Biology Gcse revision
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Living organism Characteristics
Movement
Nutrition
Respiration
Reproduction
Excretion
Growth
Homeostasis
Sensitivity
Word equation for aerobic respiration
Glucose + oxygen —> Carbon dioxide + water
Excretion definition
The removal of toxic metabolic materials and substances from organisms
Sensitivity in plants
Geo and phototropism
Examples of eukaryotic organisms
Protoctista
Fungi
Plants
Animals
Eukaryotes characteristics
Can be both single and multicellular
Contain a nucleus
Have a distinct membrane
Prokaryotes characteristics
Single called
No nucleus
The nuclear material is found in the cytoplasm
Prokaryote example
Bacteria
1.Lactobacillus
Pneumococcus
Pathogens
Bacteria
Fungi
Protoctist
Viruses
Why are viruses no classified as living organisms
Need a host cell to reproduce
Smaller than bacteria
No cellular structure
Contain either dna or rna
Level of organization in organisms
Organelle → Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ System → Organism
3 tissues in plants
Xylem
Phloem
Mesophylls
Ribosome definition
Site of protein synthesis
Vacuole definition
Contains cell sap
Supports the shape
Used for storage of certain materials
Differences between plant and animal cells
Cell wall
Chloroplasts
Permanent vacuole
Cell differentiation meaning
How cells develop the structure and characteristics needed to carry out their functions
Specialized cell definition
Cells that have gone through cell differentiation
How are RBC specialties to carry out their functions
Biconcave shape Large SA
Contain haemoglobin
What are undifferentiated cells called
Stem cells
Types of stem cells
Embryonic (embryo) any type of cell
Adult (bone marrow, skin) cells of the blood
Elements in proteins
Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
Positive color change of starch
Orange to blue / black
Positive color change for protein
Blue to violet / purple
Corms meaning
Change - the independent variable
Organism - organism being used
Repeat - carried out for reliable results
Measurement 1 - how will you measure your dependent variable
Measurement 2 - what time scale will you use
Same - what will you control
Same
Biological catalyst
They speed up the chemical reactions within the body without being used up
What happens to enzymes when their shape changes
They denature
Diffusion definition
The movement of particles from an area of low to high concentration
Osmosis def
The net movement of water molecules form an area of high to low water potential through a partially permeable membrane
Active transport def
The movement of particles from low to high concentration across a cell membrane and requires atp
Factors affecting the movement of substances
Surface area
Diffusion distance
Temperature
Concentration gradient
Photosynthesis equation
Carbon dioxide + Water → glucose + oxygen
Glucose uses in plants
Produce starch for storage
Synthesise lipids
To form cellulose for cell walls
To produce amino acids
Limiting factors
Temperature
Light intensity
Carbon Dioxide concentration
Adaptations of the leaf
Large SA for diffusion and light absorption
Thin short diffusion distance for Carbon Dioxide
Many chlorophyll to absorb light
Stomata allow CO2 to diffuse in and oxygen out
Epidermis is transparent to let light through
Palisade layer has many chlorophyll for light
Spongy mesophyll has airspace’s for CO2 increasing the surface area
Both Mineral ions and their functions
Magnesium - needed to produce chlorophyll ( lack will cause yellow leaves)
Nitrogen - needed to produce amino acids ( lack will cause stunted growth)
Why is vitamin D required
To absorb calcium and is required for strong teeth and bones
Why is vitamin A required
Needed to make pigment in the retina
Why is iron required
Needed to produce hemoglobin that helps to carry oxygen
Where is bile produced
Liver
What happens in the small intestine
Duodenum - digestion of food exiting the stomach by enzymes
Ph is around 8 - 9 so it is slightly alkaline
Ileum - absorption of water and digested food molecules
Lined with vili
Peristalsis def
It helps move food along the alimentary canal by wave like contractions
Role of enzymes in digestion
Break down large, insoluble molecules into smaller, soluble molecules that can be absorbed into the blood stream
Stages of starch and the enzyme that breaks it down
Amylase, Maltese
Starch ( amylase ) → Maltose ( Maltase ) → Glucose
What are lipids made up of
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
Bile usages
Neutralizes the acid from the stomach so that it is the optimum ph for the enzymes in the SI
Emulsifies lipids ( breaking apart large droplets into smaller ones increasing the surface area
Small intestine adaptations
Large surface area because of the villi made up of many microvilli for absorption
The villus is one cell thick for a short diffusion distance
Steep concentration gradient
ATP usages
Chemical reactions
Muscle contractions
Keeping warm
Anaerobic respiration word equation
Glucose → Lactic Acid
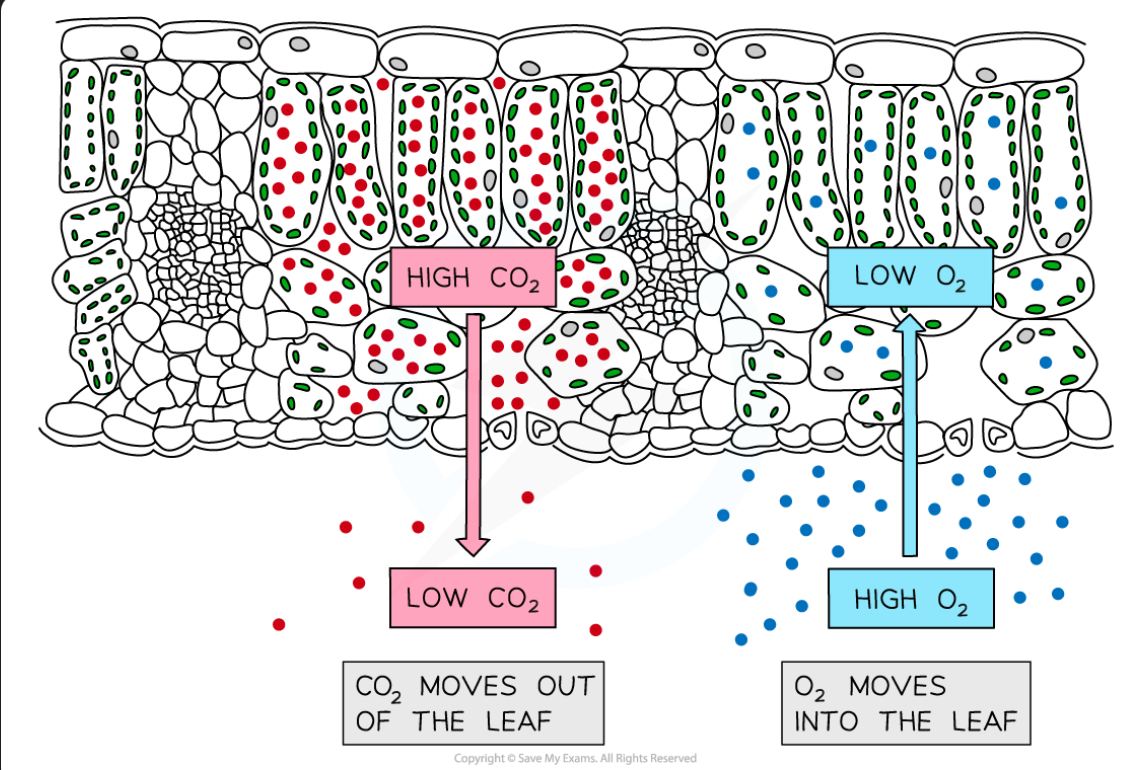
What happens in terms of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide during photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide moves into the leaf
Oxygen moves out of the leaf
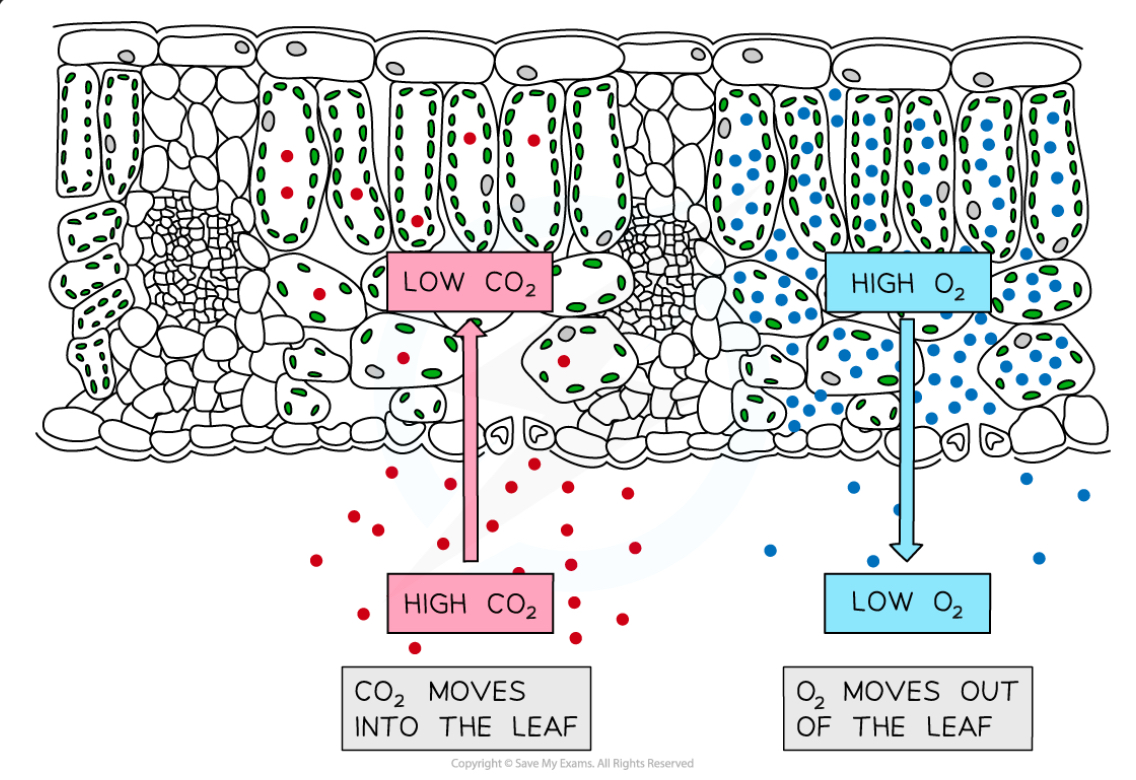
What happens in terms of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide during respiration in the leaf
Carbon dioxide moves out of the leaf
Oxygen moves into the leaf
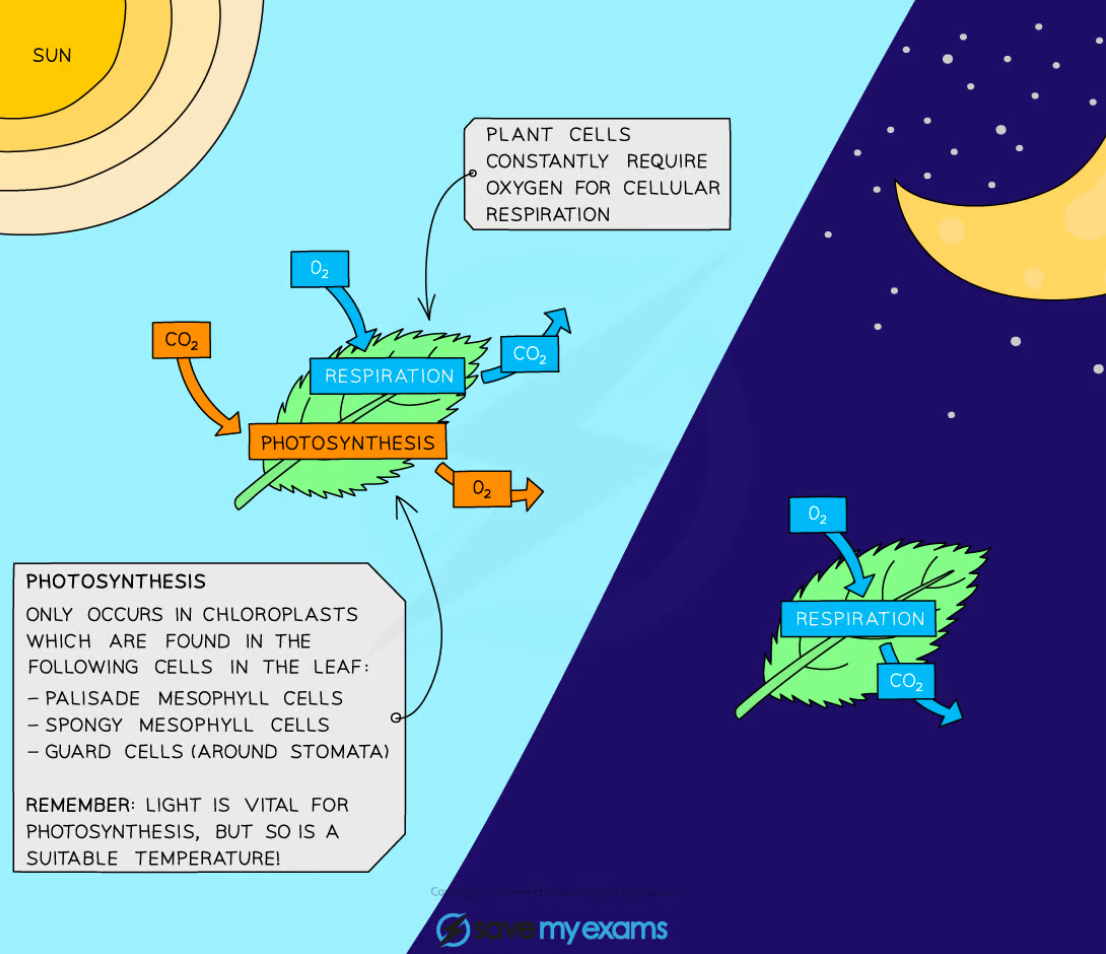
The difference in gas exchange during night and day
DAY:
Rate of photosynthesis > respiration
Night:
Rate of photosynthesis < respiration
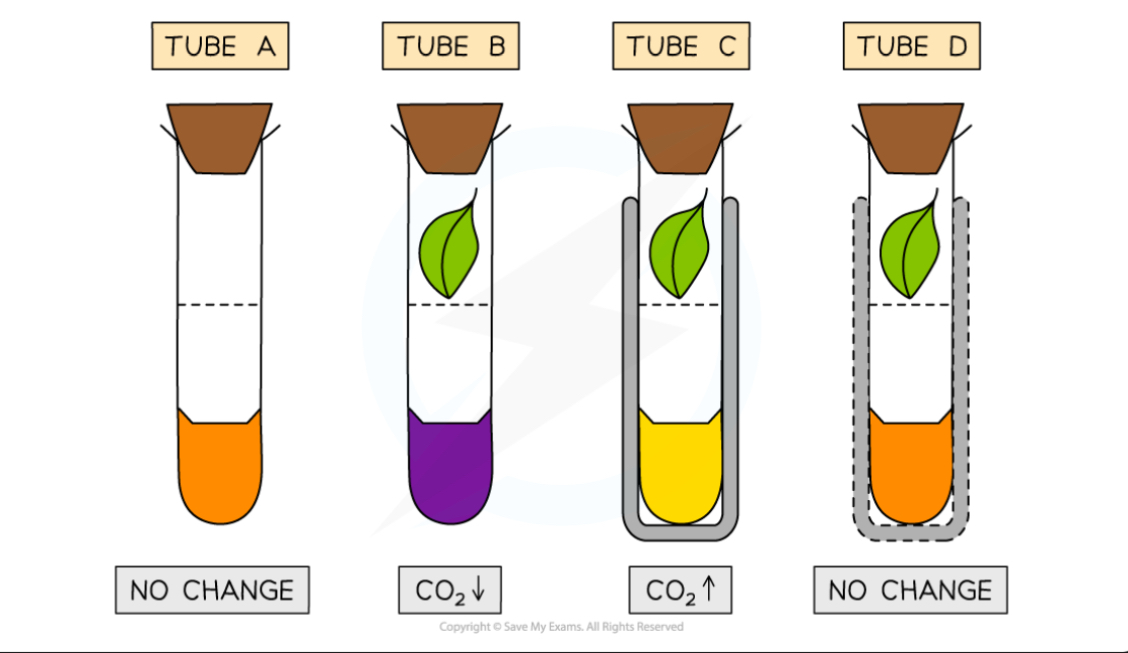
What color will the hydrogen carbonate indicator change to
Yellow if there is a high CO2
Purple if there is a high concentration of CO2
Orange if the rate of photosynthesis is equal to the rate of respiration