APHUG | Models & Theories
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Gravity
The idea is that people would be more willing to go to certain places over others. (I.e a big city like Chicago is more likely to attract people compared to a smaller city like Detroit)
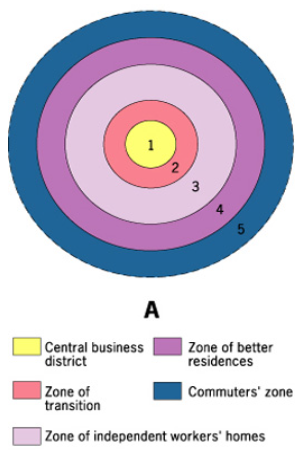
Burgess Concentric Model
Land Use Pattern
Most wealthy people living the furthest from the CBD (they didn’t want to be near the pollution)
Outdated because the industrial area has become smaller and been pushed outside of the inner rings of the city
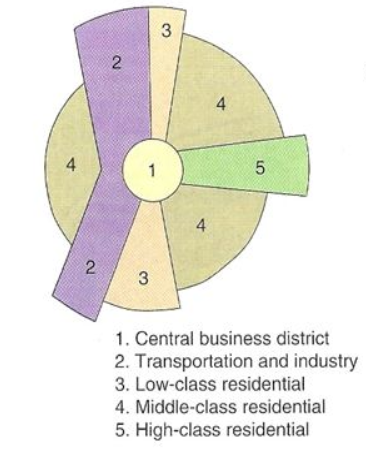
Hoyt Sector Model
Land Use Pattern
Uses CBD as the center point, however has focused more on transportation
Difference: Business locate near transport routes to have easy access to customers
Outdated because the suburbs, boom burbs, and edge cities caused business to locate in different places.
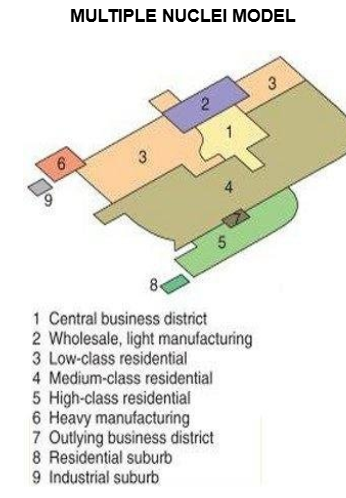
Multiple Nuclei Model
Land Use Pattern
Tries to describe the change that cities have gone through due to technology and transportation. It also has more CBD’s
If people wanted things to be near them, they would be (pull factor), if they didn’t they then they weren’t (push factor)
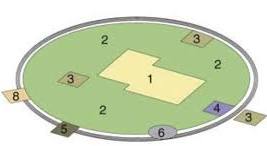
Galactic Model
Land Use Pattern
Post-Industrial. Takes in the advancements in tech & transportation, and that people prefer to live farther outside the cities and can travel into the cities now
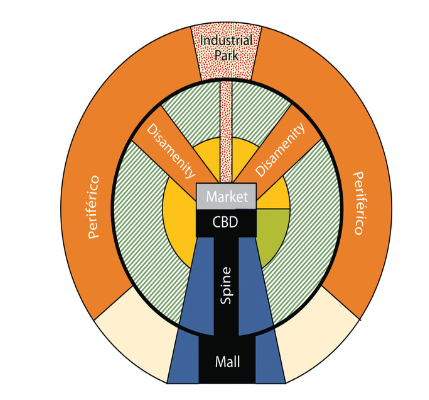
Latin American City Model
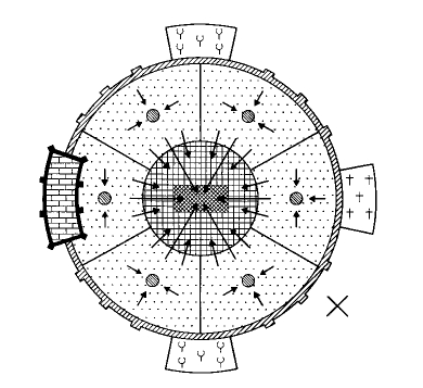
Muslim Model
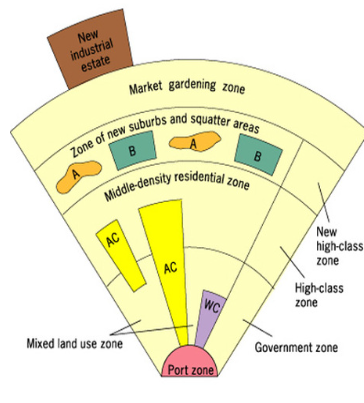
Southeast Asian City Model
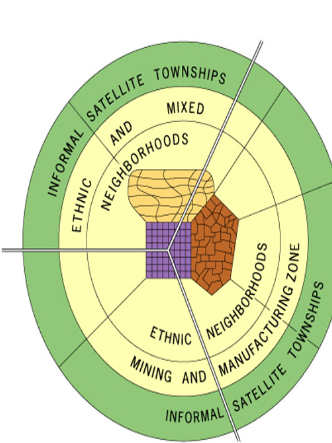
Sub-Saharan African City Model
Christallers Central Place
Explains the distribution of cities, settlements, goods, and services based on range. High and Low Order goods
Assumptions
Humans will always purchase goods from the closest place that offers the good
Whenever demand for a certain good is high, it will be offered in close proximity to the population
Can only exist on Isotropic Plane (area surrounding an urban center) with equal distance between units
Evenly distributed resources and population
Human Development Index
Takes in
Life expectancy
How many years of attending school
How any years your expected to attend school
GNI per captia
Gender Inequality Index
Takes in
How many women die during pregnancy per 100k LB (MDC = Low, LDC = High)
How many women give birth from ages 10-19 per 1k (ARD) (MDC = Low, LDC = High)
How many women in government (No pattern)
Can women go to secondary school (1-12th) (MDC = High, LDC = Low)
What jobs women have (No pattern)
0-1 (Higher = More inequality and vis versa)
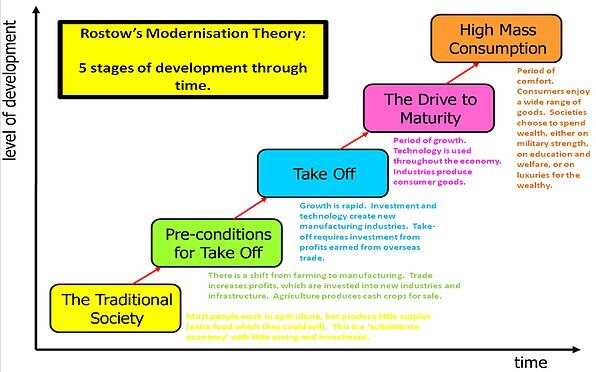
Rostow’s Theory of Dev.
Criticisms
Based on NA and Western Europe and not all countries wanna be like them
Scale & Uneven Development (I.e India could fit in stage 3 or 4)
Not all countries will go in this order due to wars, corruptions, and natural disasters
Focus on one country and doesn’t take Globalization into account
Doesn’t take into account that countries have dif climates, landforms, access to natural resources, relative location. That help or hinder dev.
Doesn’t take into sustainability. Mass consumption = bad for environment
Doesn’t take in Colonialism and its impact as it most countries that get to the top did via colonialism and countries today can’t do that.
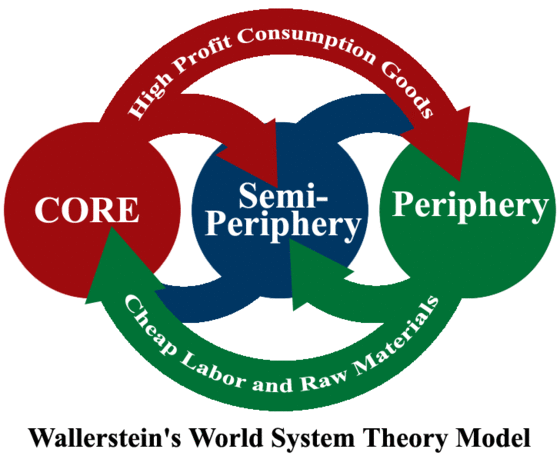
Wallerstein World system Theory
Explains Uneven Development through a global perspective that categorizes countries into core, semi-periphery, and periphery nations. This theory emphasizes that economic and political power dynamics determine the development of different regions.
Alfred Weber: Least Cost Theory/Indus. location theory
Minimize three categories of costs to increase profits:
Transportation (Bulk gaining & Bulk-Losing)
Labor (US - $$$, India - $. Companies move parts (outsource) or all of it (offshore) outside US, machines replace workers)
Agglomeration (Industries coming together to share cost of infra., lower trans. cost, and keep eye on competition)
Raveinsteins Laws of Migration
Common patterns that migrants share:
Most move a short distance.
Migration happens in steps
Long-distance migrants more likely to move to big cities
Every migration generates a counter-migration
Male = Migrate more and longer distance, Female = Migrate less and shorter distance
Economic factors are the main cause of migration.
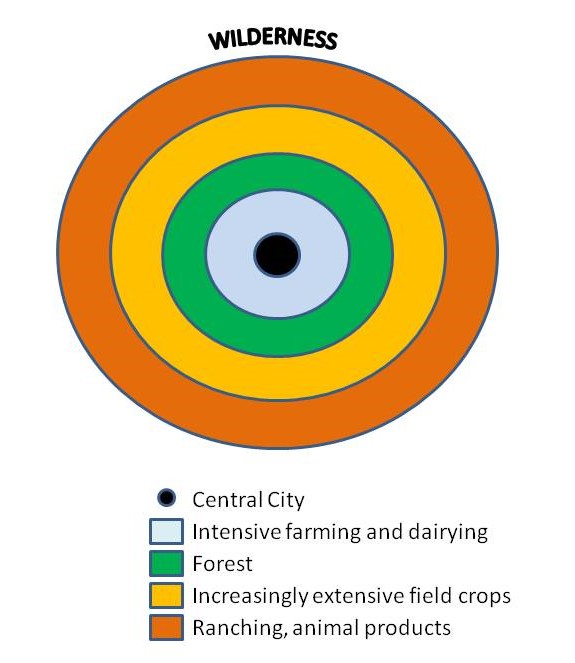
Von Thunen Model
Assumptions
All land is flat and the environment is the same everywhere.
No barriers to transportation.
Farmers using oxcarts to transport goods to market.
Farmers consider how quickly a product spoils and how much it costs to transport when deciding how to farm.
Primary Sector
Extraction of raw materials and natural resources from the earth’s surface. (I.e mining, fishing, agriculture, forestry)
Secondary Sector
Processing and manufacturing raw materials into a finished product. (I.e factories & manufacturing)
Tertiary Sector
Service sector that focuses on moving, selling, and trading products in primary and secondary sectors. (I.e retail, marketing, design, restaurants, shipping)
Quaternary Sector
Knowledge-based sector, focusing on research and information creation and transfer. (I.e Investment banking, real estate, college professors, education, software developers)
Quinary
Highest levels of decision making, includes top officials in government and business. (I.e Congress, CEOs: Decisions impact millions)
Special Economic Zones (SEZ)
An area that has less environmental regulations and tax incentives (Ex. 2018 India has new SEZ with little energy rules)
Export Processing Zones (EPZ)
a company can import plant, machinery, and store things without charge (Ex. Maquiladoras along the US-Mexico border (Tarrif Free))
Free Trade Zone (FTZ)
A zone where tariffs and trade barriers are not present when trading between two countries
Zones
Territorial Sea: Up to 12 nautical miles of sovereignty; commercial vessels may pass, but non-commercial vessels may be challenged.
Contiguous Zone: Coastal states can enforce laws on customs, immigration, and sanitation.
Exclusive Economic Zone: Coastal states can explore, extract , minerals, and manage up to 200 nautical miles.