chromosones and genomes (pre midterm)
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lec 10-12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
what state does dna exist in during interphase
chromatin
how does dna behave in isotonic vs low salt buffers
low salt: dna strongly attracts proteins so dna<protein
beads on a string
isotonic: native chromatin structure is preserved, 1:1 ratio of protein:dna
nucleosome
histones with dna wrapped around
beads separated bt linker dna
each protein core has 147 bp wrapped around
how many subunits do histones have
8, 2 of each:
H2A
H2B
H3
H4
solenoid and two-start helix model
made of condensed fibre like chromatin
stabilized by H1
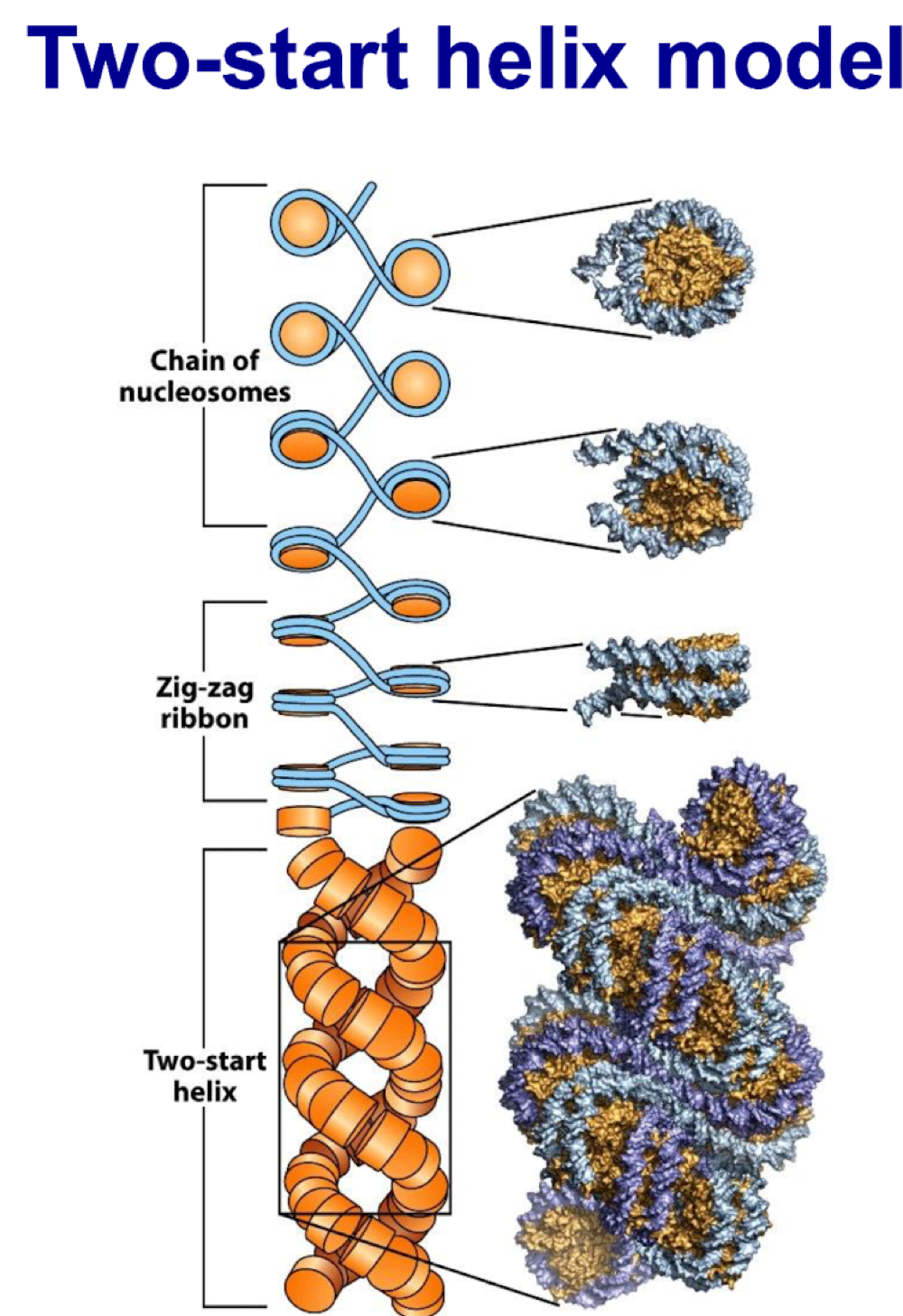
how is chromatin condensation regulated
modyfying histone tails at the N or C terminals
how can the charges of side chains be changed?
methylation
phosphorylation
ubiquitination
acetylation of lysine (neutralizes positive amino)
polytene chromsones
on drosophila salivary glands
interphase chromosones
repeated replication without separation leads to parallel chromatids
polytene chromosones and transcription
chromosone shoes econdensation with transcription activation
puffs are linked with active RNA pol II
SMC proteins
moderate looping of chromatin
klesin is widely conserved in evolution by euks and bacteria
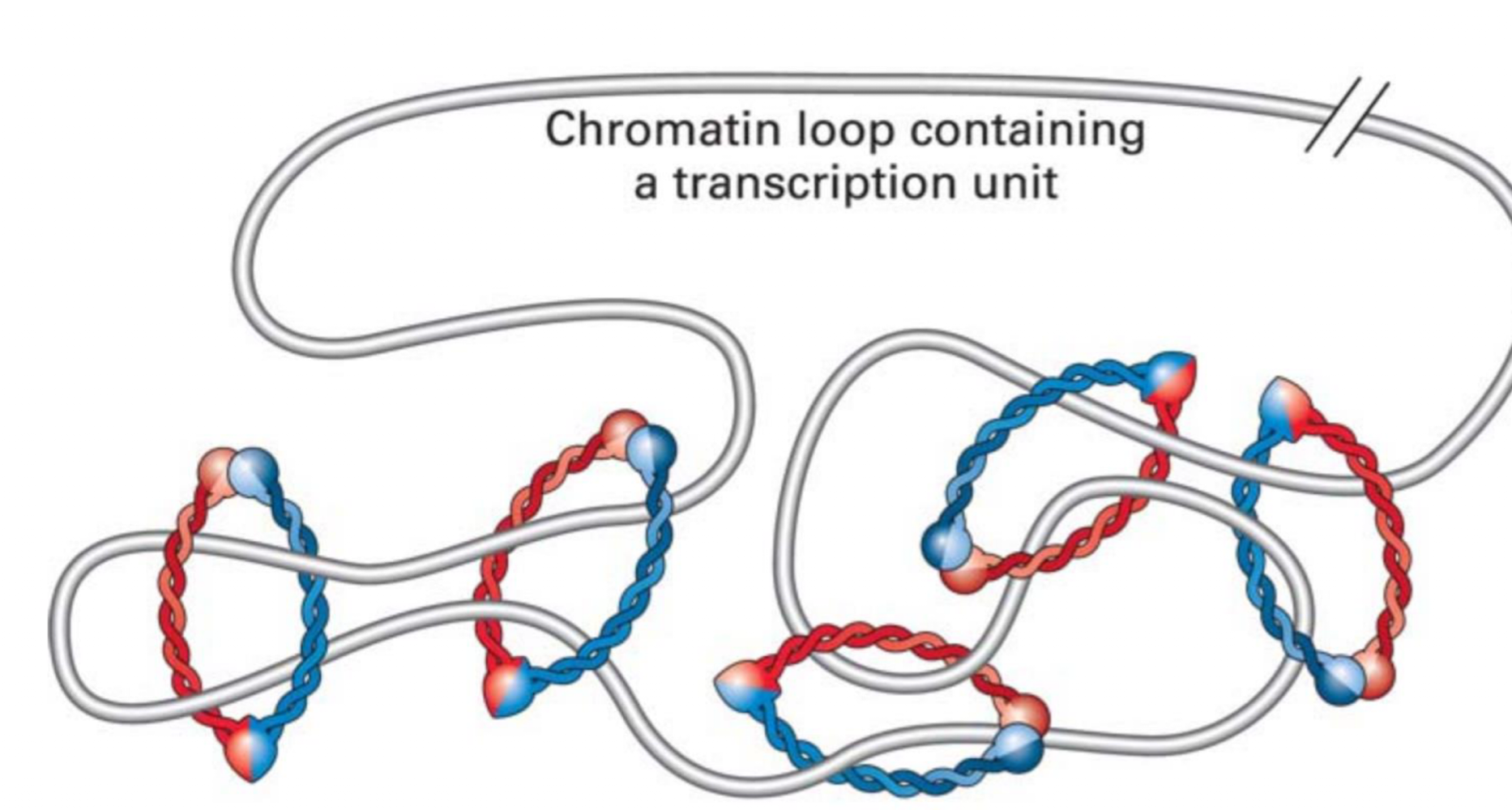
who condeses chromosones during metaphase?
condensins (SMCs)
condensin II forms central scaffold with loop around it
condensin I further compacts the loops
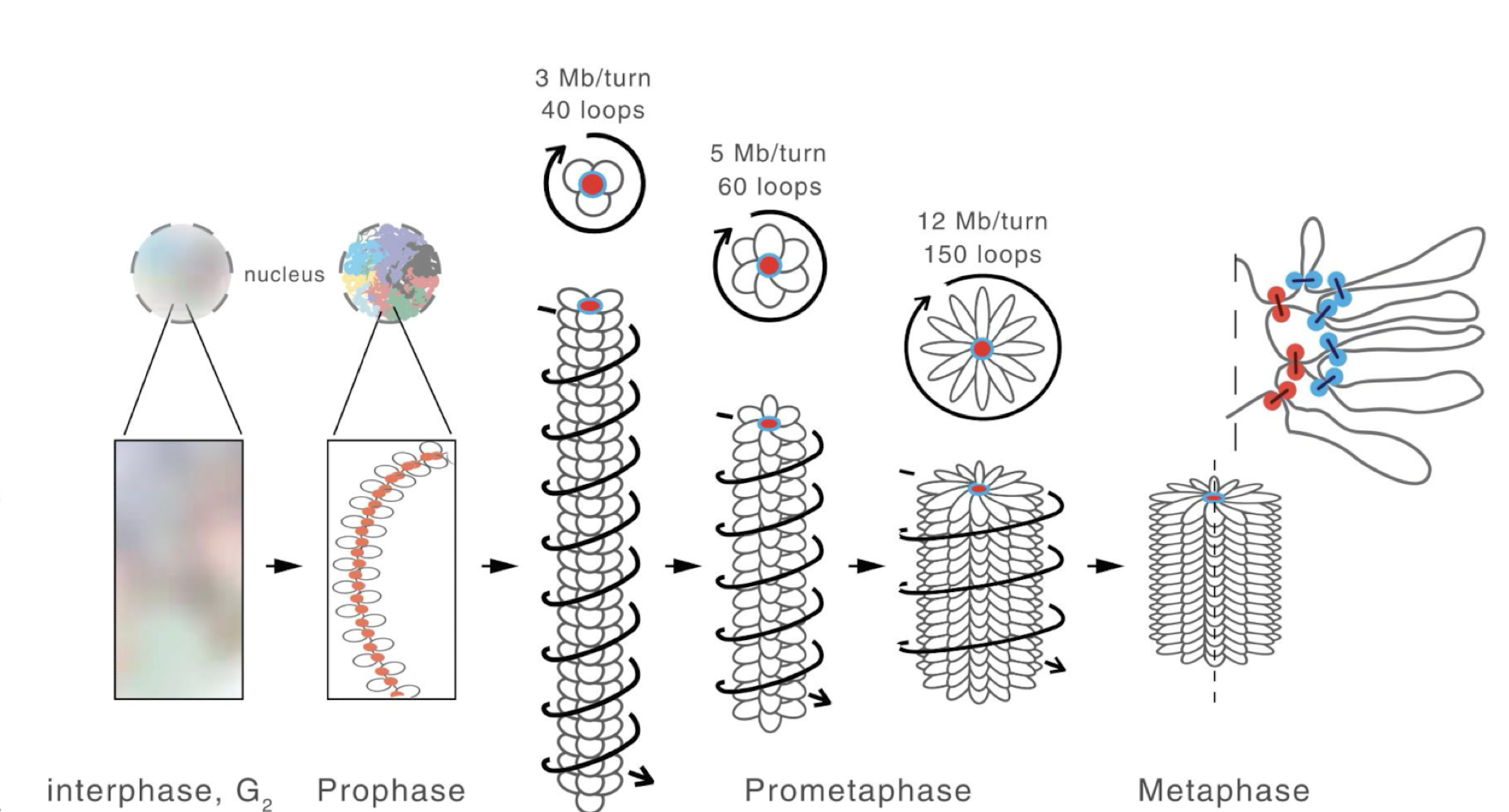
what structure do mitotic chromosones have
series of loops wrapped around a protein core
3 requirements for replicaton and inheritance
origin of replication
centromere
2 telomeres
we havee these 3 things in each mitotic chromsone
how does telomerase work
reverse transcriptase
has its own RNA template compliment to the telomeric DNA
give primase more template DNA to prime on
CENP-A
centromeric protein A
centromere specific histone variant that links to the kinetochore
replacement for H3 histone
kinetochore connects to centromeres and microtubules
what do control regions consist of
promoters
cis-regulatory factors
isoforms
made when genes are alternitavely processed and transcribed to get multiple different transcripts from the same gene
gene family
set of related genes formed by duplication of an orginal single copy gene
ortholog vs paralog genes
ortholog: same protein in a different species
paralog: closely related protein in the same species
duplication occurs then they evolve differently
simple sequence repeats (SSR)
6% of our genome
noncoding
minisatellite dna
microsatellite dna
hypervariable nature is exploited for fingerprinting
minisatellite dna
SSRs
repeats 14-100 bp
longer than those of microsatellites
arrays are 1kbp-5kbp long
often in centromere/telomere region
microsatellites
repeats are 1-4bp long
formed by dna slippage
arrays are 600bp, much shorter than minisatellite
seen in transcription units
what cauzes neuromuscular diseases
expansion of microsatellite dna through replication slippage
how much of dna is transposons and what type?
40% retrotranposon
3% DNA transposon
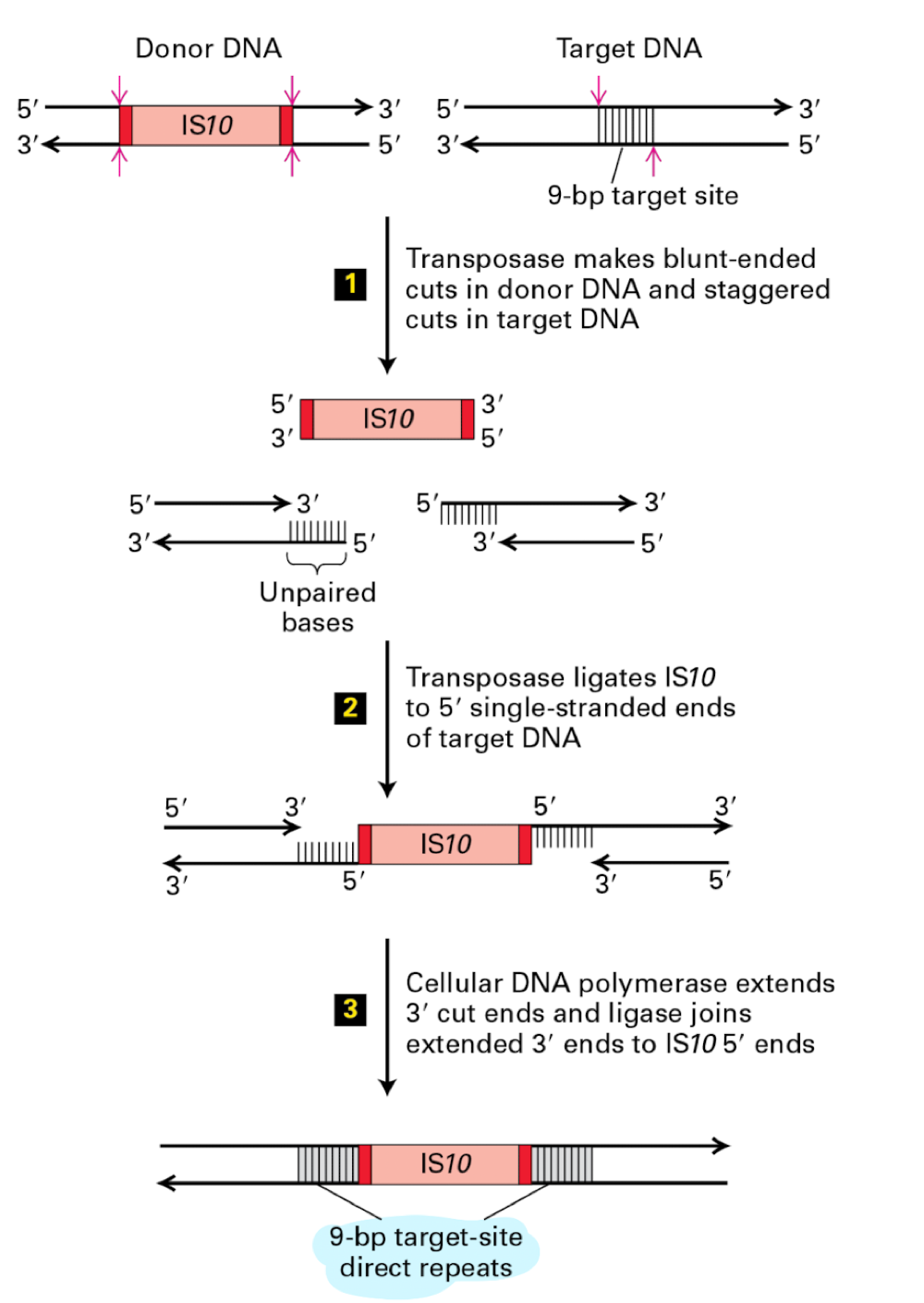
how do DNA transposons work
dna transposase is cut anx paste into new dna segment
target dna is cut to have sticky ends
donor dna is cut bluntly
causes 9bp duplication
LTR retrotransposons
long terminal repeats, 8% of genome
cannot form infectious particles or coat proteins so cannot leave the cell
similar to retroviruses
encode reverse transcriptase and integrase
how do LTRs work
trancribed into and RNA copy
retrotranscriptase turns rna into dna in the cytoplasm
uses trna as primer
dna is moved to nucleus, then integrase mediates insertion into genome
LINEs and SINEs
lines are longer
both are nonviral dna retrotransposons
LINEs are 21% of genome
SINEs are 13%
ORF1 and ORF2
regions on LINEs and SINEs
orf1 encodes rna binding protein
ORF2 encodes reverse transcriptase and a nuclease
how often are protein coding genes solitary/single copy
25-50% of the time
rest occur in multiple copies
how do LINEs insert dna
rna is made and exported from nucleus
ORF1/2 translate and bind the rna
rna protein complex goes to nucleus
nucleae cuts dna strand at an AT rich area
dna end are used as primase
gramm negative bacteria
have outer membrane arond cell wall
opposite of most bacteria
how many chromosones do most bacterial cells have
1
which direction are genes translated in bacteria
highly transcribed genes are translated in the same direction as th replication fork progression so that mistakes are head to tail
operons
regions that share a promotor and are transcribed together
form polysctrinic mrna
polycistrinic mrna
formed by operons
code for multiple proteins
who folds bacterial dna
gyrase (DNA topoisomerase) introduces torsion to compact dna
SMC proteins form loops with the dna
no histones involved
nucleoid
structure bacterial dna is folded into by proteins
can have the origin of replication in the centre or at the poles
which organelles are endosymbionts
chloroplast and mitochondria
what about organellar dna resembles prokaryotes?
circular shape
lack of introns
gene products resemble prokaryotic rnas and proteins
human mtDNA
encodes 37 genes
lacks introns
encodes stuff for respiraton and translation
gene products stay in mitochondria
cpDNA
chloroplast genome
much larger than mtDNA genome
encodes 100-200genes
ricksettsia genus
mitochondrial ancestor
lokiarchaea
close relative of eukarotes ancestor cell
inheritance in mtDNA
cytoplasmic inheritance
mitochondria are evenly (number) and randomly (type) split between daughter cells