cell structure
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
what is cell theory
All organisms are composed of one or more cells
Cells are the smallest living things and the basic unit of organization of life
Cells can only come from pre-existing cells.
why is cell size limited
small size allows cells’ metabolic processes occur rapidly to maintain homeostasis
what happens as the cell size increases
the relative surface area decreases and demand for nutrients increases
what determines the speed at which nutrients and wastes are moved into or out of the cell
surface area available, temperature, the concentration gradient, and distance that the nutrients have to travel
what is the SA:V
surface area to volume ratio
.
.
what happens when cell becomes to large
they have to divide or die
how do some cells increase their surface area
they have in-foldings (especially cells involved in absorbtion)
how do you find the SA:V
calculate the surface area and the volume of a cell, divide the surface area by the volume and set it up as a proportion
what does a high SA:V ratio mean
the cell is more efficient
what does a low SA:V ratio mean
the cell is less efficient
what is a prokaryote
simple, single celled organism
what is a eukaryote
complex, single or multi-celled organisms
did prokaryotes or eukaryotes come first
prokaryotes
when did prokaryotes first emerge
about 3.8 billion years ago
what are the features of prokaryotes
they have a cell membrane, cytoplasm (cytosol), ribosomes, cell wall and naked DNA
they have no membrane-bound organelles
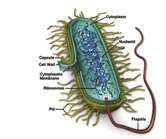
what are examples of prokaryotes
E. coli, H. pylori
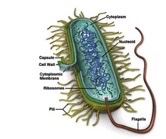
what does the cell wall do
it prevents dehydration, protects, and provides structure
what are the features of eukaryotes
they have membrane-bound organelles like a nucleus, chloroplast, mitochondrion, and endoplasmic reticulum. they also have a cell membrane, cell wall, cytosol, and ribosomes like prokaryotes
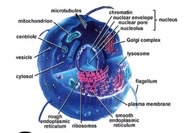
what are examples of eukaryotes
plant and animal cells
what are organelles
sub-cellular structure that have specific jobs to perform in the cell,
what organelles have a double membrane
nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria
what organelle doesn’t have a membrane
ribosomes
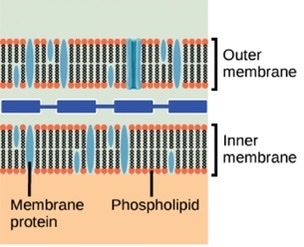
what makes up the organelle membranes
phospholipids
what is the plasma/cell membrane
a phospholipid bi-layer that controls the movement of nutrients and wastes in and out of the cell
why does the cell membrane have to be large
they have to be large enough (surface area) to efficiently transfer materials
what do some cell membranes do to increase their surface area
they have folds in the membrane increase the efficiency and absorption
what is the cytoplasm/cytosol
the thick, semi-solid fluid that is found inside the cell (70-80% water)
what is inside the cytoplasm
the organelles and all the nutrients the cell needs (glucose, amino acids, lipids)
what occurs in the cytoplasm
protein synthesis
what is the nucleus
the organelle that houses the DNA of a cell and is seen as a roundish organelle
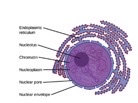
what is the nuclear envelope
the phospholipid bi-layer membrane that surrounds the nucleus
what does the nuclear envelope have
contains permanent pores to allow RNA to travel in and out of the nucleus
what is the nucleoplasm
the thick, semi-solid liquid found within the nucleus
what does the nucleolus do and where is it found
makes ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins
it’s found in the center of the nucleus and looks like a darker ball
what is chromatin
unwound DNA in the nucleus
what is a chromosome
wound DNA in the nucleus
what is found in the nucleus
nucleolus, chromatin, chromosomes, nucleoplasm, and is surrounded by the nuclear envelope
what does a ribosome do
protein synthesis
are ribosomes membrane-bound organelles
no!
where are ribosomes found
they are free floating in the cytoplasm or attached to endoplasmic reticulum
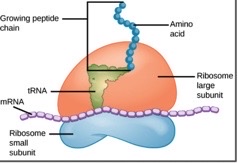
what kind of ribosomes do prokaryotes have
70S (smaller)
what kind of ribosomes do eukaryotes have
80S (larger)
what makes up ribosomes
2 subunits of large and small and ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
what types of cells have the most ribosomes
cells that make proteins (like skin cells)
what is mitochondria
organelle that make ATP which is used for energy within the cell
what is ATP
adenosine triphosphate
what type of cells are ATP found in
they’re found in cells that undergo aerobic respiration (use oxygen)
what is the phospholipid bilayer like in mitochondria
it has a phospholipid bi-layer with embedded proteins for the electron transport chain and inner folds (cristae)
the outer layer is smooth
what is the cytoskeleton
what is the matrix
fluid in the mitochondrion (where the Kreb’s cycle occurs)
what are vacuoles
large sacs that function in storage and transport
what do vacuoles do in plants
they store water
what do contractile vacuoles do
they regulate water concentrations and will pump out excess water by contracting
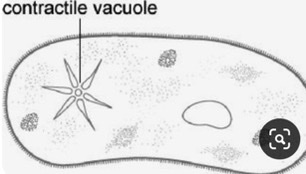
what eukaryotic cells are centrosomes found in
animal cells
what are centrosomes
organelles that function in cell division (thought to pull the duplicated chromosomes to the poles during cell division)
what is inside centrosomes
centrioles
what do centrioles do
pull chromosomes to opposite poles during meiosis/mitosis
what type of eukaryotic cells are lysosomes found in
animal cells (l)
what are lysosomes
organelles that have hydrolytic enzymes used in the breakdown (lysis) of things
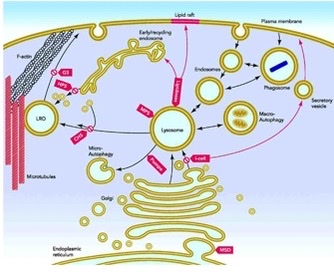
how do lysosomes protect the cell
they aid in destroying foreign proteins (antigens) and boost immunity
what is the pH in lysosomes like
it’s lower for the digestion of macromolecules
what eukaryotic cells are cell walls found in
fungi and plants cells
what is the cell wall
rigid structure made of cellulose (plants), chitin (fungi), or peptidoglycan (prokaryotes) that surrounds the cell
what does the cell wall do
it protect the cell, prevent dehydration of the cell, and also to provide support to the cell
what eukaryotic cells are chloroplasts in
plant cells
what do chloroplasts do
photosynthesis and ATP synthesis
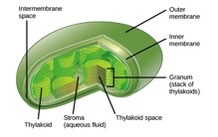
what are thylakoids
discs filled with a fluid called stroma used in light-independent reactions
what are grana
stacks of thylakoids
what is chlorophyll
pigment that captures and converts light energy into sugar and oxygen
what structures are in chloroplasts
thylakoids, stroma, grana, and chlorophyll
what are the two types of endoplasmic reticulums
smooth and rough
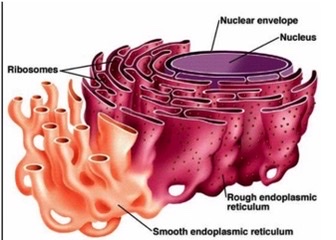
what are the features of the smooth er
makes carbs, lipids, steroids, helps with detoxing meds, and has no ribosomes attached
what are the features of the rough er
has ribosomes attached and help “finish” or modify proteins
what does the golgi apparatus do
it sorts, packages, and tags lipids and proteins before they are transported
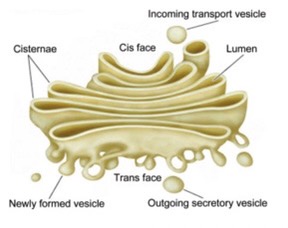
what types of cells have lots of golgi
cells that secrete saliva
what is the endomembrane system
organelles that are continuous with the plasma membrane and work to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins
what organelles are part of the endomembrane system
endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, nuclear envelope, and vesicles
what is the cytoskeleton
protein filaments that provide structure and support to the cell
what is cilia
hair like organelles that do locomotion
what does the cytoskeleton do
they aid in transporting vesicles in the cell and make and move flagella and cilia
what is flagella
tail like organelle that does locomotion
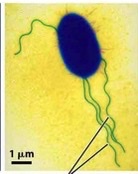
what is a vesicle
structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer
-
-
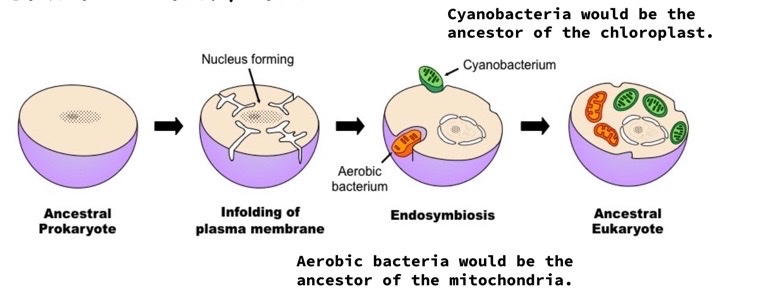
what is Theory of Endosymbiosis
an evolutionary theory that the mitochondria and chloroplast were once prokaryotic cells that were engulfed by a eukaryotic cell
what evidence supports the theory of endosymbiosis
mitochondria and chloroplasts have different dna from the dna in the nucleus and have a double membrane (indicates that in addition to their own membrane, these organelles picked up some of the plasma membrane when engulfed)
what is apoptosis
cell death/suicide
when does apoptosis occur
when cells have been injured, have undergone mutations, are no longer functional
what is the extracellular matrix
the space outside of cells
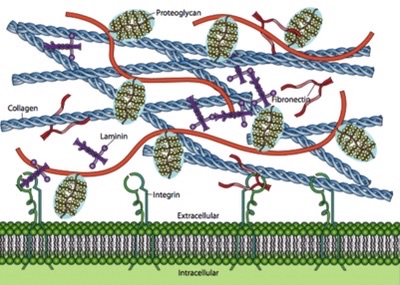
what does the extracellular matrix do
holds cells together and allow cell-to-cell communication and contains wastes released from the cell
what are the types of cell junctions
plasmodesmata, tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions
what are the characteristics of plasmodesmata junctions
they’re found in plants and are composed of channels between neighboring cells for the movement of water and nutrients
what are the characteristics of tight junctions
they’re found in animal cells and are watertight channels between adjacent cells
what are the characteristics of desmosomes junctions
they’re found in animal cells; protein filaments from one cell enter into the plasma membrane of the adjacent cell
what are gap junctions
found in animal cells and transport nutrients