Engineering Manufacture - Metals
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Ferrous Metals
Metals that contain iron

Examples of ferrous metals
Mild steel
Stainless steel
Cast iron

Non-Ferrous Metals
Metals that do not contain iron
Examples of non-ferrous metals
Copper
Aluminium
Lead

Alloys
A mixtures of two or more metals
Precious Metals
Rare non-ferrous metals

Examples of precious metals
Gold
Silver
Platinum

Alloys
Mixtures of two or more metals and other elements
Examples of alloys
Brass
Bronze

Examples of the aesthetic properties of metal
Colour
Surface texture
Shine
Examples of the functional properties of metal
Cost
Purpose
Weight
Size
Examples of the mechanical properties of metal
strength, plasticity, ductility, hardness, brittleness, malleability.
Examples of the forms metals comes in
Bar
Sheet
Which metals are (usually) magnetic?
Ferrous metals
Rusting
The corrosion of ferrous metals

Which metals are generally not magnetic?
Non-ferrous metals
What happens to non-ferrous metals left exposed to the air?
Oxidation
Oxidation
A layer formed on the surface of a non-ferrous metal
Properties of cast iron
Good compressive strength, hard, more brittle than other ferrous metals, poor corrosion resistance
Advantages of cast iron
Good for casting, cheap
Disadvantages of cast iron
Difficult to machine, has to be protected
Uses of cast iron
Anvils, engineering vices, engine blocks, machine tool beds

Properties of low carbon steel
Ductile, malleable, tough, lower strength than other steels
Advantages of low carbon steel
Stronger than most non-ferrous materials, relatively low cost
Disadvantages of low carbon steel
Cannot be hardened
Uses of low carbon steel
Nails and screws, nuts and bolts, car bodies

Properties of high carbon steel
Strong, hard
Advantages of high carbon steel
Can be hardened
Disadvantages of high carbon steel
Not as tough as lower carbon steel, difficult to form
Uses of high carbon steel
Tools (saw blades, hammers, chisels)

Properties of aluminium
Lightweight, heat and electricity conductor,
ductile, malleable and good resistance to corrosion

Advantages of aluminium
Lower density than steel, easily drawn and cast, recyclable.
Disadvantages of aluminium
More expensive than steel but not as strong and difficult to weld
Uses of aluminium
Drinks cans, aircraft panels

Properties of copper
Good conductor of electricity, good corrosion resistance, malleable and ductile

Advantages of copper
Easily drawn into thin wires and sheets, can be recycled and easily soldered
Disadvantages of copper
Expensive, will tarnish/change colour over time
Uses of copper
Wires, water pipes, jewellery
Properties of tin
Easy to melt, soft, low toxicity level, high corrosion resistance, malleable
Advantages of tin
Non toxic, corrosion resistant, low melting point
Disadvantages of tin
Soft (so usually alloyed)
Uses of tin
Solder, tin can plating

Properties of zinc
Low melting point, heat conductor, corrosion resistant
Advantages of zinc
Good for die-casting
Disadvantages of zinc
Brittle
Uses of zinc
Street lamp posts, motorway safety barriers.

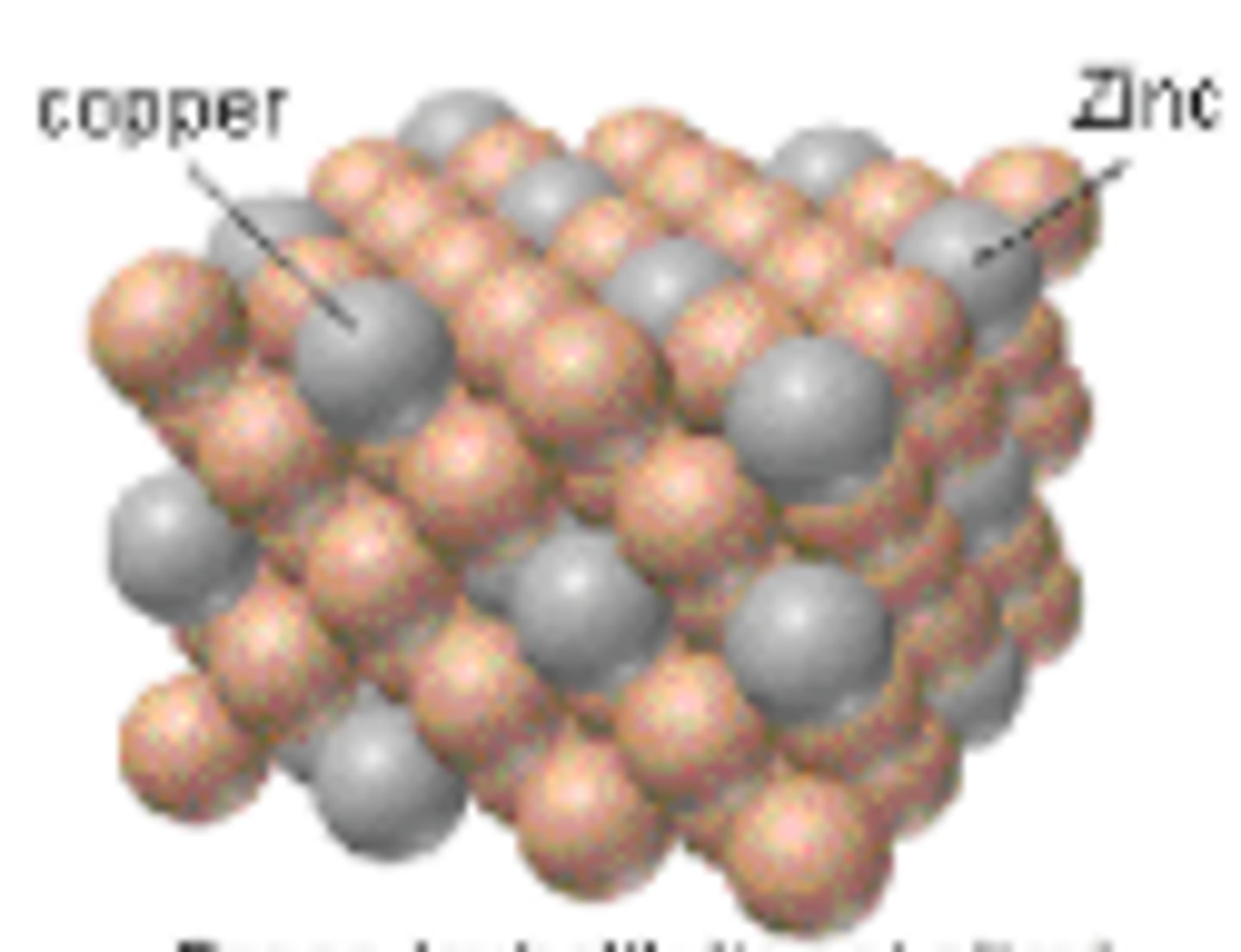
Properties of brass
Good corrosion resistance, casts well, good conductor of heat and electricity, alloy of copper and zinc
Advantages of brass
Can be machined to a high finish
Disadvantages of brass
Difficult to cast
Uses of brass
Doorknobs, musical instruments

Properties of stainless steel
Strong, hard, good corrosion resistance
Disadvantages of stainless steel
Difficult to machine, relatively expensive
Advantages of stainless steel
Doesn't rust
Uses of stainless steel
Cutlery, medical equipment, sinks

Properties of high speed steel
High hardness, high wear resistance and high heat resistance
Advantages of high speed steel
Retains hardness at high temperatures, resistant to friction.
Disadvantages of high speed steel
Can only be ground
Uses of high speed steel
Tools to be used at high speeds

Common uses of silver
Jewellery, silverware, in electronics, brazing alloys, photography
Properties of titanium
Corrosion resistant, low density, very strong
Advantages of titanium
Corrosion resistant, high strength to weight ratio
Disadvantages of titanium
Expensive

Uses of titanium
fighter aircraft, artificial hip joints, pipes in nuclear power stations
Properties of bronze
Hardness: resistance to scratching and wear,
Tough: resistance to breaking or bending,
Corrosion resistant.
Advantages of bronze
Corrosion resistant, easy cast, recyclable.
Disadvantages of bronze
Expensive
Uses of bronze
Bearing, statues,
Air, water & steam valves,
Coins.
Boat propellers

Are metals sustainable?
Metals are a non-renewable resource, but can be recycled well
Is steel sustainable?
Steel is infinitely recyclable, easily recyclable due to its magnetic properties, durable and strong (so long lasting), needs little maintenance to protect from corrosion
Is copper sustainable?
Copper can be difficult to recycle (due to its usage in small amounts in electronics etc), extraction has a high environmental toll, but has high conductivity so efficient when used for wiring
Common Shapes of metals
Round Bar
Square Bar
Hexagonal Bar
Strip
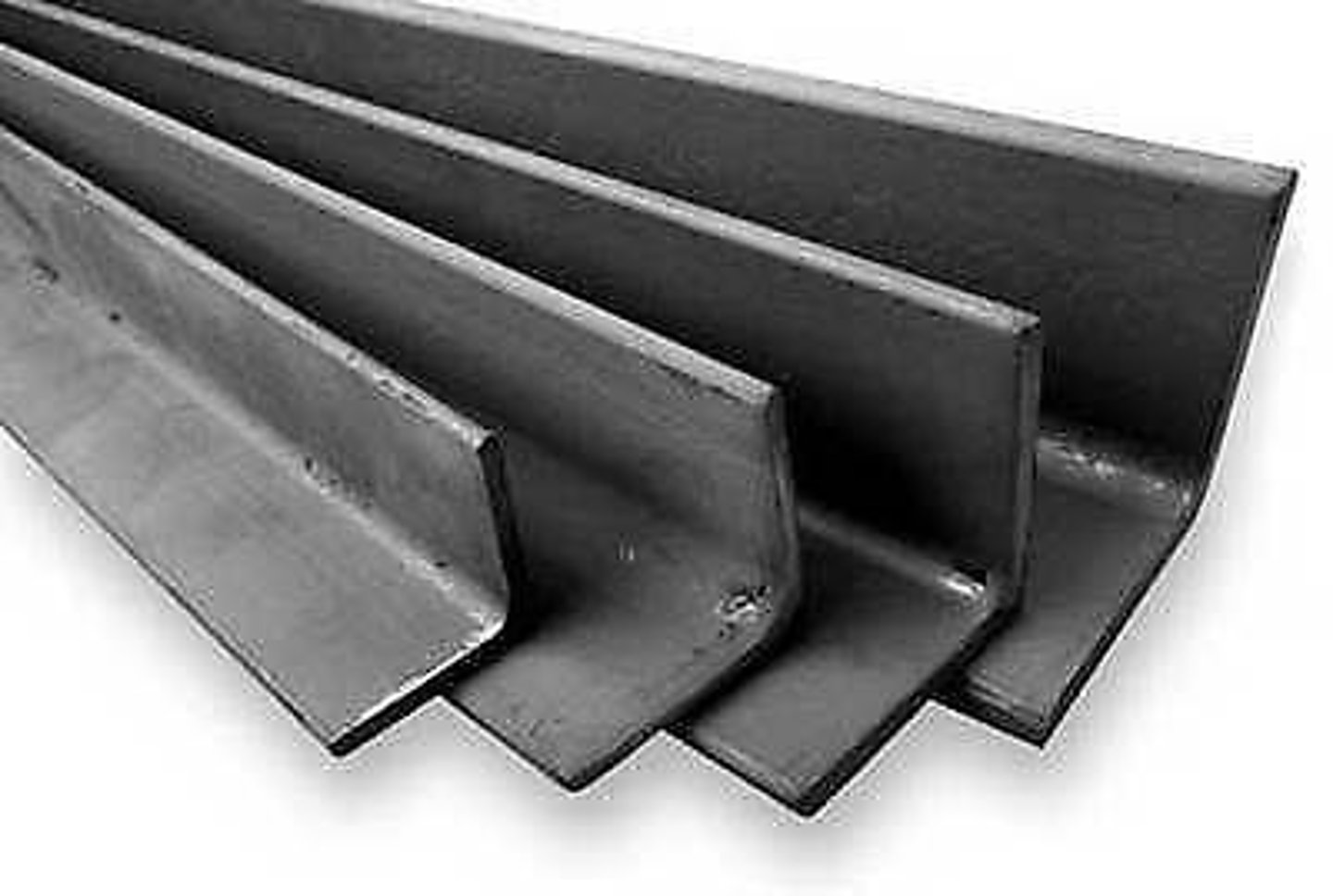
Angle Iron
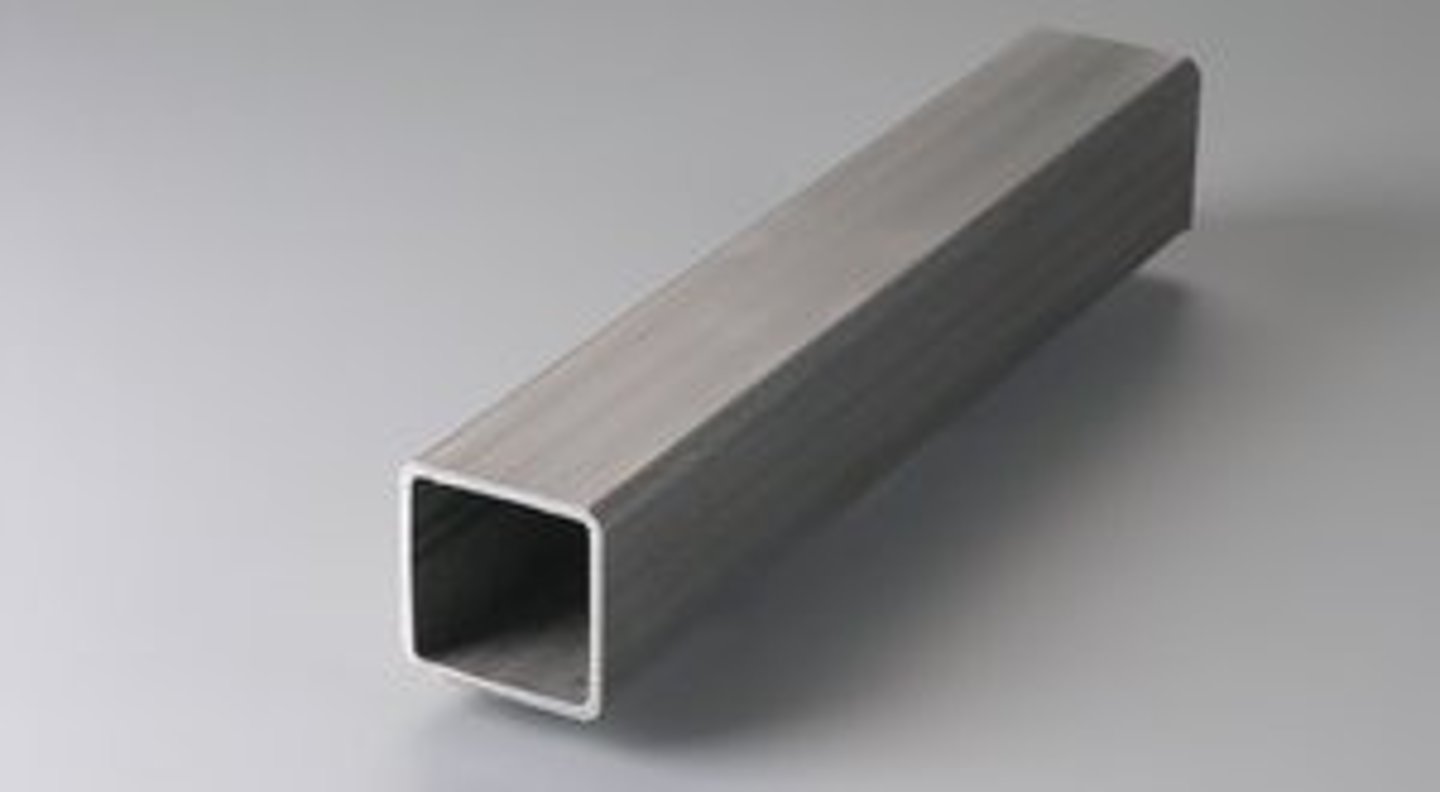
Square Tube
Round Bar / Rod
Solid round shape

Angle Iron
Piece of strap steel bent into 90 degree angle with holes in it for attaching as a brace.

Hexagonal Bar / Rod
Solid hexagonal shape

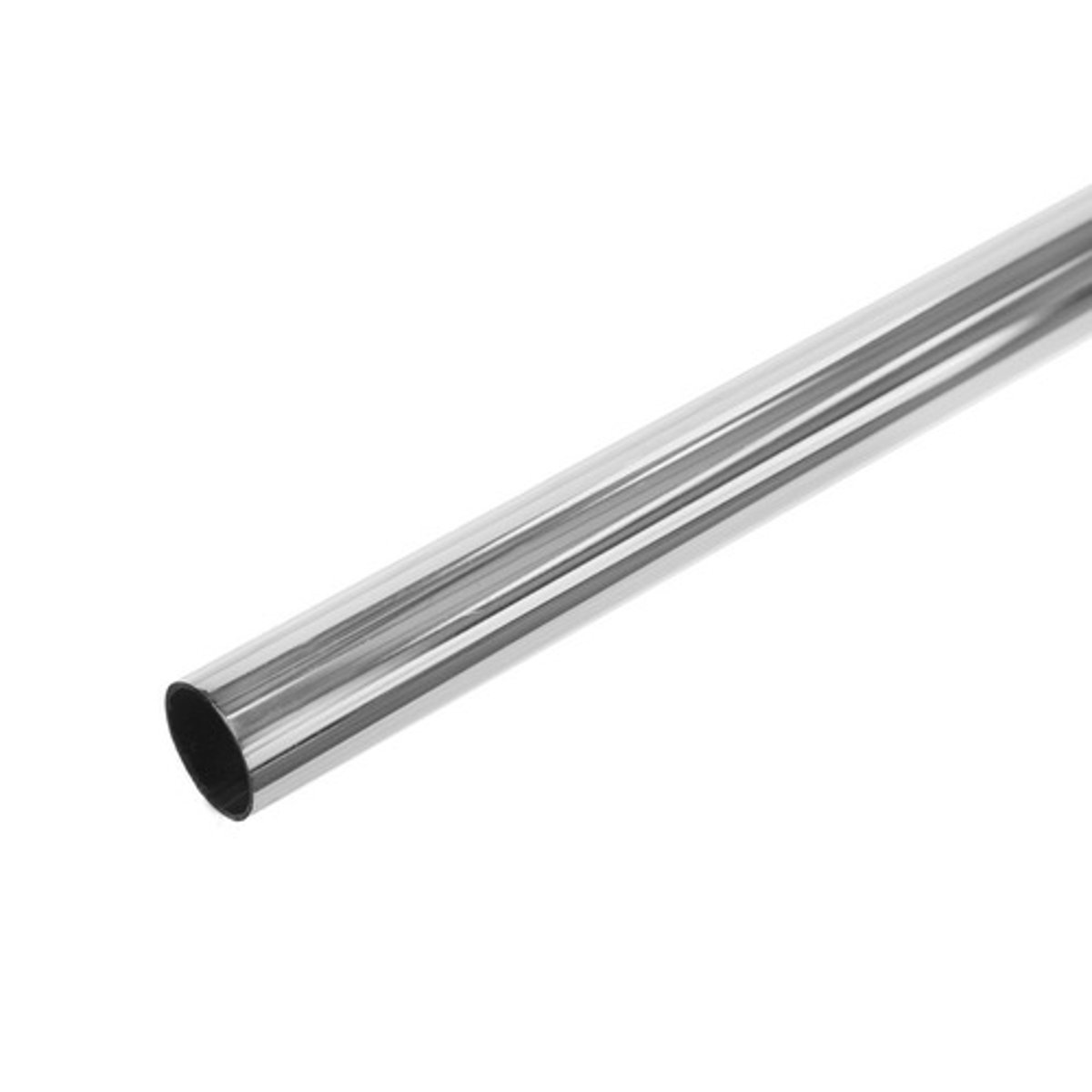
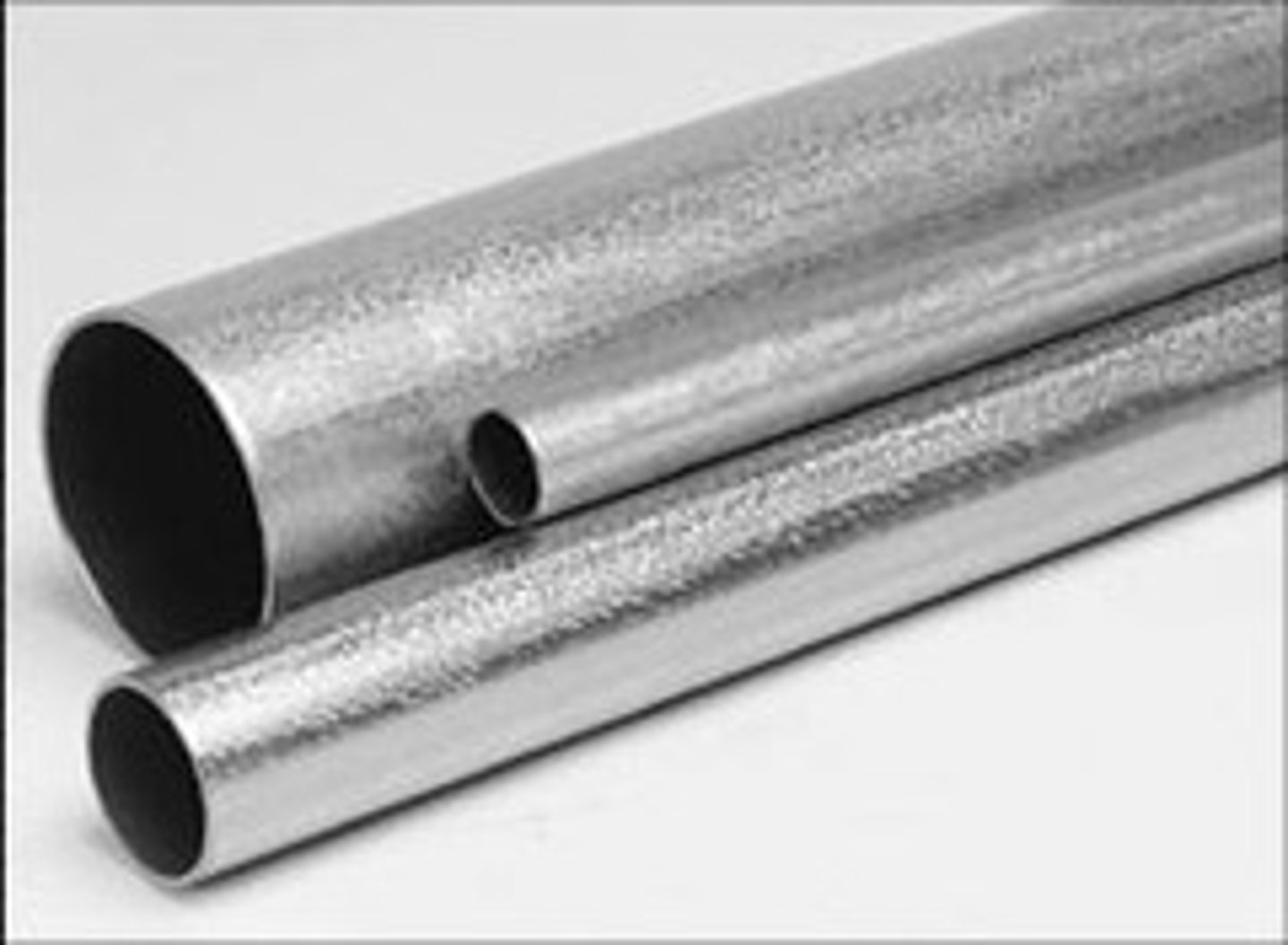
Tube
A piece of bar with a hole along its length

Square Tube

Round Tube

Strip Metal
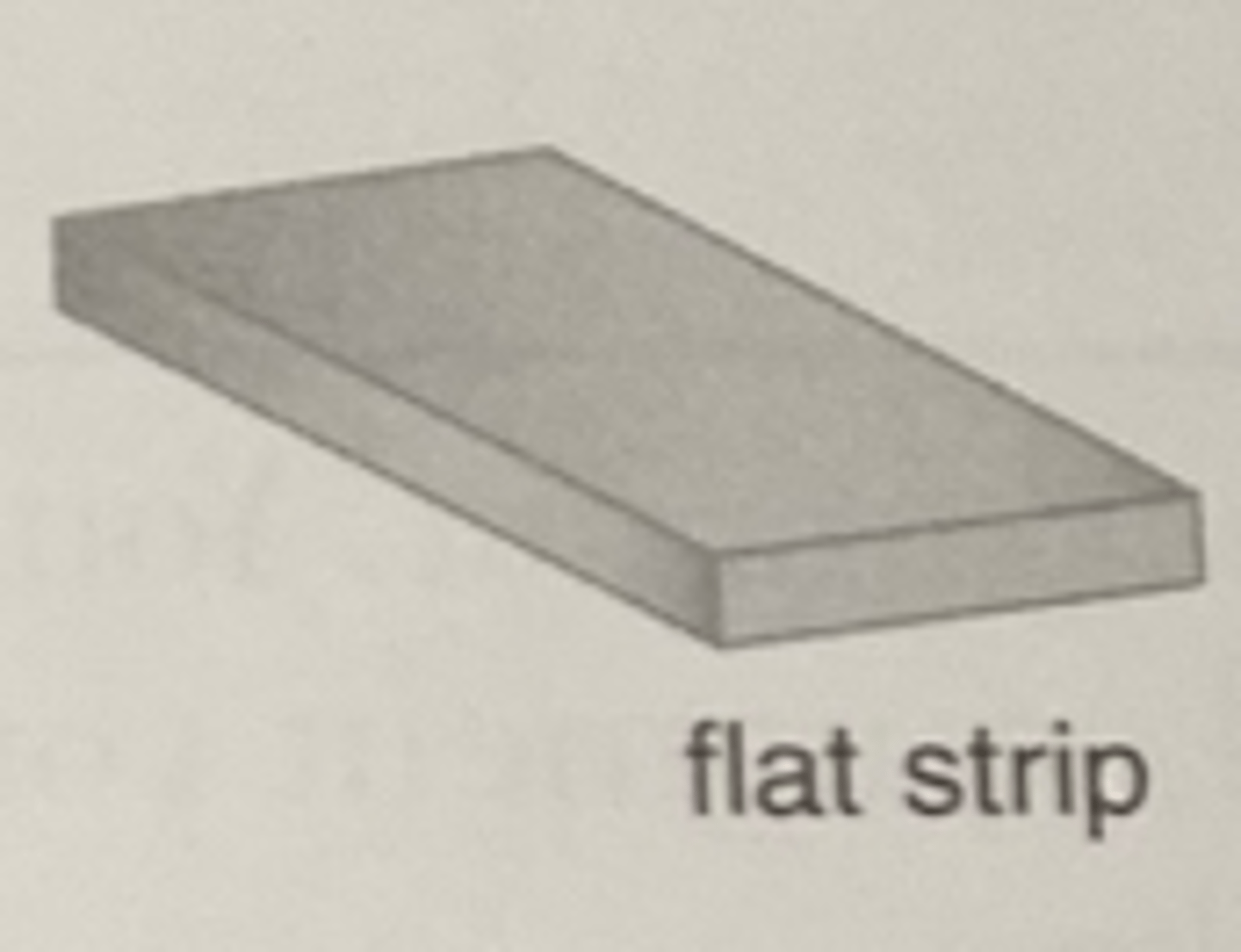
Metal Powder
