Biopharmaceutics and Oral Drug Delivery
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
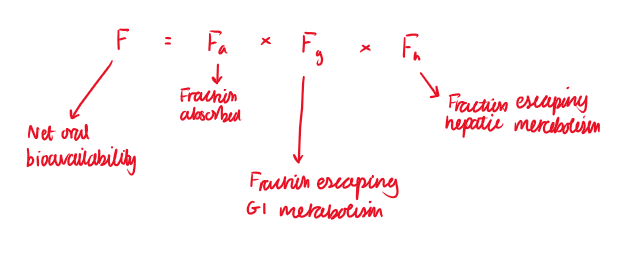
F = Fa x Fg x Fh
Fa = Fraction absorbed
Fg = Fraction escaping the GI metabolism
Fh = Fraction escaping the hepatic metabolism
F = Net oral bioavailability
Pharmacokinetics
What the body does to the drg
Pharmacodynamics
What the drug does to the body
Determinants of Pharmacokinetics
ADME
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
What is drug absorption?
The uptake of a non metabolized drug, following its release from its formulation, from the site of delivery to the systemic circulation.
Many routes of delivery (except IV) involve crossing a biological barrier
What does drug absorption involve crossing?
A biological barrier
Drug absorption in the GI tract
Dosage form is swallowed and ends up in the stomach
Enteric coating around medicine prevents it from dissolving, so medicine passes to the small intestine
The solid dosage form has to break apart and go to solution. The human body cannot absorb solids.
Solid dosage form turns to particles in suspension, then becomes molecules in solution, and can then be absorbed across the epithelium (the biological barrier in the GI tract) which can then be absorbed into the blood and transported to the liver
What are some factors that affect absorption of small drugs in the GI tract?
pH = Ionisation, solubility
Hydrogen bonding
Size
Lipophilicity
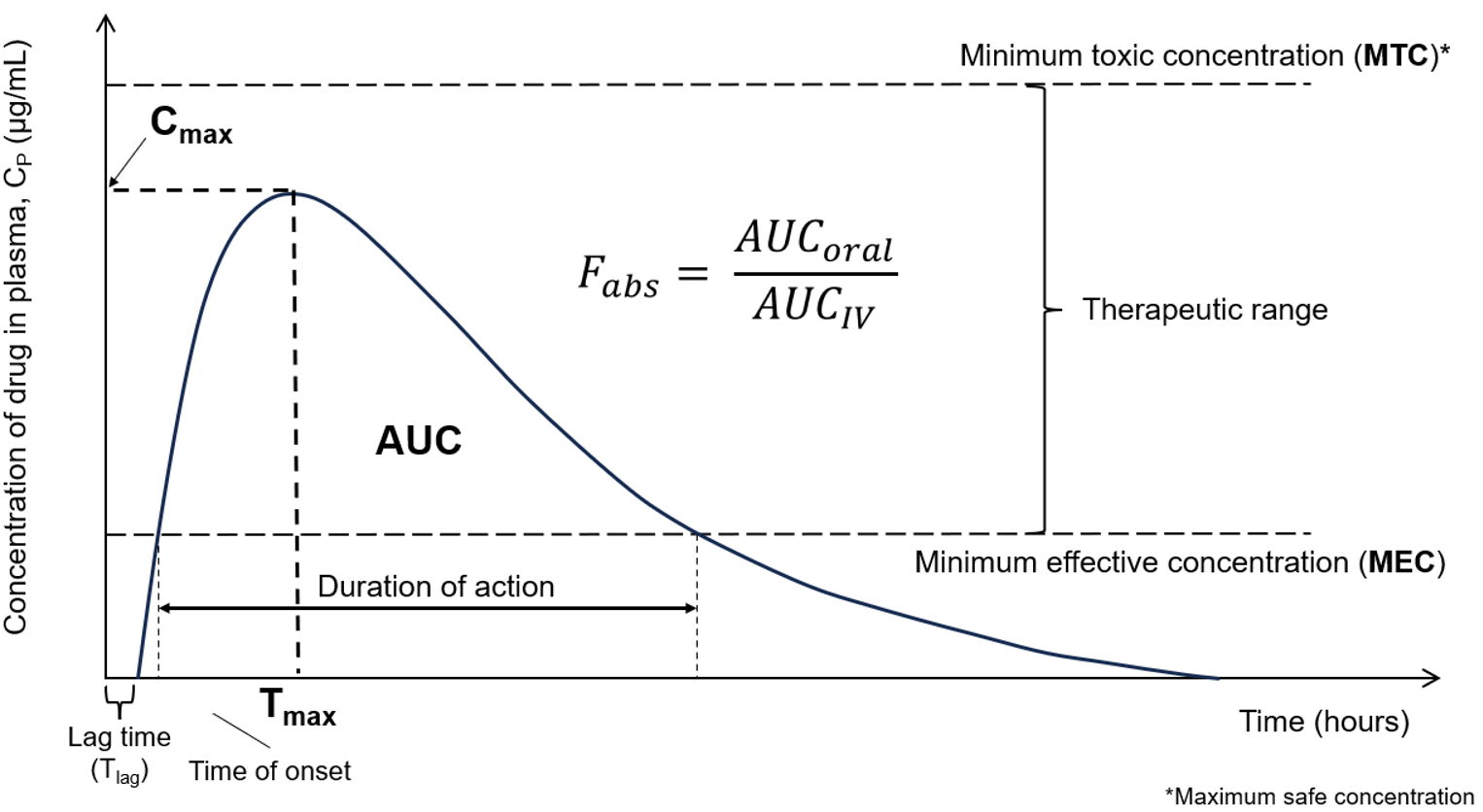
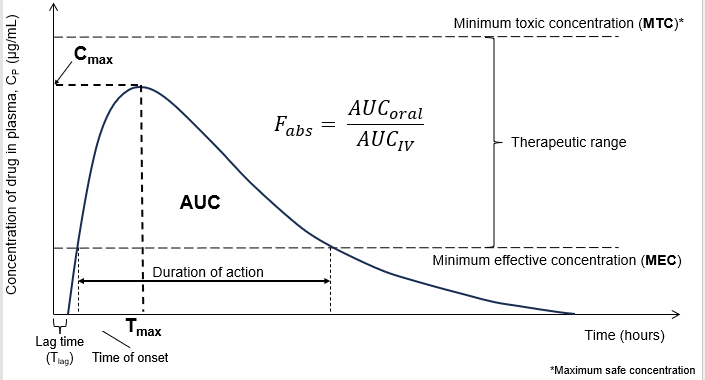
Drug Plasma concentration vs Time
Biopharmaceutics
The study of the interactions of the medicine with the biological system, allowing the optimisation of DDS
Bioavailability
The bioavailability of the drug is a measure of the quantity of drug which reaches its site of action and the rate at which it gets there.
Plasma concentration of drug VS Time