Unit 3: Sense and Perception
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
sensation
The process of detecting physical energy from the environment through our senses (like seeing, hearing, or touching)
perception
The way we interpret and make sense of the sensations we receive, allowing us to understand what we are experiencing.
bottom-up processing
Starting from the basics; building up an understanding from small sensory details to form a full picture. No prior knowledge is used.
top-down processing
information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations
inattentional blindness
failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
change blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment
transduction
conversion of one form of energy into another. In sensation, the transforming of stimulus energies, such as sights, sounds, and smells, into neutral impulses our brain can interpret
psychophysics
The study of how physical stimuli (like light and sound) relate to our psychological experiences (like brightness and loudness)
absolute threshold
the minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50 percent of the time
signal detection theory
a theory predicting how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus amid background stimulation. Assumes that there is no single absolute threshold and that detection depends partly on a person’s experience, expectations, motivation, and alertness
subliminal perception
below one’s absolute threshold for conscious awareness (detect less than 50% of the time)
priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of certain associations, thus predisposing one’s perception, memory, or response (if you see the word yellow and then shown a list of words, you most likely would choose banana bc they are associated)
difference threshold
the minimum difference between two stimuli required for detection 50 percent of the time. We experience the difference threshold as a just noticeable difference
Weber’s law
to be perceived as different, two stimuli must differ by a constant minimum percentage (rather than constant amount)
sensory adaptation
diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation
perceptual set
a mental tendency/assumption to perceive one thing and not another
Hit/Miss
In signal detection theory, a "hit" occurs when a stimulus is present and correctly detected, while a "miss" happens when the stimulus is present but not detected.
false alarm
When you think you detect a stimulus that isn’t actually present.
Correct rejection
When no stimulus is present, and you correctly don’t detect anything
Just Noticeable Difference (JND)
the smallest change in a stimulus that you can detect (slight inc in volume)
Receptor Cells
specialized cells that respond to sensory stimuli and send signals to the brain
Receptive field
An area on your skin where touch receptor cells detect pressure
Sensory Coding
the process by which sensory receptors convert physical stimuli into neutral signals that the brain can understand
Visual Sensation
the initial detection of light and color by the eyes before it is interpreted by the brain
Distal stimulus
the actual object or event in the outside world that you’re looking at or sensing
proximal stimulus
The image of the object formed on the sensory receptors (like the retina) when you perceive something
Accomodation
the process by which the eye changes lens shape to focus near or far objects on the retina
Optic Chiasm
The point in the brain where the optic nerves from each eye meet and cross over to the opposite side of the brain
Serial Processing
Processing one piece of information at a time, step-by-step
Parallel Processing
The brain's ability to process multiple aspects of a stimulus simultaneously, such as color, depth, motion, and shape (driving a car); more automatic and subconscious
Convergence
A binocular cue where the eyes move inward to focus on a close object, providing depth perception.
Young-Helmholtz Theory (Trichromatic Theory)
the retina has three types of color receptors (red-long cones, green-medium cones, blue-short cones) that combine to form other colors
Opponent Process Theory
color vision is enabled by opposing pairs of colors (red-green, blue-yellow, black-white) where some neurons are stimulated by one color and inhibited by its opposite. (see green after starring at red for a while)
Place Theory
in hearing, the theory that links the pitch we hear with the place where the cochlea’s membrane is stimulated
high-pitched sound = vibration is detected at the base of the cochlea.
the deeper tones = vibrations toward the apex of the cochlea
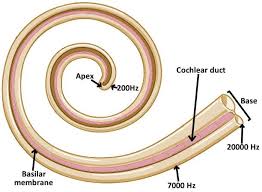
Frequency Theory
in hearing—rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone, thus enabling us to sense its pitch (If the frequency of the sound is 50 Hz, the nerve fibers would fire at approximately 50 times per second, providing the brain with the information necessary to identify the pitch)
Conductive Deafness
Caused by problems in the ear canal or middle ear (ear infections)(mechanical system); hearing aids help
Sensorineural Deafness
caused by damage to the inner ear (cochlea’s receptor cells) or auditory nerve (aging or loudness); hearing aids don’t help
olfaction
sense of smell
Cutaneous Receptors
nerve receptors in the skin that respond to touch, pressure, pain, and temperature
Tactile Receptor
A type of cutaneous receptor specifically for detecting touch and texture.
Cold fibers
respond to cold stimuli
Warm fibers
respond to warm stimuli
Vestibular Sense
tells you if you are physically upright without eyesight—balance; relies upon the semi circular canals located in your ears
Kinesthesis
the sense that detects body position and movement; perceives the extent, direction, or weight of movement. (know where your arms are when your eyes are closed; dribble basketball w/o looking)
Habitutation
involve a more active learning process; decreased response to a repeated stimulus over time (ignoring); cognitive level
Selective Attention
capacity to react to certain stimuli selectively when several occur simultaneously; choosing what to pay attention to
Cocktail Party Phenomenon
being able to focus one’s auditory attention on a particular stimulus while filtering out a range of other stimuli (listen to one voice among many); more subconscious
Filter Theories
attention operates as a filter that allows certain stimuli to be processed while block out others
Divided Attention
the ability to respond to multiple stimuli simultaneously; multi-tasking; often results in decrease in performance
Gustav Fechner
coined the term psychophysics; making connection between matter and mind; public and private
Ernest Webner
used signal detection theory in real-world situations
Gestalt
principles used to make order out of perceptions so that we see things as connected and not just random bits of info
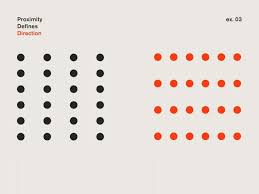
Gestalt Proximity
objects close together will be viewed together visually
Gestalt Closure
the brain is good at filling in gaps to create a whole
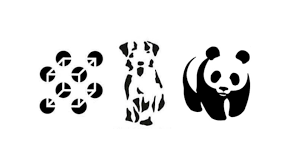
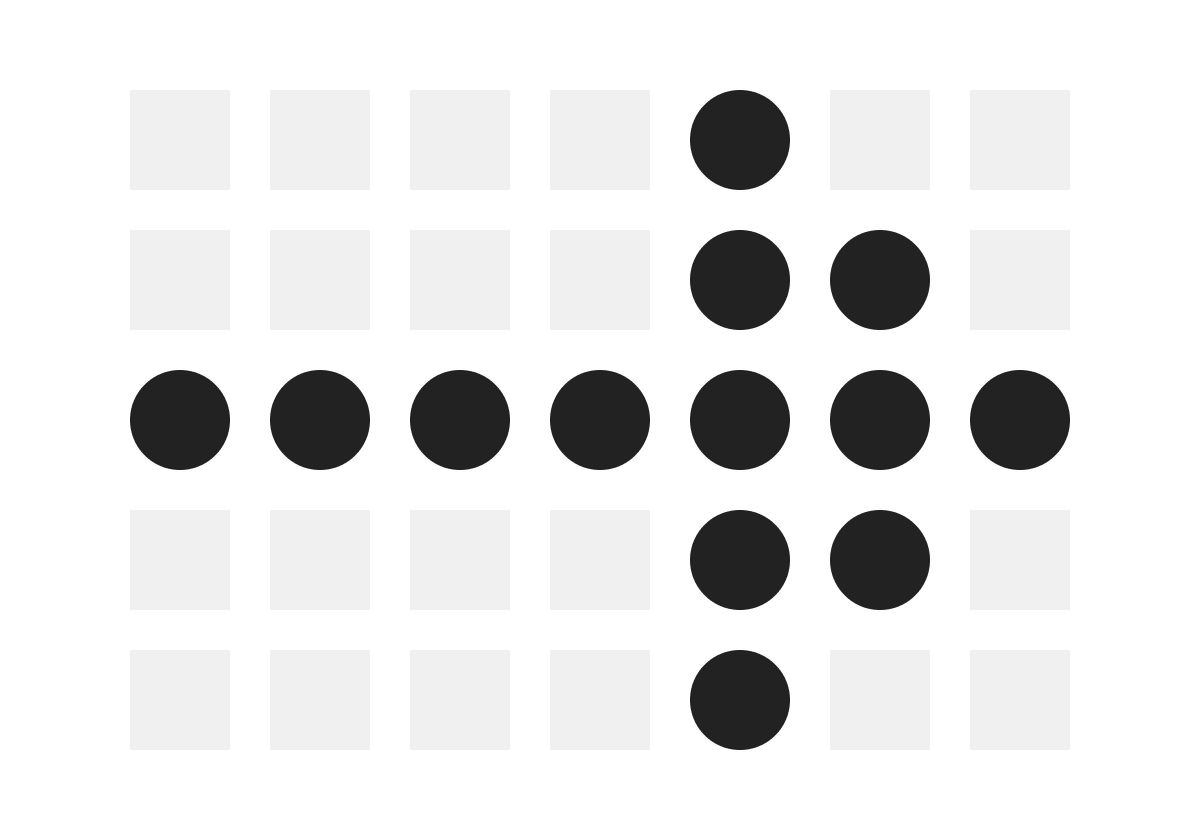
Gestalt Similarity
two items that share attributes will be visually grouped together
Gestalt Continuity
a line will always appear to continue traveling in the same way
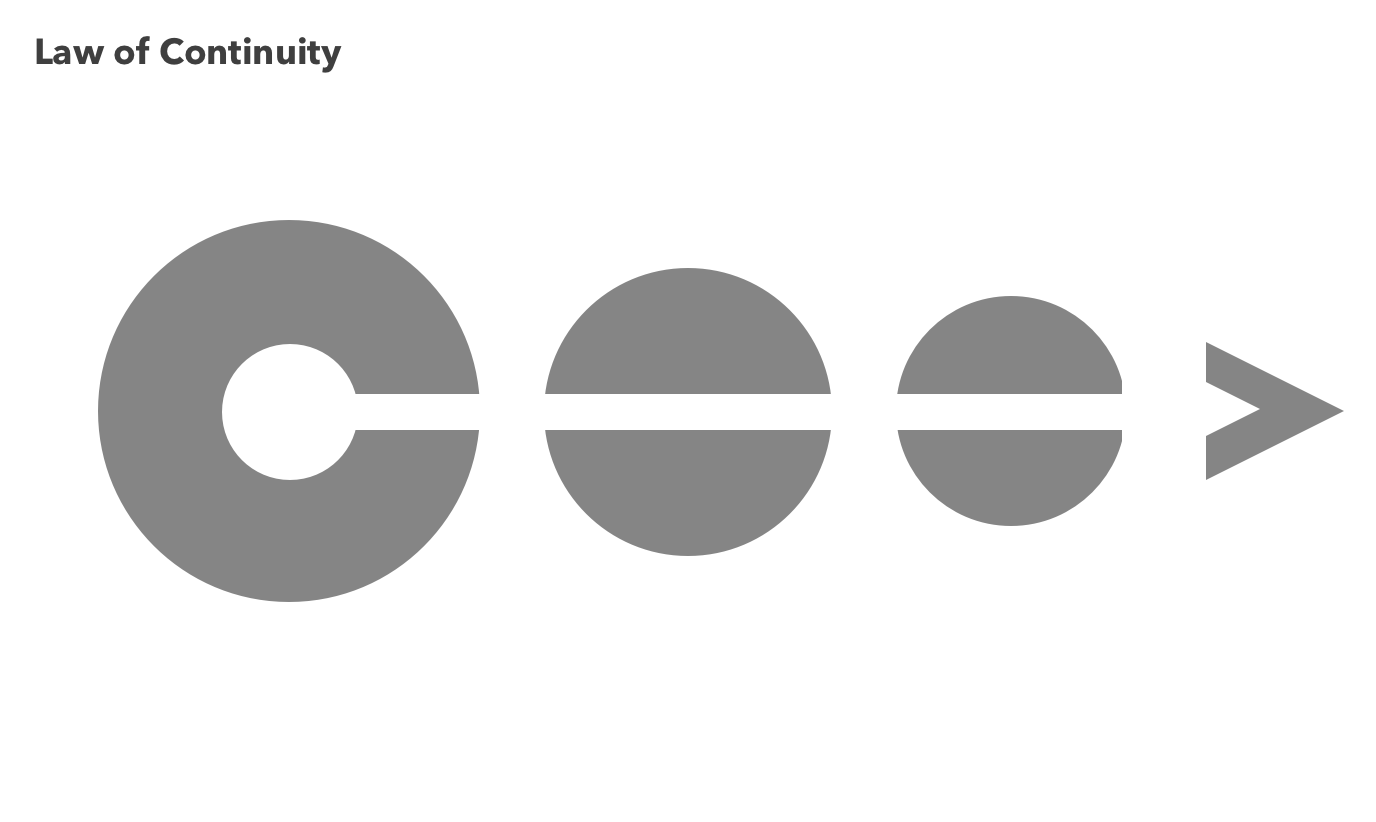
Gestalt Figure and Ground
sometimes, the blank space is just as important as the filled space

Binocular Depth Cues
depth cues, that depend on the use of two eyes; rely on the slightly different images that each eye receives due to their separation.
Law of Pragnanz
we tend to perceive things in the simplest, most stable form
Phi Phenomenon
an illusion of movement created when two or more adjacent lights blink on and off in quick succession
Stroboscopic effect
the illusion of movement when a series of static images or lights are shown in quick succession (in film and animation)

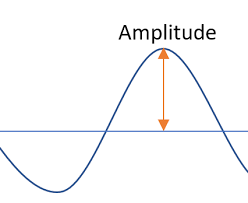
Intensity
amplitude; amount of energy in a light wave is determined by height of a wave (higher wave=more intense light)
Perception of Color
our minds perceive the color of light of the color being rejected
Pupil
adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters
Iris
a ring of muscle that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening; adjusts its size in response to light levels in the environment. When it's bright, the pupil becomes smaller (constricts) to limit the amount of light entering the eye. In low light, the pupil becomes larger (dilates) to see better in dim conditions
Lens
transparent structure behind pupil that changes shape to focus images on the retina (focus light onto the retina, about 1/3, does fine tuning)
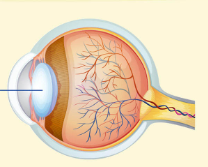
Cornea
transparent outer covering of the eye (responsible for about two-thirds (2/3) of the eye's ability to focus light)
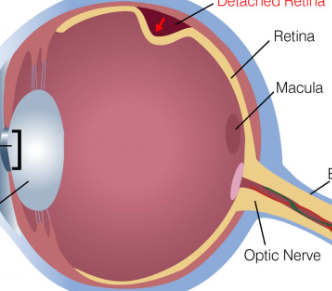
Retina
contains visual sensory receptors (photoreceptors in it capture light and convert it into electrical signals)
Fovea (Retina)
point of central focus; contains most of eye’s cones (color); visual acuity (see finest details); center part of retina
Optic Nerve
pathway to the brain’s visual cortex
Blind spot
occurs at the location in the retina, where the visual cortex exits to the brain, there are no receptors there; spot in the retina where the optic nerve connects
Nearsighted (Myopia)
eye is elongated; nearby objects are seen more clearly[lens causes light to focus too soon (in front of the retina)]
Farsighted (hyperopia)
eyes are shortened; faraway objects are seen more clearly [lens (or eye shape) causes light to focus too late (behind the retina)]
Photoreceptor Cells: Rods and Cones (Retina)
peripheral retina; detect black, white and gray; twilight or low light
near center of retina; fine detail and color vision; daylight or well-lit conditions
Bipolar (retina)
receive messages from photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) and transmit to ganglion
Ganglion (retina)
Its axons form optic nerve; neurons in the retina that receive signals from bipolar cells and send visual information to the brain’s visual cortex via the optic nerve.
Blindsight
you can see something but can't consciously recognize or be aware (perceive) of it.
Feature Detector
cells in the visual cortex of the brain that respond selectively to specific features of complex stimuli (edges, angles, length, movement)
David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel
discovered feature detectors in visual system
Colors
the way our brain interprets different wavelengths of light, with each wavelength corresponding to a different color in the visible spectrum; visible/optical light
Visible/Optical Light
only a small sample of total electromagnetic spectrum; most light is invisible to our eyes
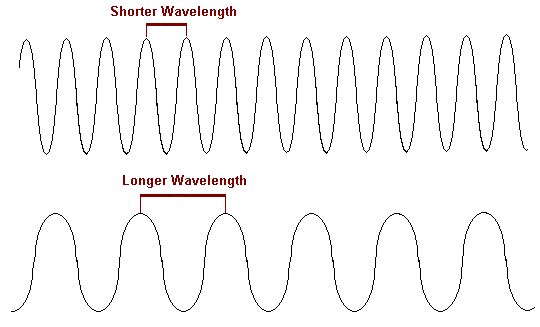
Wavelength
distance from the peak of one light wave to the next; distance determines hue (color) of the light we perceive
short WL=high freq (blue, high pitched, high energy & precision) (X-ray)
long WL=low freq (red, low pitched, penetration, long distance) (radio waves)
Intensity
amplitude, brightness; higher wave=more intense light
Saturation
more= more intense or pure it looks.
less=appears more washed out or grayish.
Monochromats
zero (daylight uncomfortable; no colors) or only one type of functioning cone type (can’t discriminate colors; only shades of red/blue/green) and respond to light like a black/white film
Dichromats
only one malfunctioning cone type; 2 ok cones
Apophenia
experience of seeing meaningful patterns or connections in random/meaningless data (seeing a face on a car based on car parts)
Frequency (pitch)
Hz; number of complete wavelengths that pass through a point at a given time determines pitch; long wl=low freq; short wl=high freq
Intensity (loudness)
volume, measured in decibels
Olfactory nerve
transmits odors to the limbic system of the brain
Unique Olfactory system
bypasses the thalamus; impulses from nerve fibers from olfactory bulb connect to the brain at the amygdala and then to hippocampus
Gustation
sweetness, sourness, saltiness, bitterness (naturally poisonous), umani=savory
Touch
pressure, temp, pain; some areas are more sensitive—more nerve endings
Gate Theory
only a small amount of info can be processed by the nervous system at a time; flooding brain with other stimulus blocks some pain messages (sneeze while getting a shot)
nociceptors
detects pain—hot nerves and cold nerves
proprioception
includes both static (position) and dynamic (movement) awareness of your body.
Monocular Cues (depth perception)
needs only one eye to perceive depth; perspective, clearness, shadow, overlapping, gradient texture, motion parallax (objects that are closer, appear to move faster than objects that are far away)
Retinal disparity
binocular disparity; images from 2 eyes differ; closer the object, the larger the disparity (finger in front of face)
Perceptual Constancies
perceiving objects as unchanging even as light and retinal images change (4 types)
Color Constancy
tendency to perceive objects as keeping their color even though different light changes the appearance of their color