Dynamics of disease
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures 14-15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Parasite-definition
Organism that consumer part of its host without necessarily killing it
Pathogens-definition
Parasites that cause diseases
Parasitoid-definition
Insect whose larvae live in hosts that they consume
Transmission-definition
Movement of parasites from one host to the next
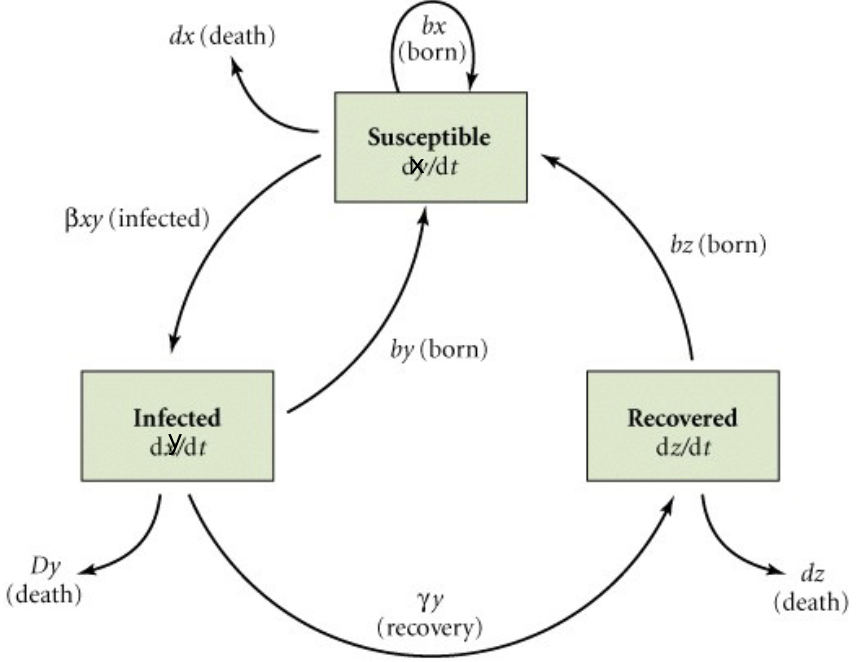
SIR Model diagram
SIR Model equations
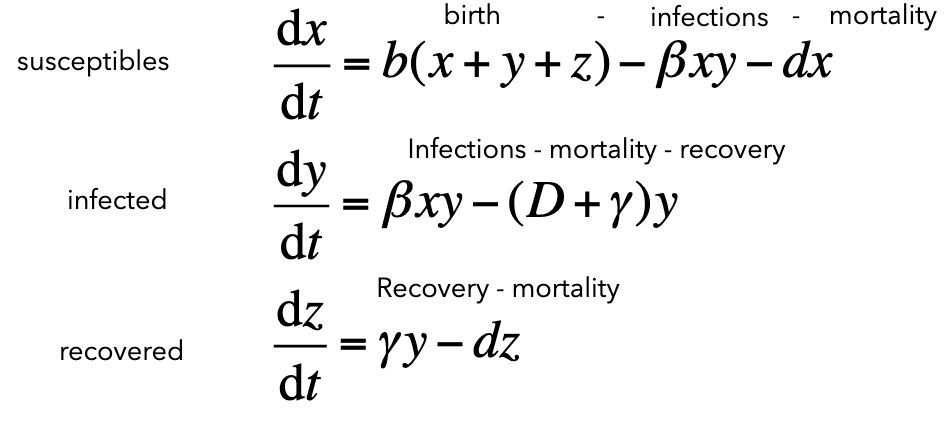
SIR assumptions
Susceptibles become infected at rate Bxy
Recovery is permanent and conveys immunity
Infected individuals can recover
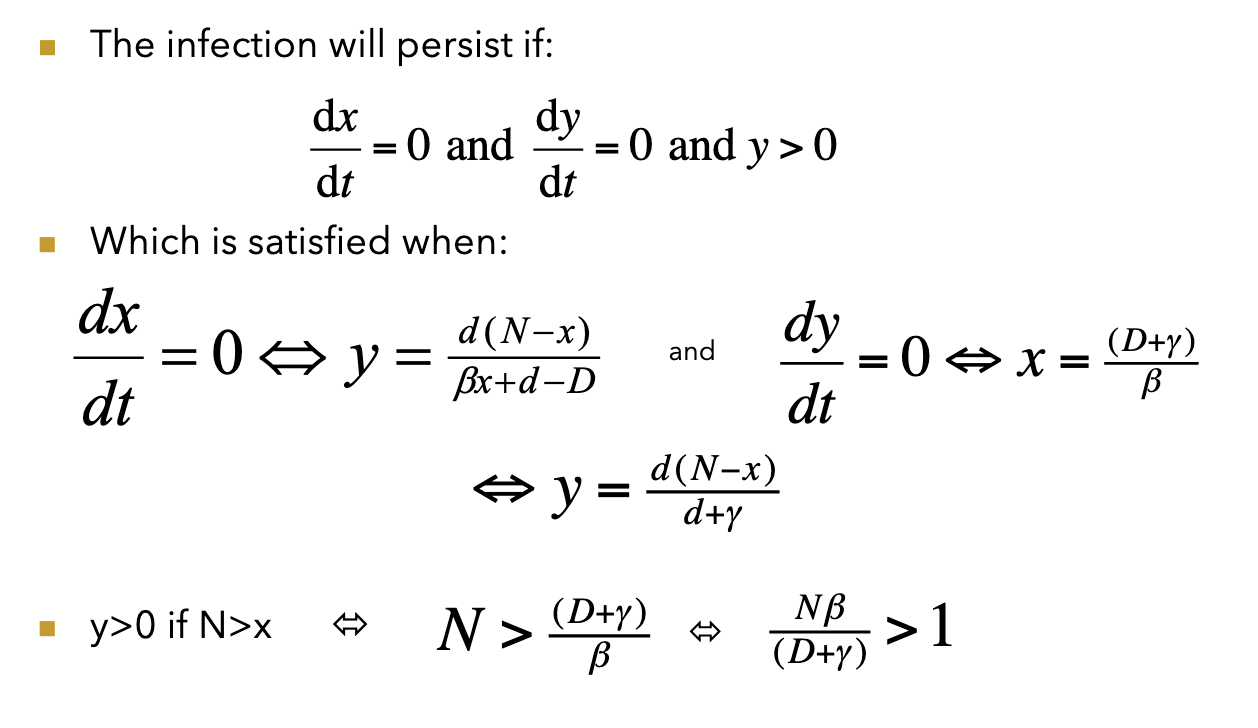
SIR threshold behaviour
SIR R(x)
R(x) is the number of individuals affected by one infected individual during its lifetime
If R(x)>1, the infection persists
R(x) depends on lifetime of infected individuals and the infection rate
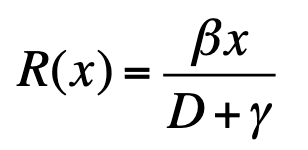
SIR Lifetime of infected individuals
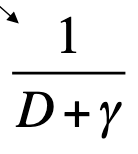
Reproductive number in a population of susceptibles (R0)
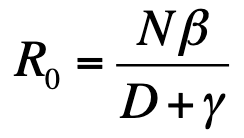
Vaccination strategies
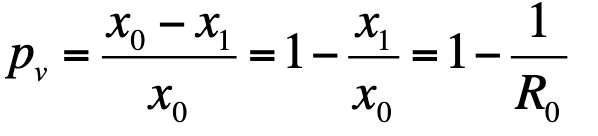
Mechanisms to explain cyclic dynamics of disease
Latency
Seasonality
Dispersal limitation
Host-parasitoid dynamics
Fluctuations in interactions explained by:
Parasitoids kill their host
Generations do not overlap