drugs/therapies