AP Psychology - Unit 13: Psychotherapy
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
trepanning
the drilling of holes in skull to release demons
exorcisms
the bringing of humans to the brink of death to release demons
asylums
hospitals for the mentally ill for the purpose of containment
Dr. Philippe Pinel
- French physician during 1790s
- worked in medical hospitals and asylums
- advocated for more humane treatment of asylum patients
- remove shackles and allow more freedom so patients will behave better
Dr. Jean Martin Charcot
- French neuroscientist and professor of anatomical pathology
- used hypnosis to treat hysteria
Joseph Breuer
- Austrian physician
- Cathartic Method: talking therapy
- under hypnosis
Bertha Pappenheim (Anna O)
- developed paranoia and delusions from childhood trauma
-treated by Breuer and Freud with hypnosis/talking therapy
Dorthea Dix
- American social reformer and nurse
- advocated for more humane treatment of mentally ill
- major figure in modernizing nursing practices
deinstitutionalization
reducing the number of patients in psychiatric hospitals by transitioning them to community-based mental health services
evidence-based interventions
therapeutic approaches and treatments that are supported by scientific research and empirical evidence
- ensuring effectiveness and reliability
therapeutic alliance
collaborative and trusting relationship between a therapist and client
- crucial for effective therapy and positive treatment outcomes
psychodynamic theory
- uncovering unconscious conflicts
- past experiences
- insight: knowing will set you free
hypnosis
guided meditation to unlock unconscious
free association
talk about whatever is on the mind
- little structure, free-slowing, no censorship
dream analysis
analysis of dreams from previous night
- latent: symbols (underlying meaning)
- manifest: storyline (what's written down)
transference
patients transfer their emotions to their therapist
- artificial displacement (take out your anger on your therapist)
- against counter-transference (therapist taking out emotions on patient)
analyzing resistances
all of the patient's attempts at resisting therapy
- people block progress when they are near a break through
humanistic therapy
- all humans are good and have potential
- conscious insight, free-will, present and future (not past)
- "clients" not "patients" and "facilitators" not "therapists"
Roger's Person-Centered Therapy
providing a supportive environment where clients can achieve self-discovery and personal growth
- people are good and seek out self-growth
- atmosphere of growth
atmosphere of growth
part of Roger's Person-Centered Therapy
1. empathy
2. unconditional positive regard
3. genuine, authentic
4. active listening
active listening
reflective (rephrase, summarize, repeat, clarify) and no advice/interpretation
logo therapy
- form of humanistic-existential therapy
- finding purpose in life/meaning
- Viktor Frankl
behavioral therapy
use of learning/behavioral therapies to change behavior
(active, directive therapy)
counterconditioning
using classical conditioning to evoke new responses to stimuli that are triggering unwanted behaviors
- exposure therapy (systematic desensitization)
- aversion therapy
exposure therapy
a person slowly faces the object of anxiety
- systematic desensitization
systematic desensitization
substituting a positive (relaxed) response for a negative (fearful) response to a harmless stimulus
- help combat anxiety with relaxation techniques
- desensitization hierarchy (go slowly)
- virtual reality options as well
aversion therapy
substituting a negative (aversive) response for a positive response to a harmful stimulus
- pairs an unpleasant state with an unwanted behavior
extinction procedures
weaken maladaptive responses through forced extinction
- flooding
- implosion therapy
flooding
lessen anxiety by exposing the patient to a carefully controlled environment
(ex) fear of snakes → hold a snake
implosion therapy
the patient imagines vividly the unpleasant event
(ex) fear of snakes → imagine holding a snake
operant conditioning
using punishers and reinforcements
(supplements other therapeutic techniques)
- token economy
- behavioral contracting
token economy
tangible objects are given as reinforcers for positive behaviors
- useful for kids, in-patient care, recovering alcoholics
behavioral contracting
written agreement (contract), outlining expectations for both patient and therapist
- concretely defined
modeling
- the patient observes another person responding appropriately to a situation
- mimics healthier coping strategies
(supplements other therapeutic techniques)
cognitive therapy
focus on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and beliefs
cognitive triad
the negative thought patterns about oneself, the world, and the future contribute to and sustain depression
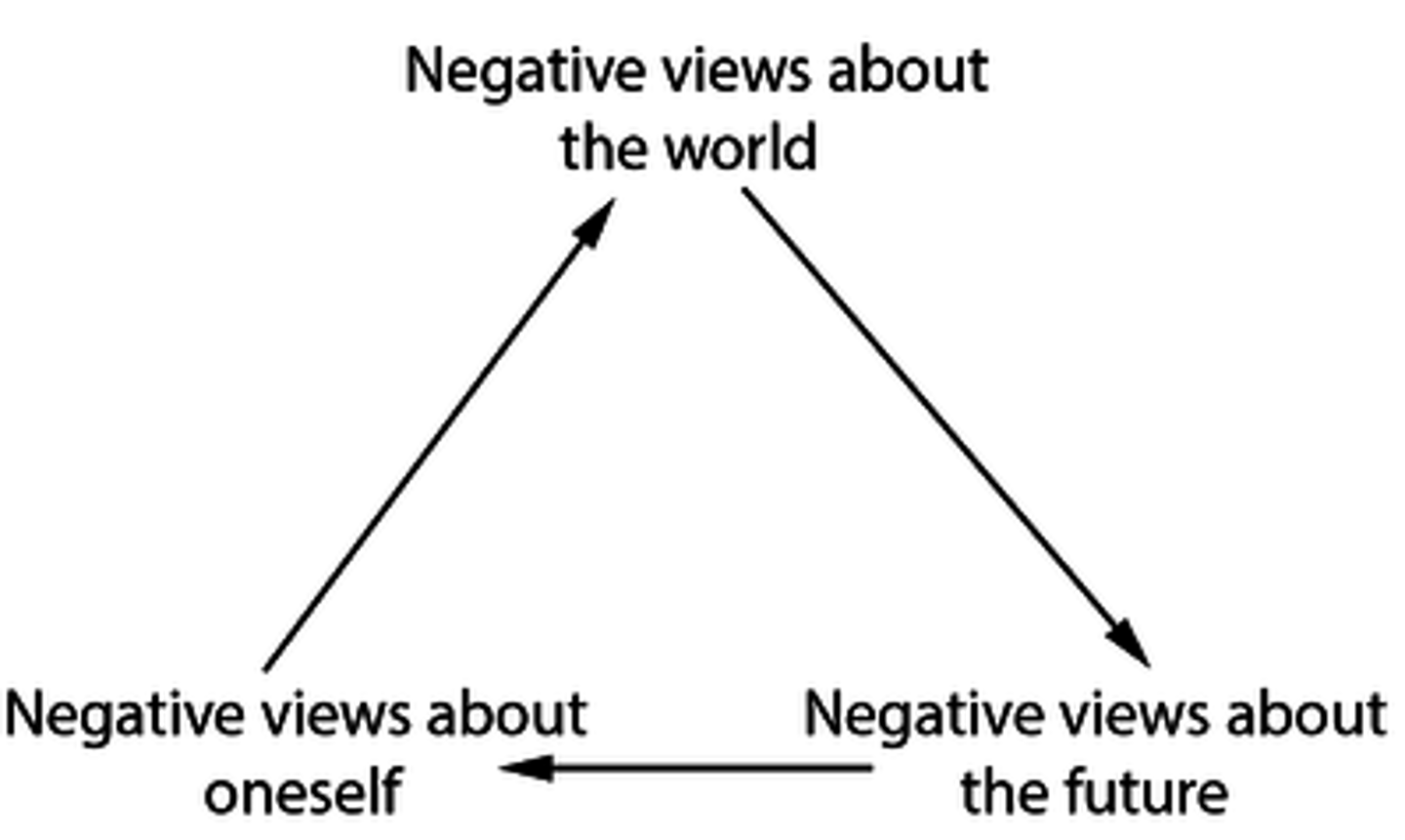
Albert Ellis' Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT/RET)
- ABCs: activating experience, false beliefs, emotional consequence
- people recite maladaptive/false thoughts
- therapist shows patient how their thoughts are dysfunctional
Aaron Beck's Cognitive Therapy
- negative self-defeating thoughts
- therapists teach adaptive thoughts to replace maladaptive ones
selective perception
thought pattern of only paying attention to certain things
cognitive restructuring
identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and beliefs, replacing them with more positive and realistic ones to improve emotional well-being and behavior
psychotropics
drugs that alter psychological processes and state of mind (used for treatment)
antipsychotic medications
- used to alleviate/treat agitation, delusions, hallucinations (schizophrenia, bipolar)
- have tranquilizing effect
- block DA receptors
- side effects: dry mouth, tremors stiffness, jerky movements, tardive dyskinesia (involuntary facial movements)
- newer/atypical are better at treating negative symptoms (+ positive symptoms)
antidepressants
used to alleviate/treat depression symptoms
- all have side effects, take time to effect, and time to adjust
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI)
antidepressants
- block 5ht reuptake
tricyclics
antidepressants
- increase 5ht and NE
monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI)
antidepressants
- increase 5ht and NE
- diet restrictions and side effects make them a last resort antidepressant
antianxiety drugs
used to alleviate/treat anxiety (short-term)
muscle relaxers
antianxiety drugs
- reduce muscle tension
benzodiazepines
antianxiety drugs
- increase GABA
- side effects: habit forming, impair alertness and attention, dangerous for OD and driving
lithium
(mood stabilizing drug)
- used to treat bipolar symptoms
- stabilizes mood swings and reduces the frequency and severity of manic and depressive episodes
lobotomy
Antonio Egas Moniz and Walter Freeman
- severed the frontal lobe from the rest of brain
- reduced excessive/destructive symptoms
- unintended side effect: vegetative state
lesioning
destroy target areas of the brain using an electrode
electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
- 150 volts pass across brain for 1-1.5 secs to trigger grand mal seizure
- goal: reset brain chemistry
- last resort (after meds) due to memory loss
transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain to improve symptoms of depression
- side effects: headaches, facial muscle spasms, lightheadedness
biofeedback
using electronic monitoring to provide individuals with info about physiological processes, such as heart rate/muscle tension
- goal: learn to control them + improve health/performance
cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
treatments that combine cognitive and behavioral techniques to address dysfunctional thoughts and behaviors
- goal: to improve emotional regulation and develop healthier coping strategies
- used for mild depressive disorders, anxiety related, impulse related (not the most intense conditions)
dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT)
a type of CBT that focuses on teaching skills for emotional regulation, distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness, and mindfulness
mindfulness
being fully aware of surroundings; present; focused
distress tolerance
teaching that you can sit in discomfort
emotion regulation
have the power to change emotions
interpersonal effectiveness
asking for what you want
eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR)
refocusing thoughts with eye movements and bilateral stimulation
- designed to alleviate trauma
- making someone relive/retell traumatic events (makes a person feel they have a tool to cope)
self help
- books, apps, etc
- will only work if a person wants to change
group therapy
(encounter groups, T-groups)
- pros: less expensive, support system, peer pressure to change
- cons: diluted, can embroil people, irrelevant issues
community mental health programs
- target environment and community as a whole
primary: prevention (keep it from occurring)
secondary: early detection (trying to catch before out of control)
tertiary: attempt to treat (problems already exist)
couples/family therapy
- systems perspective
- problems are due to entire family system/unit
- emphasis on communication and mutual respect
"Don't should on yourself, don't should on others" - Aaron Beck
health psychology
the study of how psychological, behavioral, and cultural factors contribute to physical health and illness
psychoneuroimmunology
the study of how the brain, nervous system, endocrine system, and immune system interact and affect human health and behavior
adverse childhood experiences (ACEs)
stressful or traumatic events in childhood that can have long-lasting effects on health and well-being throughout a person's life
Holmes and Rahe Stress Scale
a way to measure your level of stress
problem-focused coping
directly managing or solving the source of stress
emotion-focused coping
managing the emotional response to stress
tend-and-befriend theory
behavioral reaction to stress that involves nurturing activities to protect oneself, seeking social support to reduce stress
positive psychology
the scientific study of human flourishing to help individuals and communities to thrive