Forensics Test - Fingerprints
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Fingerprint
An impression of the pattern of ridges on the last joint of a person's finger
The study of fingerprints is also known as:
dactyloscopy
William Herschel
Required Indians to put fingerprints on contracts and used them as a means of identifying prisoners
Henry Faulds
Claimed that fingerprints did not change over time and that they could be classified for identification (true)
Alphonse Bertillon
Proposed anthropometry: body measurements as a means of identification
Francis Galton
Developed a primary classification scheme based on loops, arches, and whorls
Edward Richard Henry
Worked in collaboration with Galton, instituted a numerical classification system
Fingerprints are _____________ characteristics
individual
Fingerprints remain ____________ during a person's lifetime
unchanged
-Attempts to change it only make it more unique
Fingerprints have characteristic _______________ that allow them to be systematically classified
ridge patterns
When are fingerprints formed?
During fetal development
Which layer of skin are fingerprints on?
Dermis (2nd layer)
The __________ determine ridge structure of the fingerprints
papillae
3 basic patterns of fingerprints
Loops, whorls, arches
Delta
A triangular area
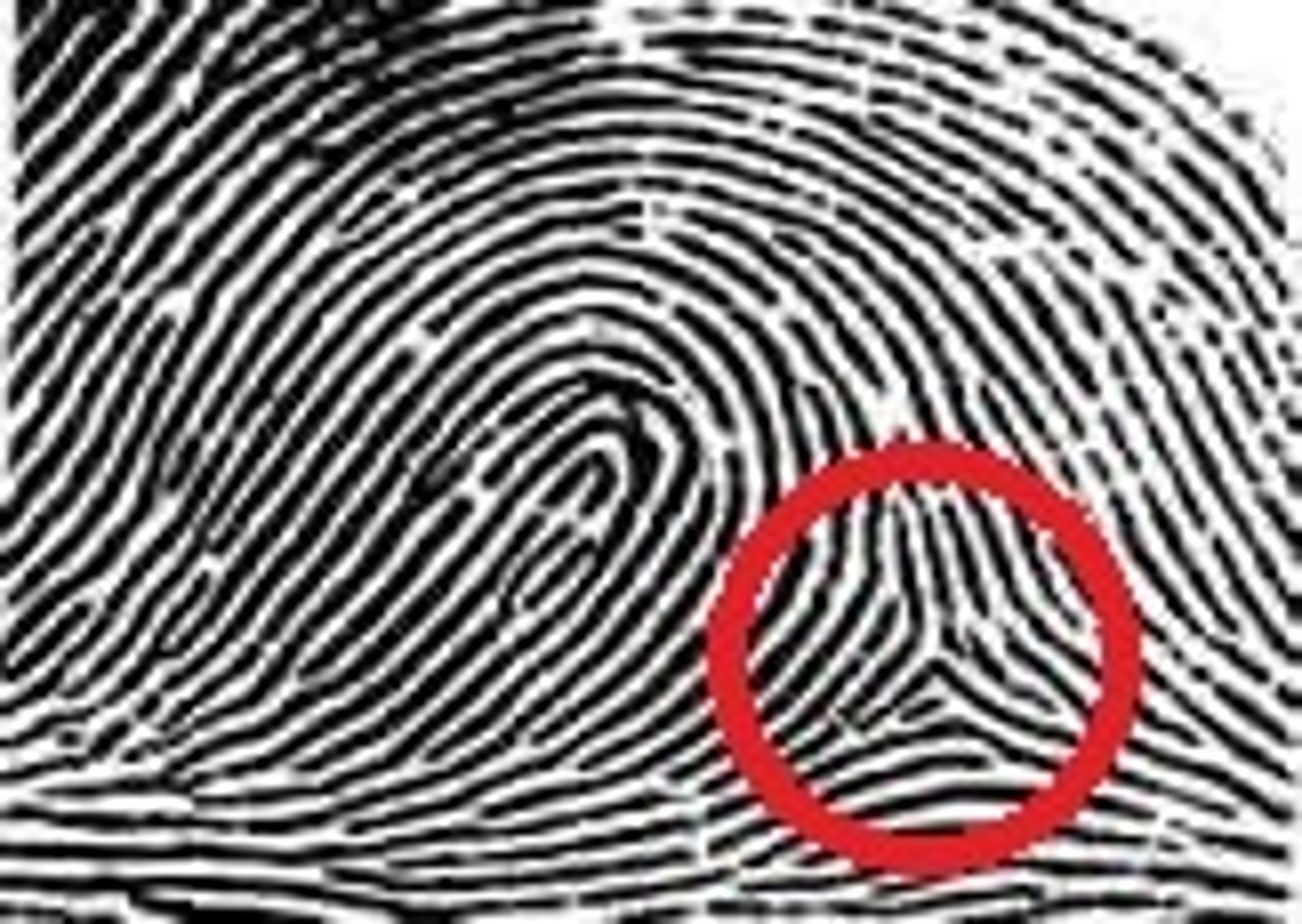

Core
Center of pattern
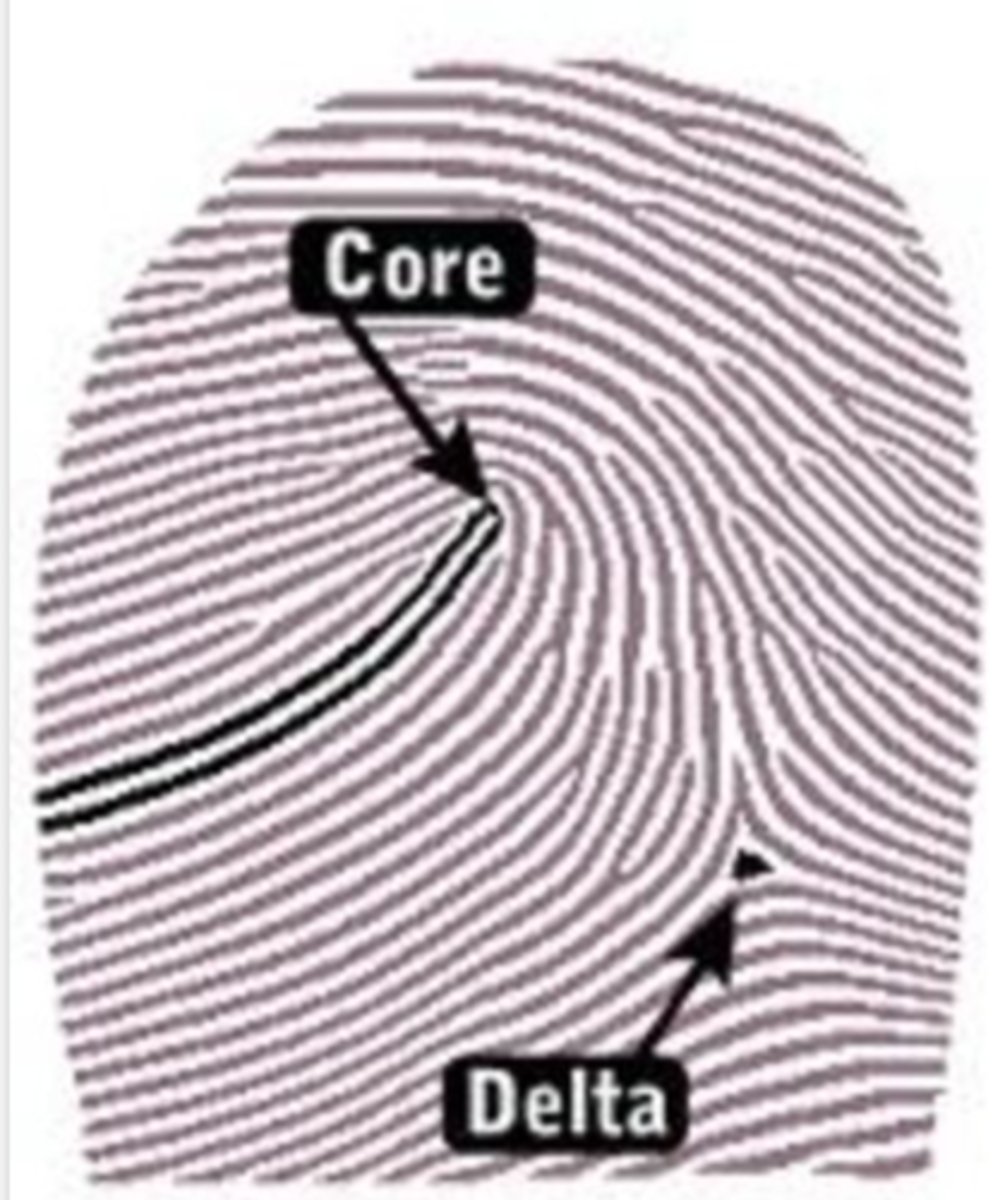
Loop
-Consists of one or more ridges which enter and exit from the same side of the print
-Must contain 1 delta and 1 core
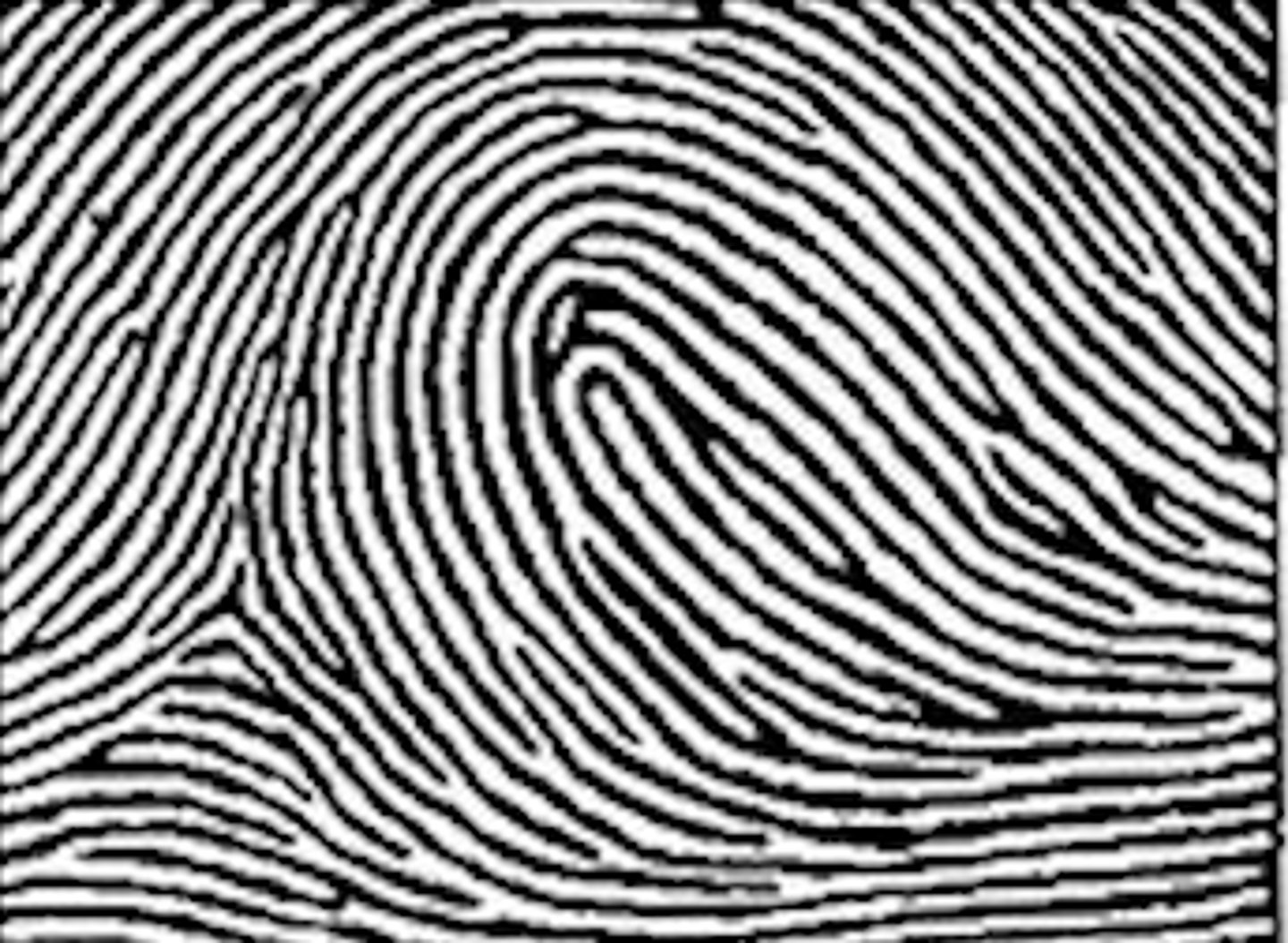

____% of all fingerprints are loops
60
Types of loops
Ulnar and radial
Ulnar loop
Enters and exits towards the ulnar bone (pinky side)
Radial loop
Enters and exits towards the radius (thumb side)
Whorl
2 deltas and a core
____% of fingerprints are whorls
35
Types of whorls
Plain, central pocket, double loop, accidental
Plain whorl
Must have at least 1 ridge that makes a complete circuit around the fingerprint (closed circle, does not enter or exit)
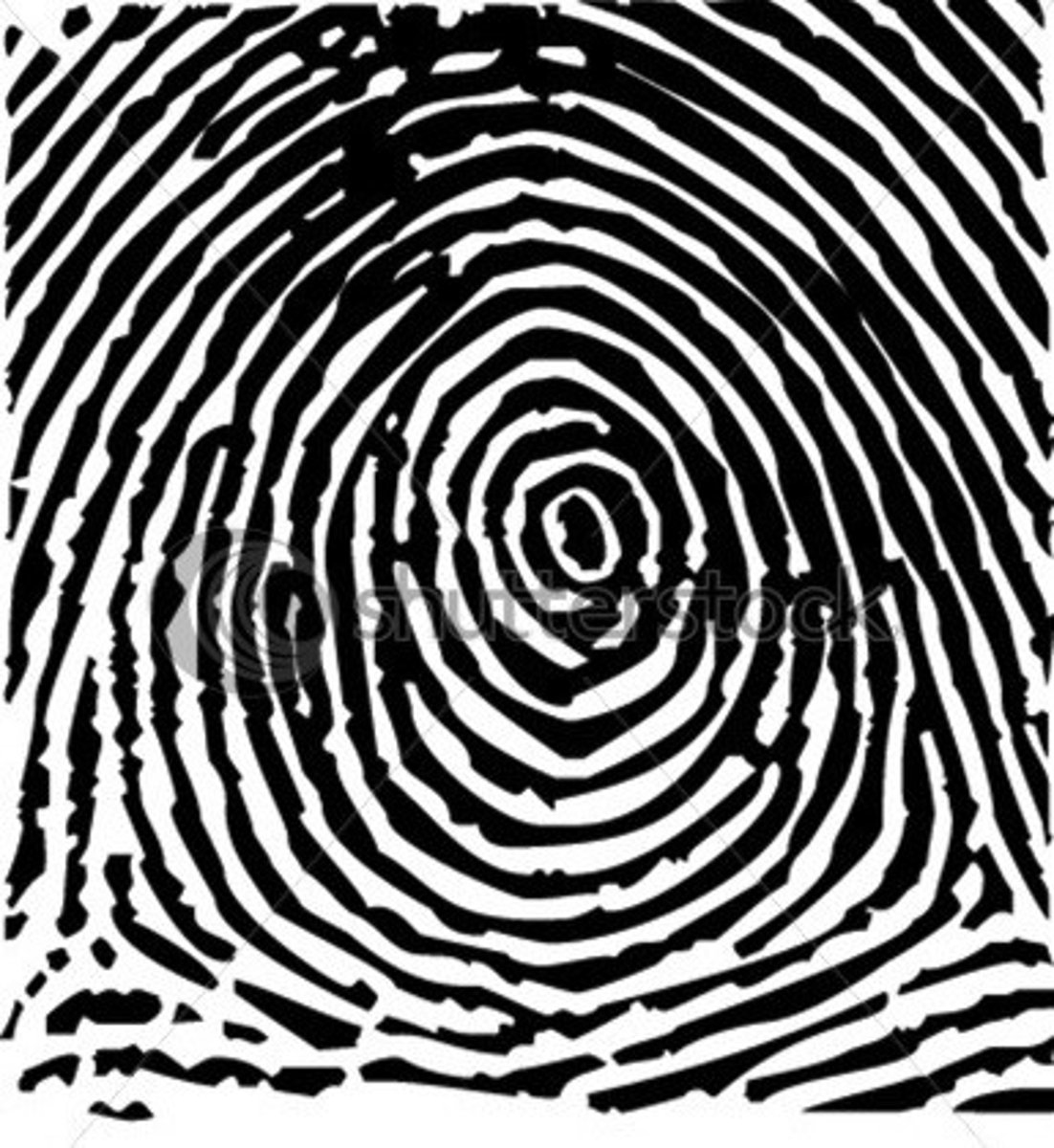

Central pocket whorl
Contains at least 1 ridge that goes all the way around inside of a loop (it looks like a loop except with at least 1 connected ridge in the middle)
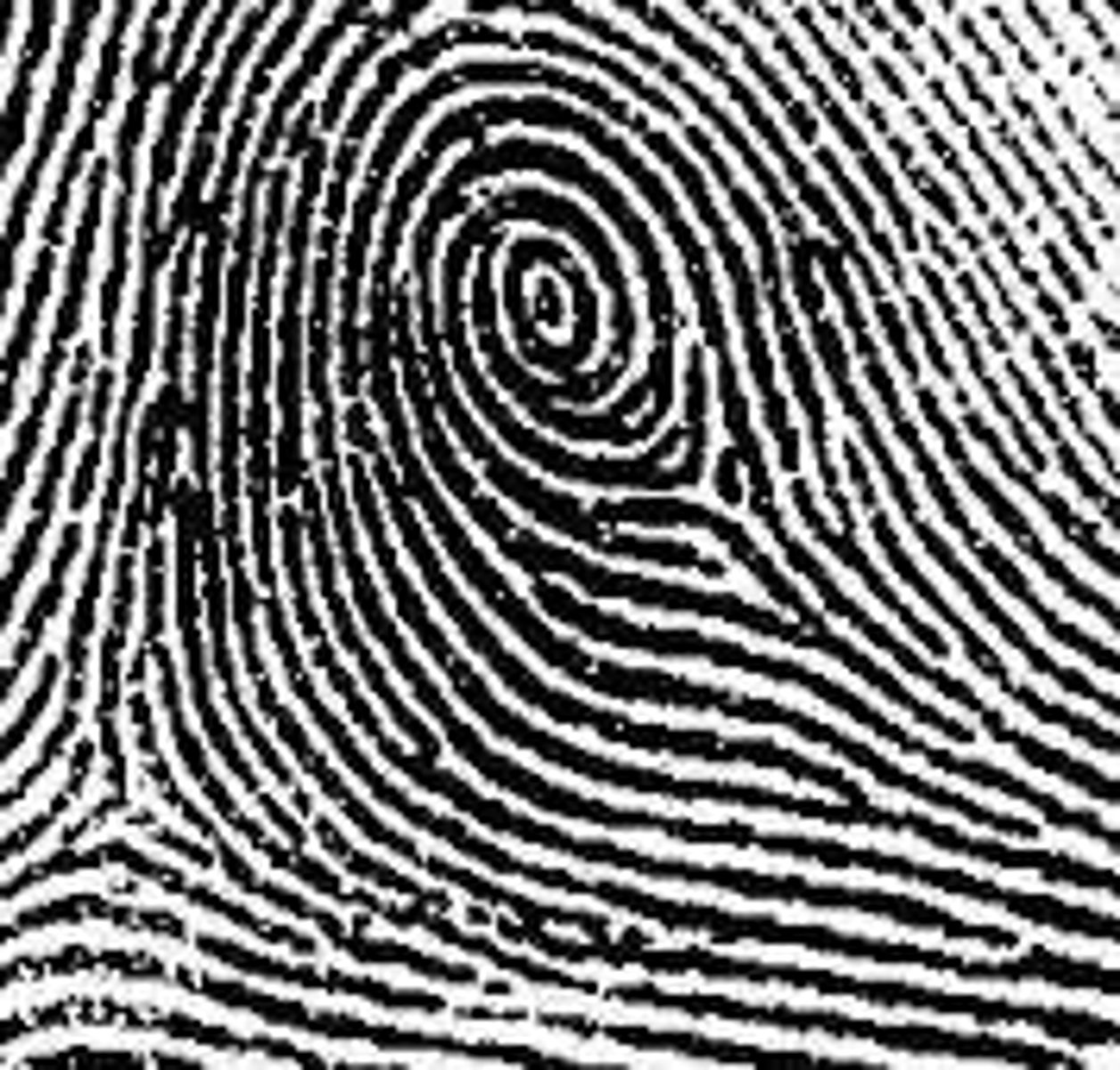

Double loop whorl
Contains 2 loops within the same point (even though they're loops, 2 deltas makes it a whorl)
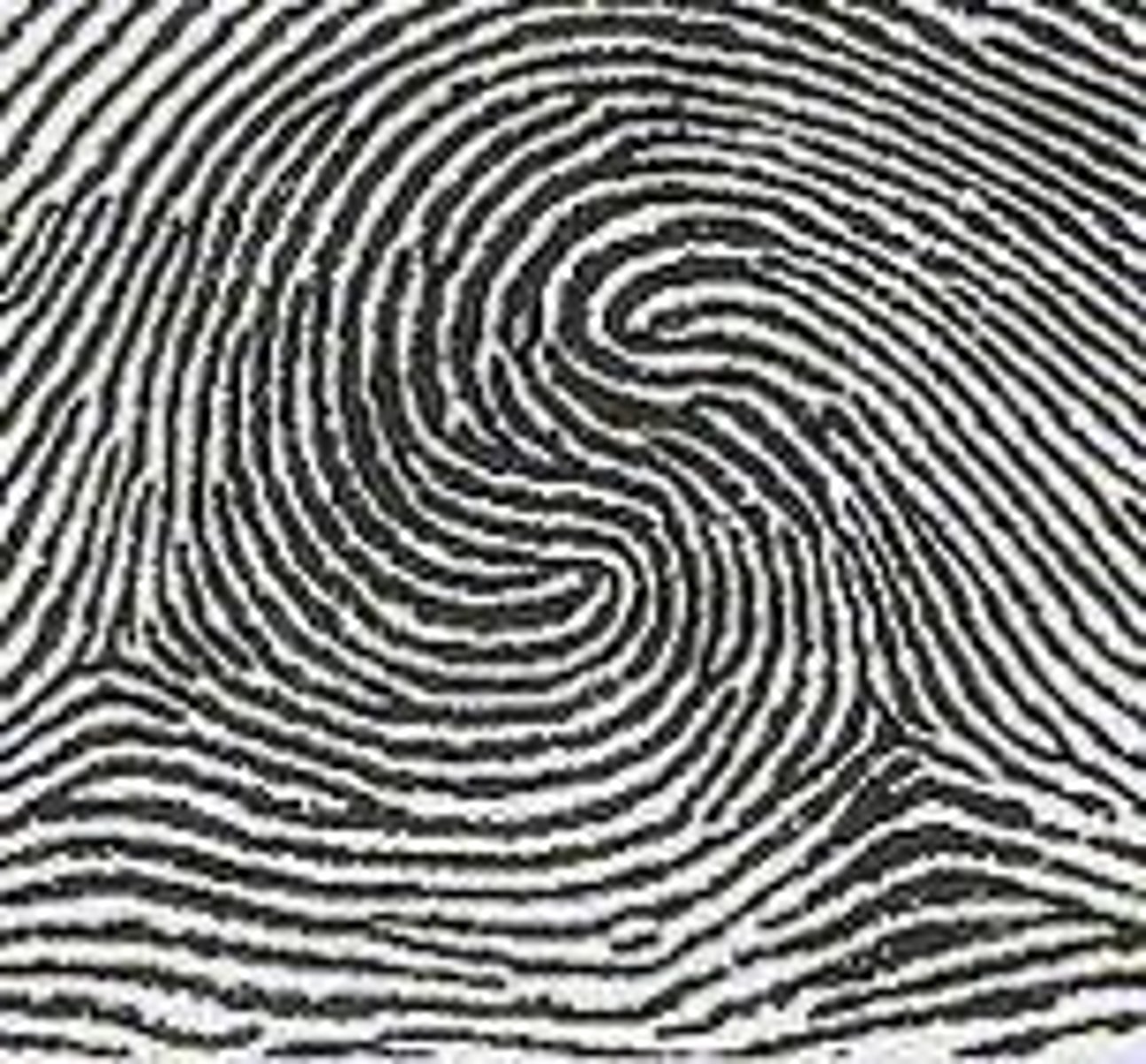

Accidental whorl
Any combination of patterns not covered by other types
Arch
No deltas and no core
____% of fingerprints are arches
5
Types of arches
Plain and tented
Plain arch
The ridges enter one 1 side and exit from the opposite side
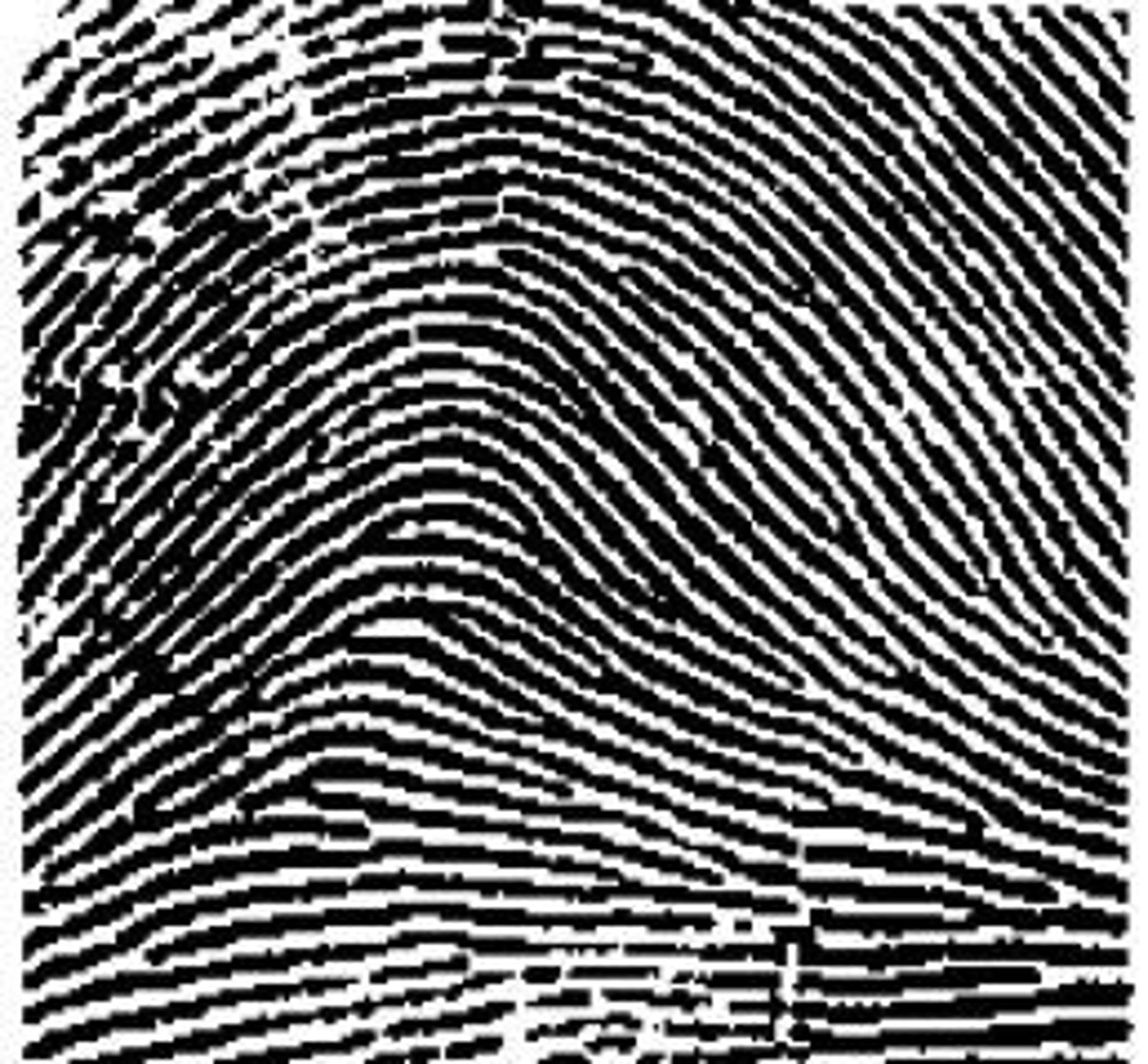

Tented arch
Same as plain arch except with a sharp peak at the center
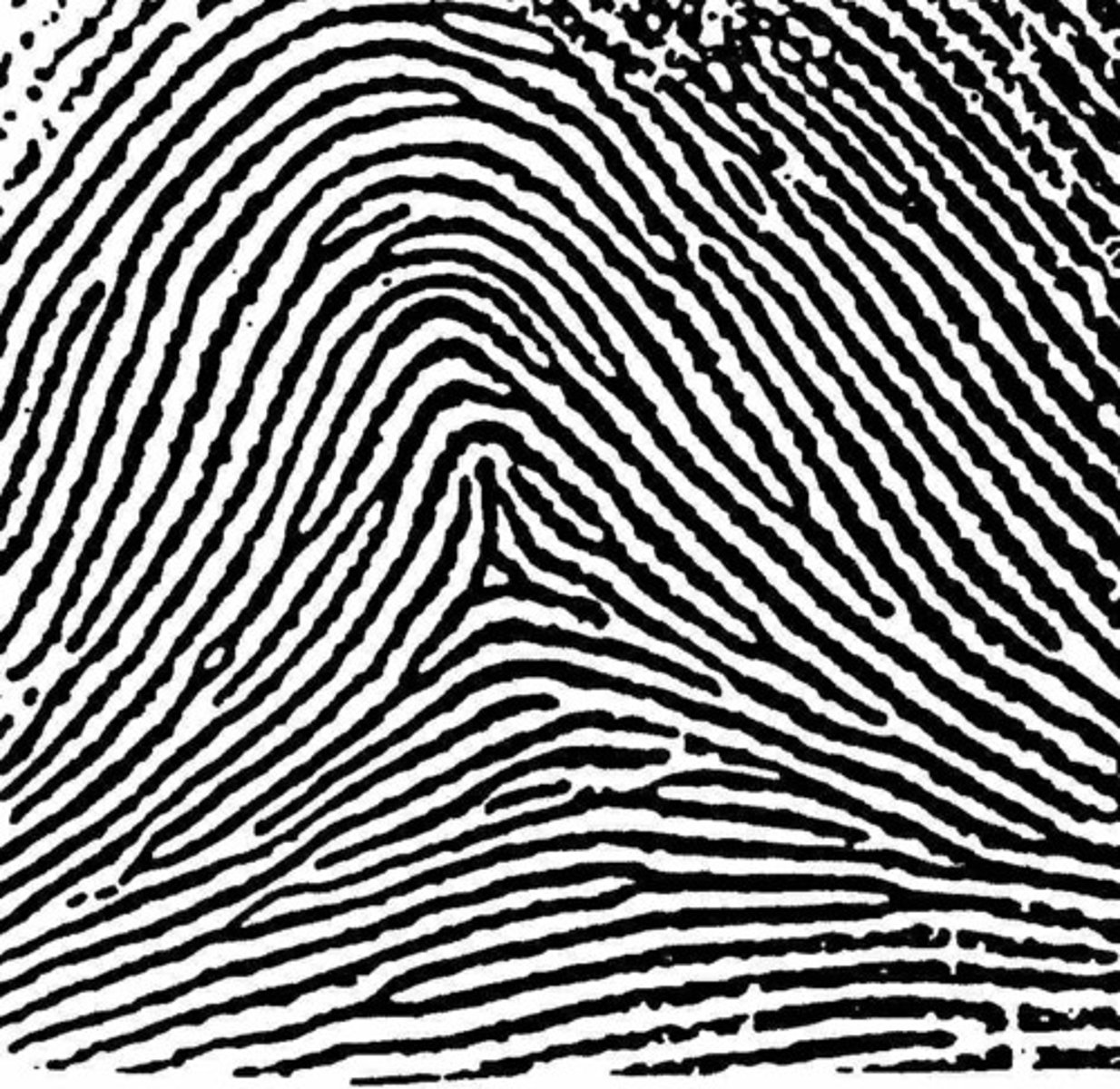

Minutiae
Parts of the fingerprint that are defining characteristics
Types of minutiae
Ridge ending, island/short ridge, bridge, eye/enclosure, delta, bifurcation, dot, spur, double bifurcation, trifurcation
Ridge ending (you probably don't have to know the definitions just the pictures but I put them because why not)
Any place where a ridge stops
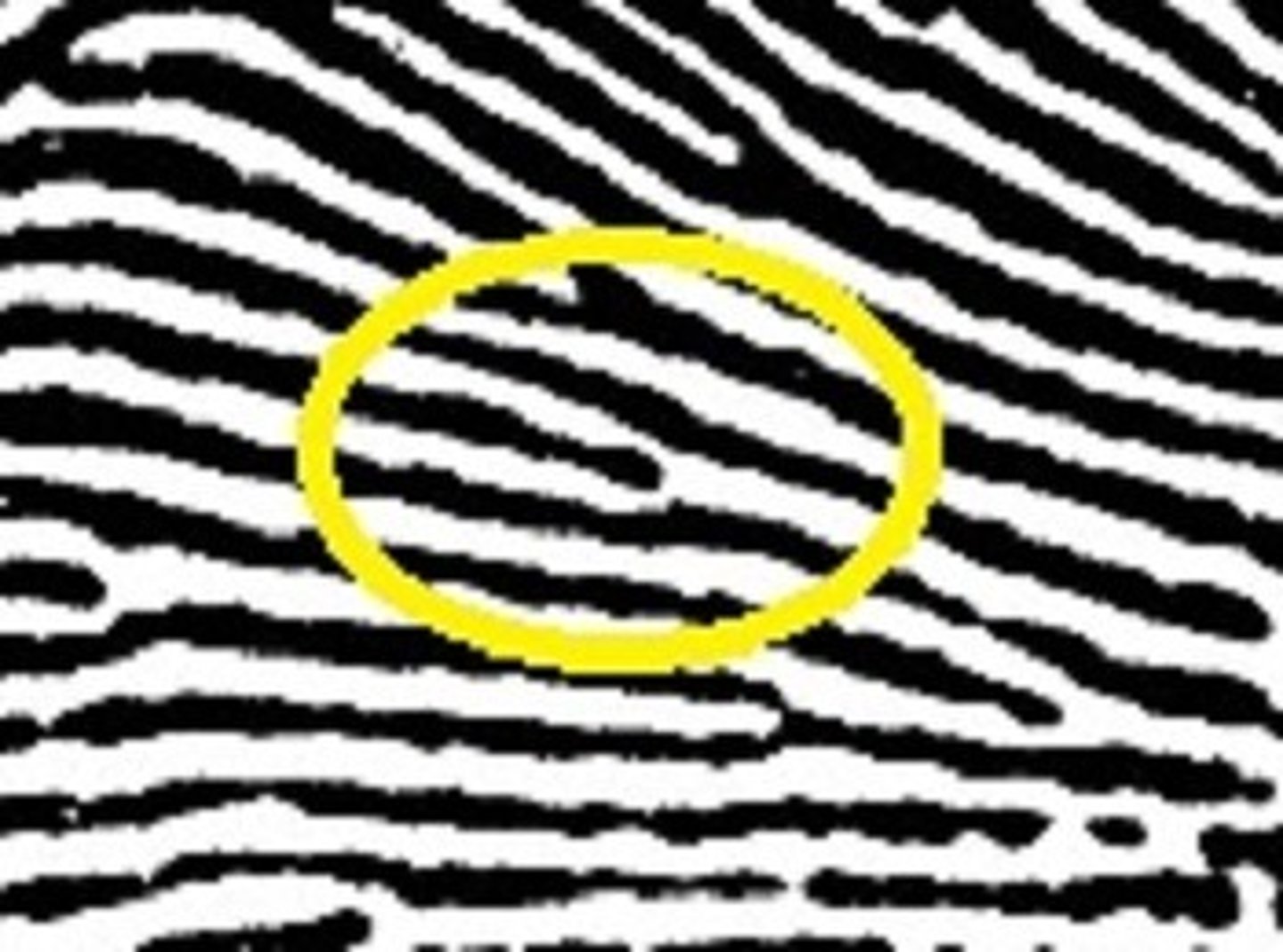

Island/short ridge
Small line
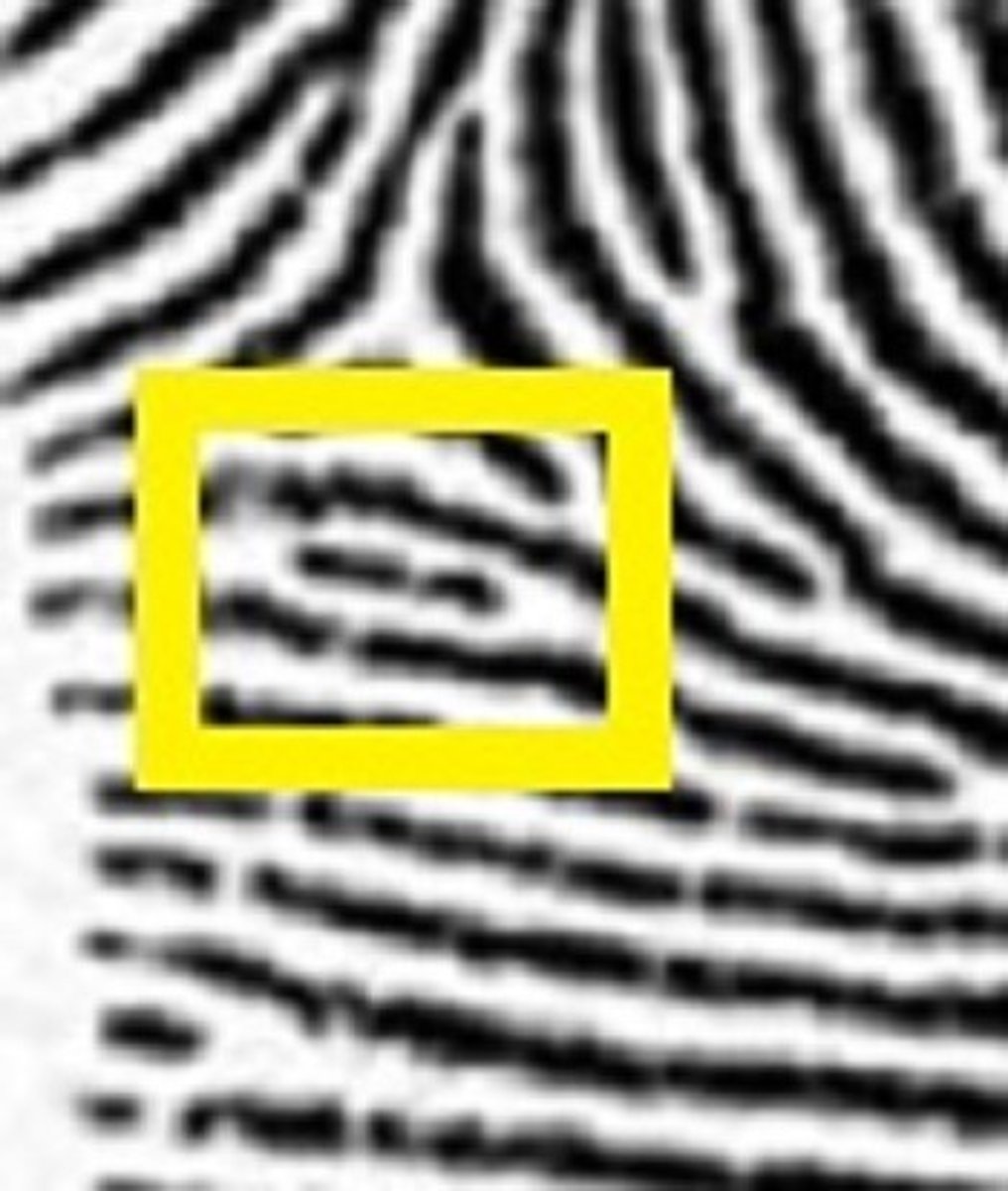

Bridge
Short line connecting two ridges
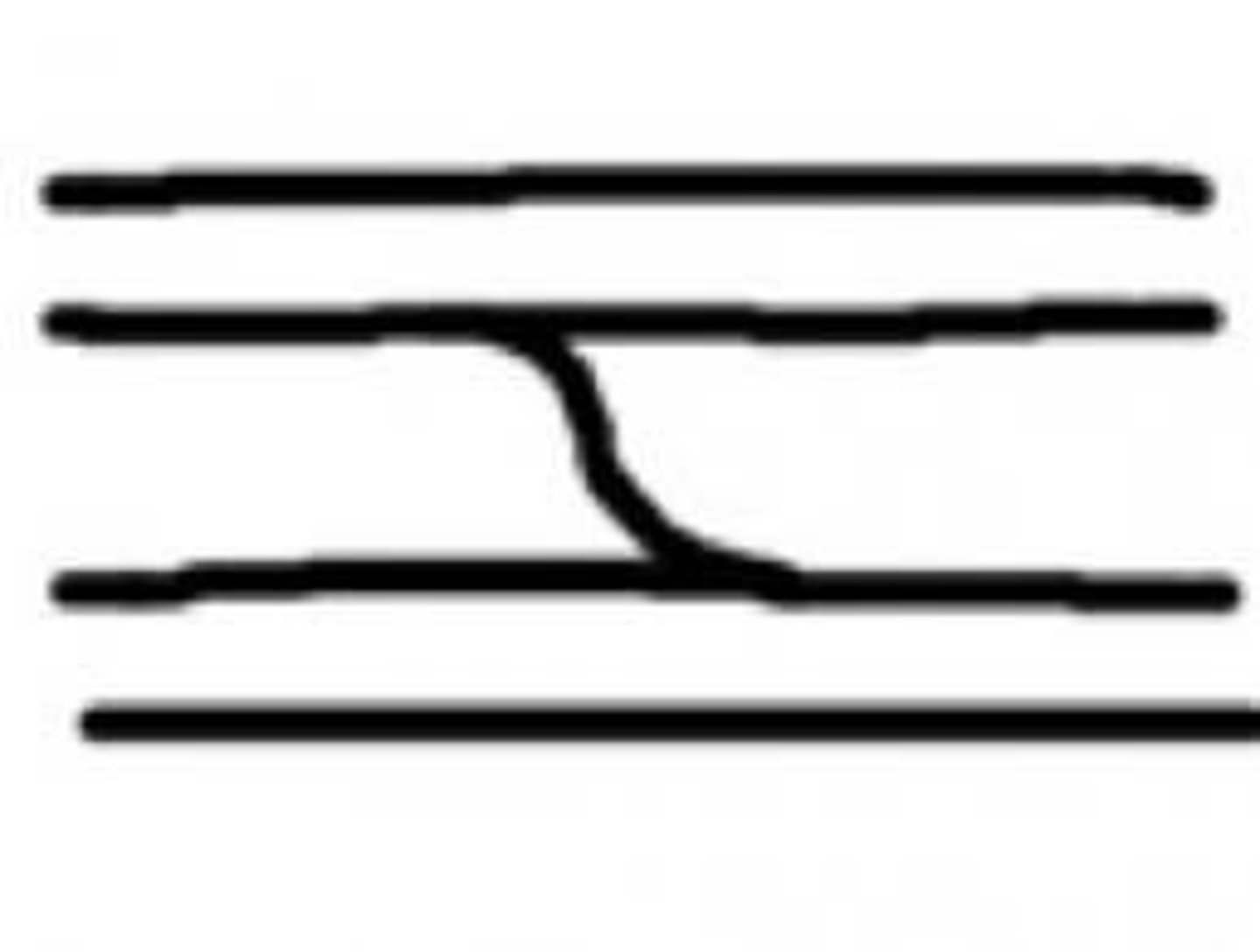
Eye/enclosure
A ridge that bifurcates and reunites a short time after to form a single ridge
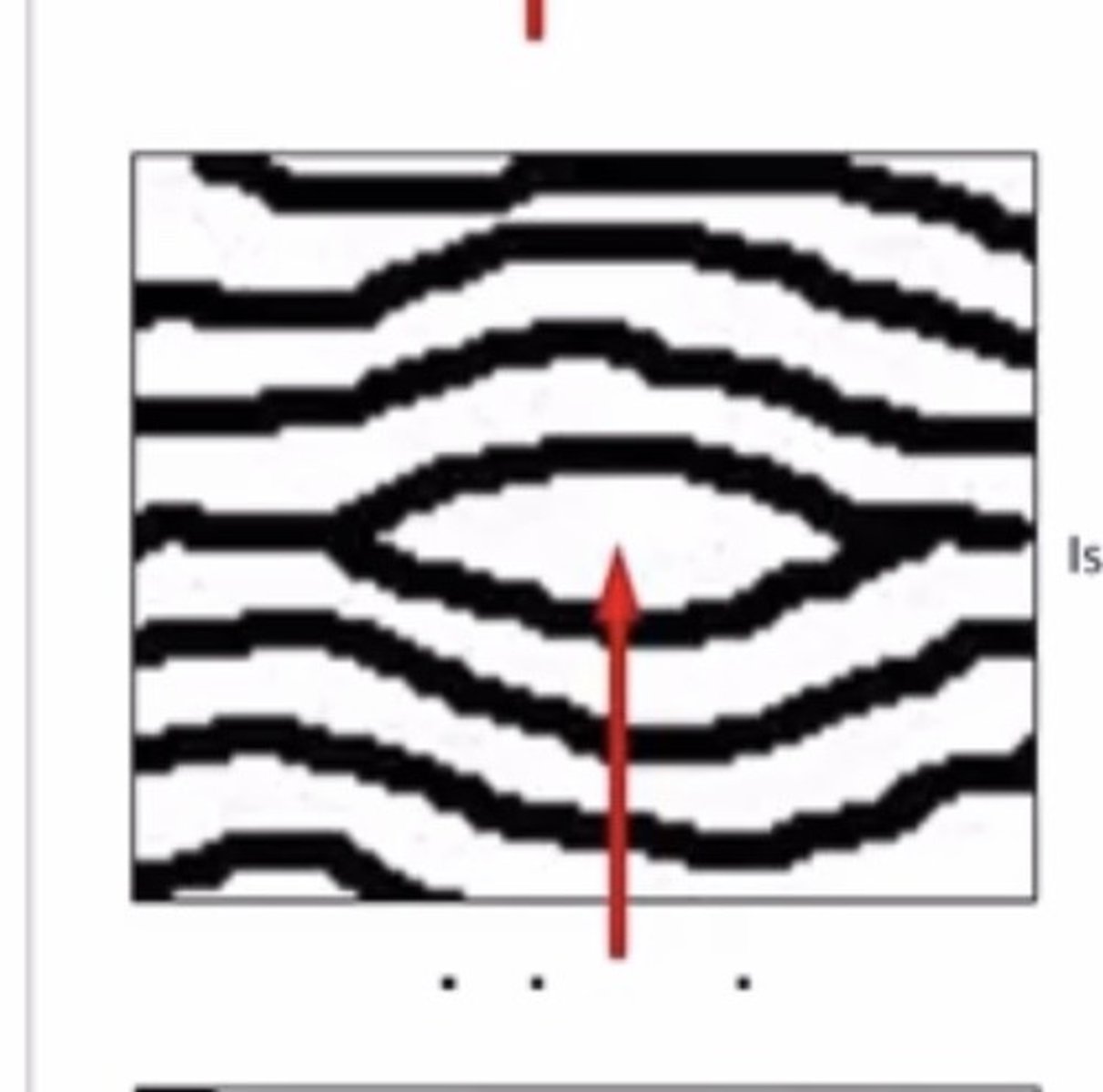
Bifurcation
A ridge that splits in 2
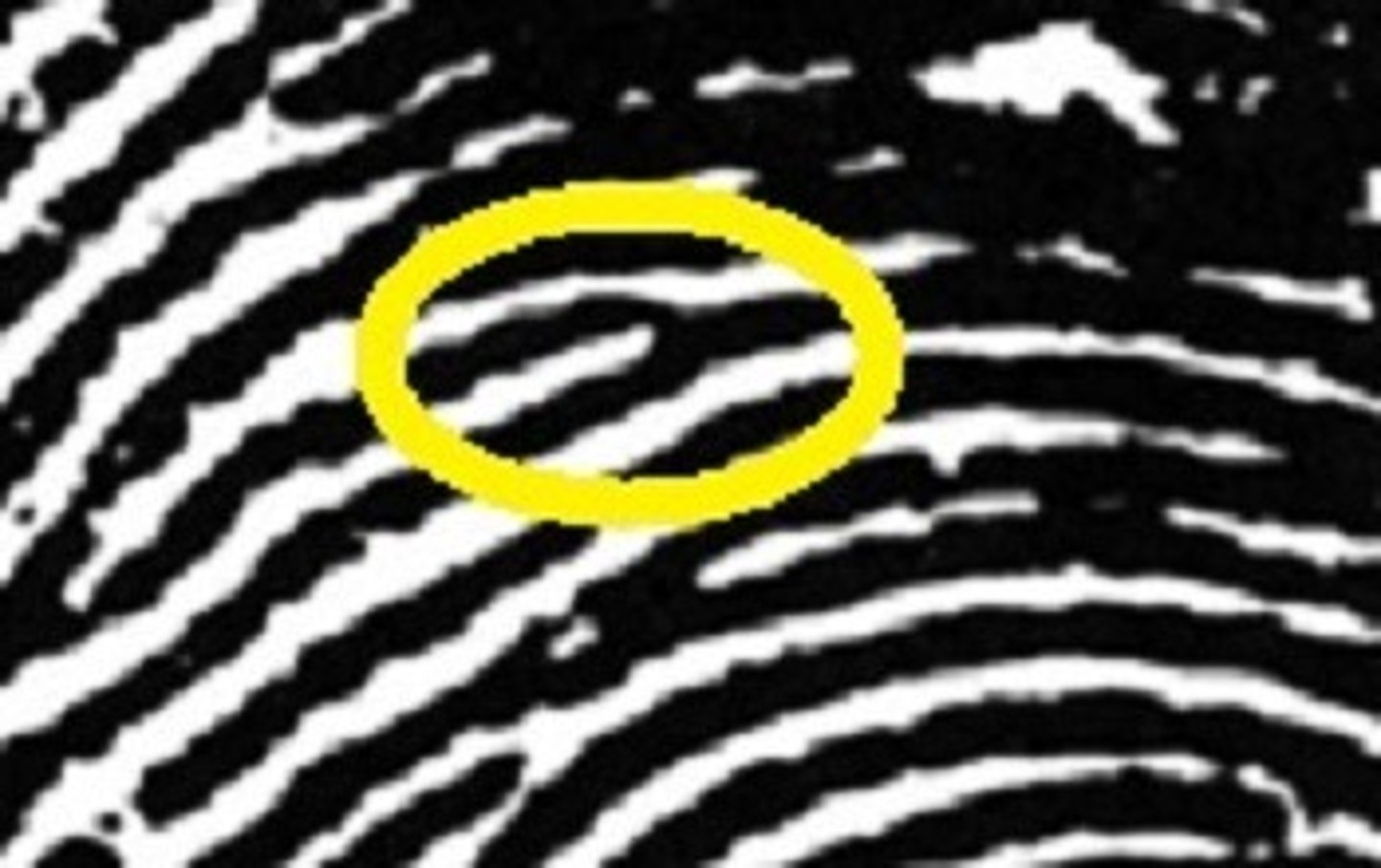

Dot
Self-explanatory i hope
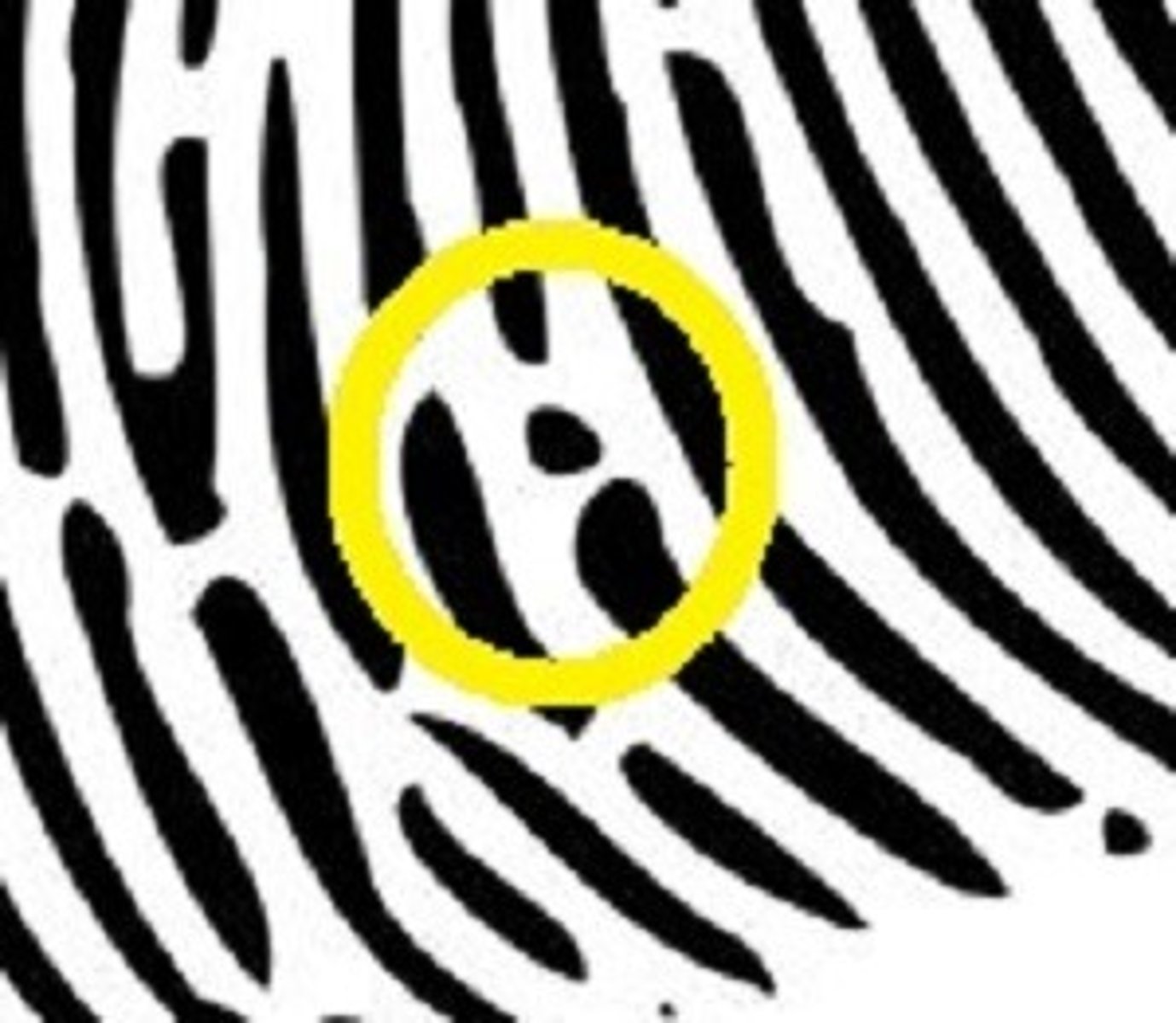

Spur/hook
A short ridge branching off another
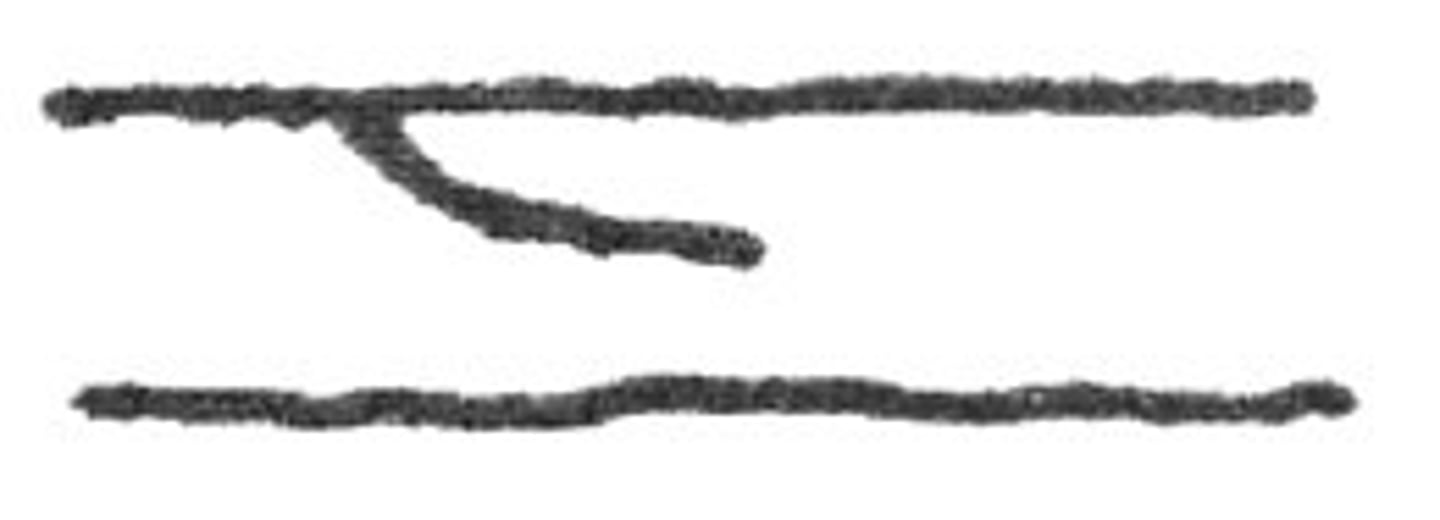

Double bifurcation
When a ridge splits and then splits again
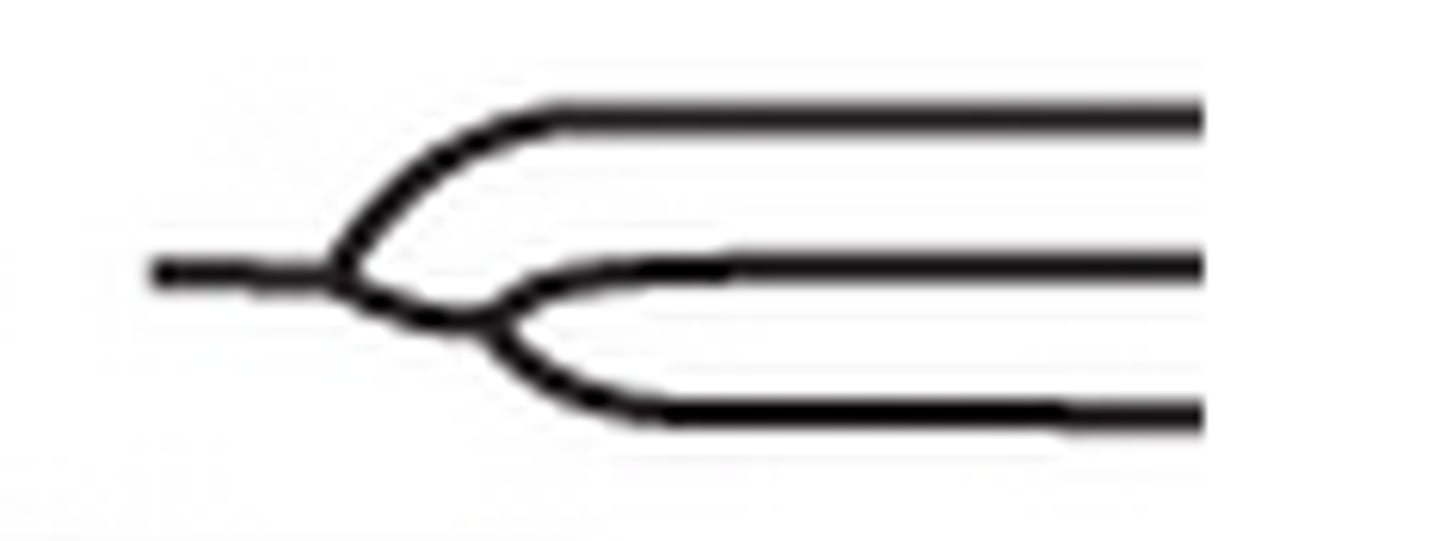

Trifurcation
A ridge split into 3
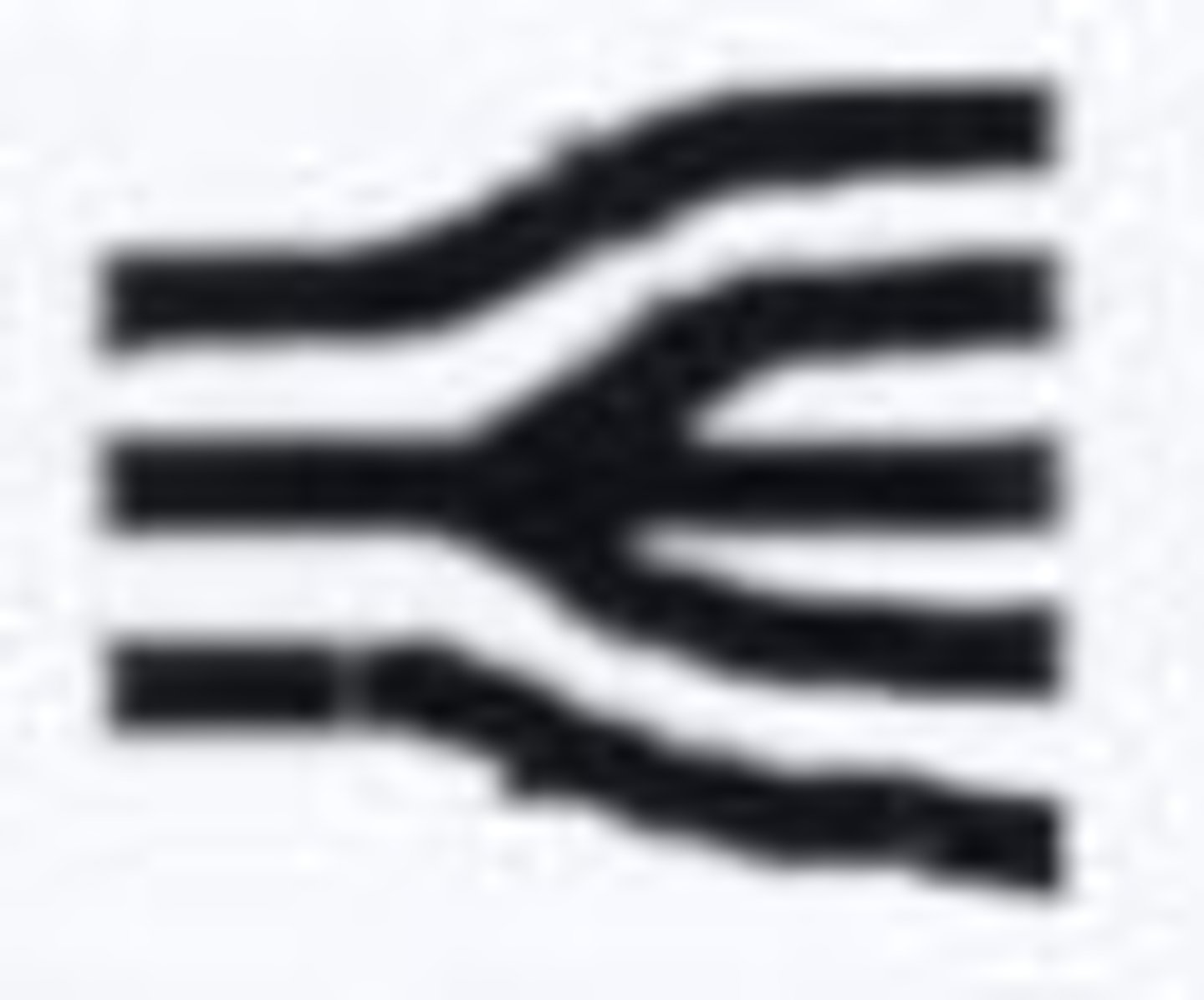

(True/false) There are legal requirements in USA on the number of points required for a match
False; no legal requirements
Most criminal courts accept _________ points of similarity
8 to 12
IAFIS
Integrated Automated Fingerprint Identification System
Allows law enforcement officials to:
- Search large files for a set of prints taken from an individual
- Compare/match a single print, usually a latent print developed from a crime scene
Why should fingerprints be the first evidence collected?
Easily smudged or destroyed
What should you do to a print before it's disturbed?
Photograph it
3 types of prints
Plastic, visible, latent
Plastic print
A 3D impression into a substance such as wax, soap, or putty
Visible print
Left by fingers coated with a colored substance like blood, grease, paint, dirt and ink
Latent prints
-Hidden or are relatively invisible
-Need processing or developing to see
-Expose/dust before photographing and removing to lab
What are fingerprints made of?
Perspiration - moisture, sodium chloride (salt), amino acids, organic/inorganic substances, and dead skin cells
Tools to develop fingerprints
-Flashlight
-Magnifying glass
-Minutiae
-Alternate light source (UV, colored filter)
-Powders
-Brushes
-Tape
Techniques to develop latent prints
-Dusting
-Crystalline iodine
-Silver nitrate
-Ninhydrin
-Superglue
What is the most common technique used to reveal latent prints?
Dusting with powder
How does dusting for fingerprints work?
1) Use a powder (regular or magnetic) that adheres to moisture
-Different colors/fluorescing metallic powders can be used to stand out against dark surfaces
2) Brushes of camel hair or fiberglass
-Magnetic wand for magnetic powder
3) Use tape to lift the powder from surface and mount it on a card to keep it permanently
Crystalline iodine
-The fumes react with oils and fats in the print
-Temporary yellow-brown color
-Highly toxic, must use fume hood
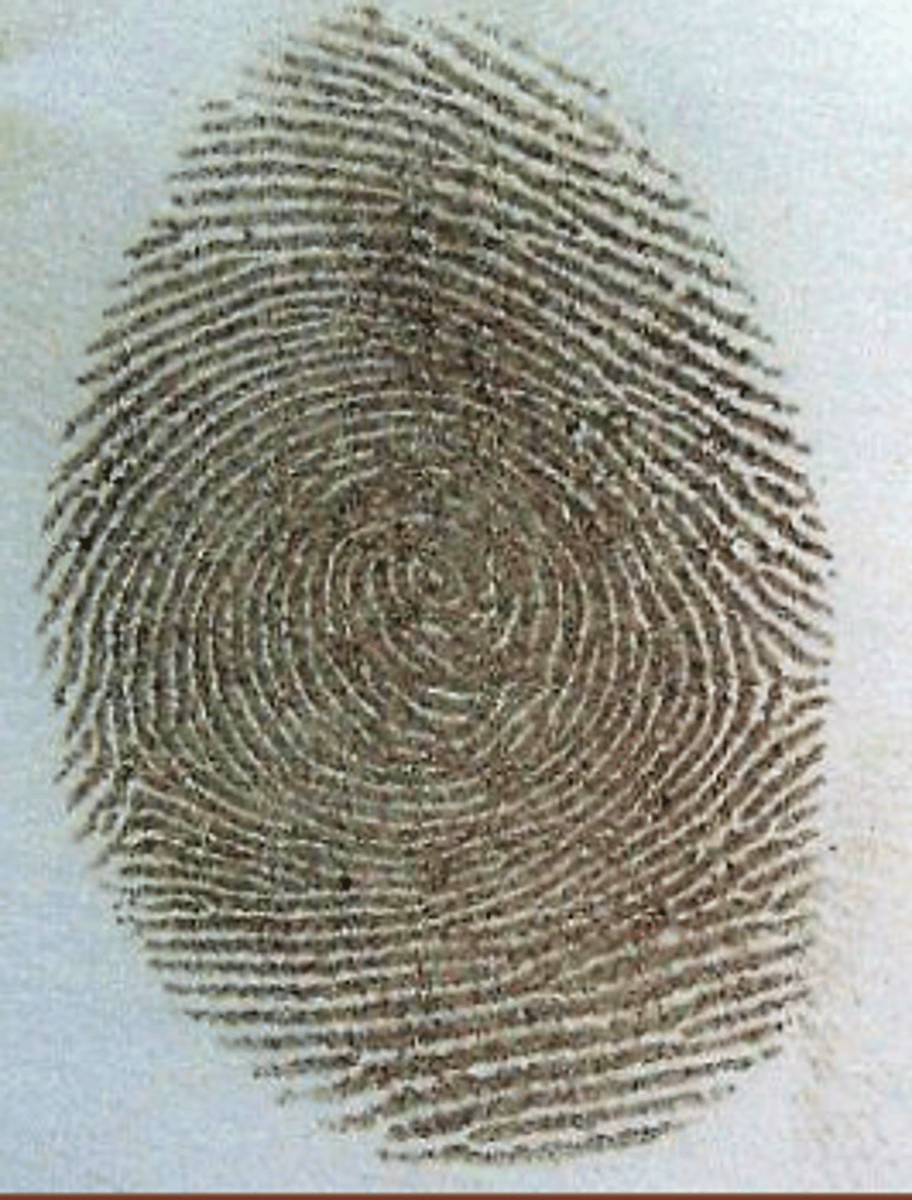

Silver nitrate
-A spray that reacts with the salt in sweat
-Turns gray when exposed to light
-Fumes are also toxic, not used much
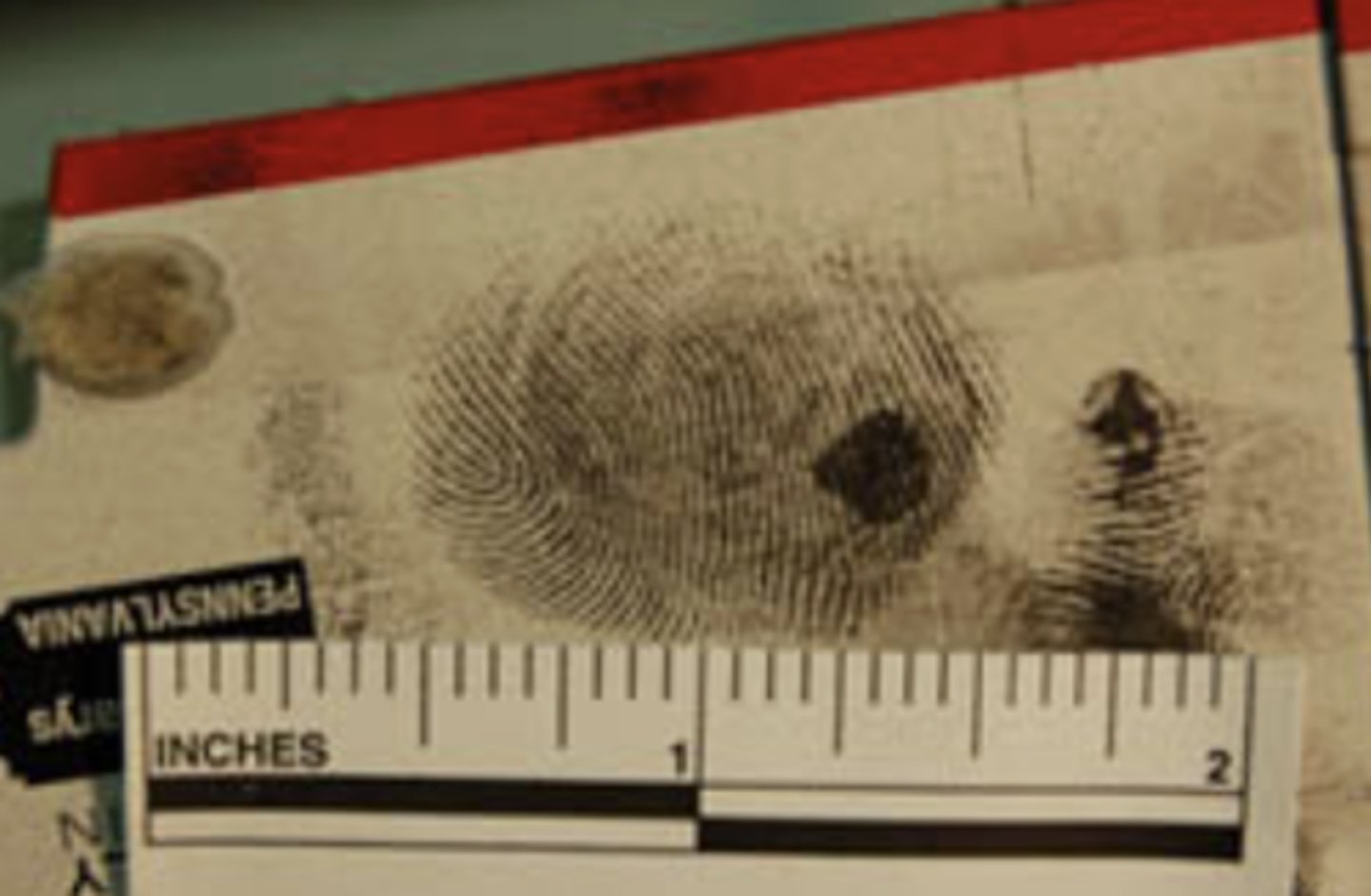

Ninhydrin
-Professionals use a spray bottle but can also dip prints in it
-Reacts with amino acids
-Purple
-Non-toxic, easy to use
What surfaces are crystalline iodine, silver nitrate, and ninhydrin mainly used on?
Fabric, paper, and wood
Which 2 methods are toxic?
Crystalline iodine and silver nitrate
Superglue
-Fumes react with water and sweat
-Crystallizes as a hard, whitish deposit
-Fixes print to surface, must then be dusted and lifted (2 steps)
What other types of prints exist?
-Foot prints and palm prints (sizes and fiction ridges are analyzed)
-Good for comparison but no database exists to use for identification