Negative feedback
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
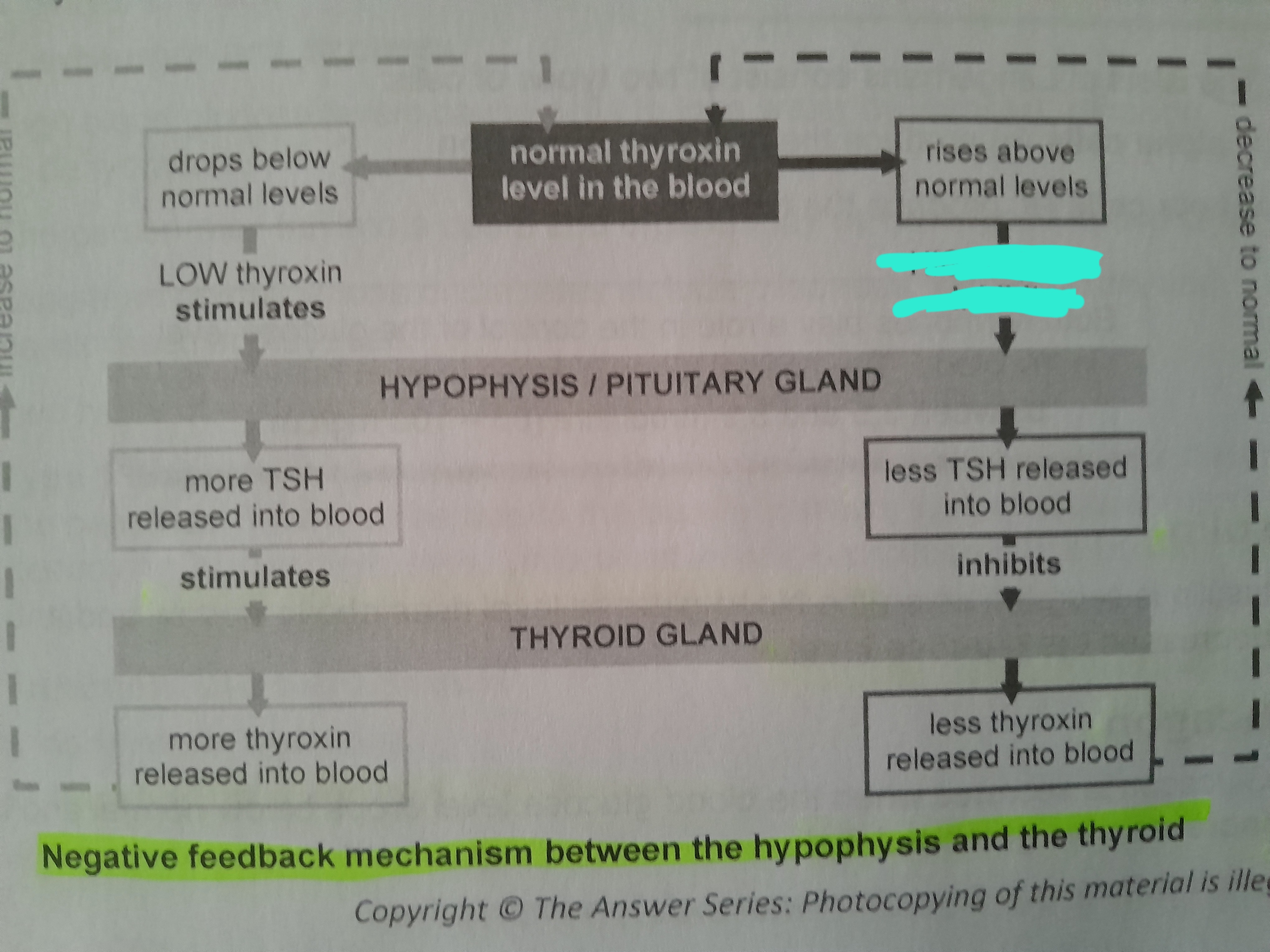
High thyroxin inhibits
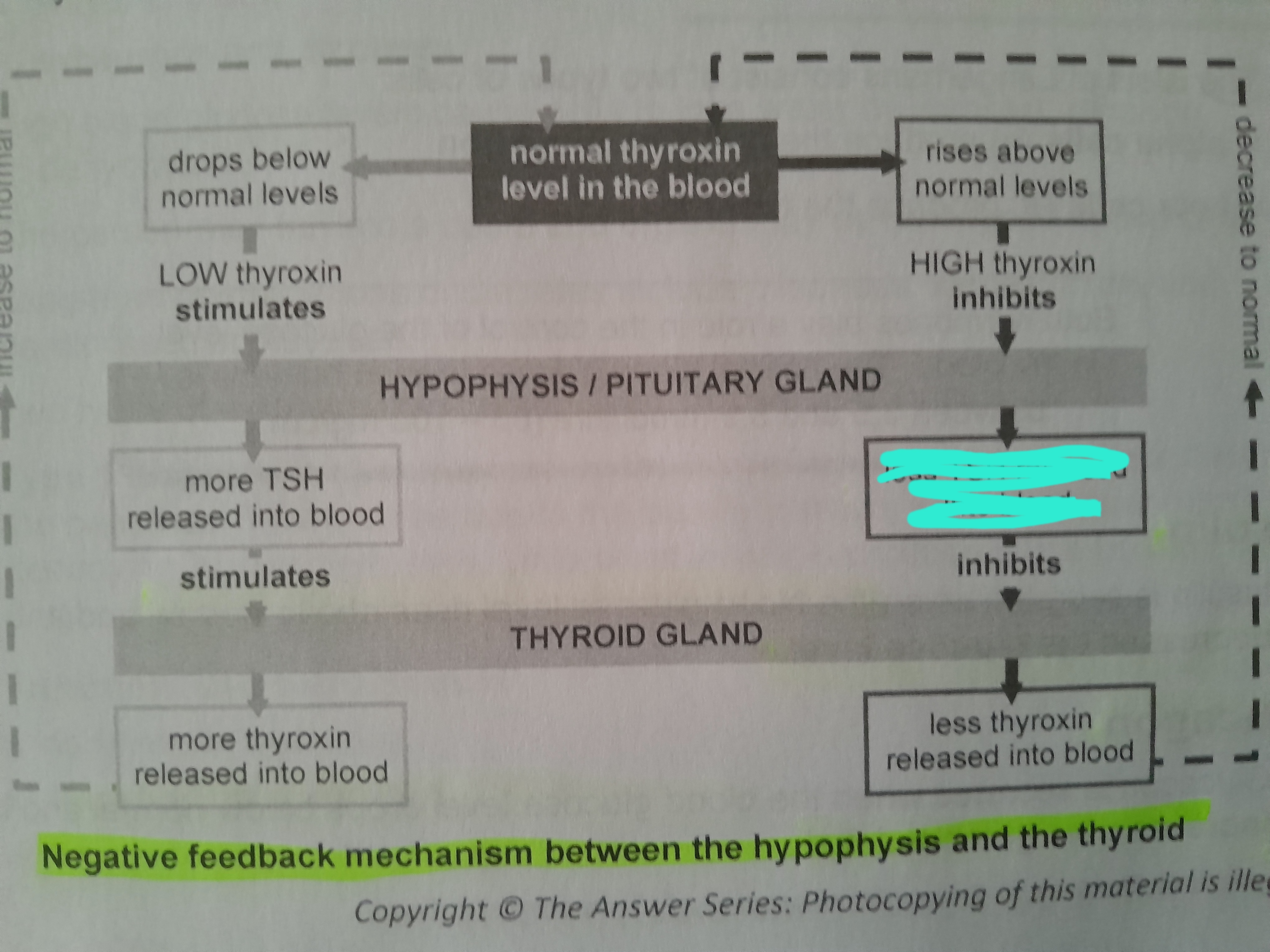
Less TSH released into blood
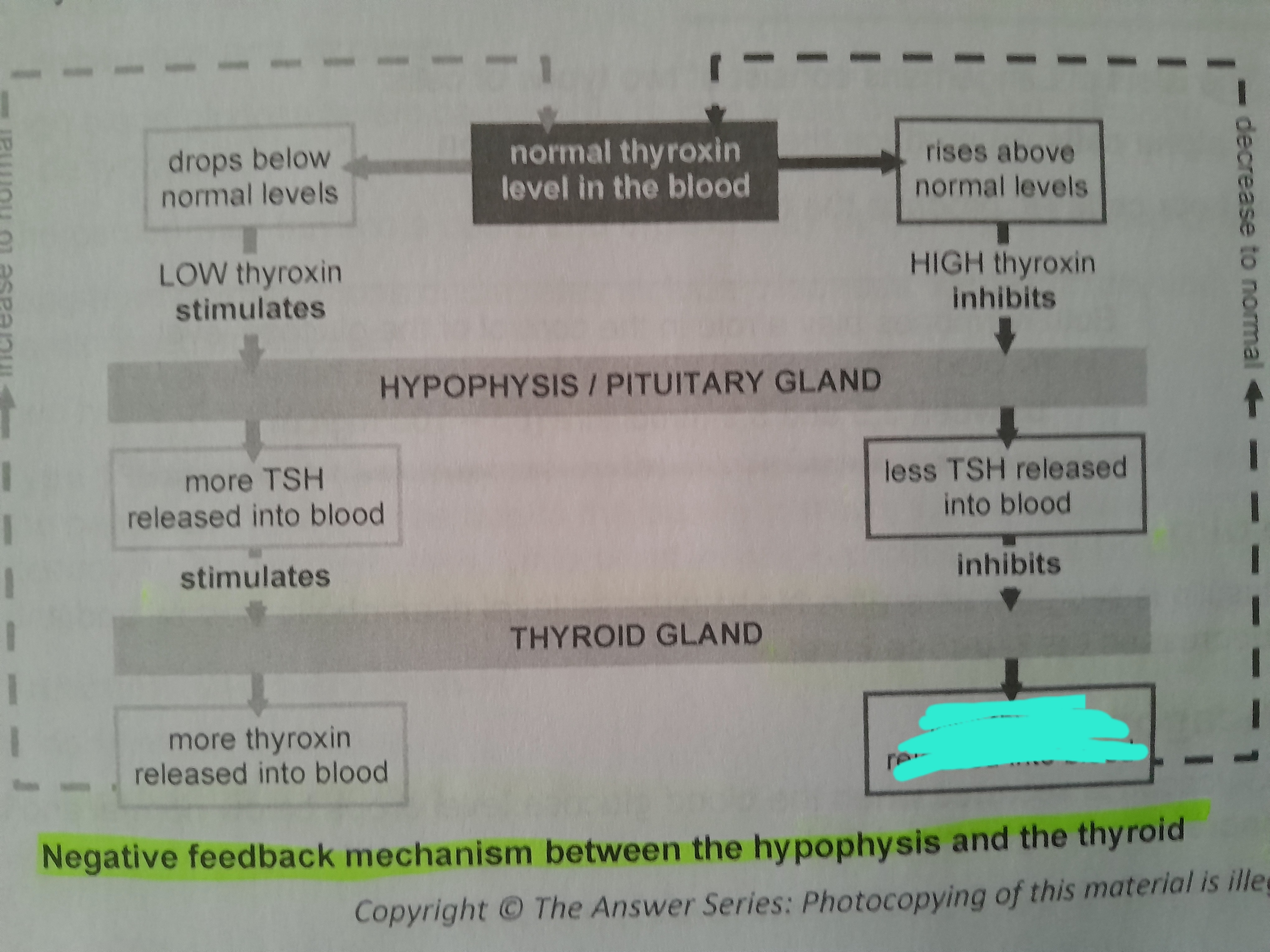
Less thyroxin released into blood
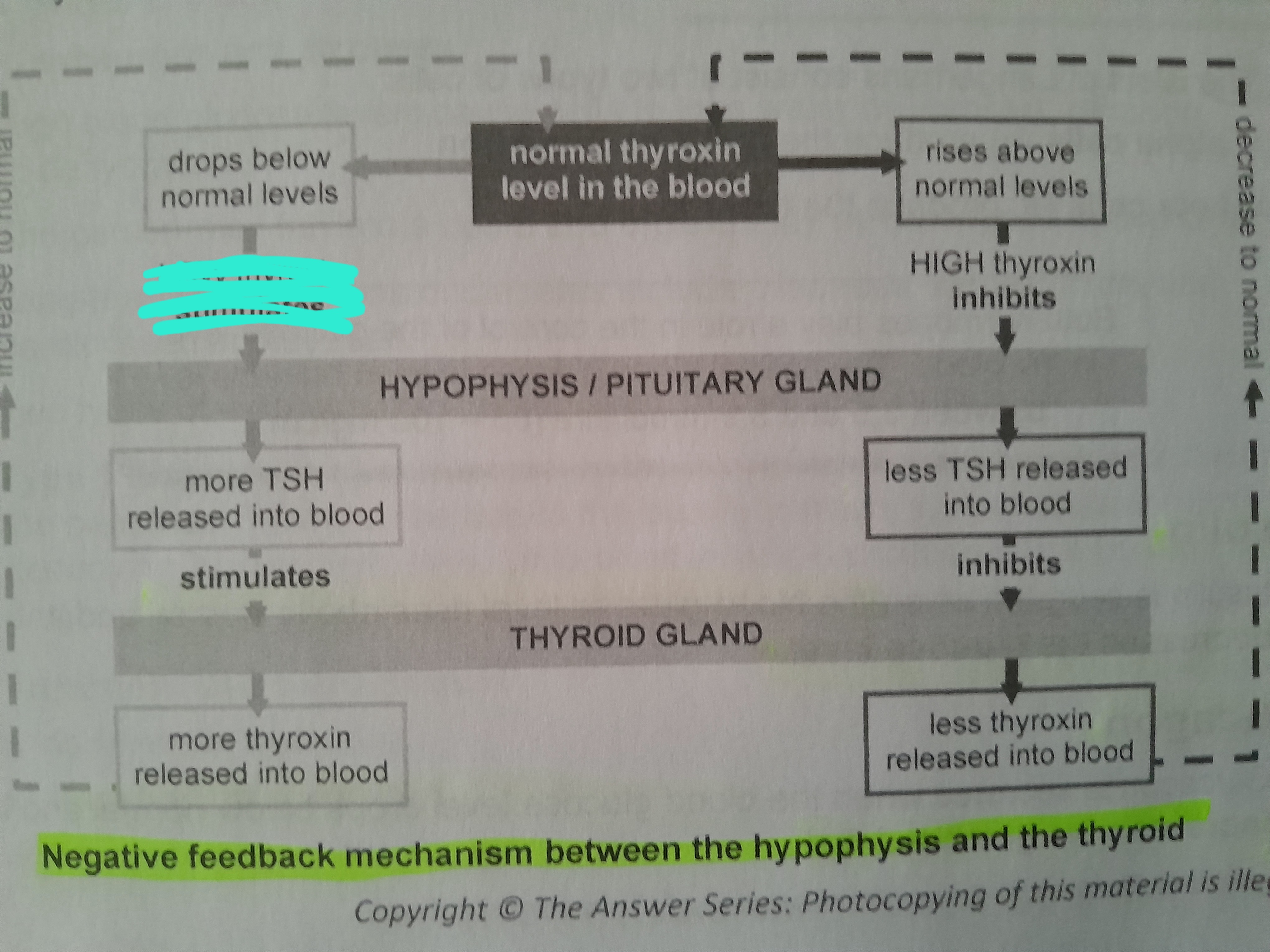
Low thyroxin stimulates
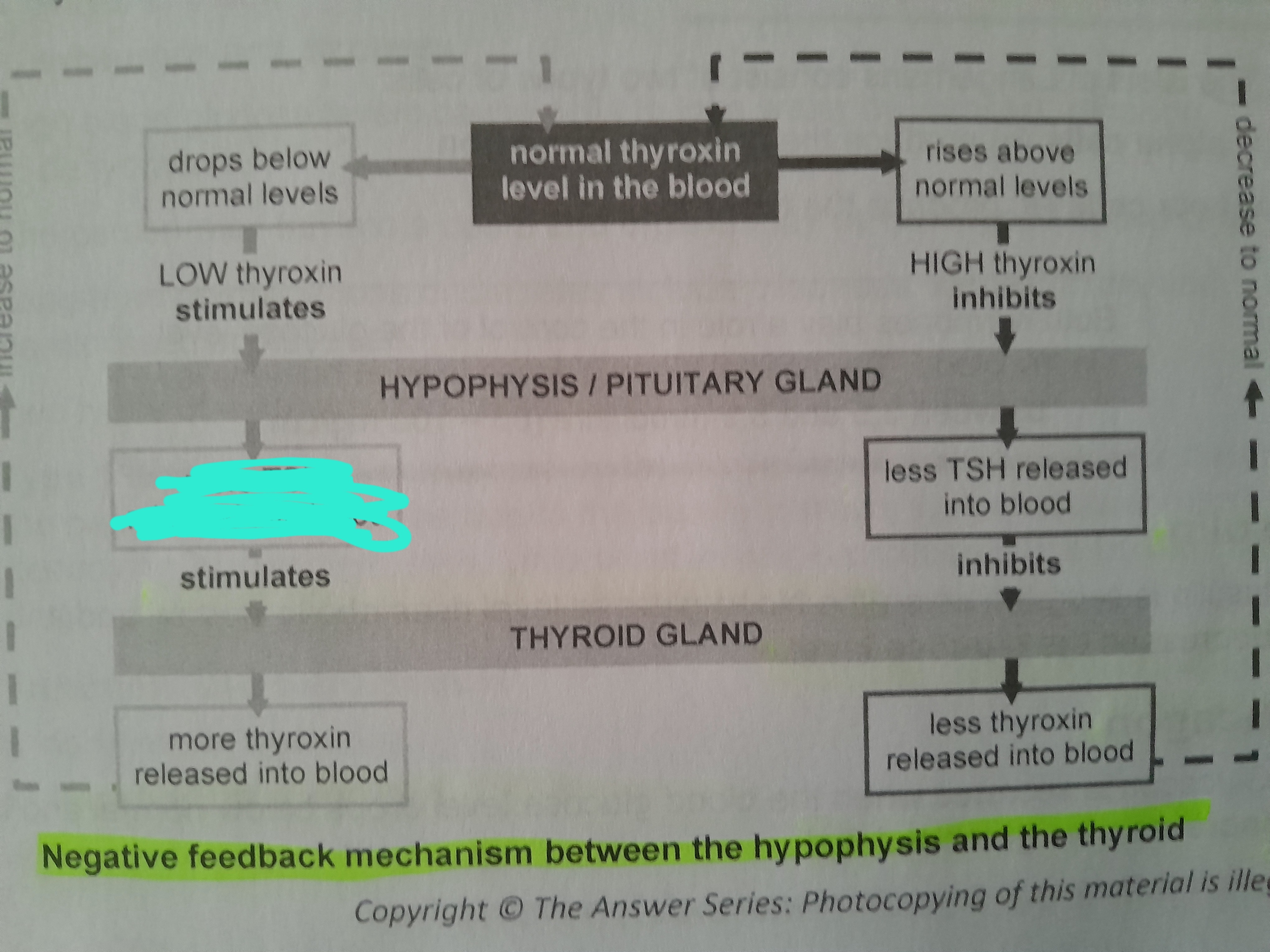
More TSH released into blood
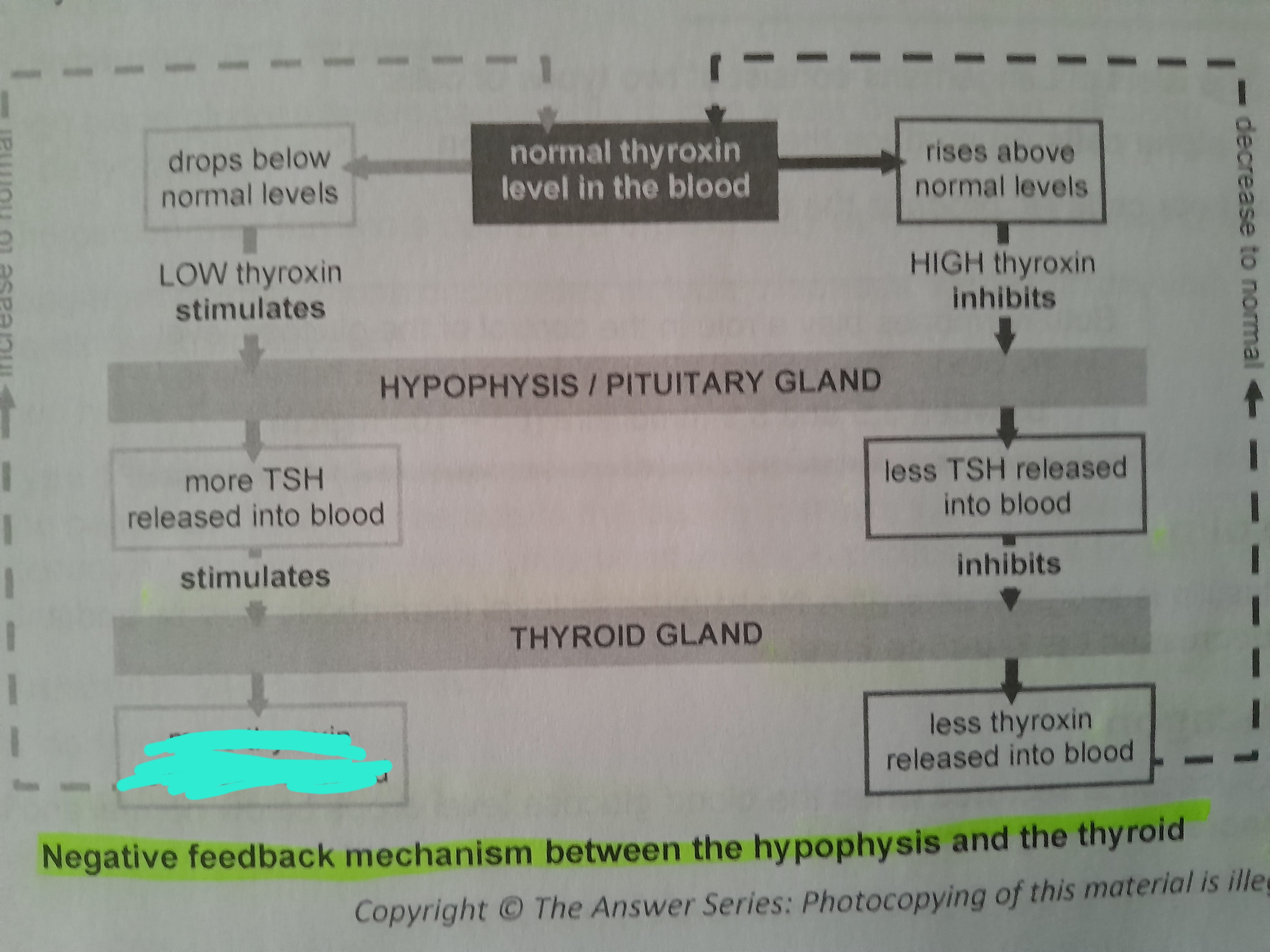
More thyroxin released into blood

Pancreas releases insulin
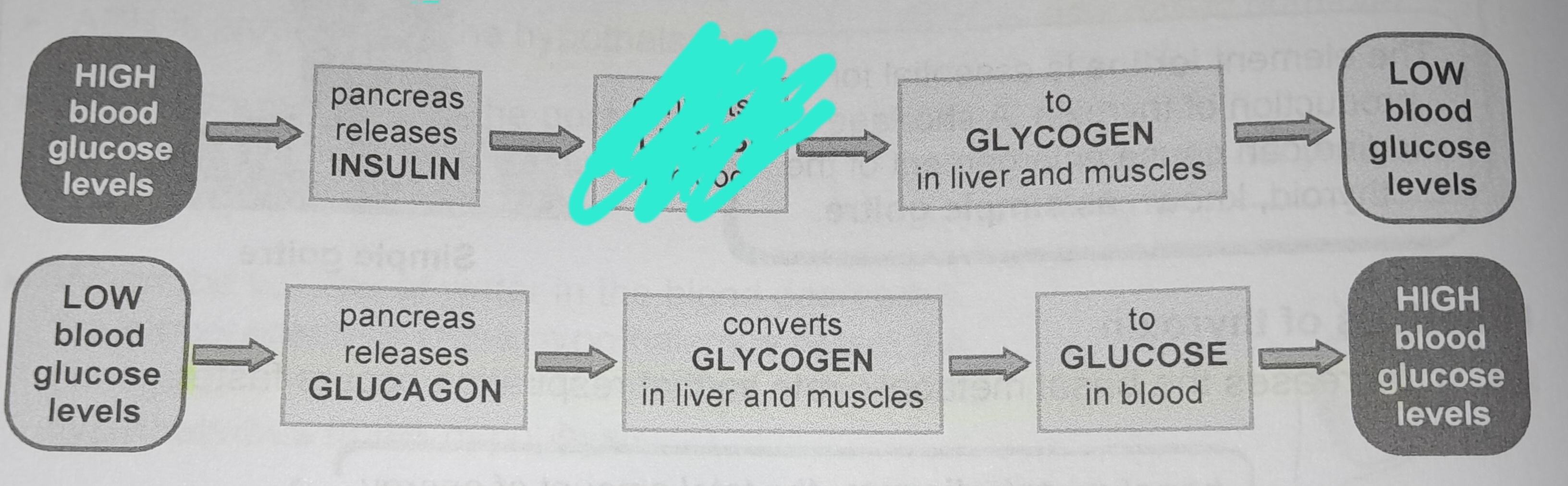
Converts glucose in blood
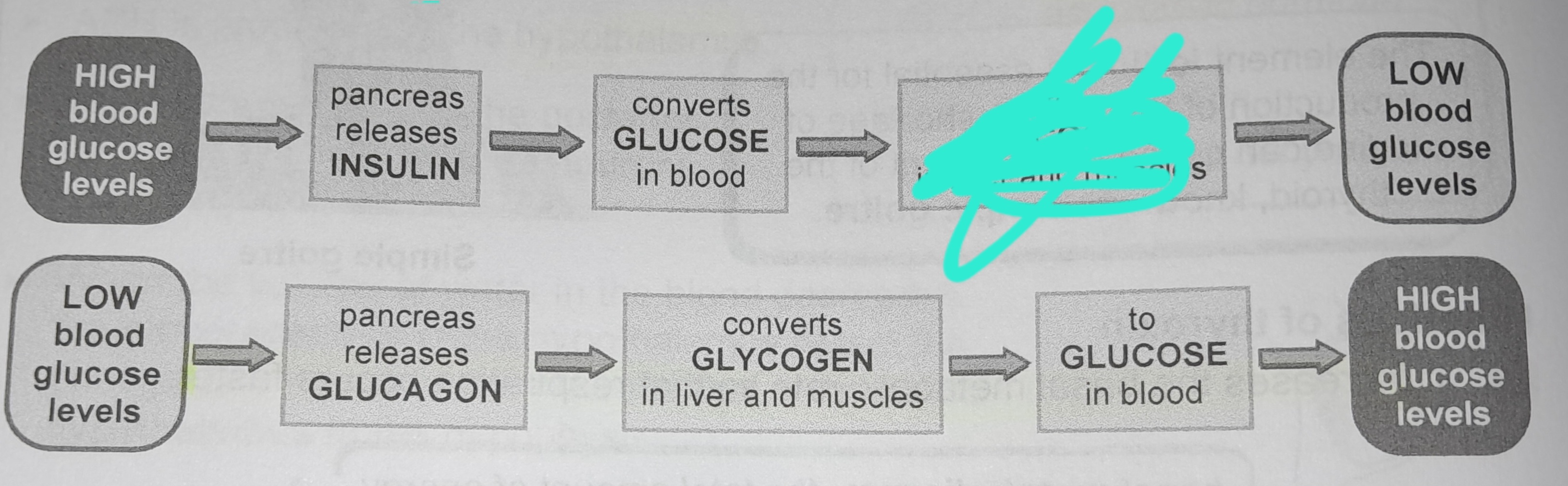
To glycogen in liver and muscles
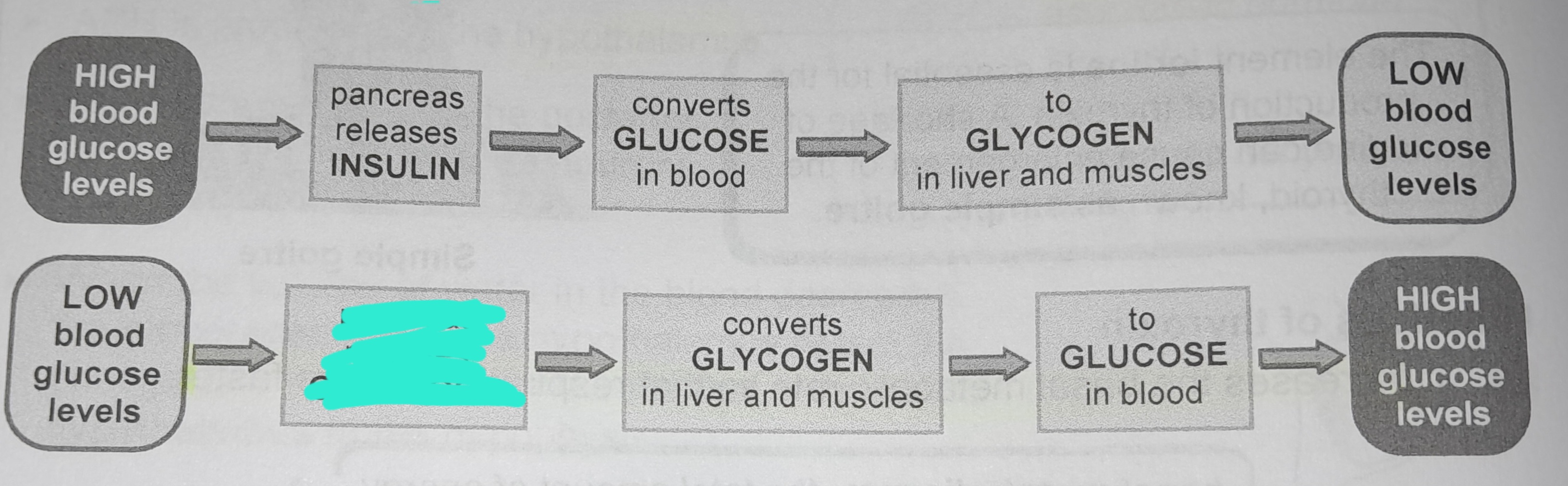
Pancreas releases glucagon
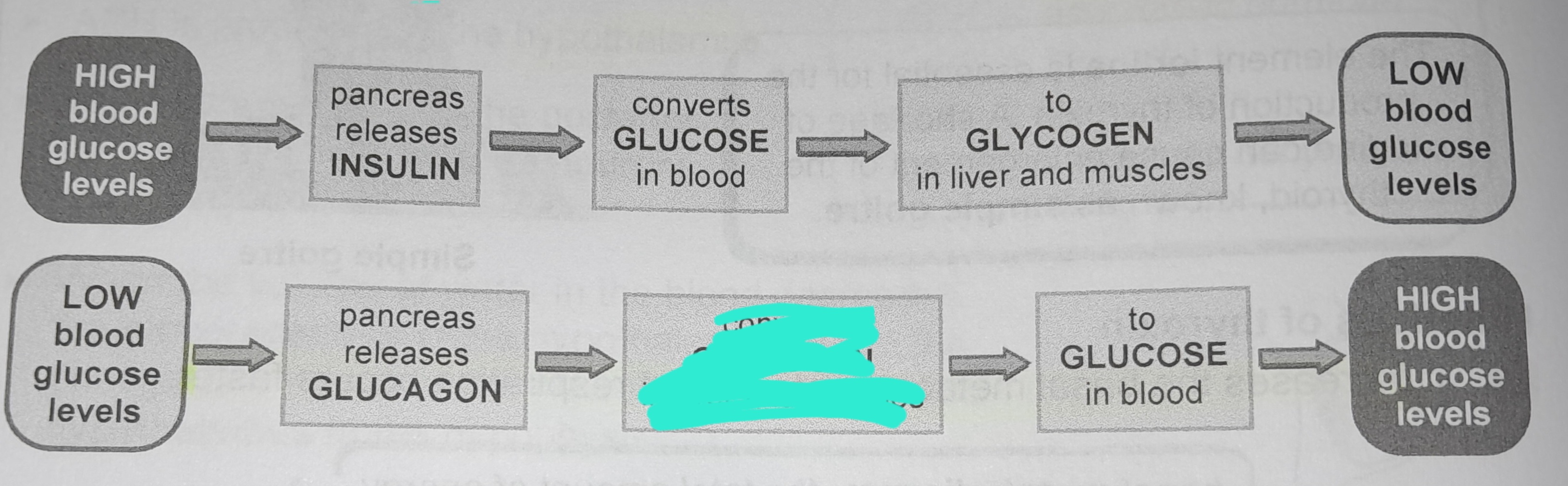
Converts glycogen in liver and muscles
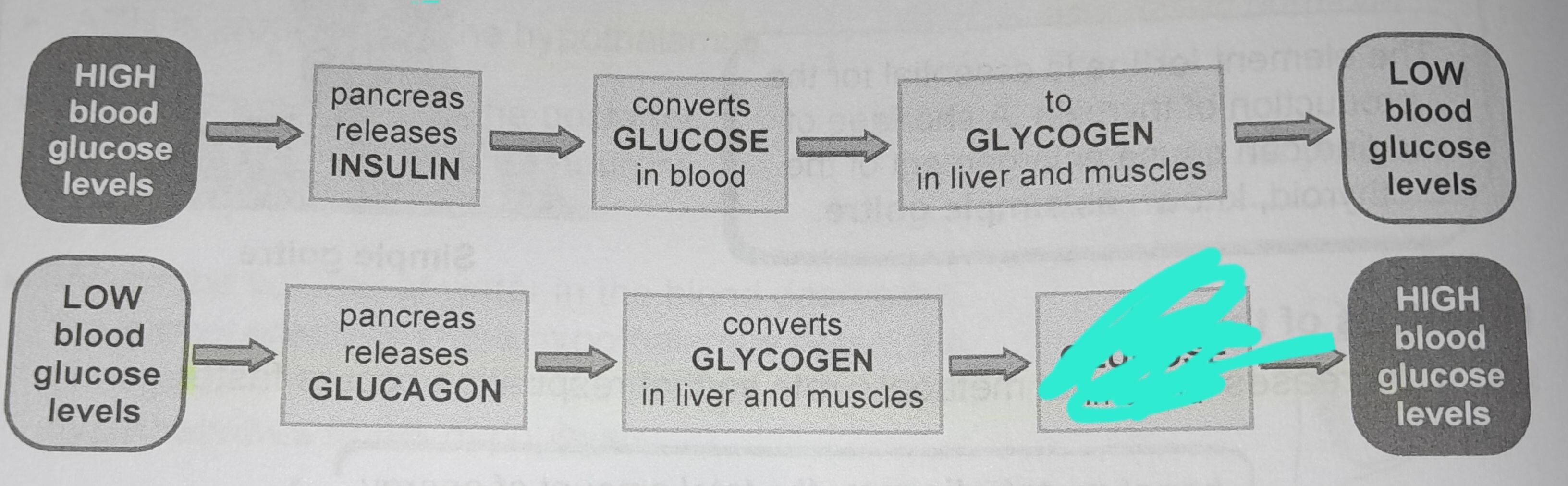
To glucose in blood
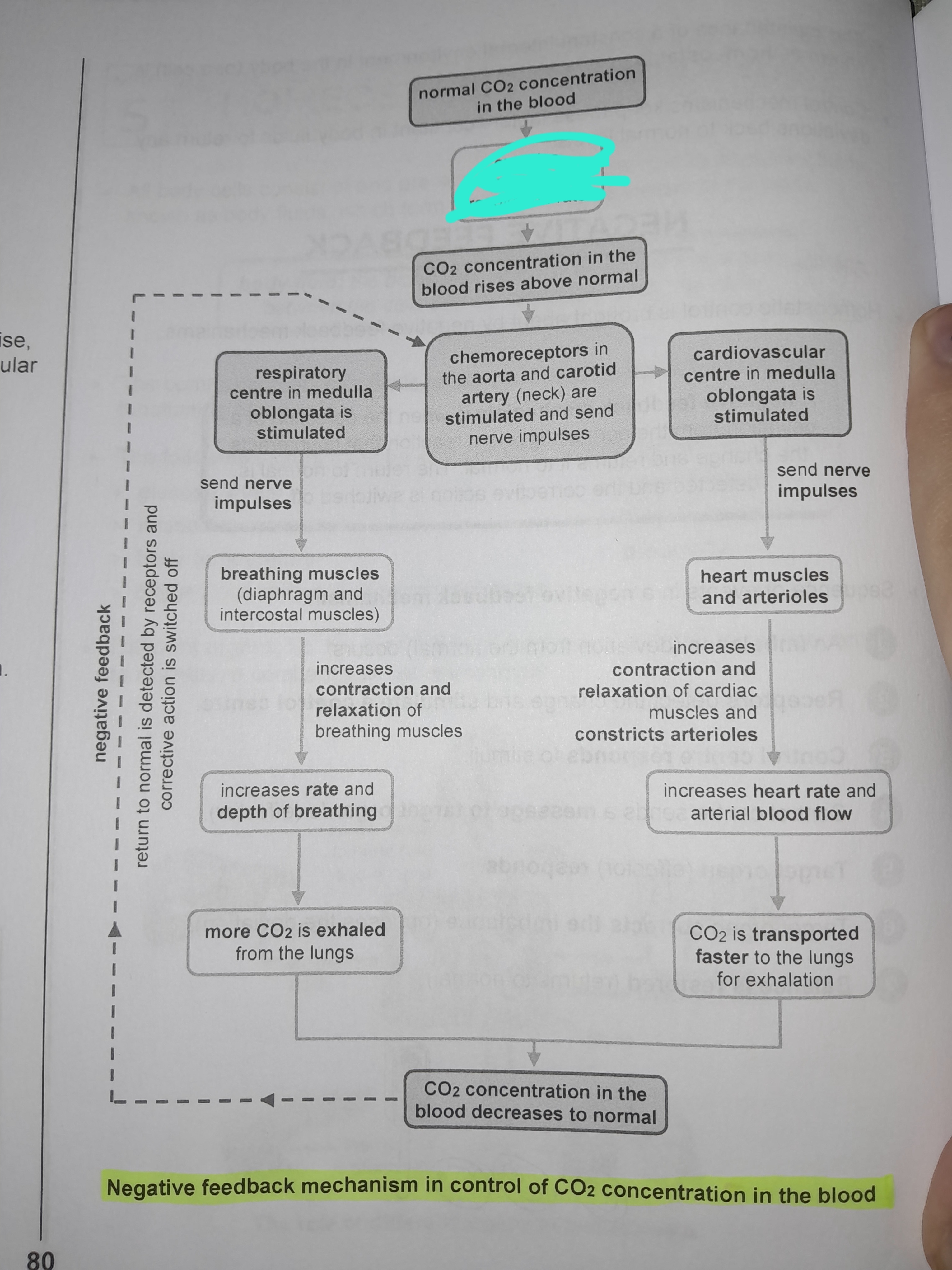
Exercise increases respiration rate
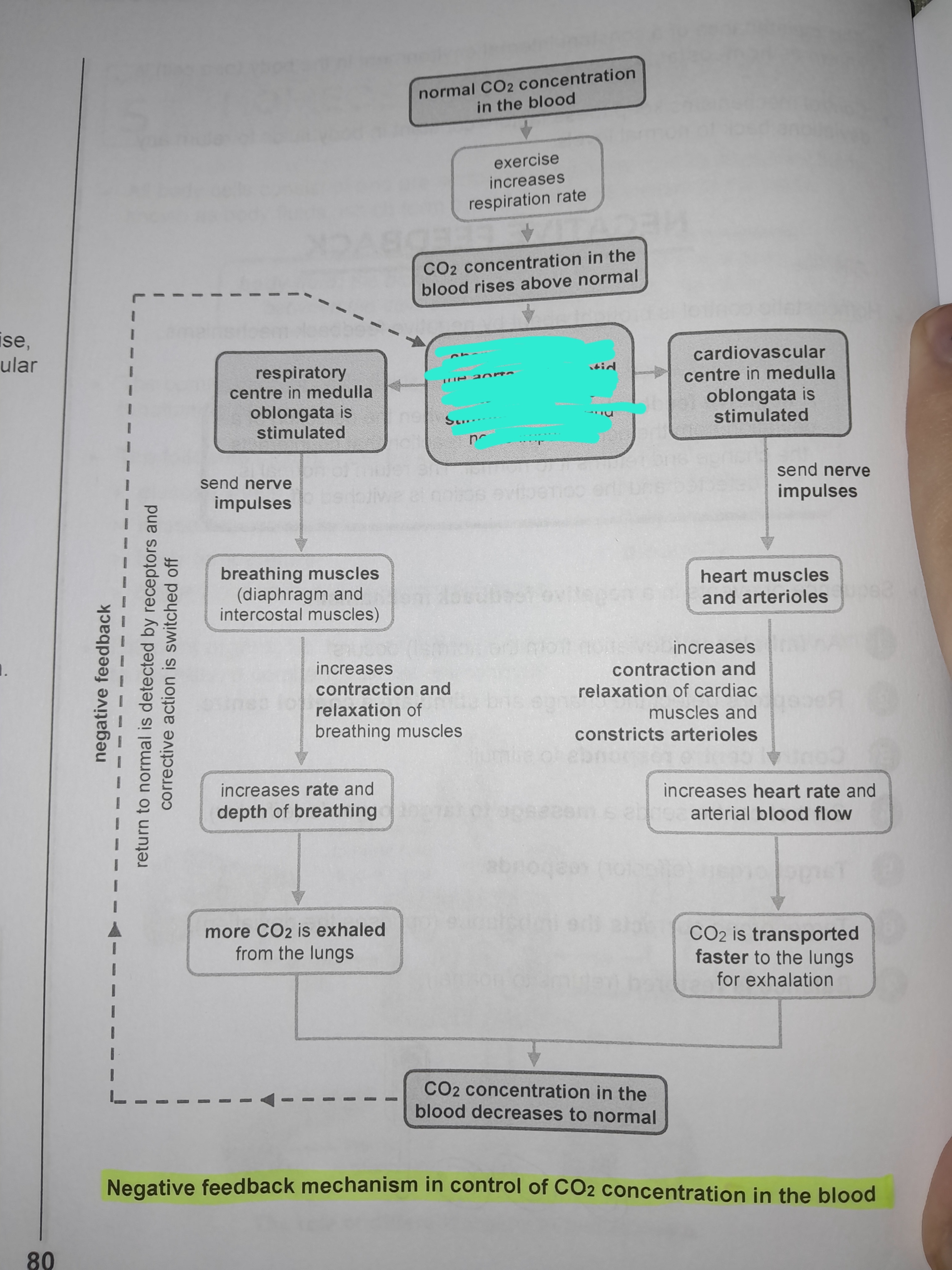
Chemoreceptors in the aorta and carotid artery are stimulated and send nerve impulses
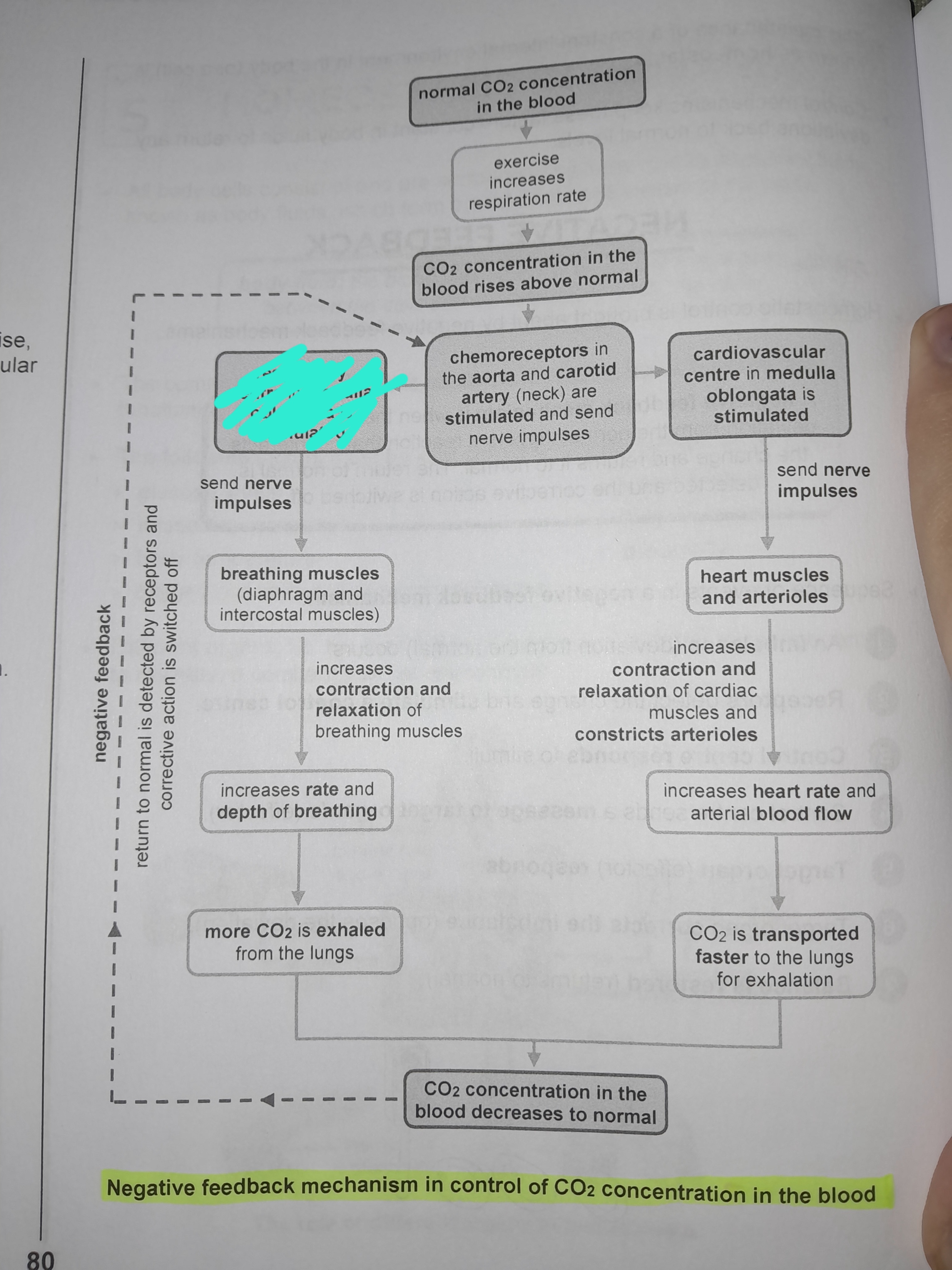
Respiratory center in medulla oblongata is stimulated
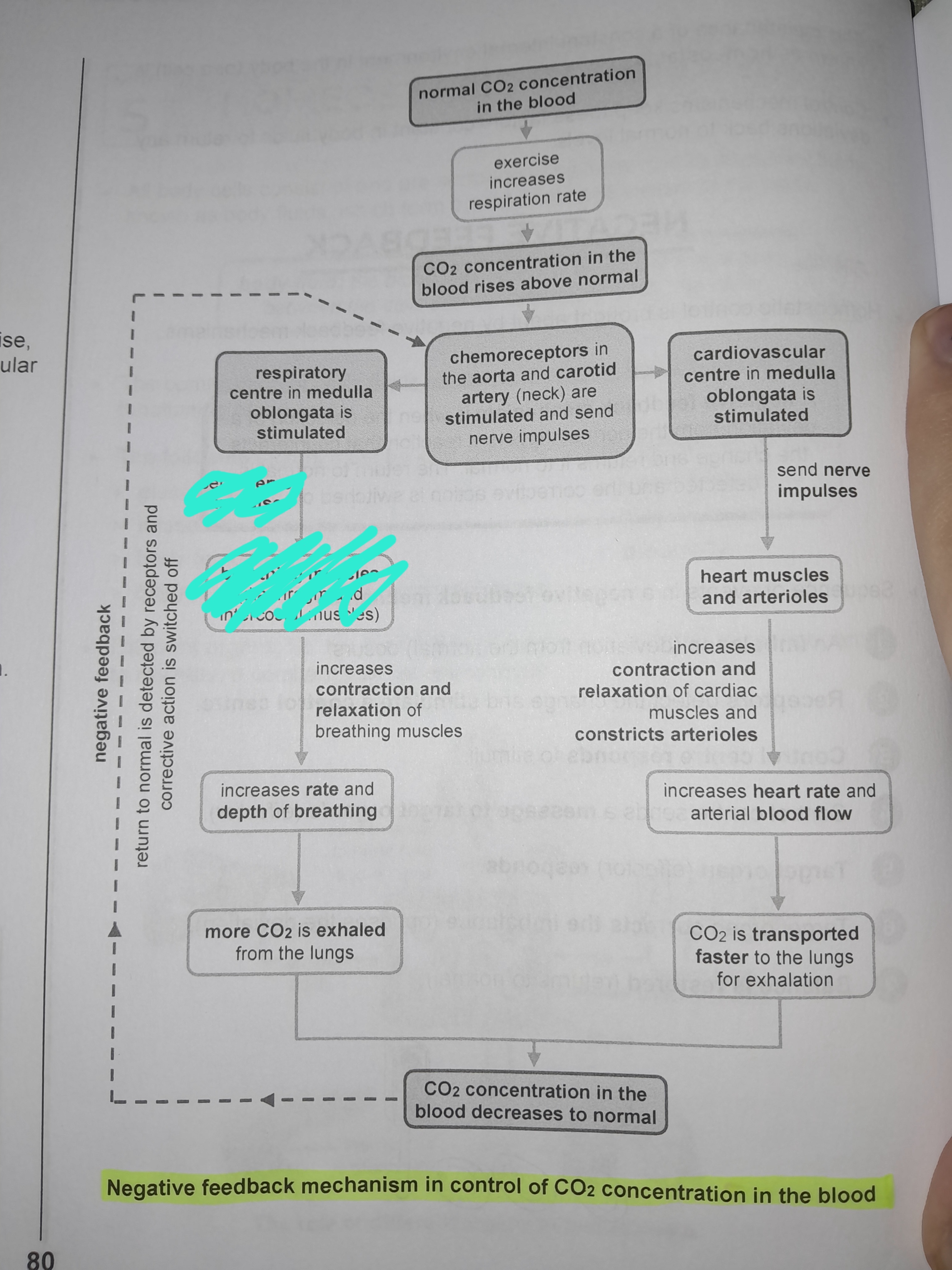
Nerve impulses are sent to breathing muscles
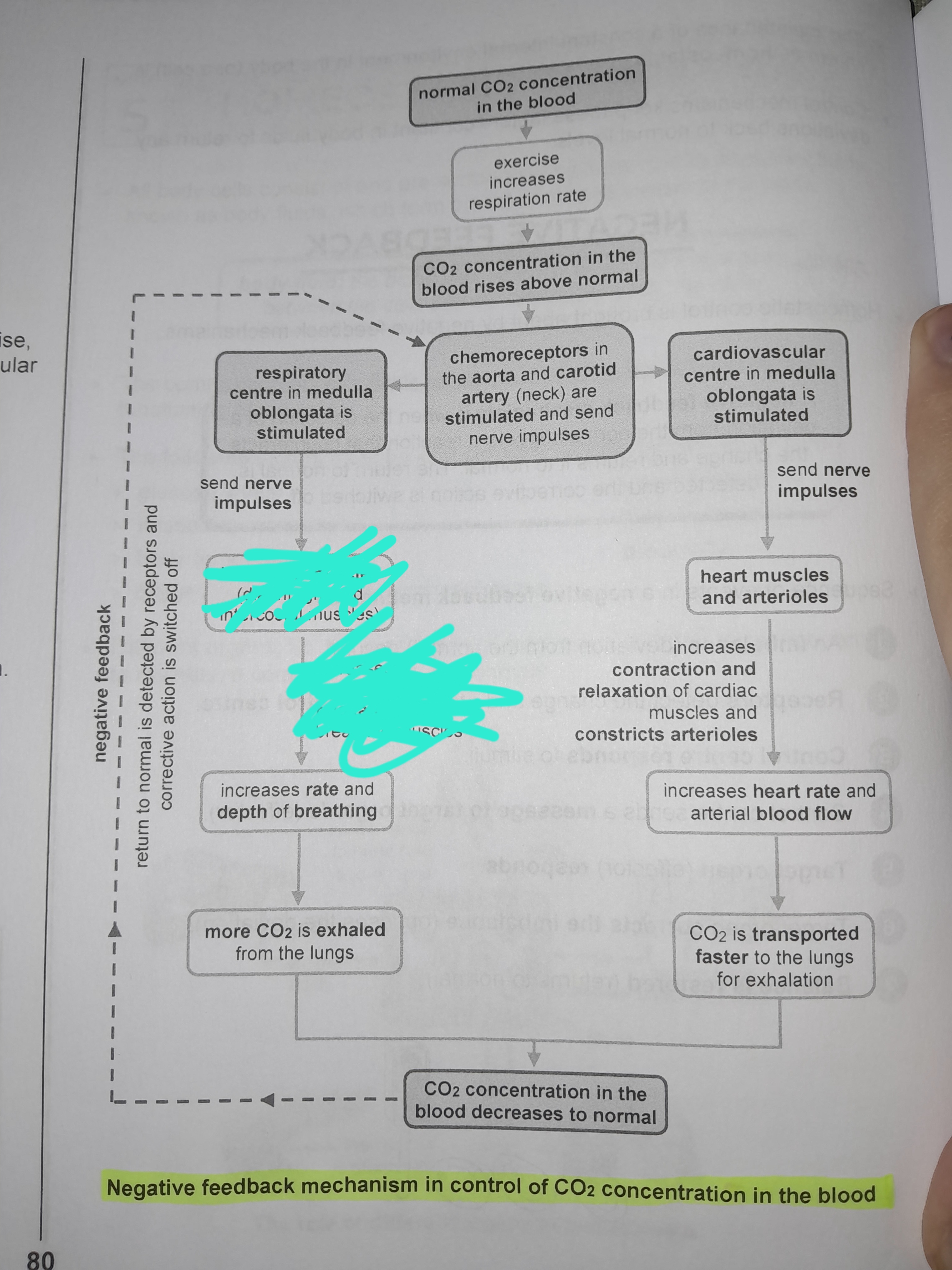
increases contraction and relaxation of breathing muscles
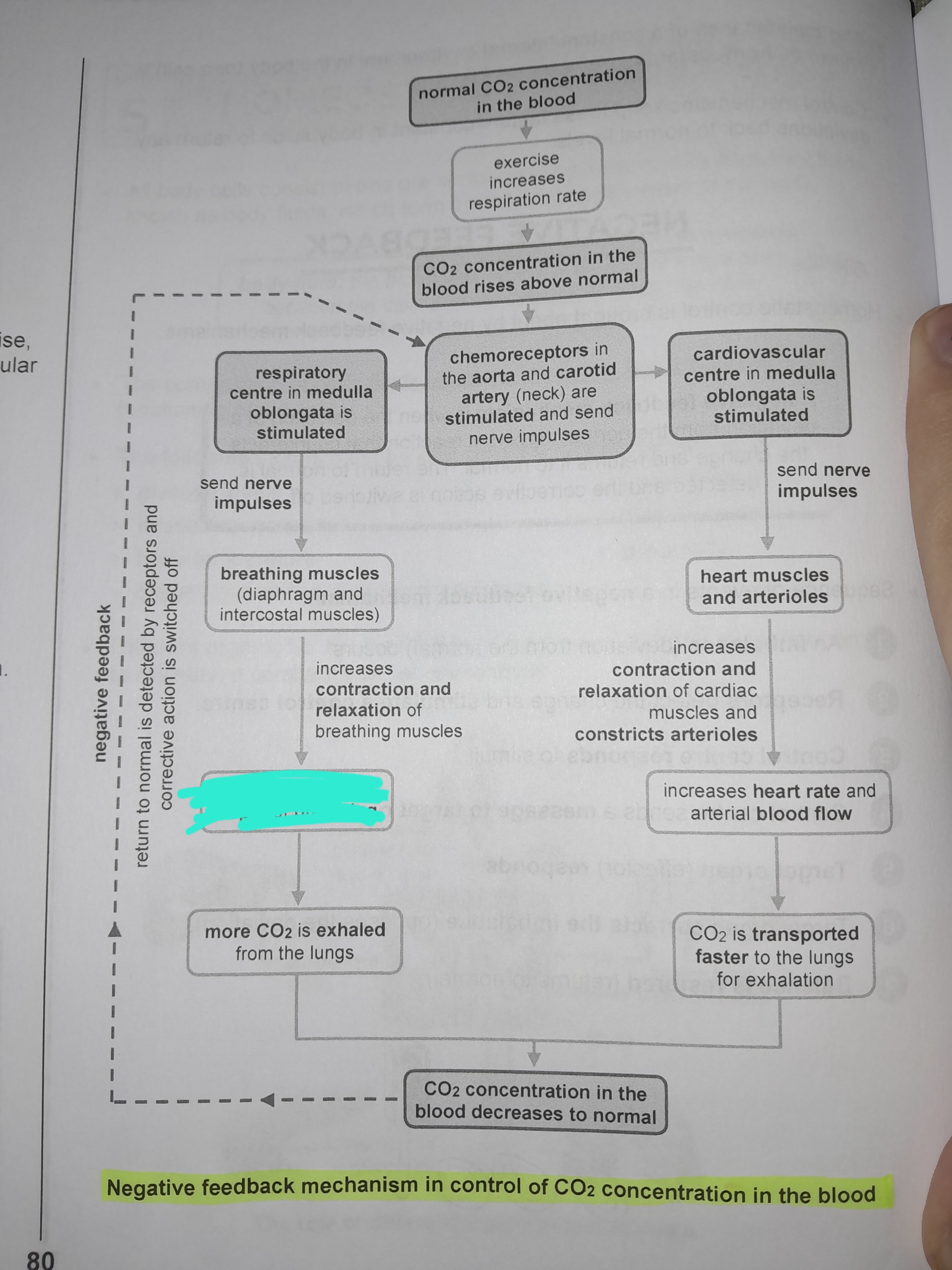
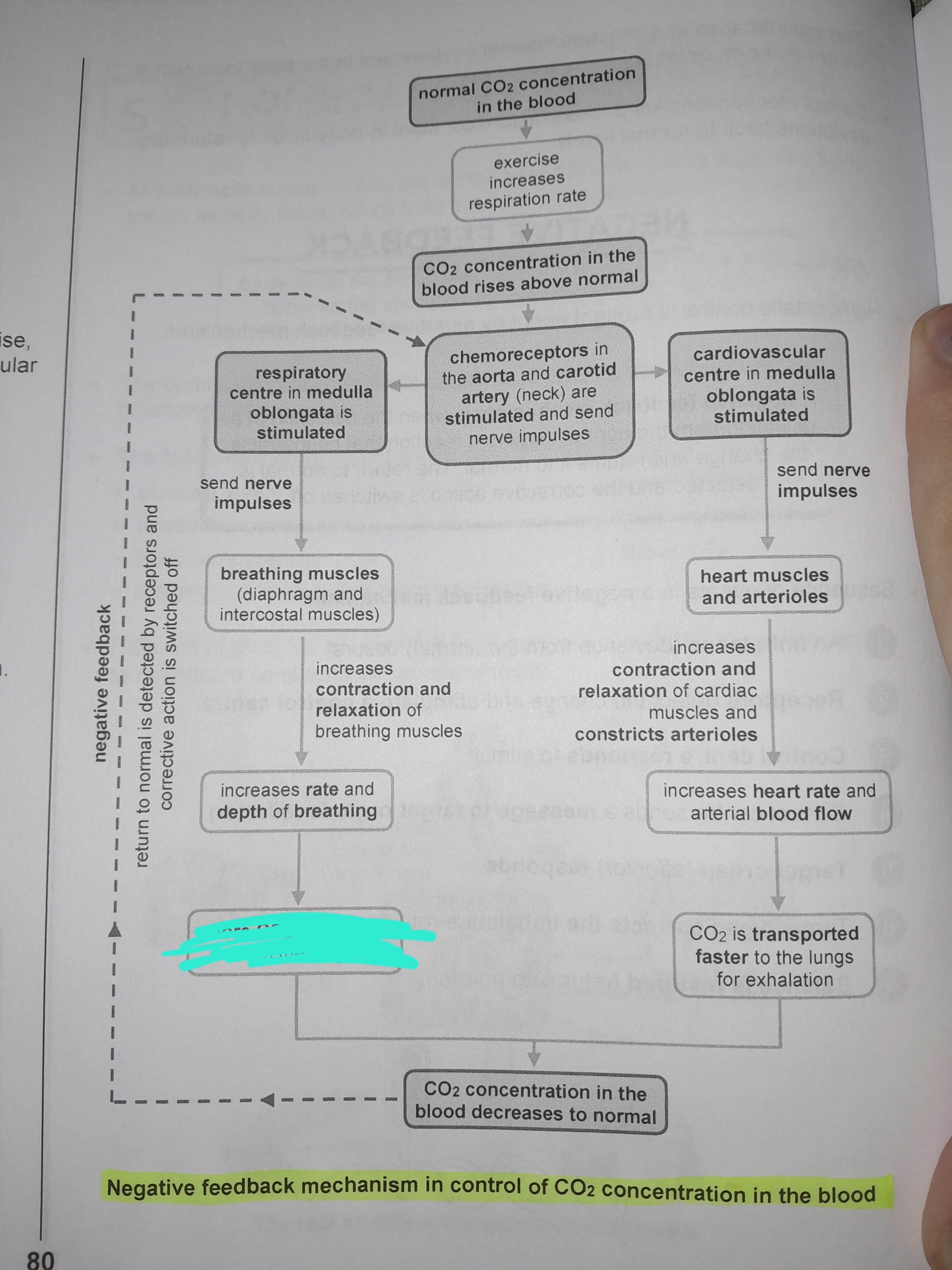
Increases rate and depth of breathing
More CO2 is exhaled from the lungs
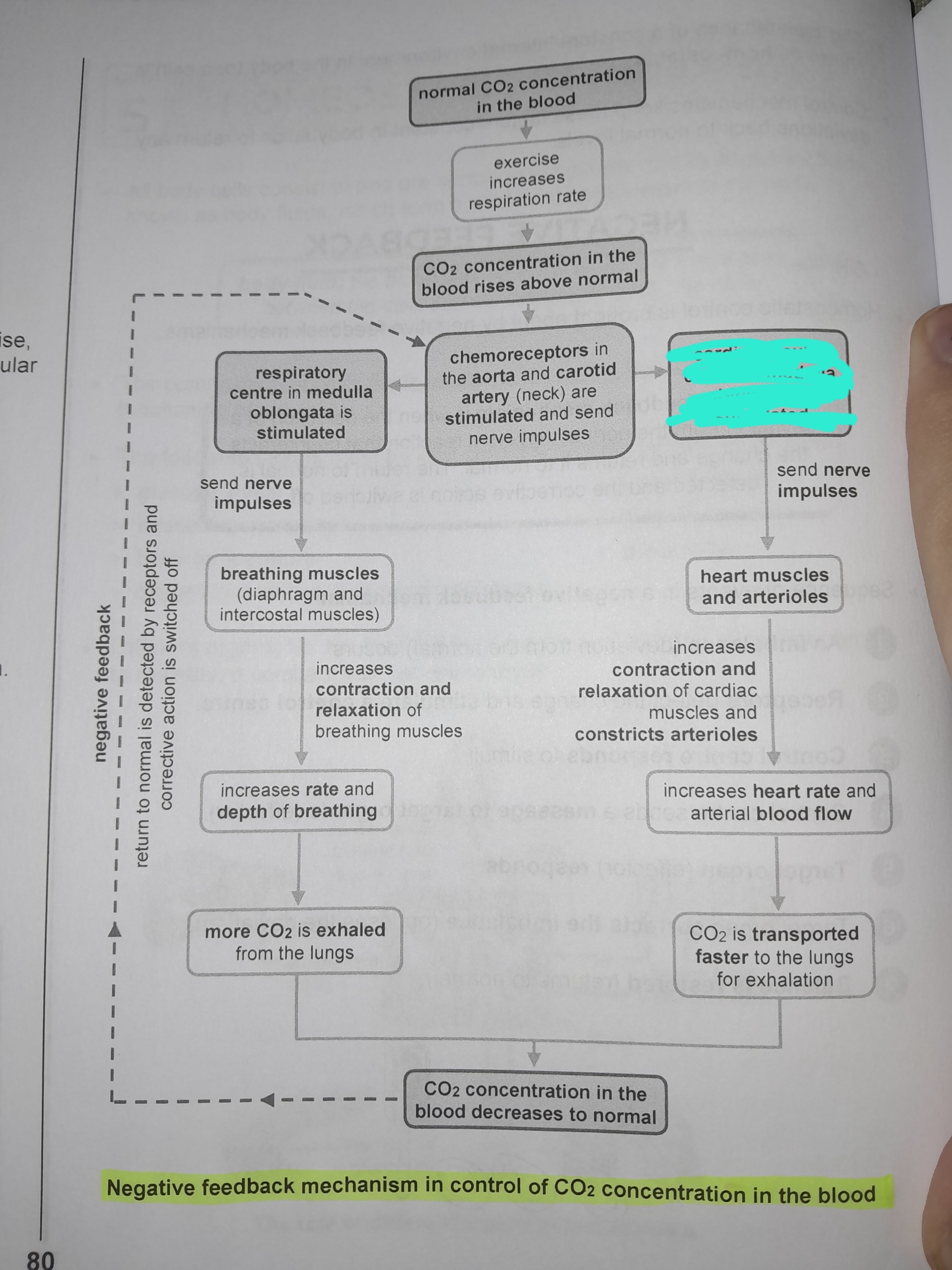
Cardiovascular center in medulla oblongata is stimulated
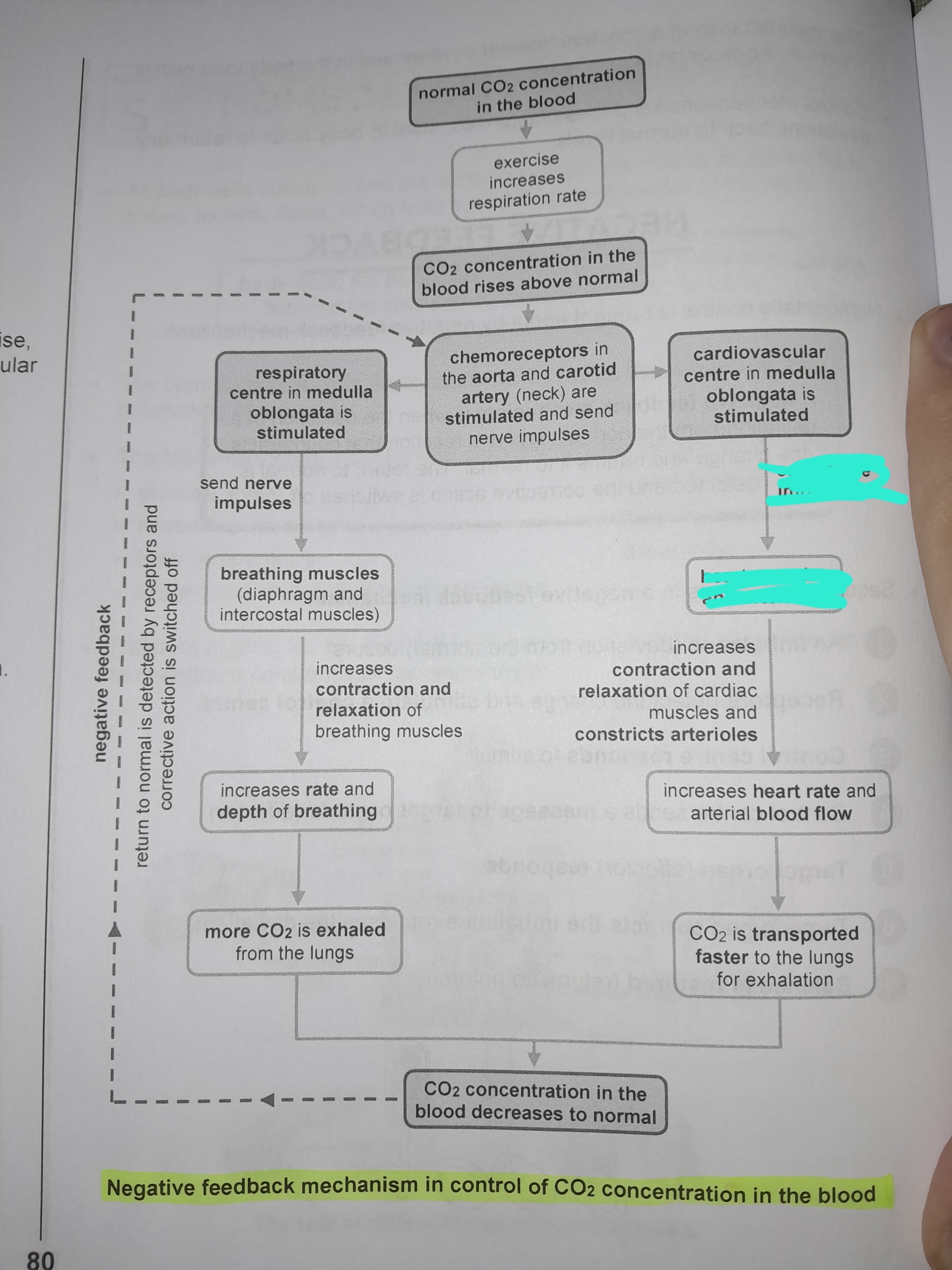
Sends nerve impulses to heart muscles and arterioles
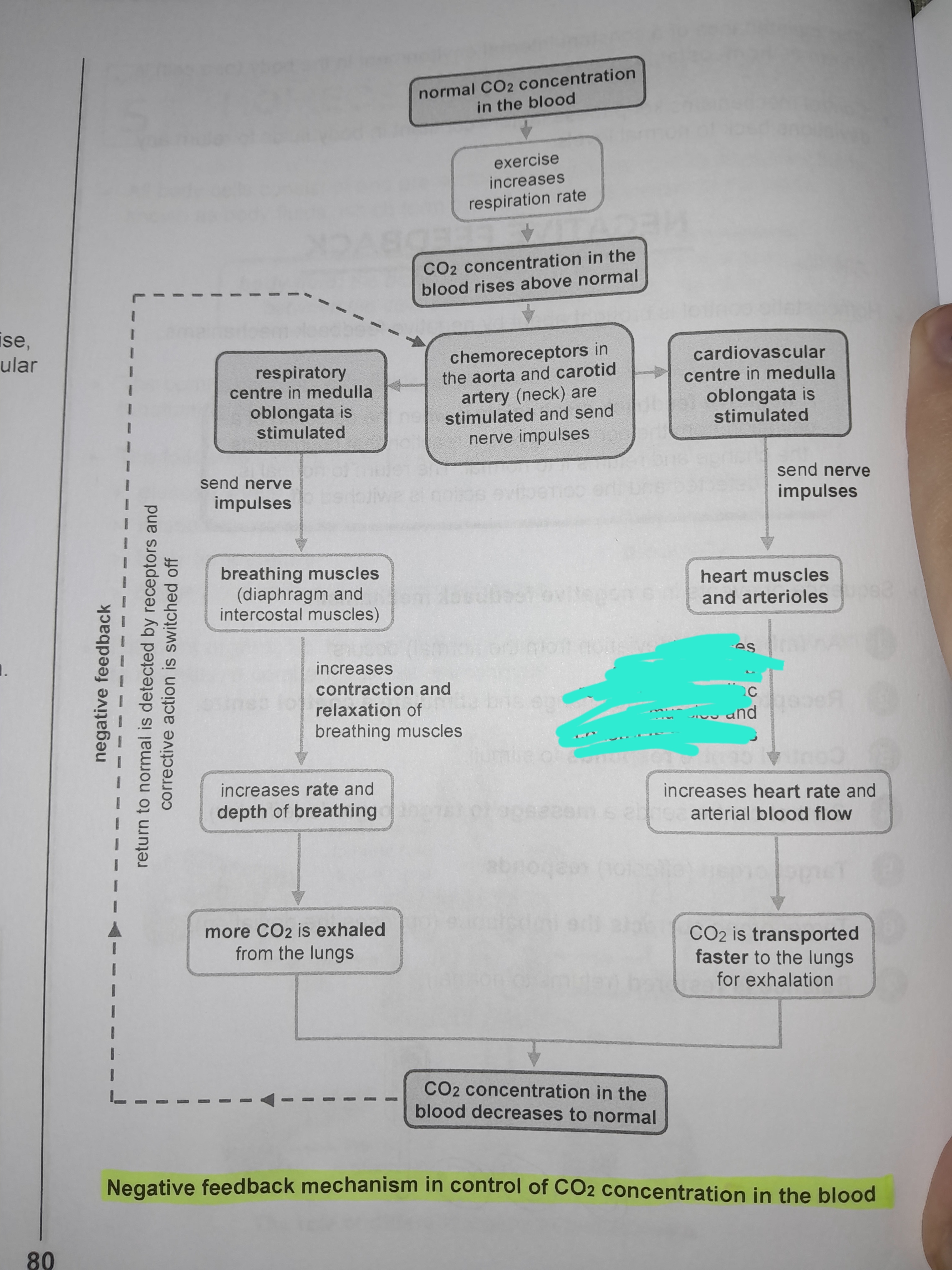
Increases contraction and relaxation of cardiac muscles and constricts arterioles
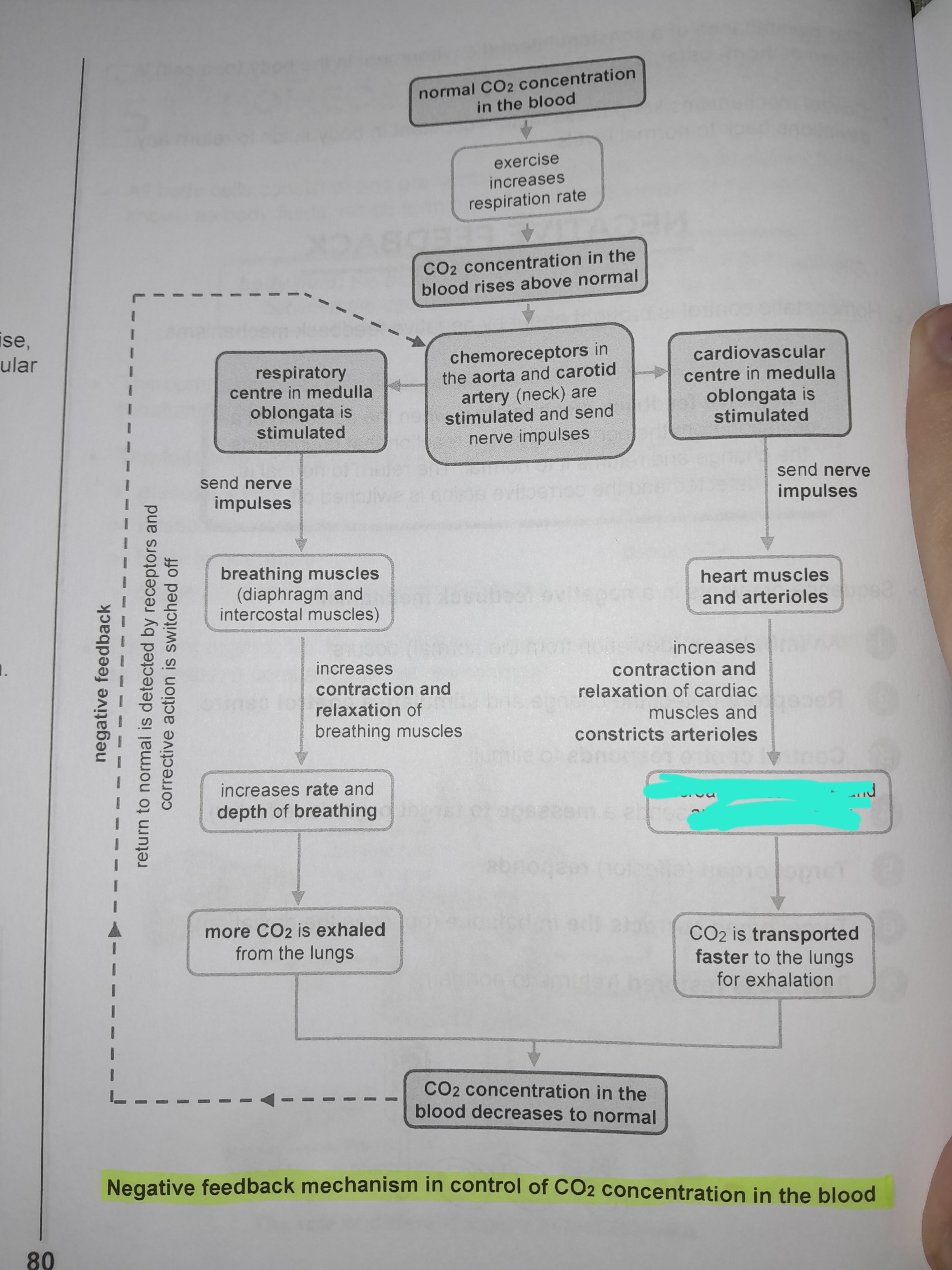
Increases heart rate and arterial blood flow
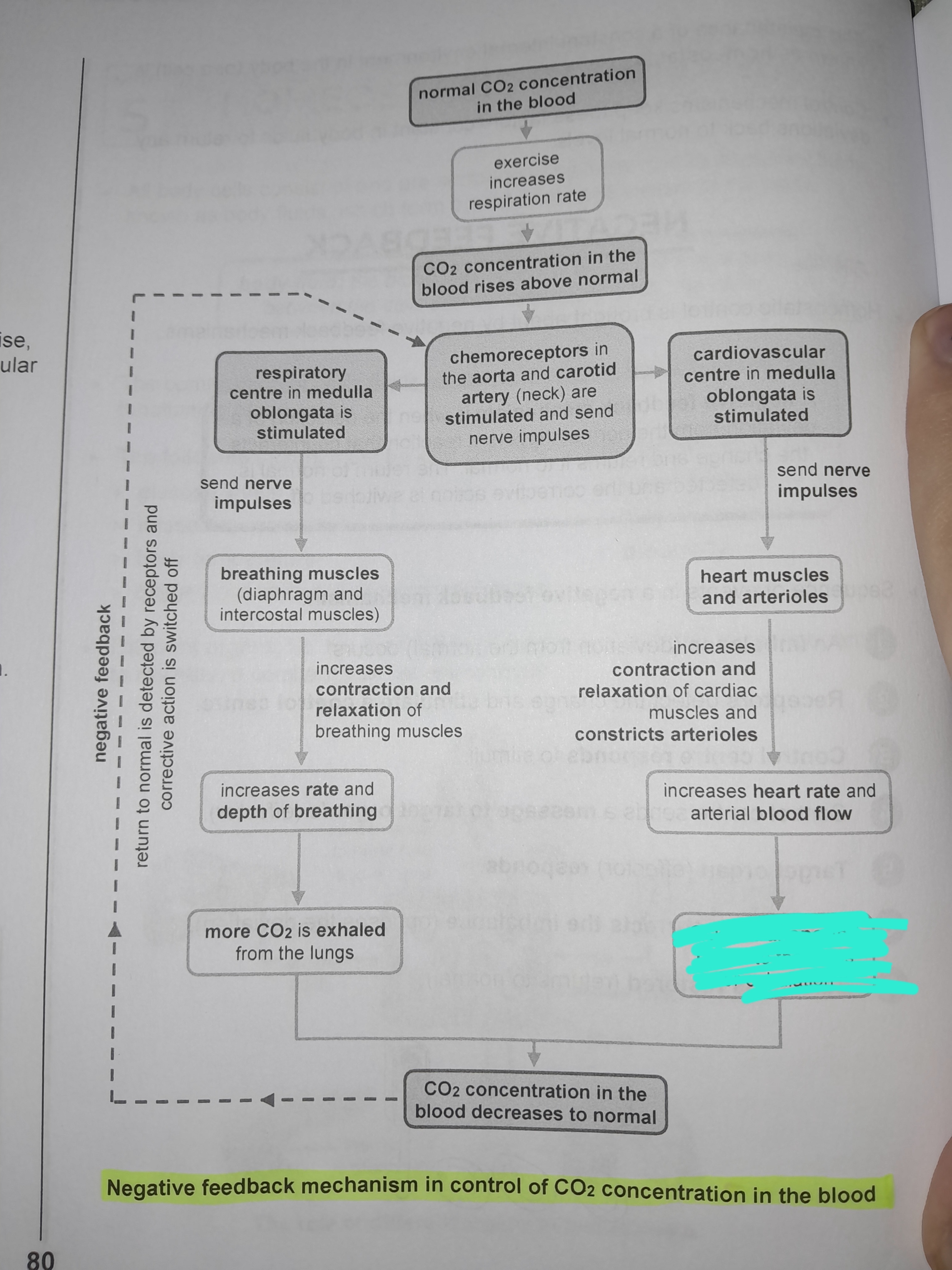
CO2 is transported faster to the lungs for exhalation
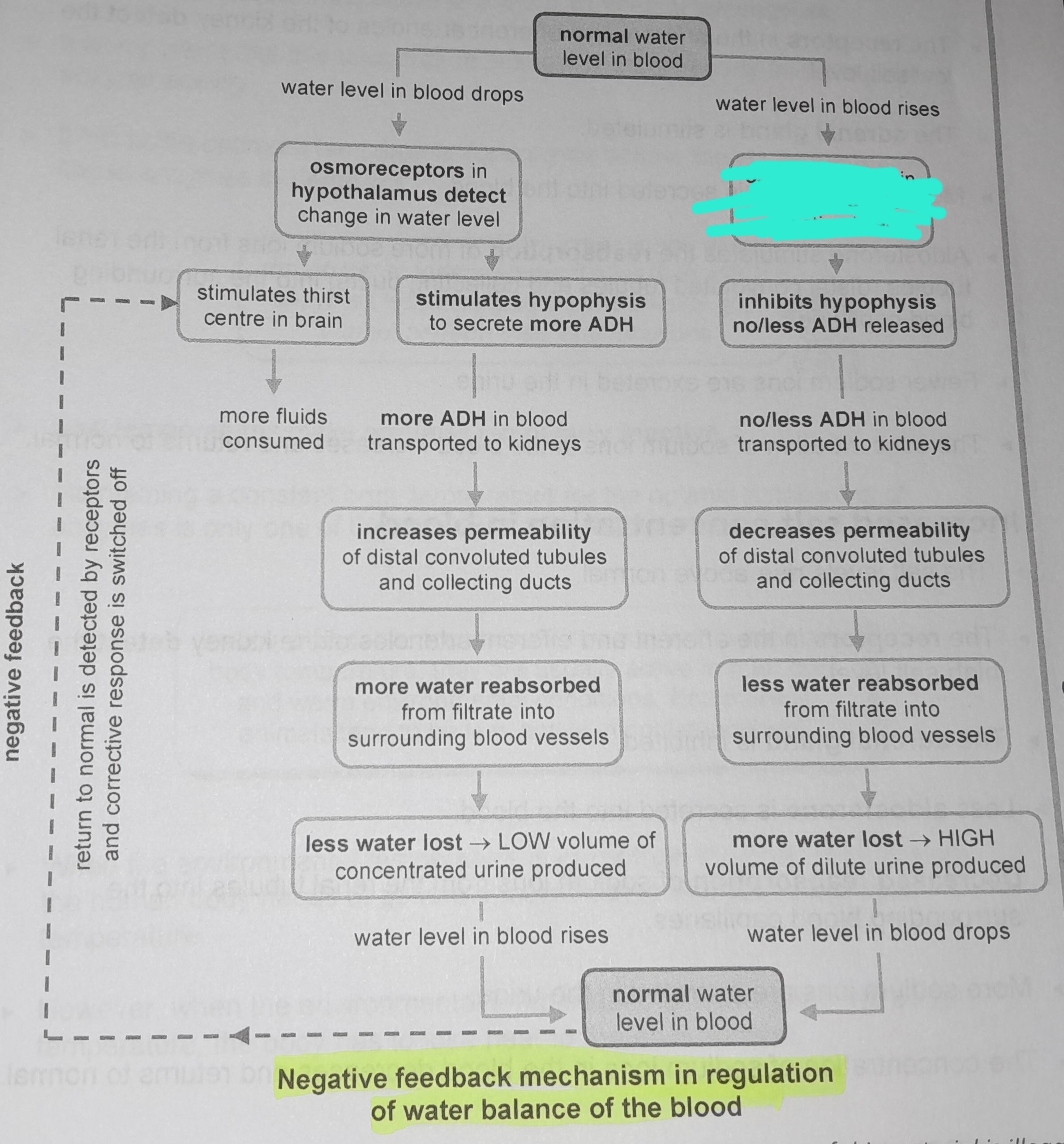
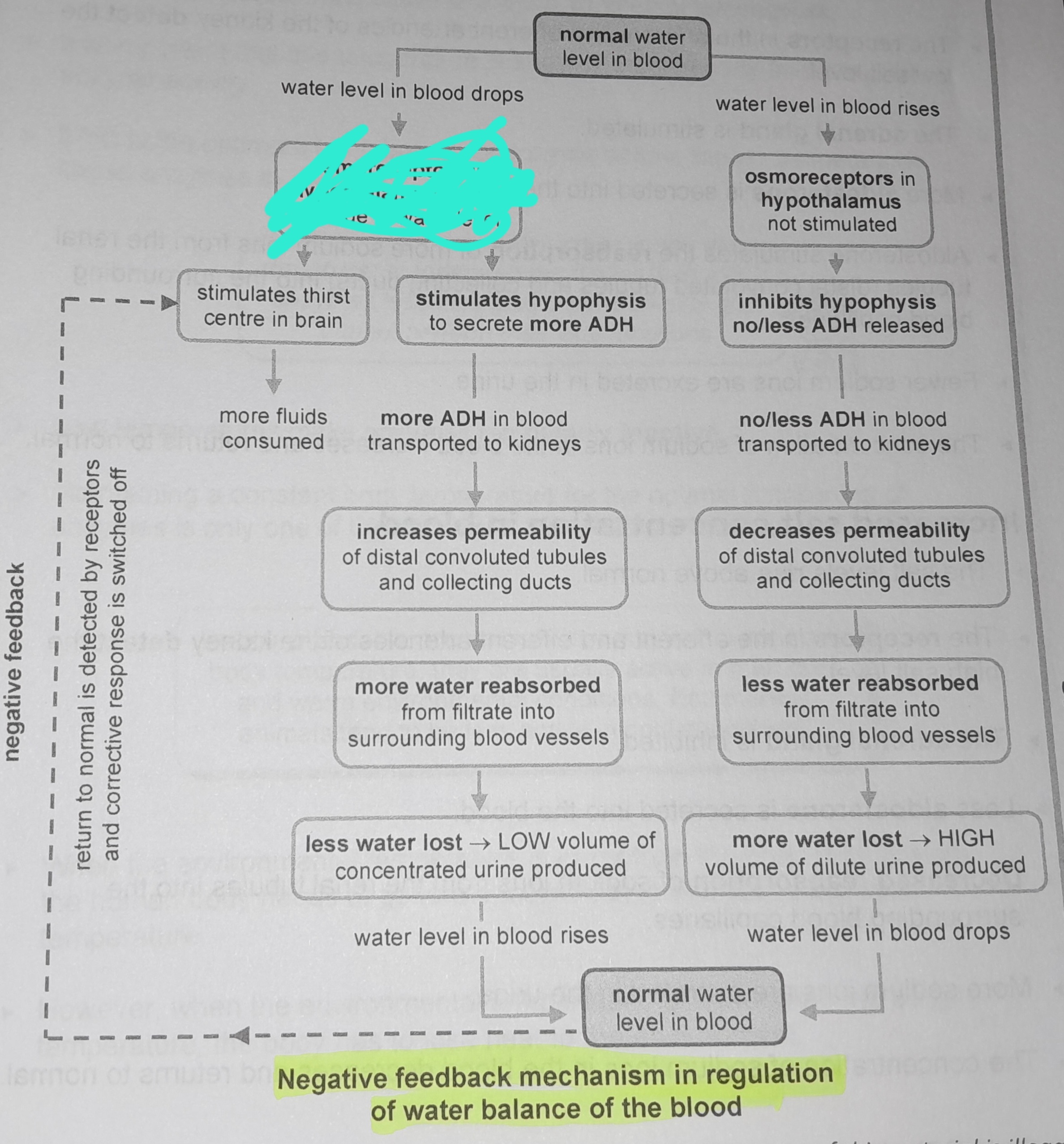
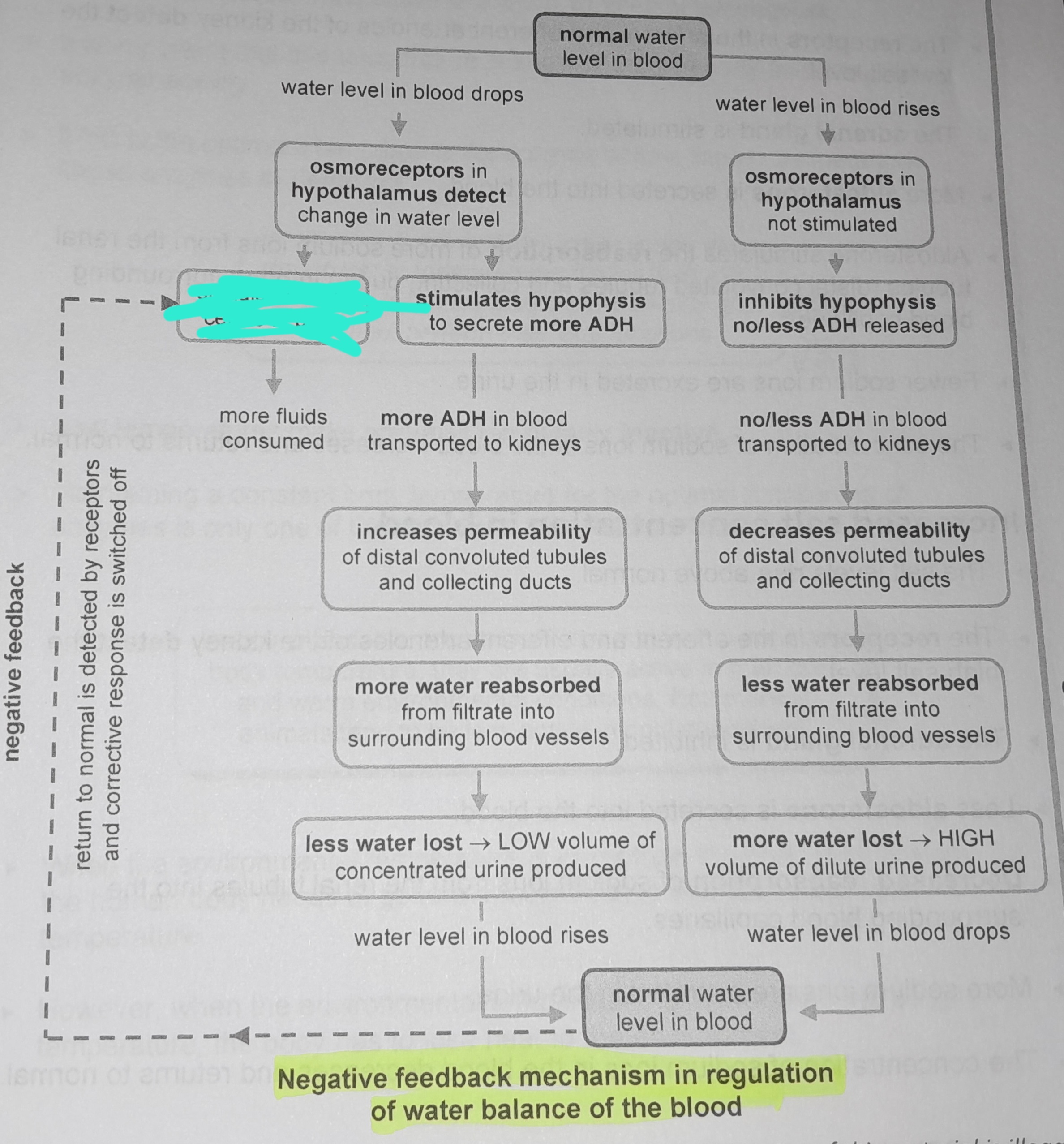
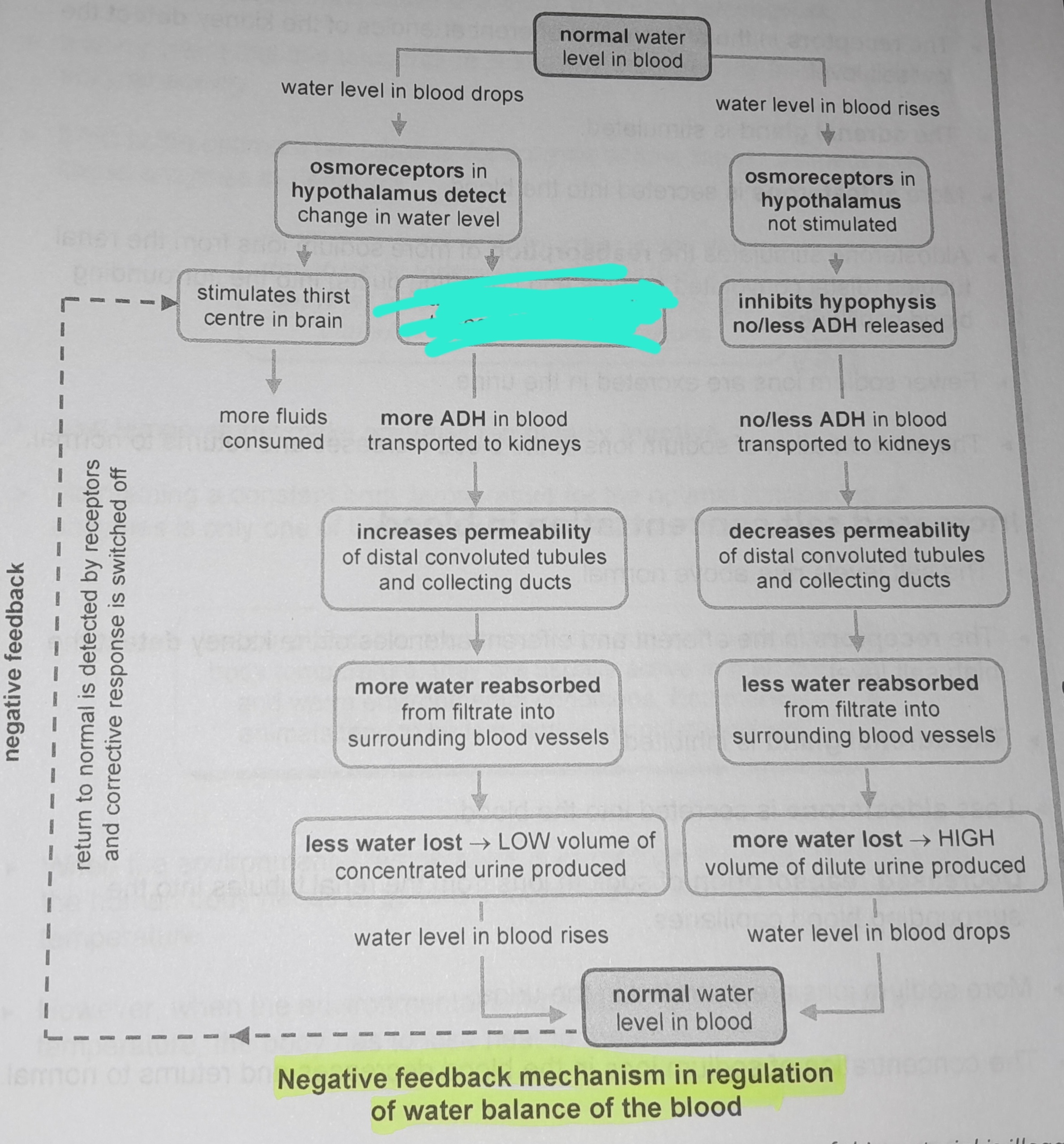
Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus not stimulated
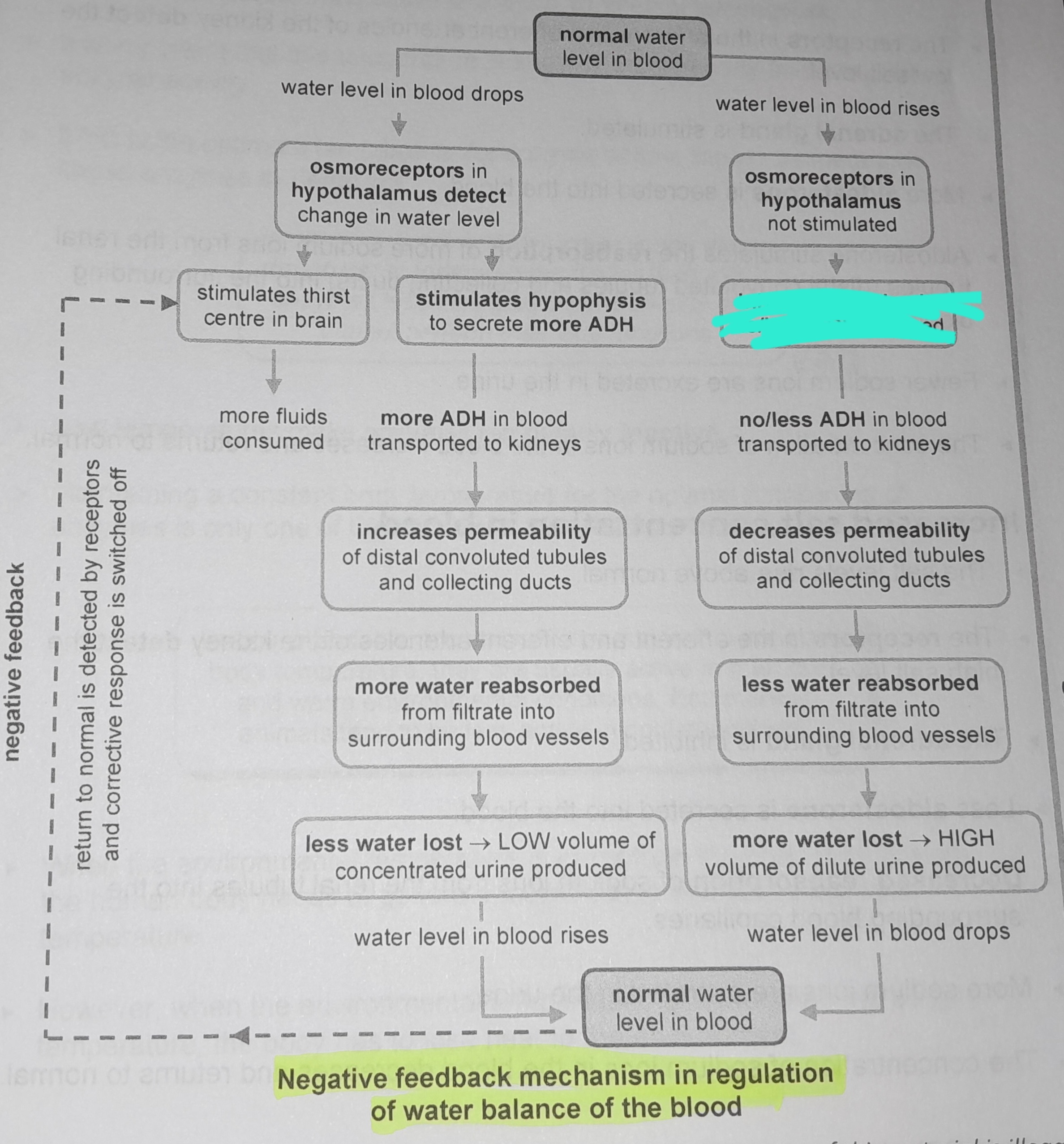
Inhibits hypophysis no/less ADH released
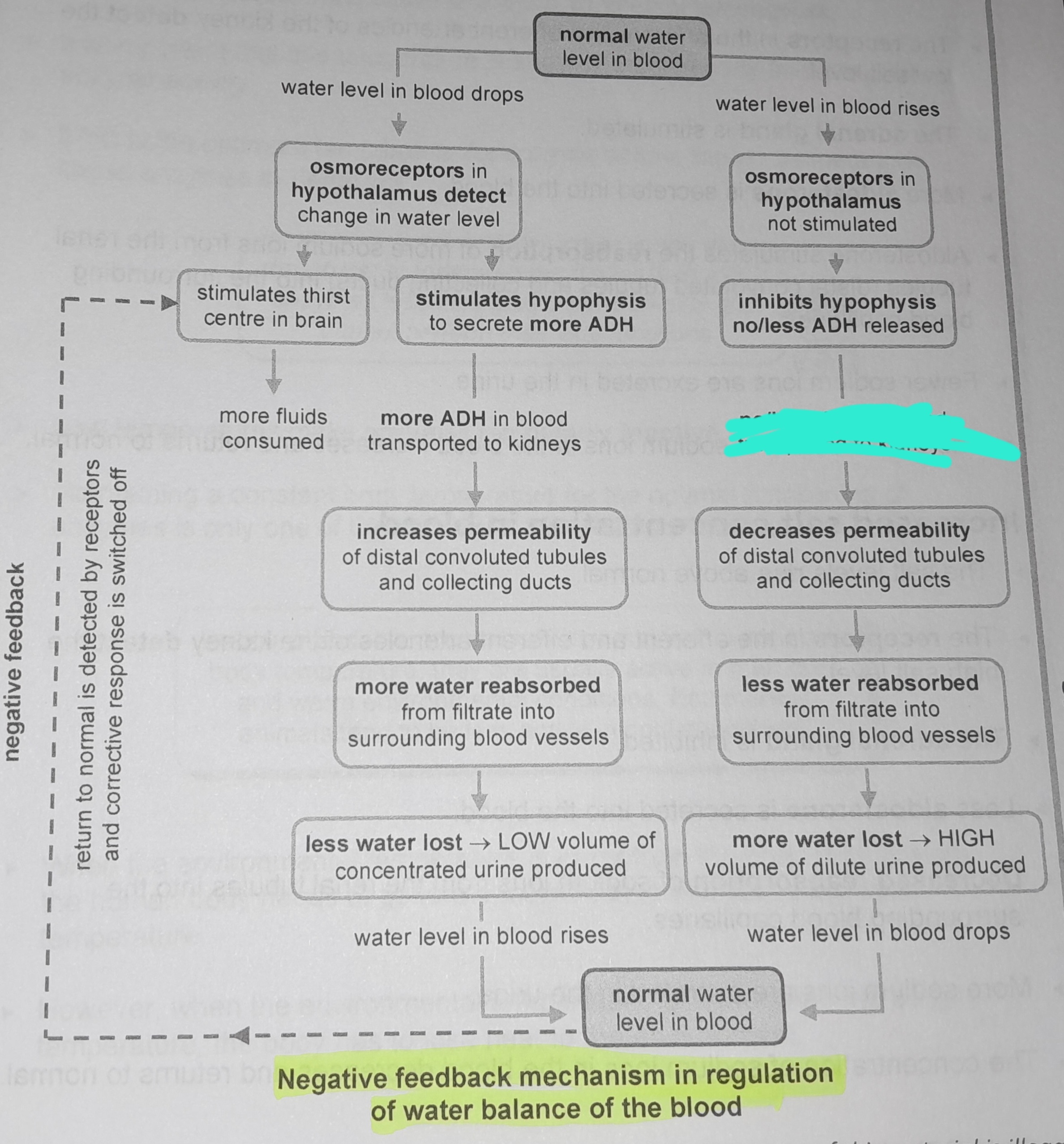
No/less ADH in blood transported to kidneys
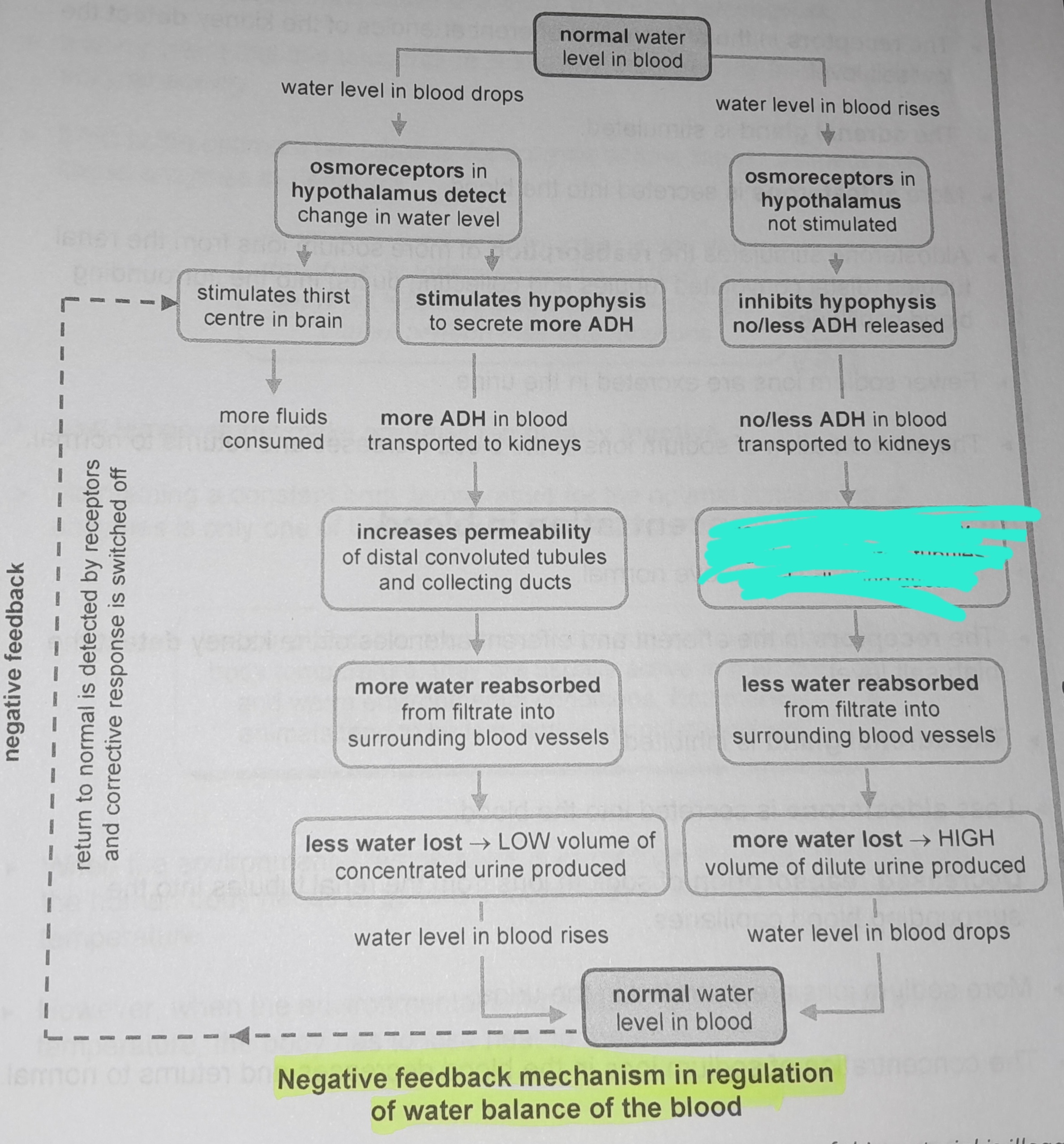
Decreases permeability of distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts
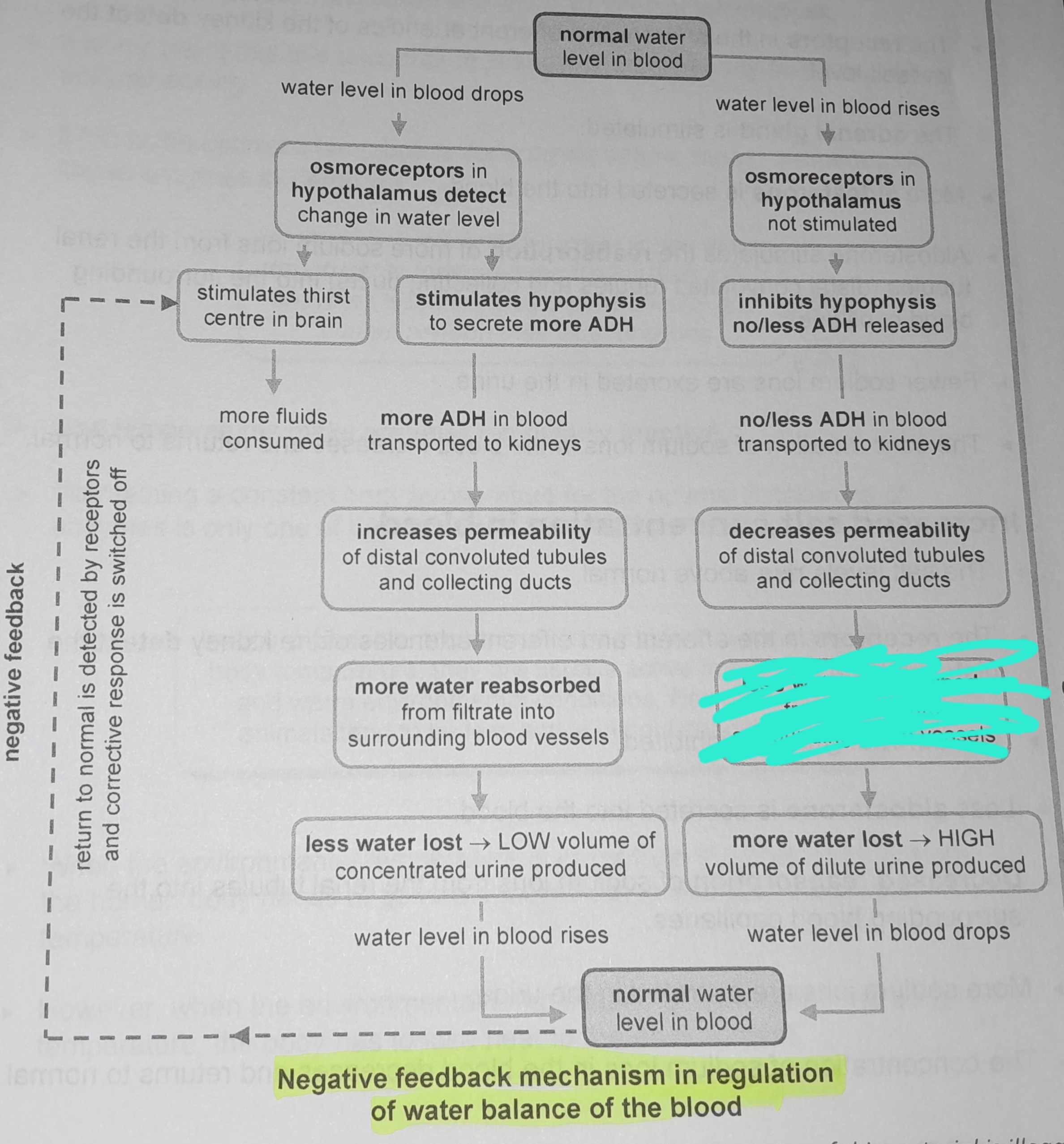
Less water reabsorbed from from filtrate into surrounding blood vessels
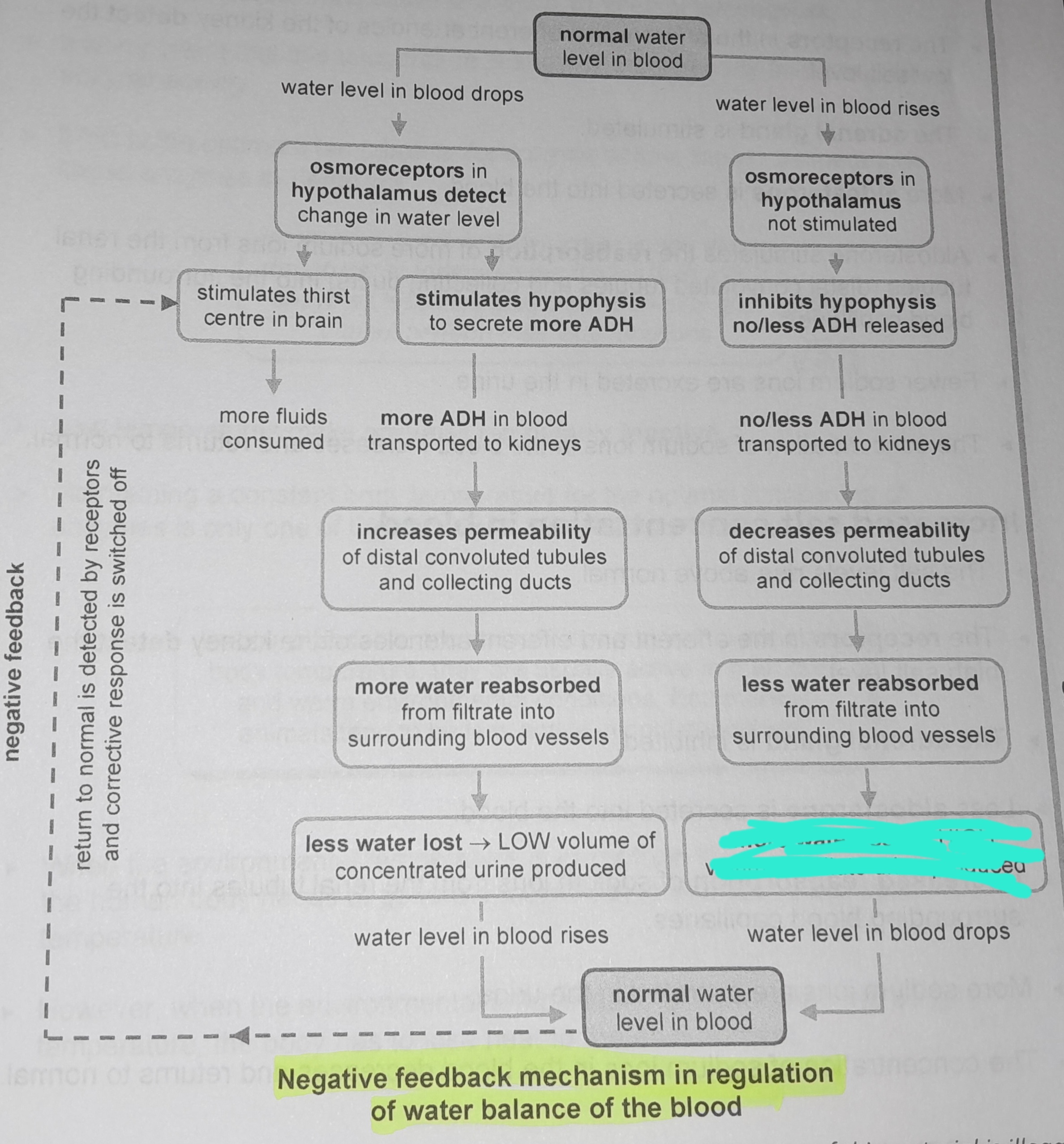
More water lost, high volume of dilute urine produced
Osmoreceptors in the hypophysis detect change in water level
Stimulates thirst in the centre of the brain
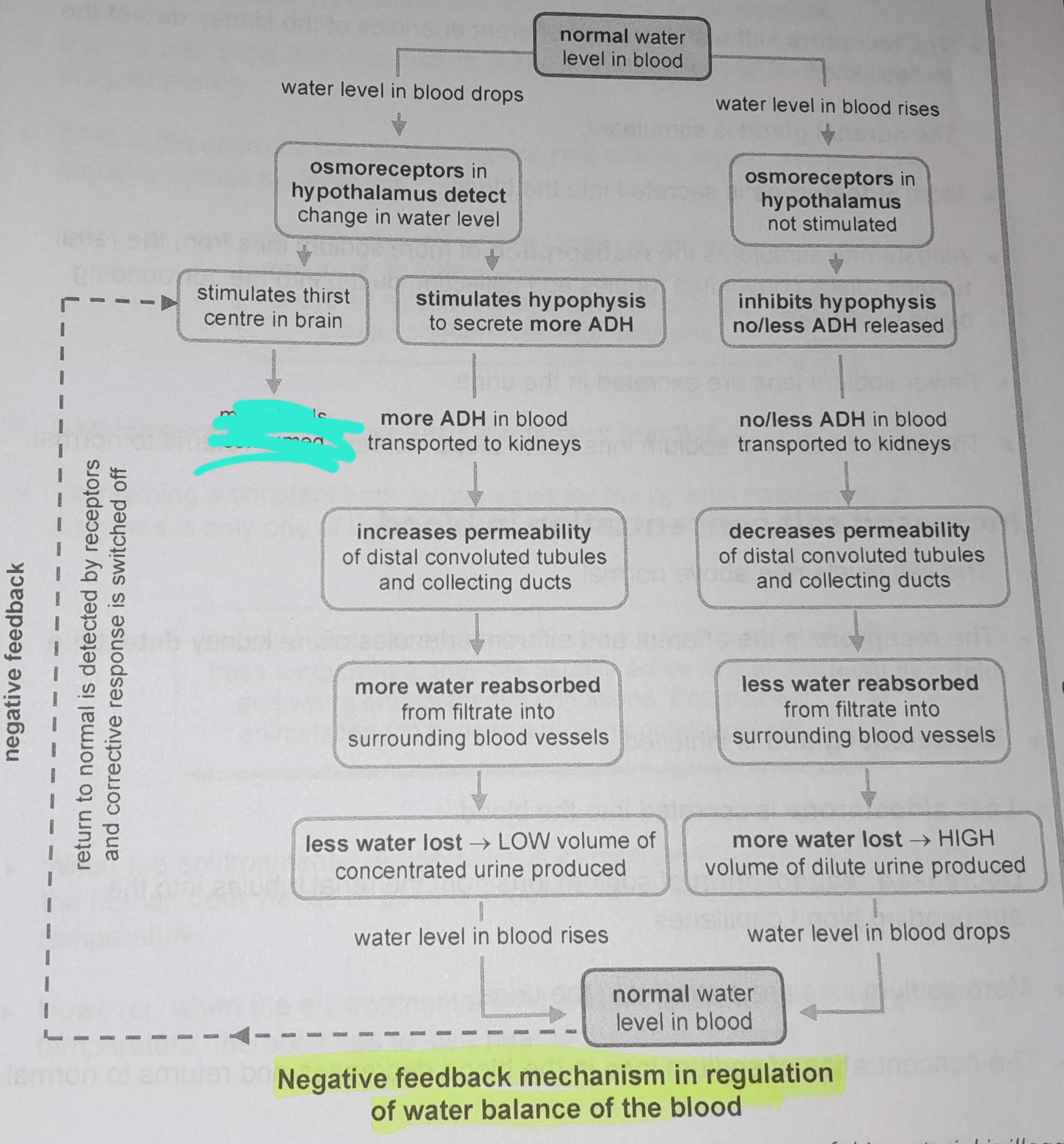
More fluids consumed
Stimulates hypophysis to secrete more ADH
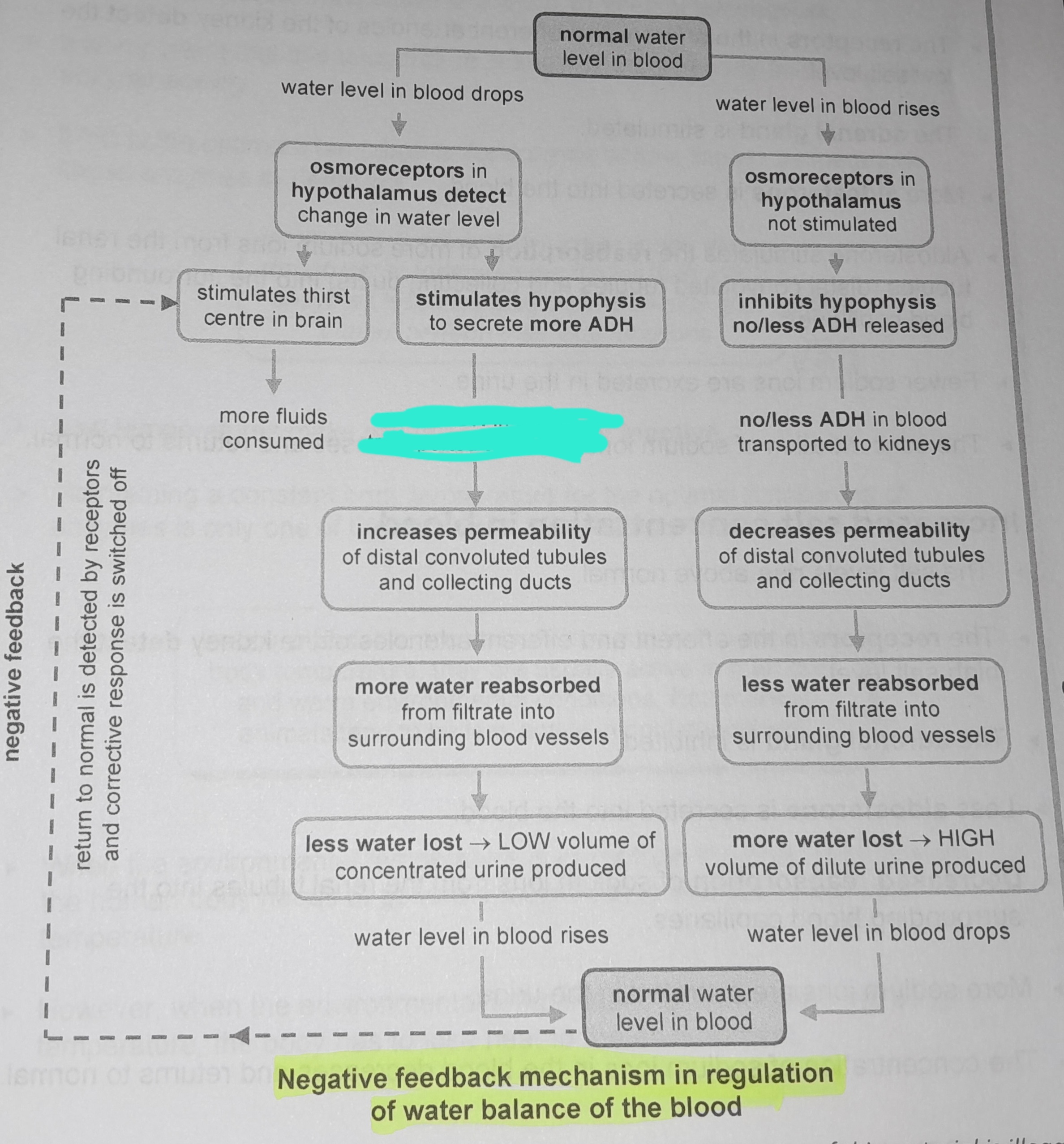
More ADH in blood transported to kidneys
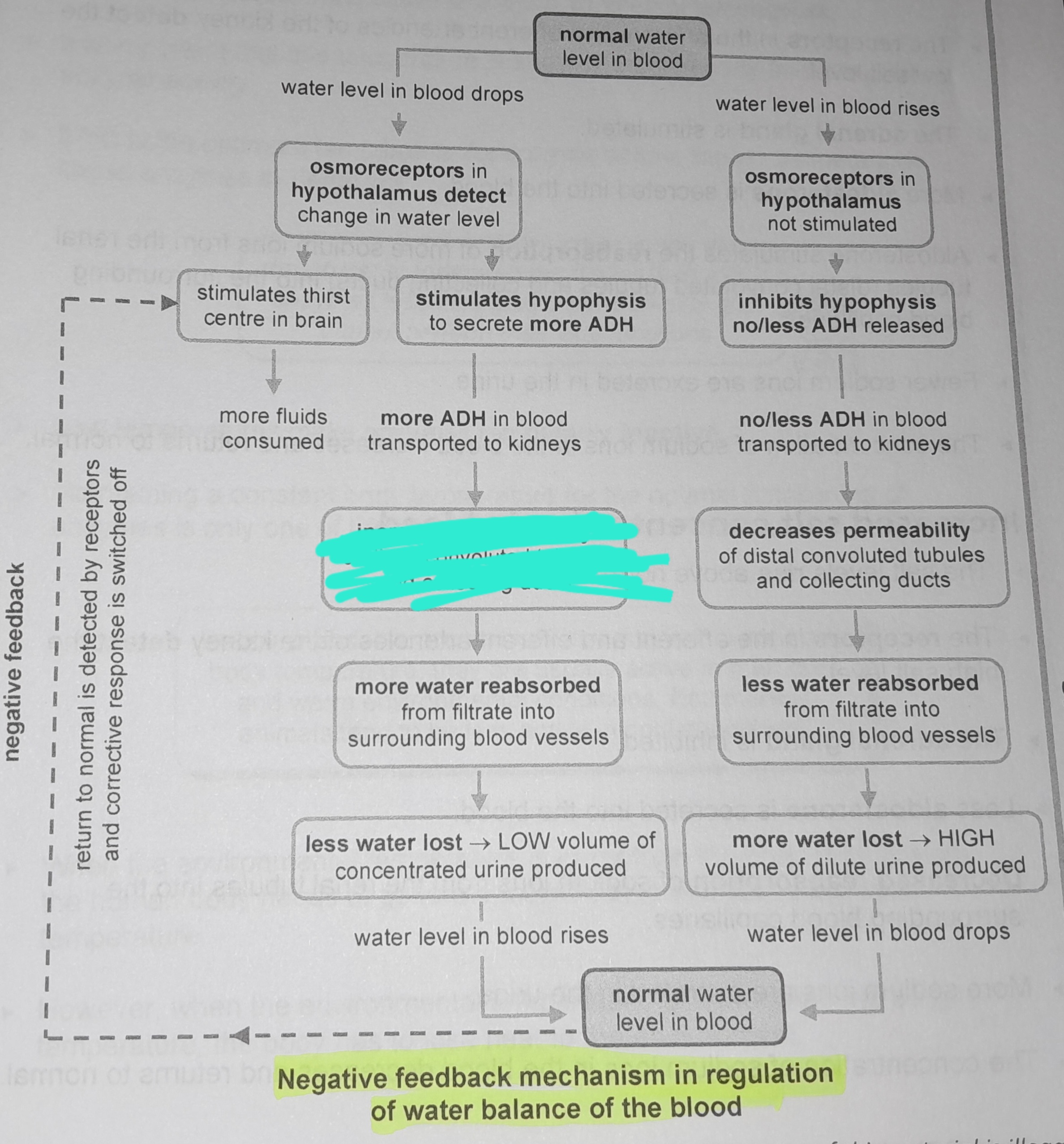
Increases permeability of distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts
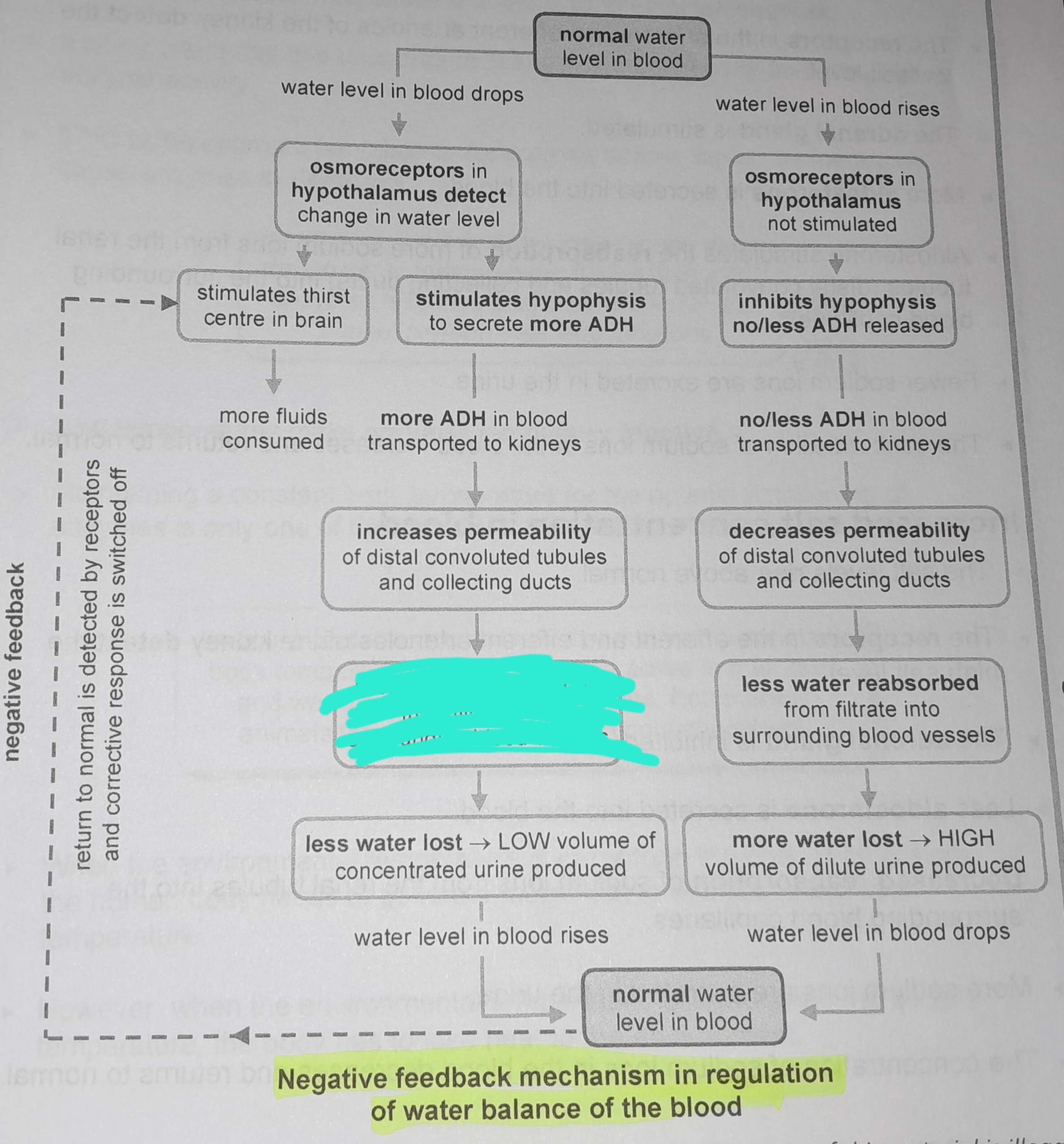
More water reabsorbed from filtrate into surrounding blood vessels
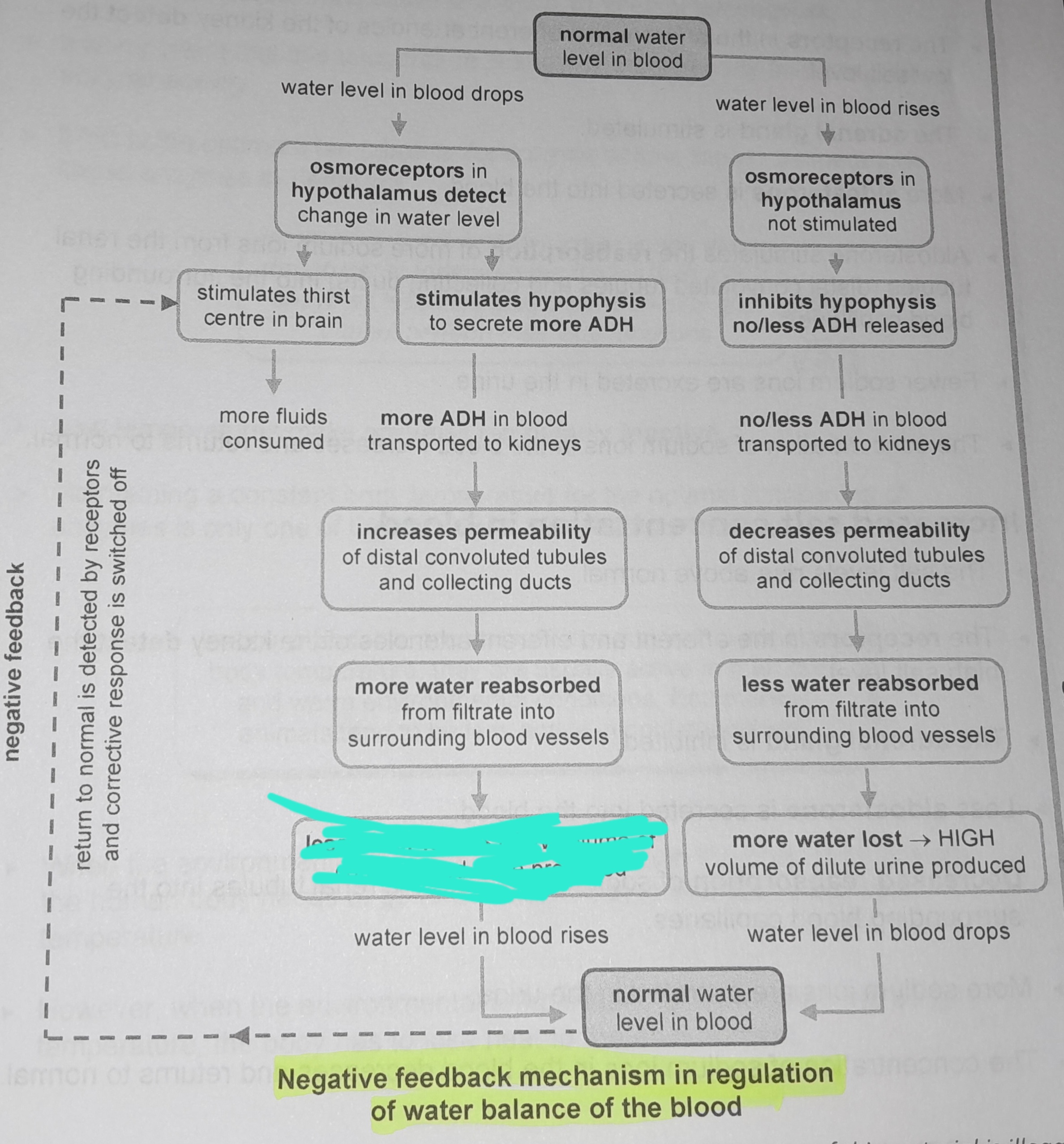
Less water lost, low volume of concentrated urine produced
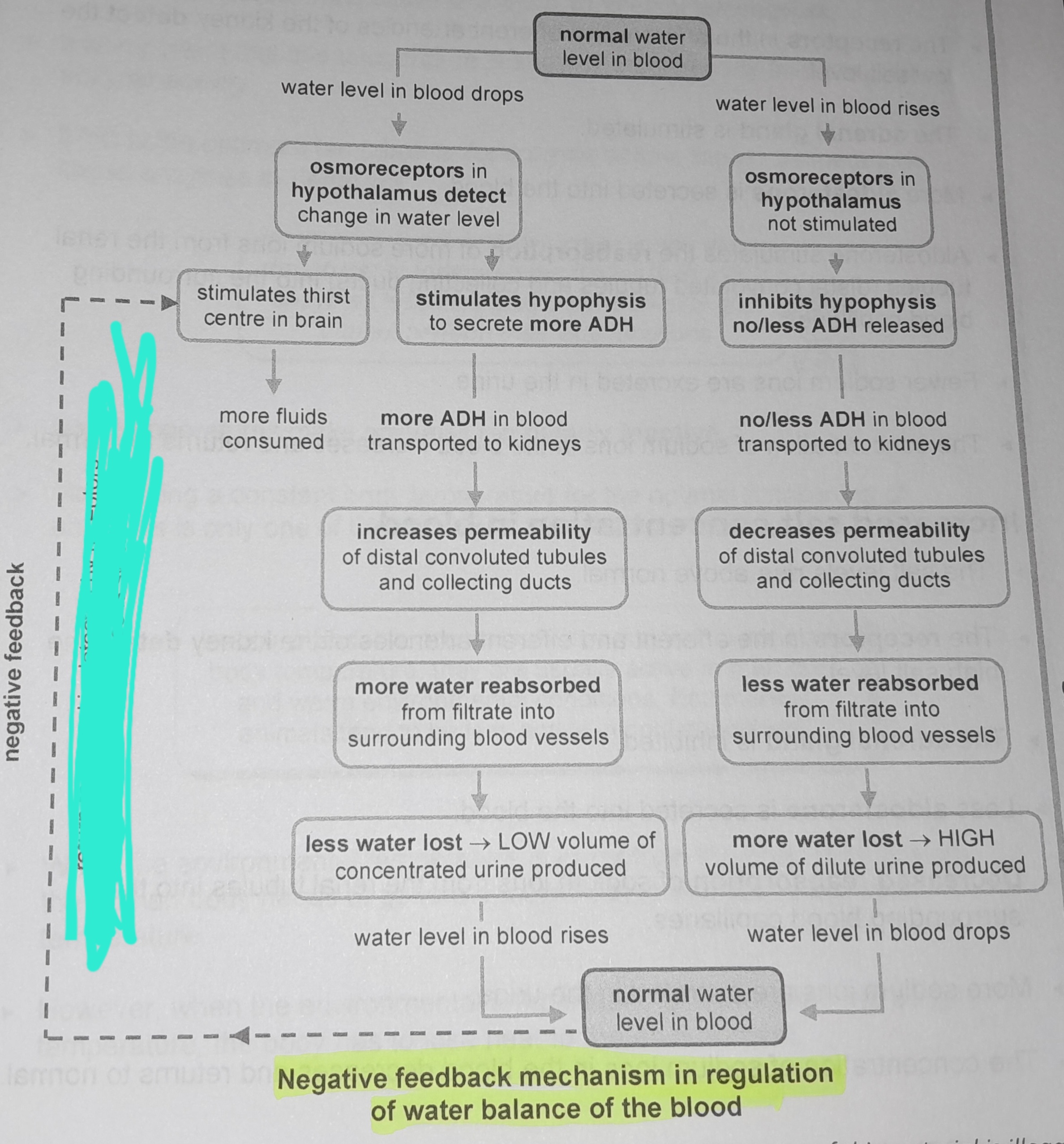
Return to normal is detected by receptors and corrective response is switched off
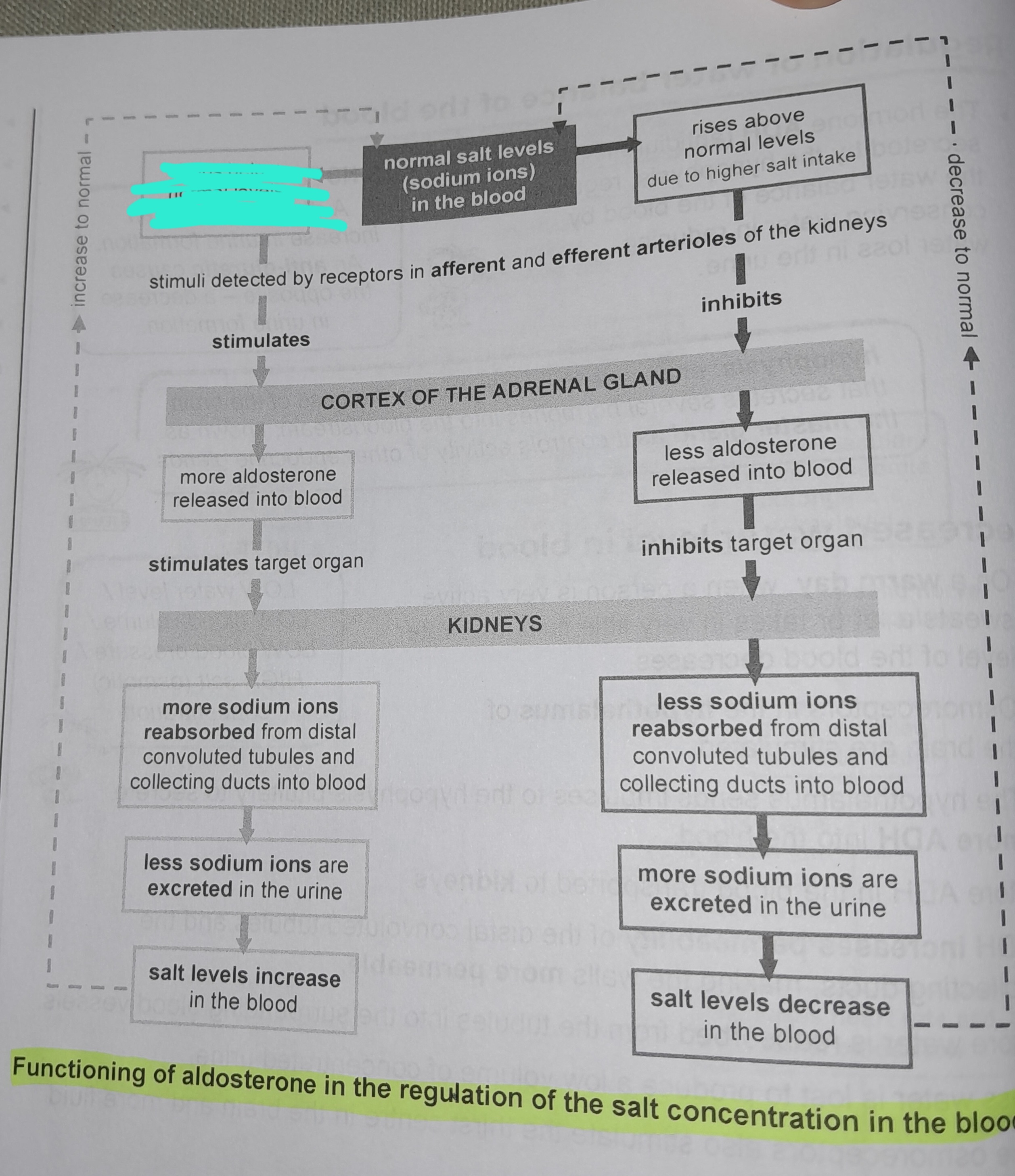
Drops below normal levels due to sweating
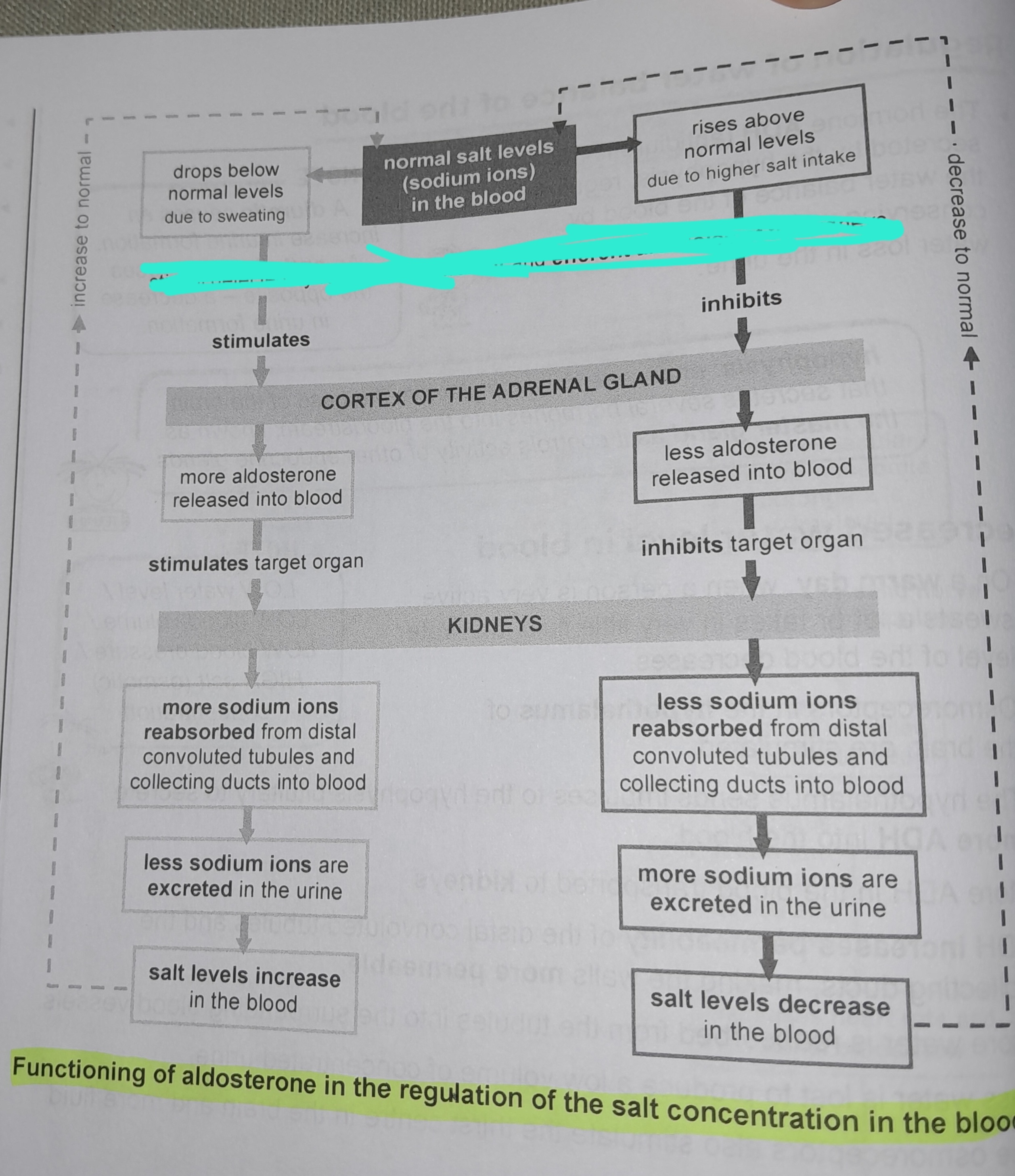
Stimuli detected by receptors in afferent and efferent arterioles of the kidneys
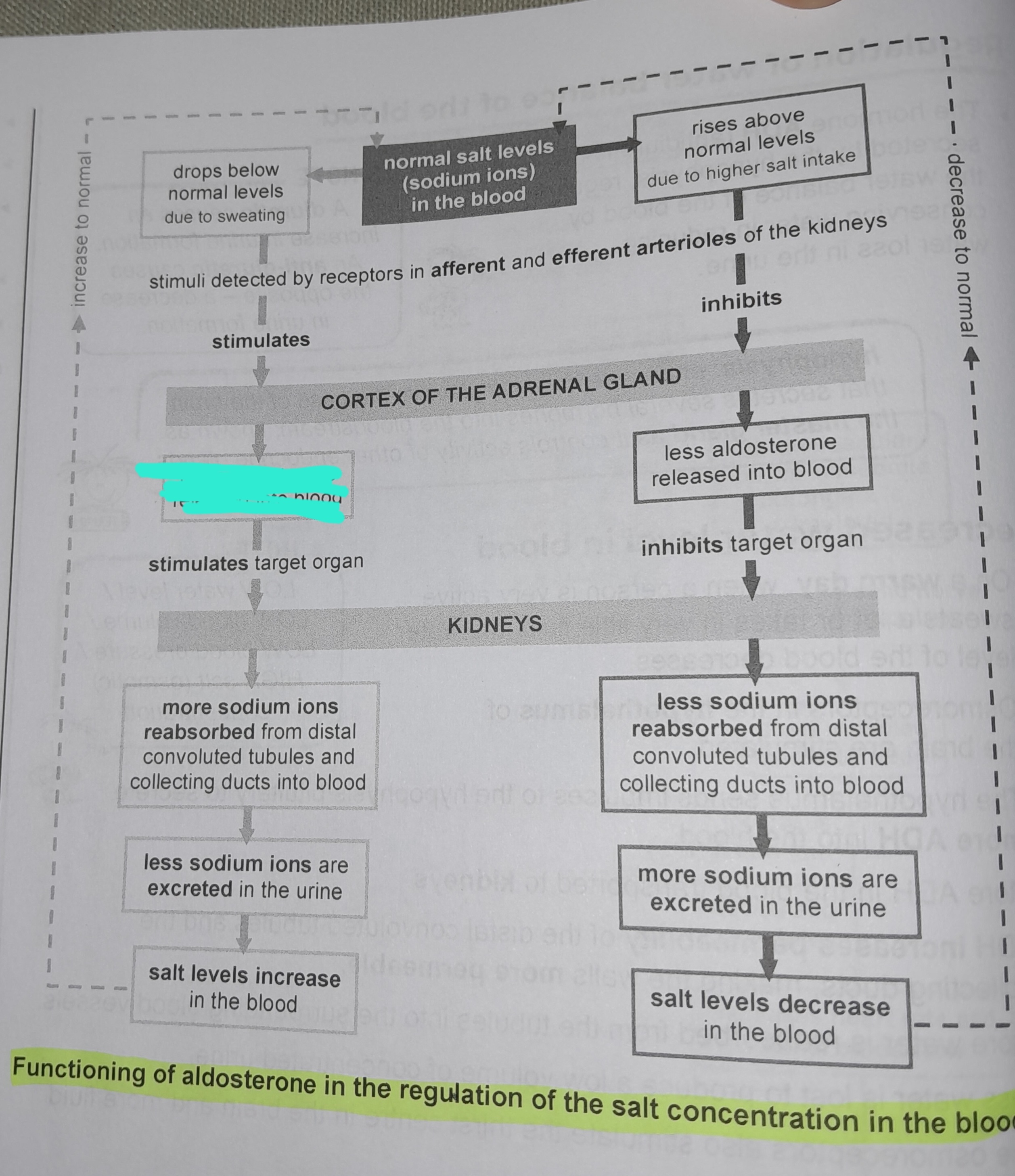
More aldosterone released into blood
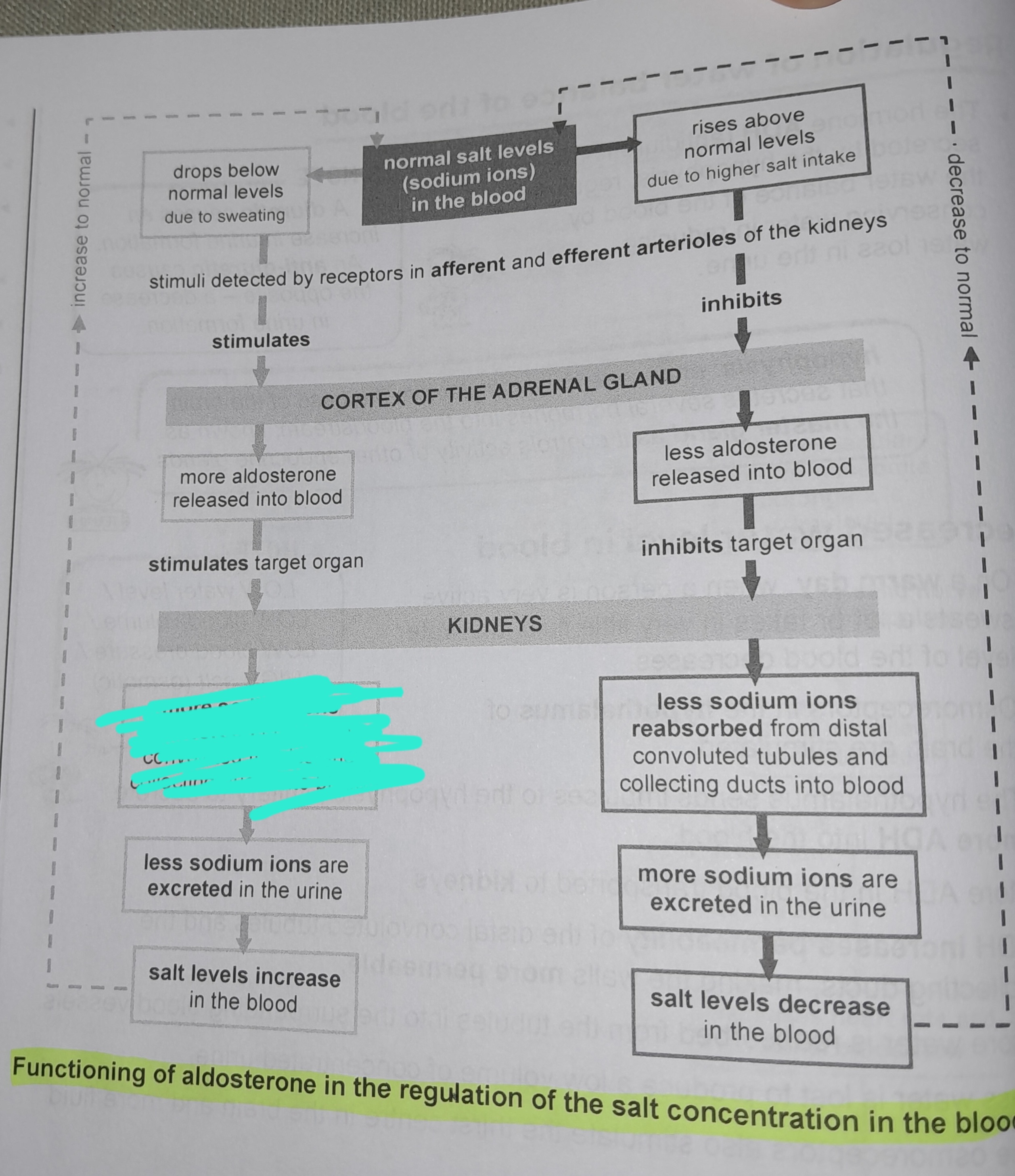
More sodium ions reabsorbed from distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts into blood
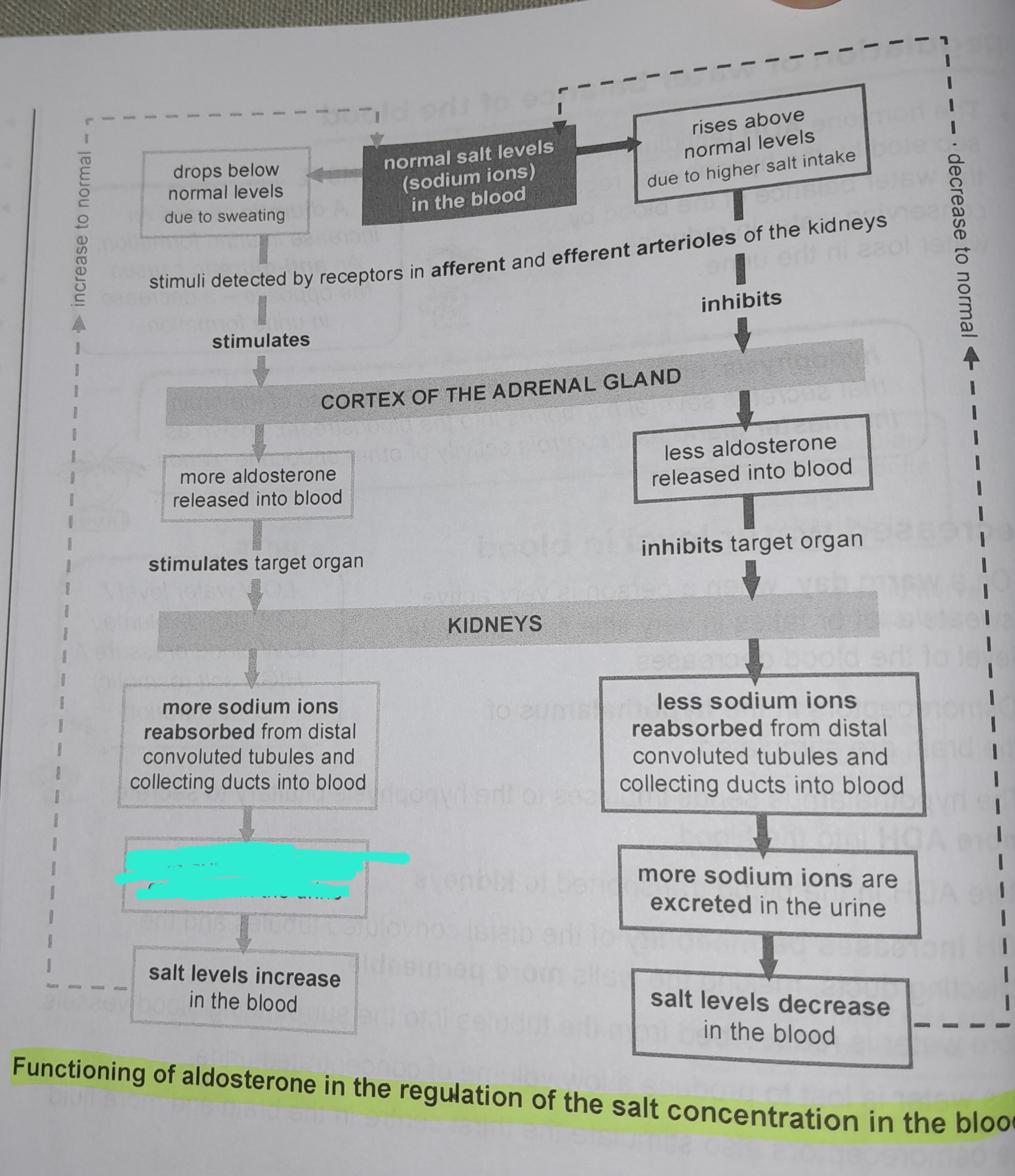
Less sodium ions are excreted in the urine
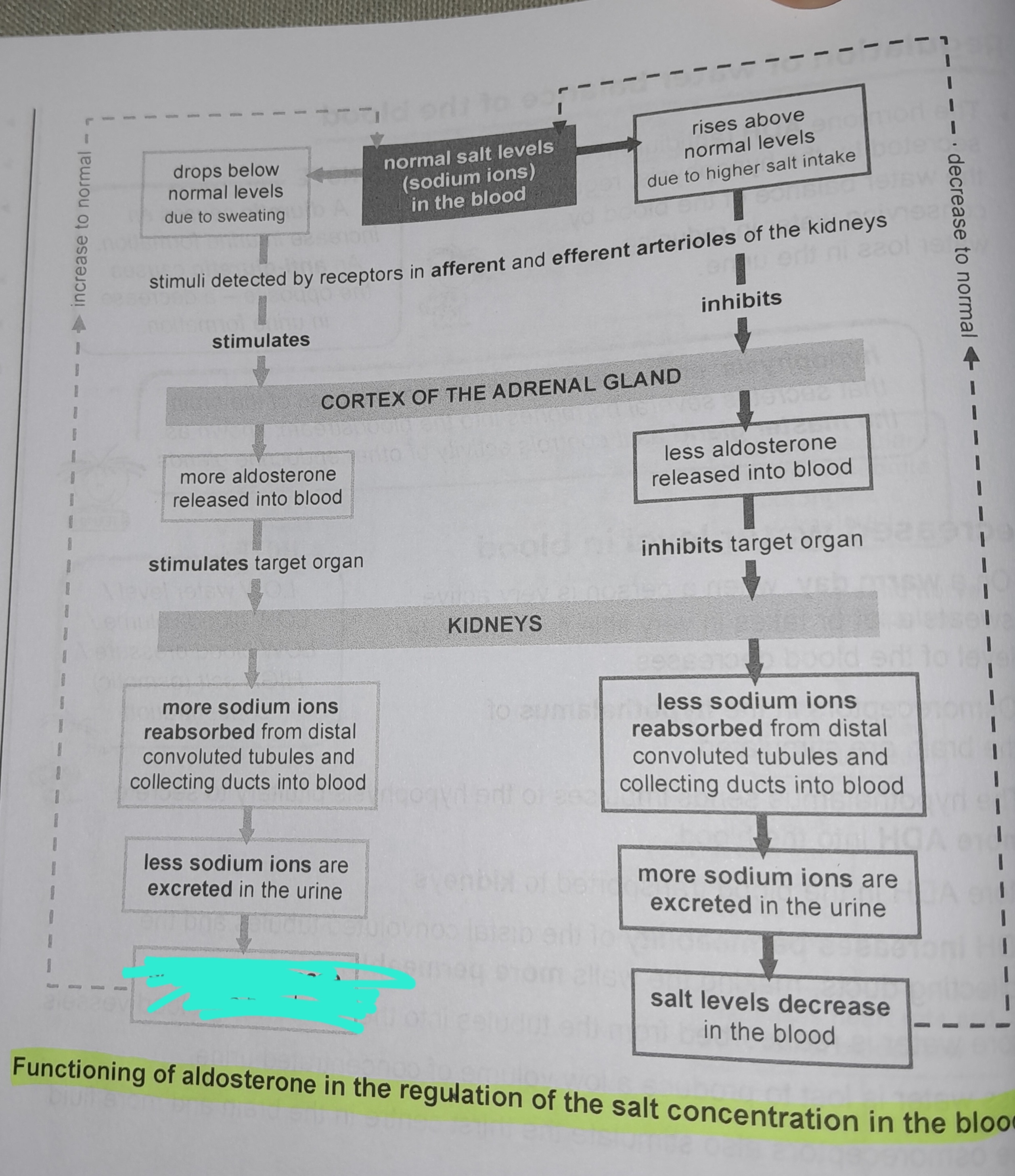
Salt levels increase in the blood
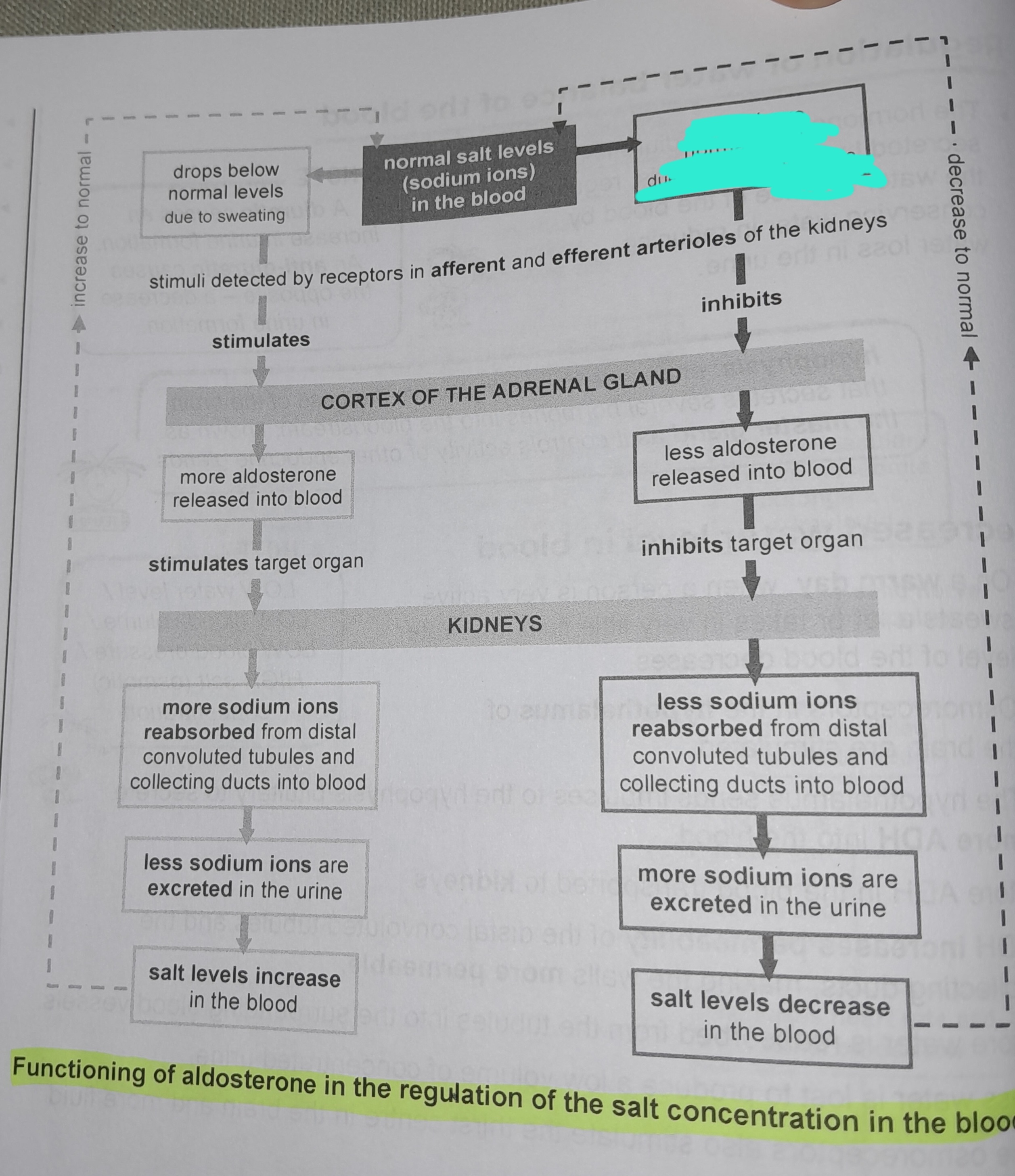
Rises above normal levels due to higher salt intake
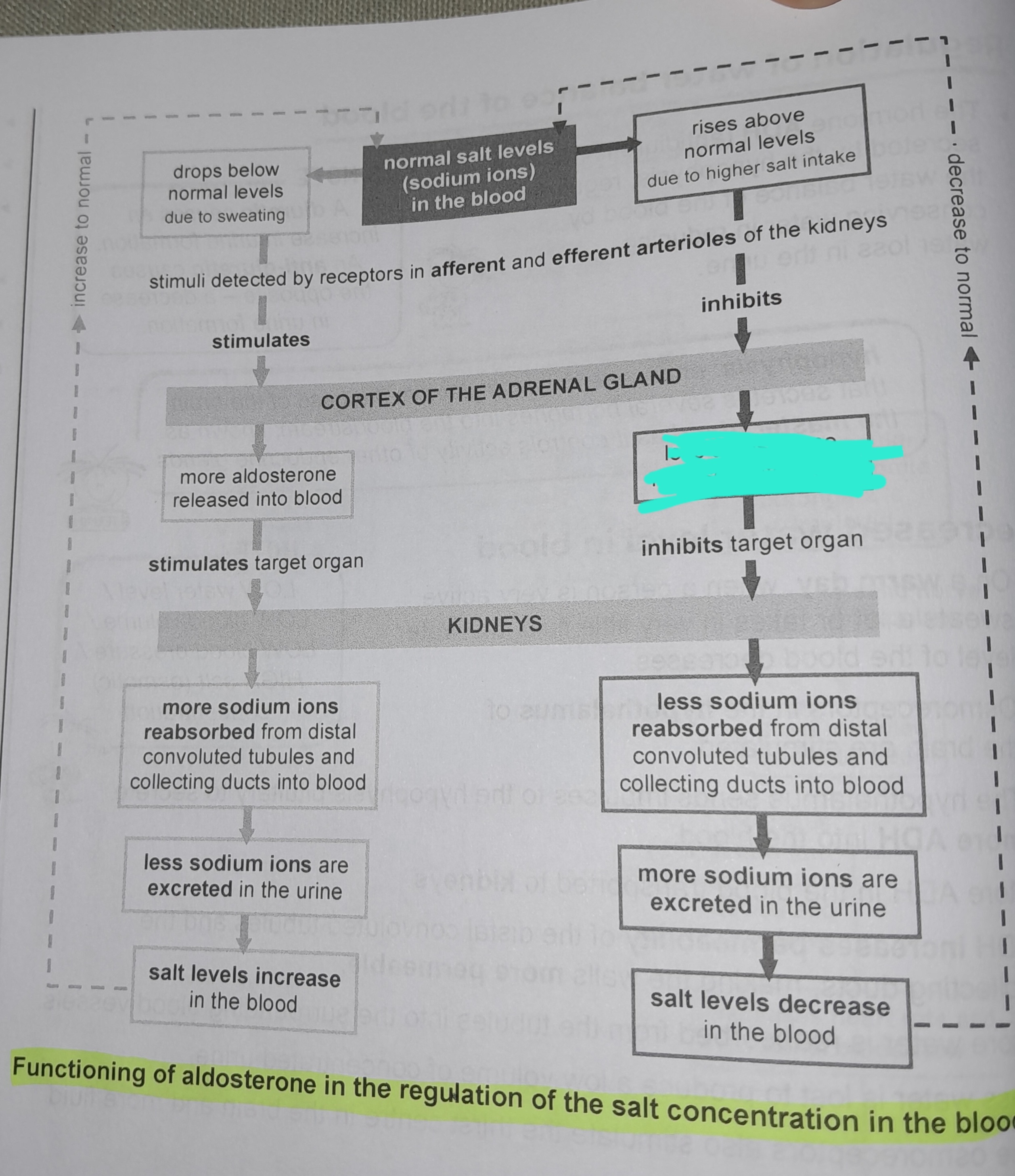
Less aldosterone released into blood
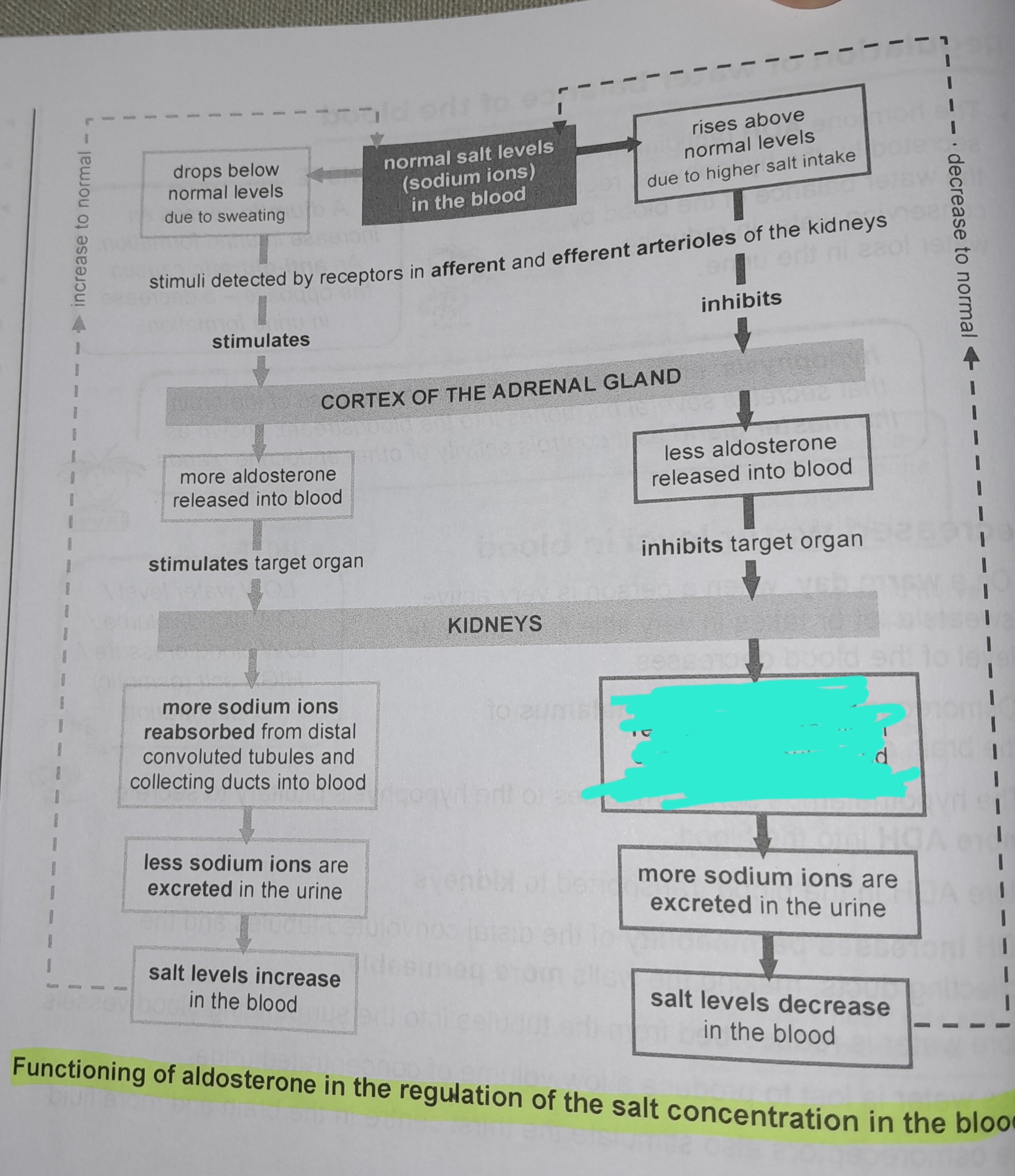
Less sodium ions reabsorbed from distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts into blood
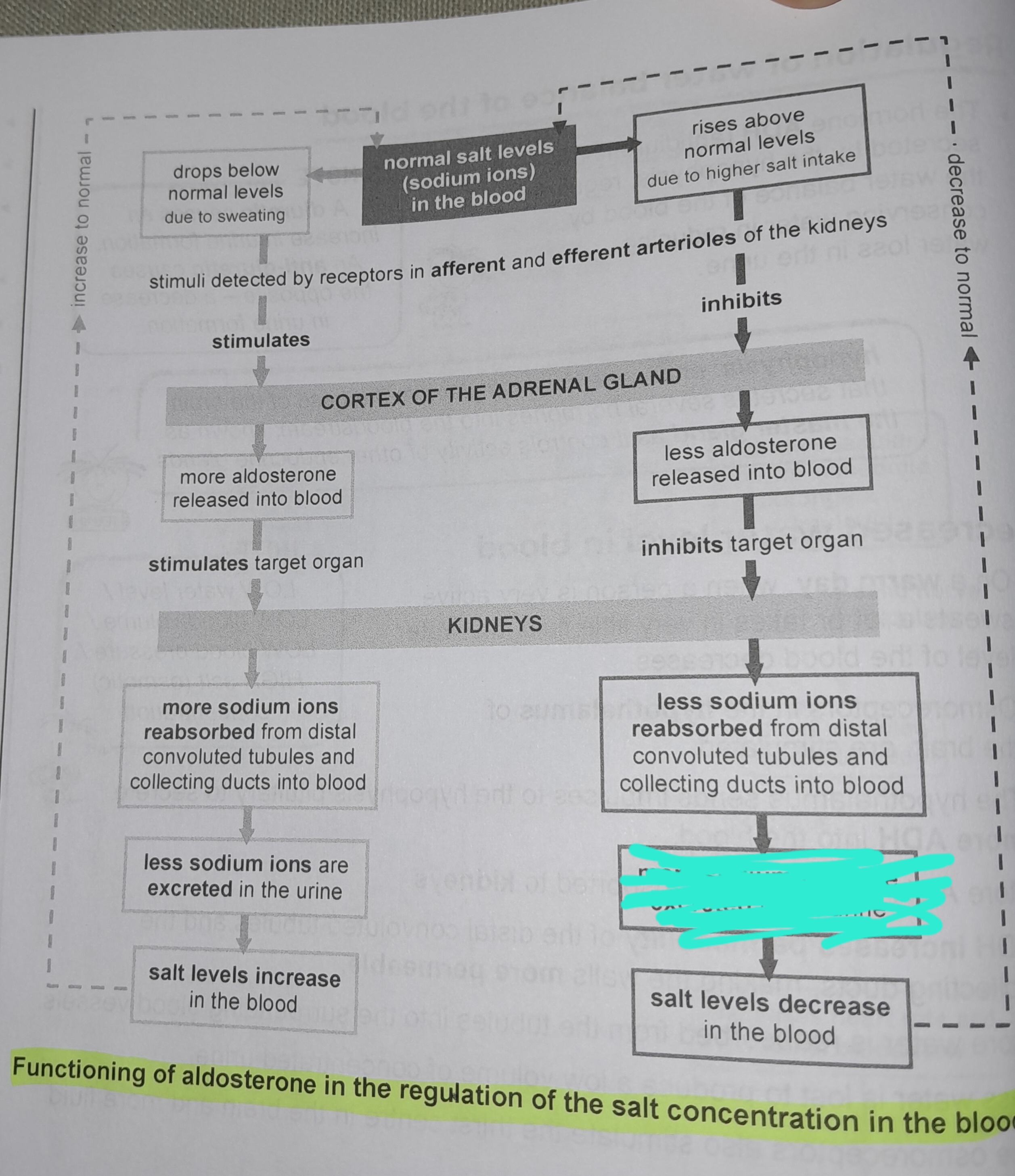
More sodium ions excreted in urine
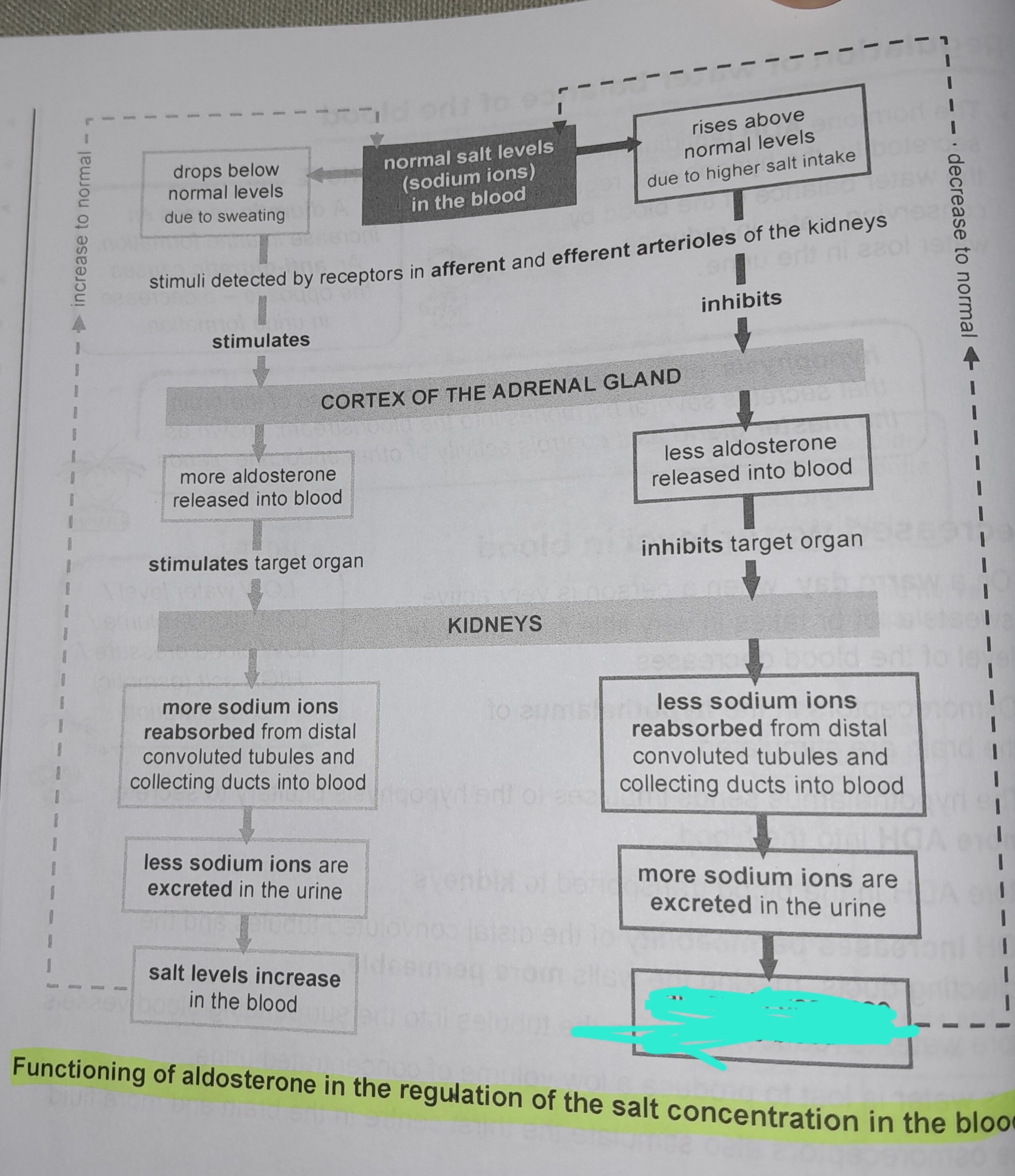
Salt levels decrease in the blood