CHP 6 musculoskeletal system disorders
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
hand muscles by median nerve (7)
abductor pollicis brevis
palmar abduction
opponens pollicis
opposition
flexor pollicis brevis
thumb MCP flexion, deep hand innervated by ulnar N
lumbricals (radial)
MCP flexion; IP ext of digits II and III
flexor digitorum superficialis (sublimis) (FDS)
flexion of proximal PIP
flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)
flexion of distal DIP to digits 2&3
flexor pollicis longus (FPL)
flexion of IP joint of thumb
muscles by ulnar n (10)
abductor digiti minimi
abduction of digit 5
opponens digiti minimi
opposition of digit 5
flexor digiti minimi
flex of MCP and opposition of digit 5
adductor
adducts CMC thumb
lumbricals (ulnar)
MCP flex; IP ext of digits 4&5
palmar interossei
adduction and assistance with MCP flexion and ext of IP of digits 2-5
dorsal interossei
abduction and assist with MCP flexion and IP ext of digits 2-5
flexor digitorum profundus
flexion of DIP joints to digits 4-5
flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU)
flex of wrist and ulnar deviation
flexor pollicis brevis
flex wrist

pollicis =
THUMB contributions
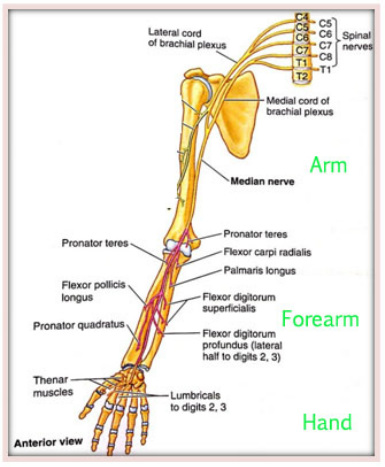
muscles innervated by median n (4)
NO hand
overall movements
Movements
wrist flex, pronation
MUSCLES
flexor carpi radialis (FCR)
flexion of wrist and radial deviation
Palmaris longus (PL)
flexion of wrist
pronator teres
forearm pronation
pronator quadratus
forearm pronation
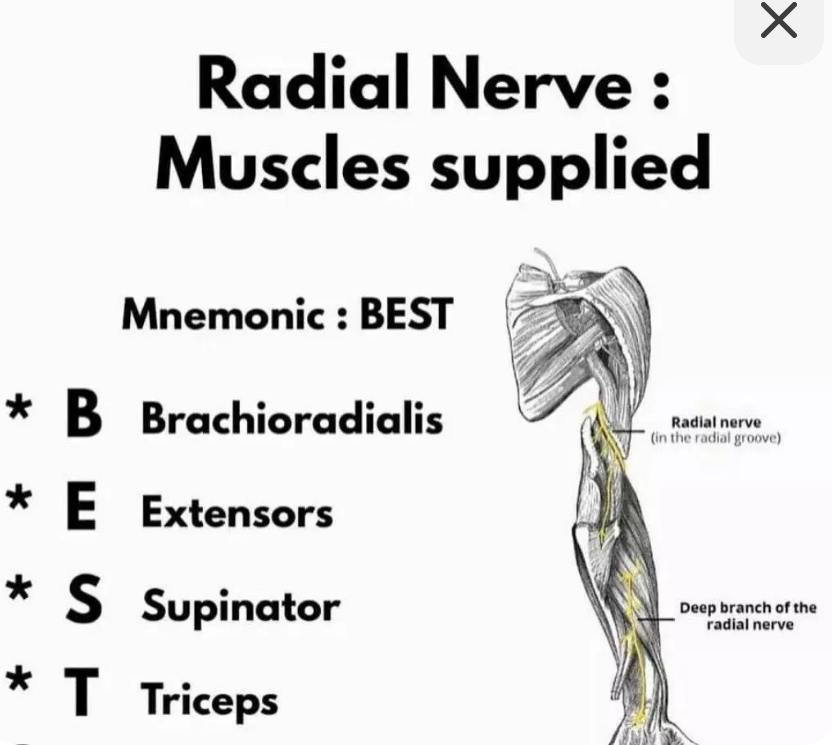
muscles innervated by radial n (13)
overall movements
BEST
EXTENSION, supination
extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB)
ext of wrist and radial deviation
extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL)
ext of wrist and radial deviation
extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU)
ext of wrist and ulnar deviation
EXT over rules ULANRIS
supinator
forearm supination
brachioradialis
elbow flex with forearm neutral
triceps
elbow ext
anconeus
elbow ext
extensor digitorum communis (EDC)
ext of MCP and ext of IP
extensor digiti minimi (EDM)
ext of MCP of digit 5 and ext of IP
extensor indicis proprius (EIP)
ext of MCP of digit 2 and ext of IP
extensor pollicis longus (EPL)
ext of IP joint of thumb
extensor pollicis brevis (EPB)
ext of MCP and CMC thumb
abductor pollicis longus (APL)
abduction and ext of CMC
Rock, Paper, Scissors
Rock = Median
flex of most digits
Paper = Radial
ext
Scissor = Ulnar
flex of digits 4-5
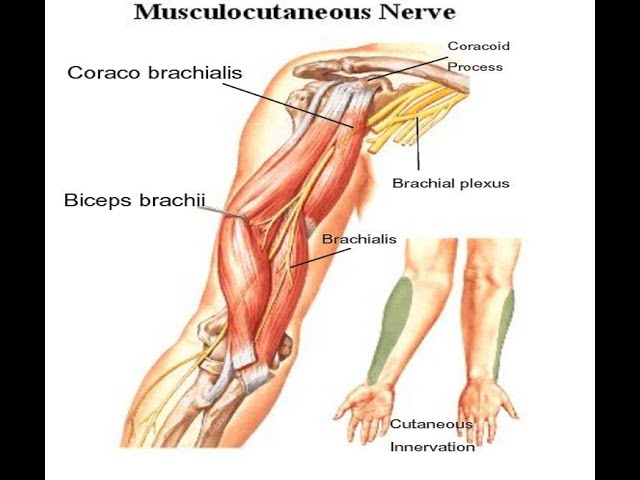
musculocutaneous n muscles (3)
MOVEMENTS
elbow flex, shoulder flex
MUSCLE
biceps
elbow flex with forearm supinated
brachialis
elbow flex
coracobrachialis
shoulder flex
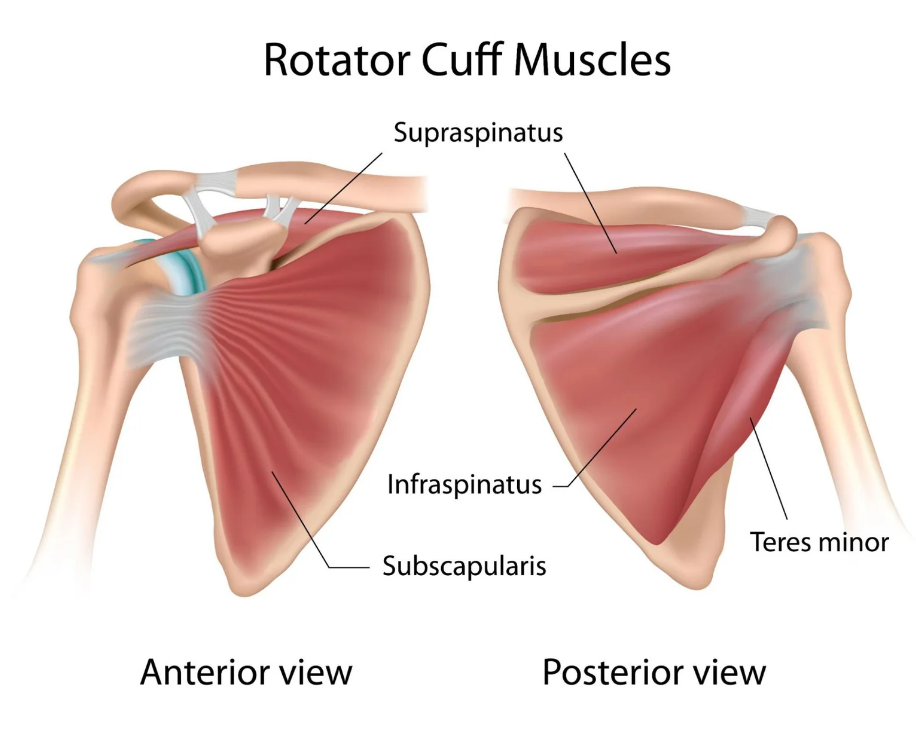
rotator cuff muscles (4)
nerves & movements
SITS
Subscapularis
subscapular n
IR
supraspinatus
suprascapular n
abduction and shoulder elevation
Infraspinatus
suprascapular n
ER
Teres minor
axillary n
ER
shoulder flexion muscles (2)
anterior deltoid
axillary n
coracobrachialis
musculocutaneous n
shoulder abduction muscles (2)
middle deltoid
axillary n
supraspinatus
suprascapular n
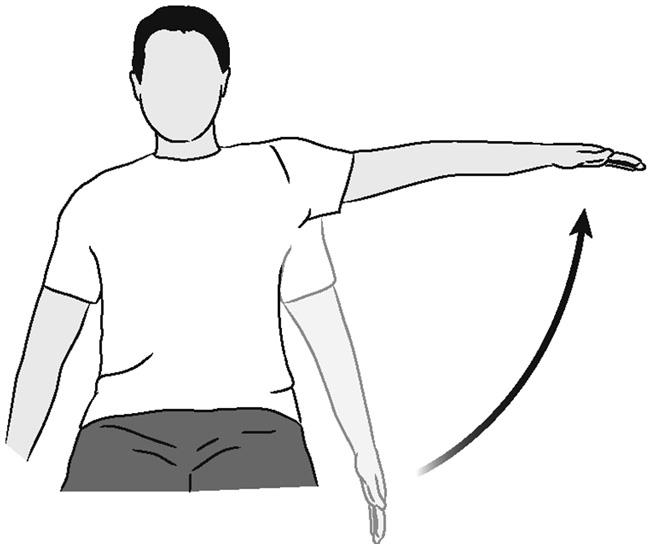
horizontal abduction muscles (1)
posterior deltoid
axillary n
horizontal adduction muscles (1)
pectoralis major
lateral pectoral n
shoulder ext muscles (3)
latissimus dorsi
thoracodorsal n
teres major
subscapular n
posterior deltoid
axillary n
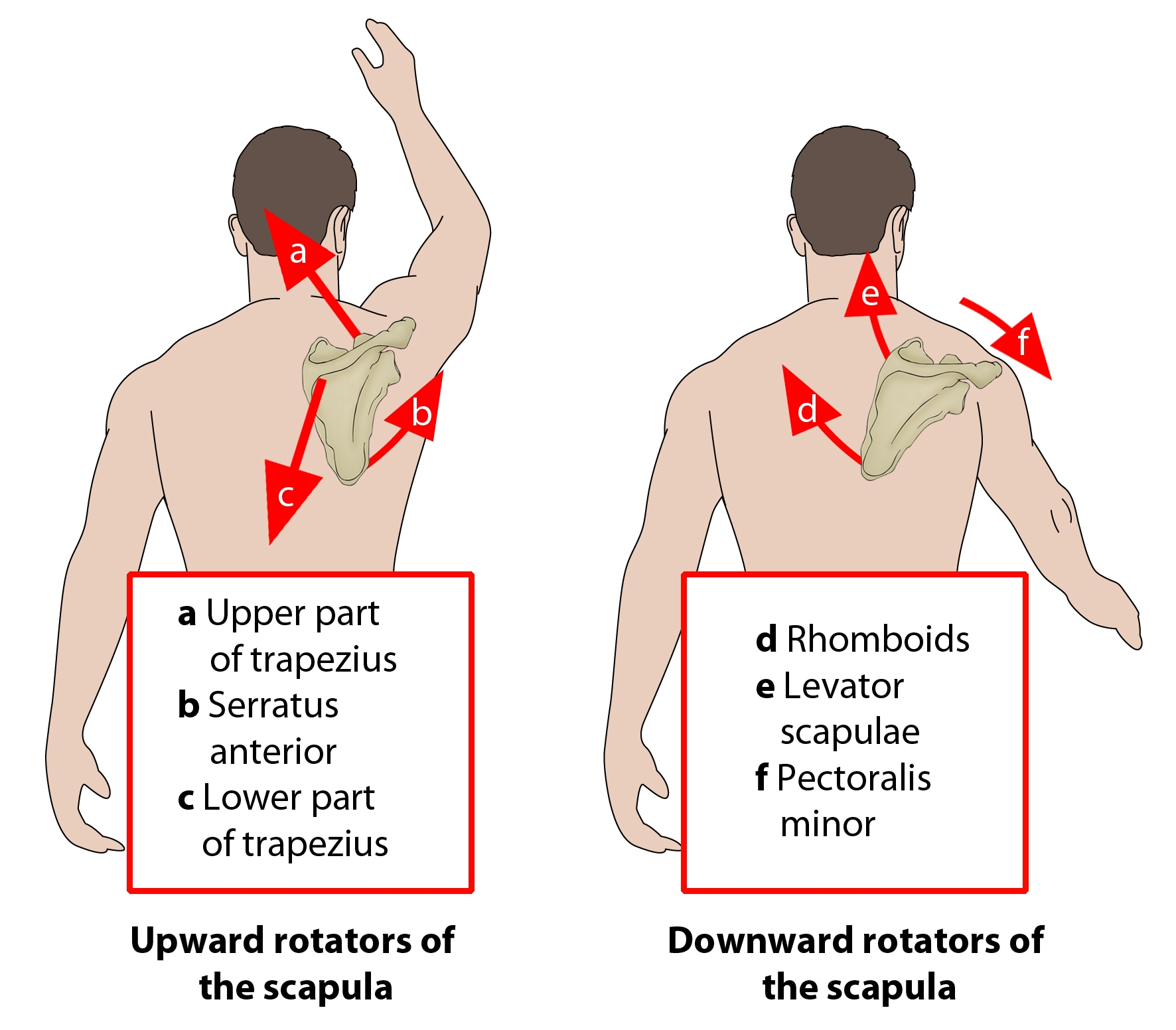
upward rotation of scapula muscles (2)
trapezius (UML)
spinal accessory n (CNXI/11)
serratus anterior
long thoracic n
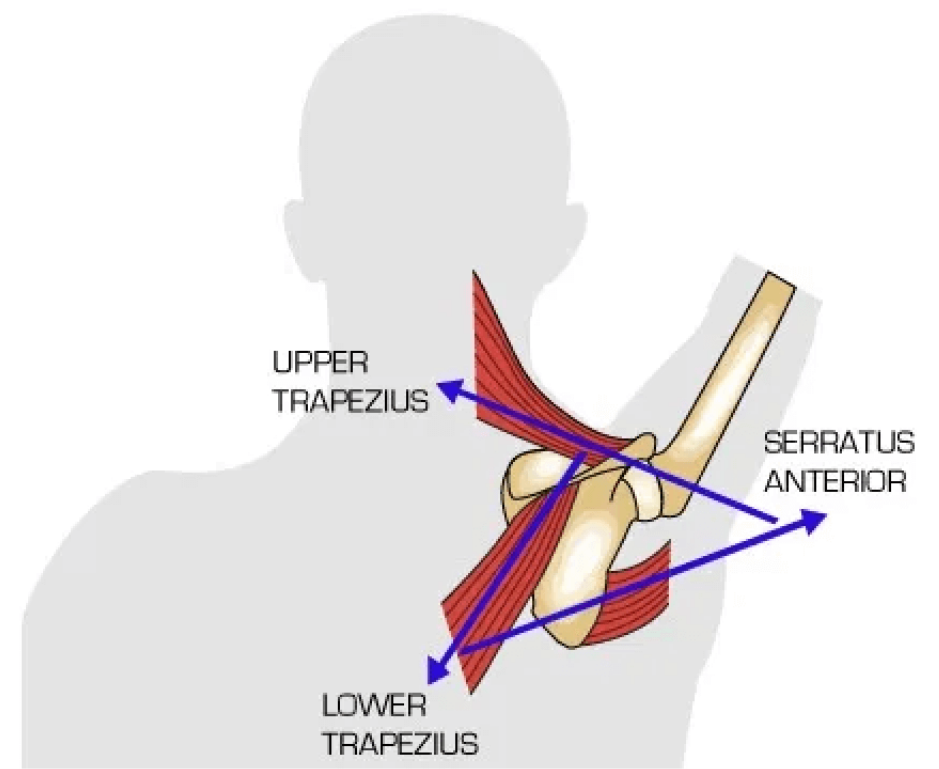
downward scapular rotation muscles (4)
levator scapulae
C3-C4
rhomboids (both)
dorsal scapular n
serratus anterior
long thoracic n
latissimus dorsi
thoracodorsal n
scapula adduction muscles (2)
middle trapezius
spinal accessory n (CN11)
rhomboid major
dorsal scapular n
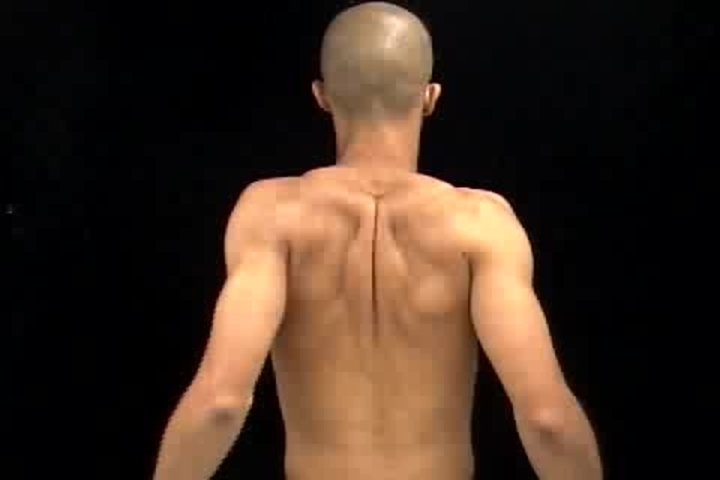

scapular abduction muscles (1)
serratus anterior
long thoracic n
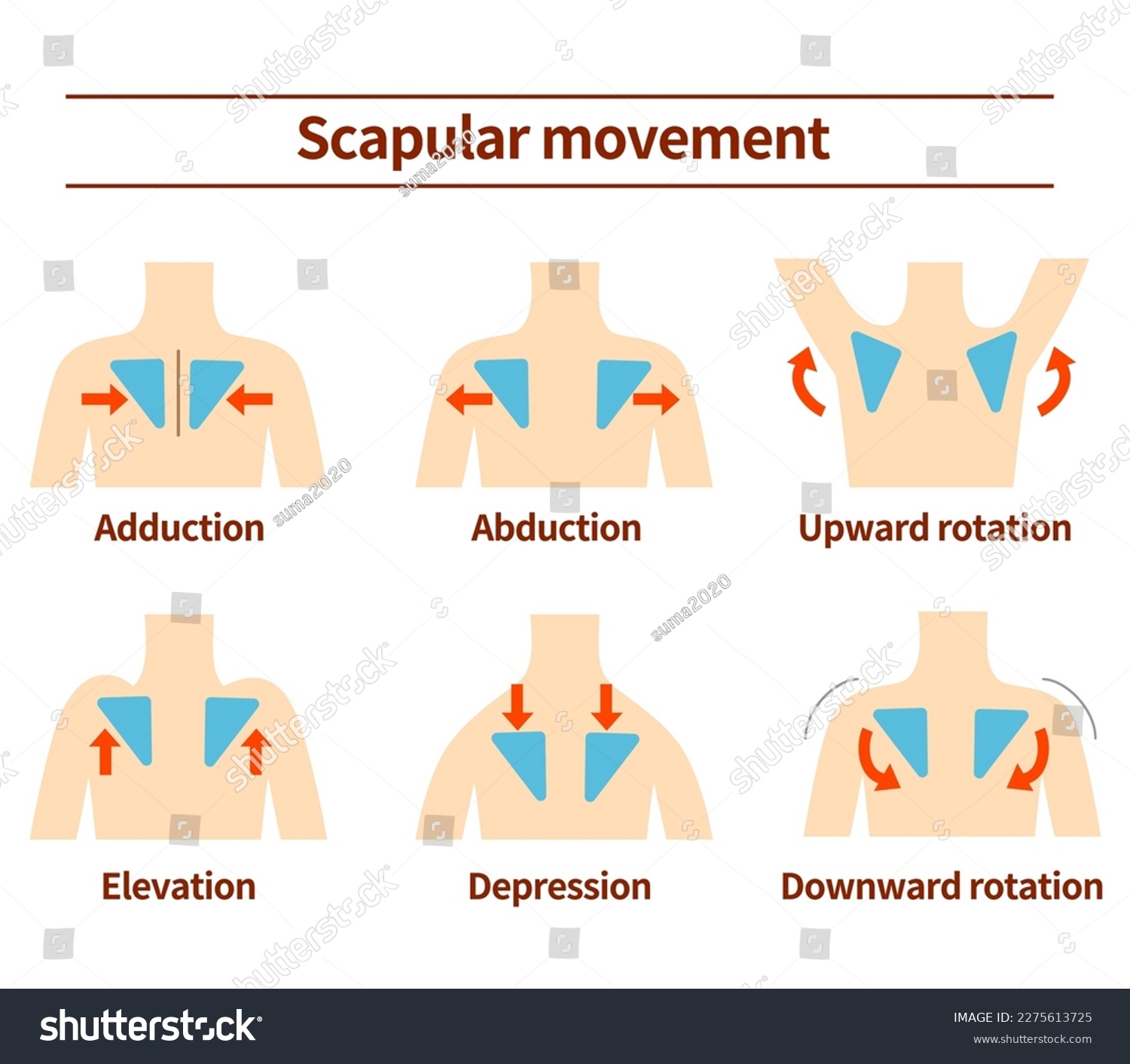
scapular elevation muscles (2)
trapezius (upper)
spinal accessory n (CN11)
levator scapulae
C3-C4
scapula depression muscles
trapezius (lower)
spinal accessory n (CN11)
dupuytren’s disease
what
cause
tx
OT intervention
disease of fascia of palm and digits
fascia becomes thick and contracts; develops cords and bands that extend into digits
CAUSE: unknown
TX: conservative tx has NOT been successful > medical tx used
OT intervention:
wound care after surgery, edema control, orthosis, AROM/PROM, scar management, occupation-based

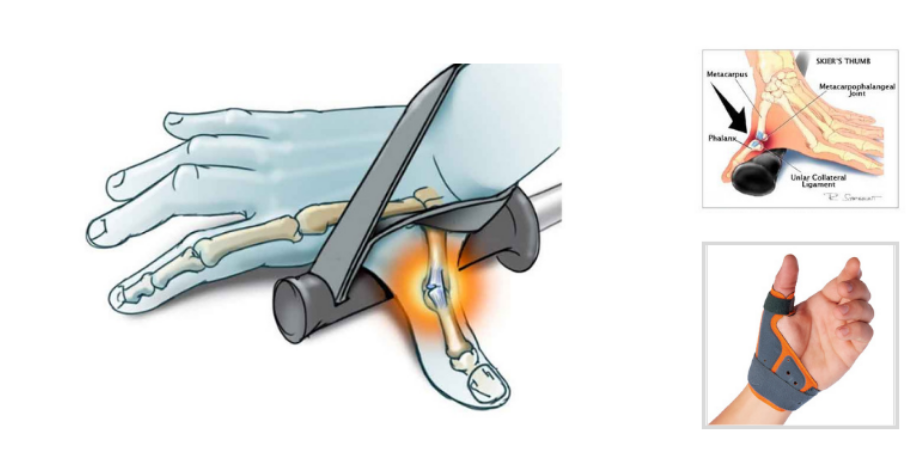
skier’s thumb (gamekeeper’s thumb)
rupture of ulnar collateral ligament of MCP joint of thumb
CAUSE: falling with thumb held on pole
OT:
conservative tx for partial tear > thumb orthosis
AROM at 2-4wks
AAROM and strengthening at 6-12wks
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
vasomotor dysfunction as result of abnormal reflex
localized or general
CAUSE: may follow trauma or surgery but actual cause unknown
SX:
severe pain, edema, discoloration, osteoporosis, sweating, blotchy skin, temp changes, trophic changes, vasomotor instability
OT:
modalities for pain and hypersensitivity
TENS during ADLs or prior to AROM
edema management
stress loading (scrubbing! and carrying!)
orthotics, ADLs, mental health
closed reduction
NON SURGICAL treatment for fractures
types of stabilization include:
short arm cast (SAC)
long arm cast (LAC)
orthosis
sling
fracture brace
open reduction internal fixation (ORIF)
SURGICAL fracture tx
TYPES:
nails, screws, plates, or wire
arthrodesis
fusion
arthroplasty
joint replacement
most common UE fractures (7)
colles fx:
fx of distal radius with dorsal displacement
smiths fx
fx of distal radius with volar displacement
carpal fx
most common is scaphoid fx, proximal scaphoid has poor blood supply and may become necrotic
metacarpal fx
phalanx fx (proximal, middle, distal)
elbow fx
humerus fx
OT intervention for fractures
immobilization phase: stabilization and healing
AROM of joints above/below fx
edema control
light ADL
mobilization phase: consolidation
edema control: retrograde, elevation, compression
orthosis
AROM, light ADLs, strengthening
pain management
cumulative trauma disorders (CTDs)
risk factors
types (4)
AKA repetitive strain injuries (RSI), overuse syndromes
RISK FACTORS:
repetition, static position, awkward postures, forceful exertions, vibration
acute trauma, pregnancy, diabetes, arthritis, wrist anatomy
TYPES:
de Quervain’s
lateral epicondylitis
trigger finger
nerve compression
de Quervain’s
what
sx
tx
stenosing tenosynovitis of abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis
sx: pain and swelling over radial styloid
positive finkelstein’s test
conservative tx
thumb spica orthosis (IP joint free)
activity modification
ice massage over radial wrist
gentle AROM
post op tx
thumb spica orthosis and gentle ARM (0-2wks)
strengthening, ADL (2-6wks)
unrestricted ax (6wk)
lateral epicondylitis
what
tx
AKA tennis elbow
degenerative changes of tendon’s origin as result of repetitive microtrauma
overuse of wrist extensors (extensor carpi radialis brevis)
conservative tx
elbow strap, wrist orthosis
ice and deep friction massage
stretching
activity modification
as pain decreases > add strengthening
trigger finger
tenosynovitis of finger flexors (A1 pulley)
caused by repetition and use of tools that are placed too far apart
conservative tx
hand or finger based trigger finger orthosis
scar massage
edema control
tendon gliding
activity modification
tendon repairs
early mobilization prevents adhesion and facilitates wound/tendon healing
OT GOALS:
incr tendon excursion
improve strength at repair site
incr joint ROM
prevent adhesion
facilitates resumption of meaningful roles
duran protocol
passive flexion and extension of digits
0-4wks dorsal blocking orthosis
exercise in orthosis for passive flexion
2.5wks passive place/active hold exercises
manage edema, scar management
4-6wks AROM with wrist and fingers relaxes, tendon gliding
6-8wks gentle strengthening
12wks return to regular fxn
early active mobilization for flexor tendon repairs general principles
min of 4 strands in procedure
close communication with surgeon
experienced OT
orthosis used
6wks begin light ADL
8wks gentle strengthening
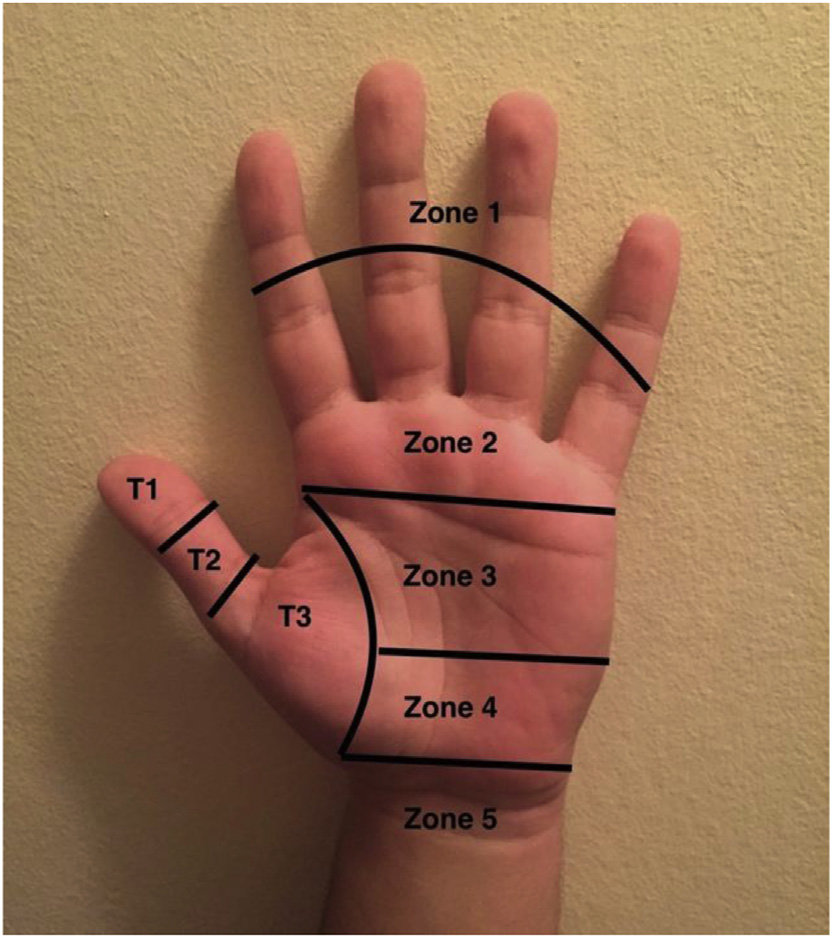
Zones I and II
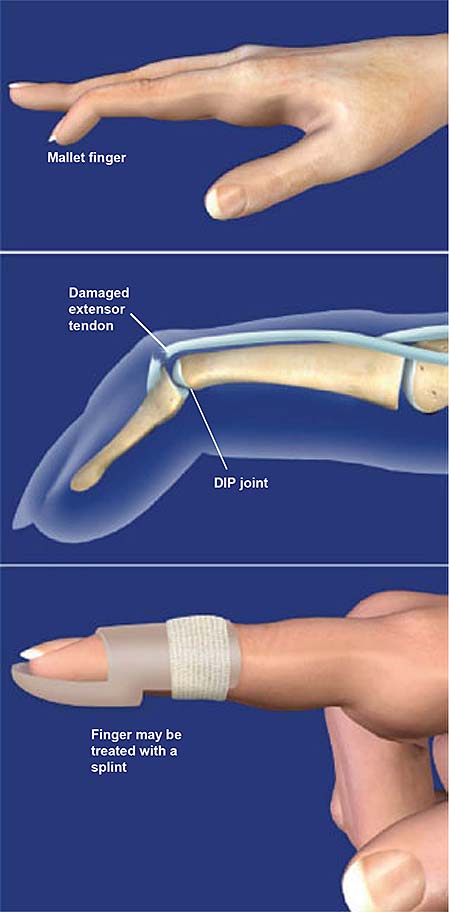
mallet finger deformity
0-8wks: DIP extension orthosis
6-8wks: gentle AROM
orthotics worn at night and btw exercises
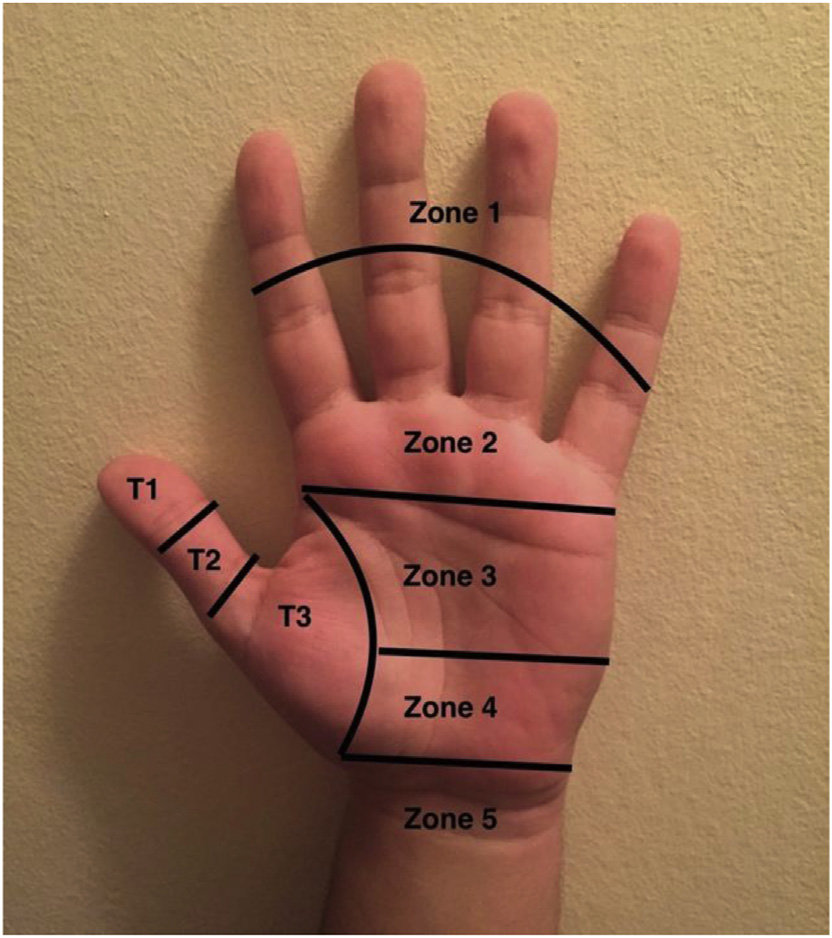
Zones III and IV
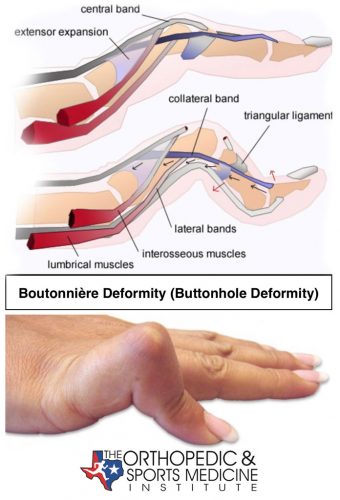
boutonniere deformity
0-6wks: PIP extension orthosis (DIP free)
AROM of DIP
two common types of nerve injuries
compression or nerve entrapment
laceration or avulsion injury
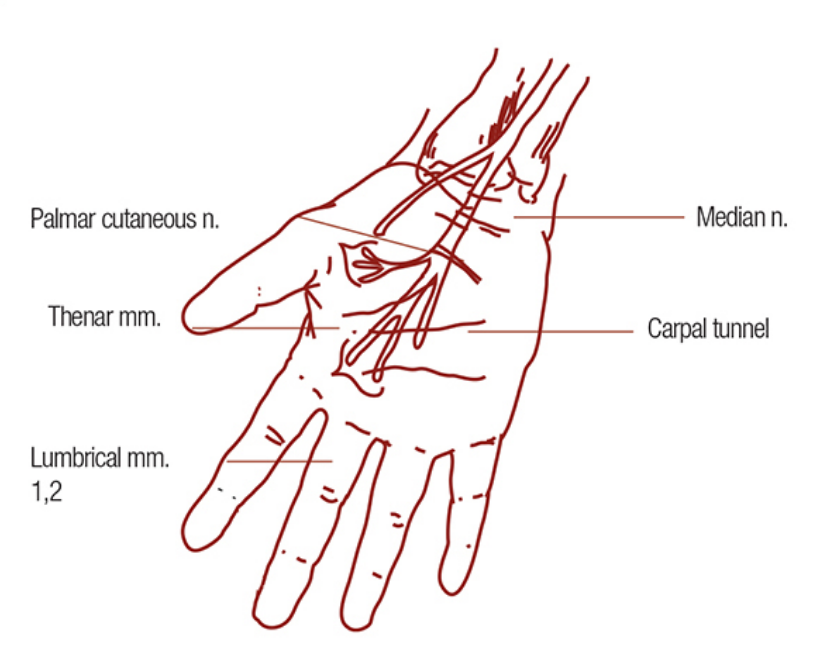
carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)
median n compression
CAUSE:
narrowing of carpal canal due to swelling/pregnancy, inflammation, hypertrophy and anatomical anomalies, cumulative trauma
SX:
numbness and tingling of thumb, index, middle, and radial half of ring fingers
paresthesias at night
dropping things
positive tinel’s test, positive phalens sign
atrophy at thenar eminence
conservative tx
wrist orthosis in neutral
median nerve gliding
activity modification, ergonomics
post op tx
edema control, AROM, scar management, nerve & tendon glides, sensory re-education, strengthening, ergonomic/work modification
cubital tunnel syndrome
ulnar n compression at elbow
2nd most common compression
CAUSE:
pressure at elbow and extreme elbow flexion
SX:
numbness and tingling along ulnar aspect of forearm and hand
pain at elbow with elbow flexion
weakness of power grip
froment’s sign, tinels sign
conservative tx
elbow orthosis at 30deg flex
elbow pads
ulnar nerve gliding
post op tx
edema control, scar management, AROM (2wks), strengthening (4wks)
radial nerve palsy
radial n compression
CAUSE:
Saturday night palsy, compression due to humeral shaft fx
SX:
weakness or paralysis of extensors at wrist, MCPs, and thumb
wrist drop
conservation tx
dynamic wrist and MCP extension orthosis
work/activity mod
strengthening
post op tx
AROM, strengthening (6-8wks), ADLs
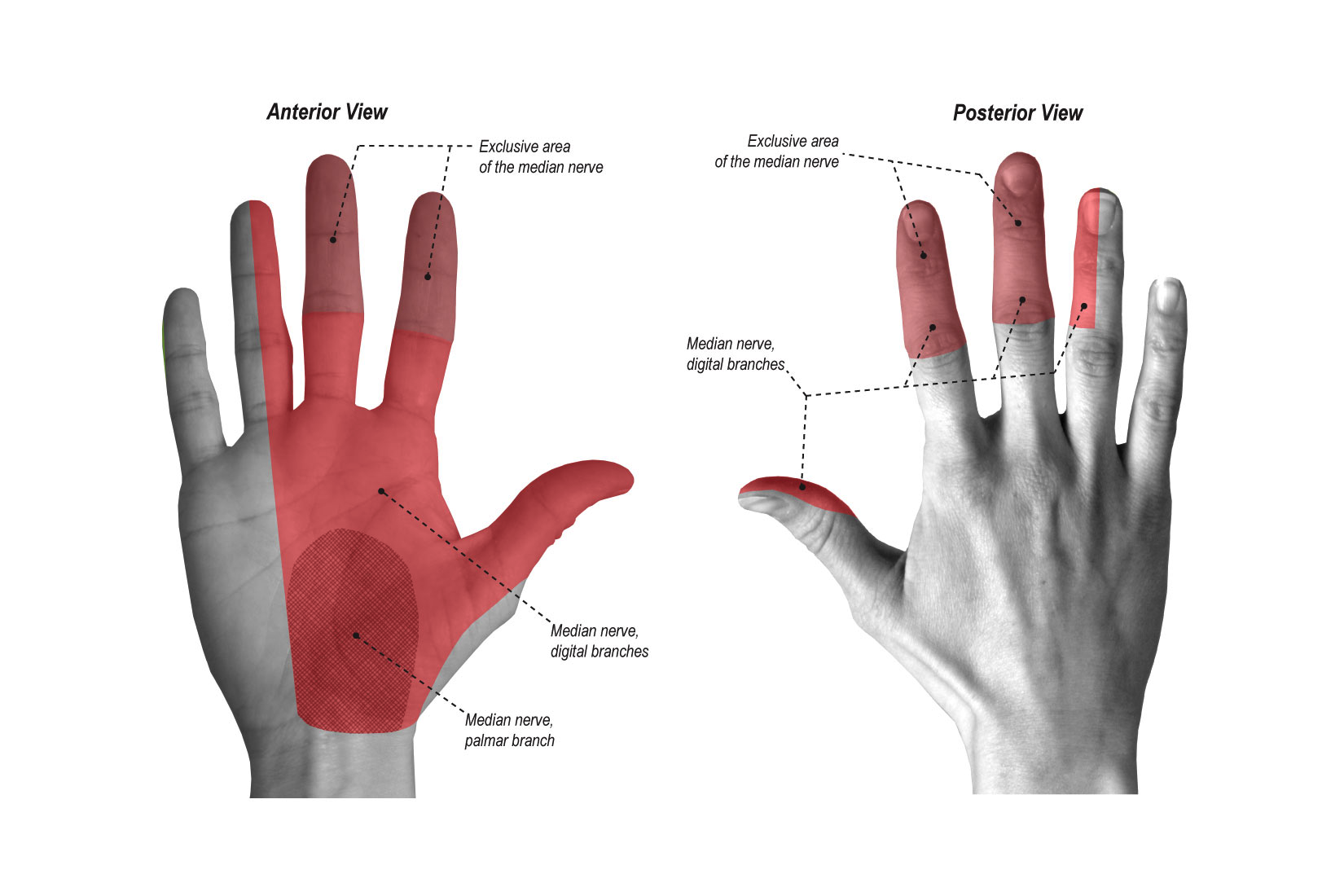
median n laceration
sensory loss to
central palm, digits 1-3, and half of digit 4
dorsal middle & distal phalanges of digits 2,3, and half 4
motor loss
LOW
MCP flexion of digits 2-3
thumb opposition, abduction and flexion of MCP (weak pinch)
HIGH
flex of DIP at digits 1-3
flex of radial wrist
deformity
flat thenar eminence
claw of index and middle finger
OT tx
orthosis, A/PROM, strengthening, scar management, sensory re-education
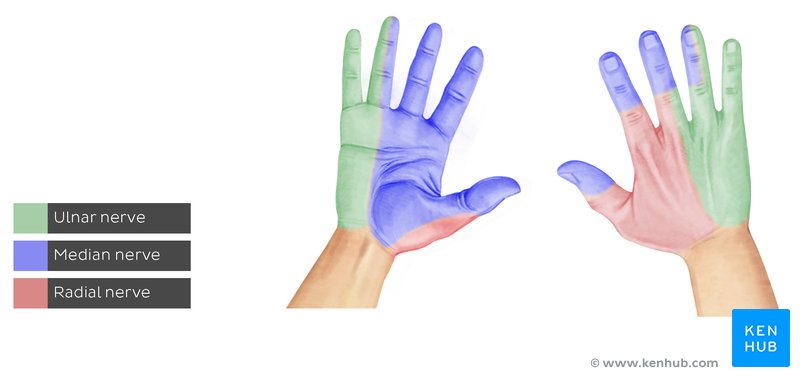
ulnar n laceration
sensory loss
ulnar aspect of palmar and dorsal surface
motor loss: loss power grip, decr pinch
LOW
adduction and abduction of MCP
MCP flex of digits 4-5
flex and adduct of thumb
abduction, opposition, and flexion of digit 5
HIGH
flexion of ulnar wrist
flex of DIP of digits 4-5
deformity
claw hand
flat metacarpal arch
froments sign
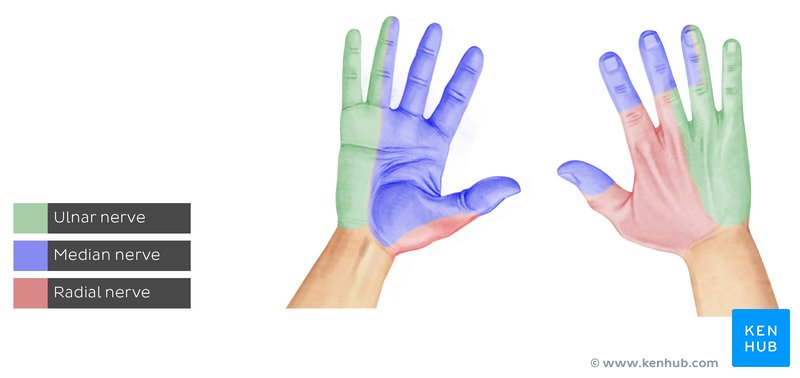
radial nerve lacerations
sensory loss
dorsal forearm, radial dorsal palm, half of digits 1-3
motor loss: loss of extension
LOW
wrist ext
MCP ext
thumb ext
HIGH
elbow ext
deformity
wrist drop
rotator cuff tendonitis
impingement at coracoacromial arch
CAUSE:
overuse, curved acromion, weakness of RTC, weak scapula, ligament tightness, trauma
conservative tx
activity mod to limit should use (no above shoulder height)
sleep positioning
decr pain w/ positioning, modalities, rest
strengthen
post op tx (arthroscopic, open repair)
PROM (0-6wk)
AAROM/AROM (6-8wks)
strengthening (8-10wks)
resume activity (12wks)
adhesive capsulitis
frozen shoulder
STAGES:
freezing: shoulder becomes painful at end ranges
OT: address pain w/modalities, gentle A/PROM, home exercise program
frozen: less pain, loss of motion, capsule pattern
OT: modalities (heat > cold), A/PROM, HEP
thawing: pain subsides and ROM returns
OT: stretching, ROM, function
restricted PROM of shoulder
capsular pattern: greatest limitation is ER > abduction > IR > flexion
CAUSE:
inflammation, immobility, diabetes, parkinsons
shoulder dislocation
anterior most common
CAUSE:
trauma, overuse
OT
ROM (avoid abduction + ER)
strengthen
rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
systemic, symmetrical, and widespread affect
most common in small joints of hands
remissions and exacerbations
phases
acute: inflammatory process of synovial lining
unknown cause
SX:
pain, stiffness, limited ROM, fatigue, weight loss, inflammation/swelling, social isolation, deformities
deformities common
ulnar drift with sublux of MCP
boutonniere
swan neck
zig zag
boutonniere deformity
flexion of PIP joint and hyperextension of DIP
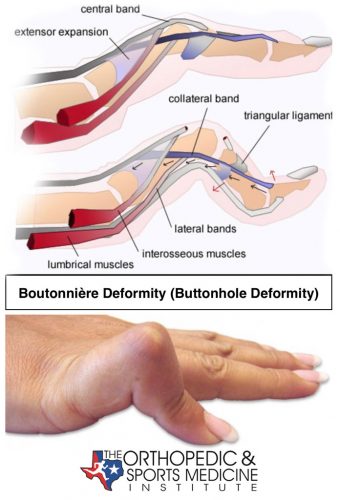
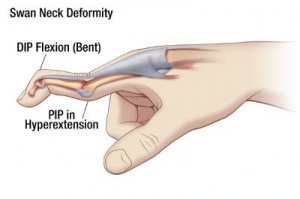
swan neck deformity
witch finger
hyperextension of PIP and flexion of DIP
osteoarthritis (OA)
degenerative joint disease
not systemic but wear and tear
commonly affects large weightbearing joints
attacks hyaline cartilage
CAUSE: genetics, trauma, CTD, endocrine/metabolic diseases
SX:
pain, stiffness, limited ROM, bone spurs
heberden’s nodes at DIP
bouchards nodes at PIP
osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)
dysfunction of one of several genes responsible for producing collagen for development of bone structure and strength
present at birth, no cure
mild to severe
type 1: mild
type 4,5,6: moderate
type 2,3,7,8: severe (2 is most)
SX:
brittle, malformed bones
growth problems, loose joints
OT:
education, activity mod
weightbearing, protective splinting, positioning
arthrogryposis multiplex congenita (AMC)
congenital joint contractures involving two or more joints
detected in utero or at birth
often a RESULT of other diagnosis
NON progressive, no cure
unknown cause
SX:
joint contractures, limited ROM
vary due to source diagnosis
typical cognitive development
OT
gentle ROM, weight bearing, strengthening
activity/enviro mod, training
hip fractures
due to trauma, osteoporosis, or pathological finds (cancer)
types
femoral neck, interochanteric, subtrochanteric
get weightbearing status!! from surgeon
common complications: avascular necrosis, nonunion, degenerative joint disease
posterior approach hip precautions & adaptive equipment
PRECAUTIONS:!!!!!
no hip flexion greater than 90 degrees
no internal rotation (toes in)
no adduction (crossing legs or feet)
violation of precautions could result in dislocation
AE:
hip kit (reacher, shoe horn, sock aide, LH sponge)
adduction wedge
raised commode
anterior approach hip precautions & adaptive equipment
PRECAUTIONS:
no hip extension
no external rotation (toes out)
no adduction
some surgeons have a no precautions approach for anterior
AE:
hip kit (reacher, shoe horn, sock aide, LH sponge)
adduction wedge
total hip arthroplasty
caused by trauma or disease (arthritis)
types
total hip joint implant
hemiarthroplasty
posterior or anterior approach
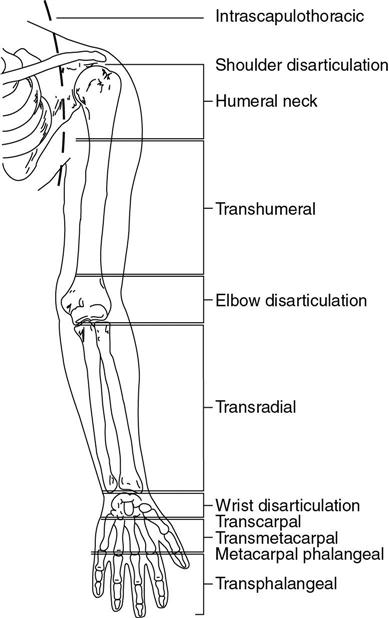
UE amputations
forequarter: loss of scapula, clavicle, and UE
shoulder disarticulation: entire UE
transhumeral (long & short)
elbow disarticulation: distal to elbow joint
transradial (long and short)
wrist disarticulation: distal to wrist joint
transmetacarpal
finger
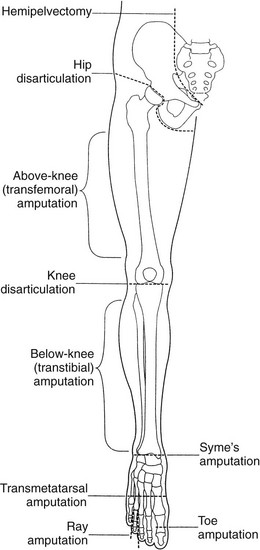
LE amputations
hemipelvectomy: half of pelvis and entire LE
hip disarticulation: at hip joint
above knee: any level on thigh
knee disarticulation: at knee joint
below knee: any level on calf
ankle (syme)
ray (metatarsal)
transmetatarsal
complete phalanges
spinal precautions and adaptive equipment
PRECAUTIONS: BLT
- no bending
- no lifting more than 5lbs
- no trunk rotation (twisting)
AE:
- back brace
body powered prostheses
use specific muscles to place tension on cable that opens or closes TD (terminal device)
two main types:
hook: used for functional ax
hand: used for cosmetic appearance
two main ways of operation:
voluntary closing: hook remains open until tension is placed on cable and closes
voluntary opening: hook remains closed until tension is placed on cable and opens
more common
PROS:
durable, provides prop feedback, less maintenance cost
CONS:
restrictive harness, decreased grip, force exerted on residual limb, can be difficult to control
myoelectric (electrically powered) prostheses
muscle contractions of two different muscle groups are used to control TD
types:
hook: allows pinch and FM manipulation (opposition)
hand: cosmetic appearances with pinch fxn
PROS
improved cosmesis, can be fitted early in recovery
incr and proportional grip, larger fxn
minimal/no harness, minimal effort for control
CONS
incr cost, high maintenance, susceptible to environment
lack of sensory feedback, incr weight
hybrid prosthesis
combo of body powered and electrically powered
most common for elbow or above elbow amputations
PROS:
simultaneous control of elbow and wrist
less weight, incr grip
CON
harness, may be difficult to operate
passive prosthesis
static, used for cosmetic appearances, can be passively adjusted to assist with carrying or grasping
PRO
no harness or cables
cosmetic restoration
low maintenance, lightweight
CON
no active grasping fxn
activity specific prosthesis
generally no harness or control cable
designed for specific work or leisure task
PRO
allows enhanced fxn and task specific participation
minimal harness or cabling
durable, low maintenance, reduce wear and tear on primary prosthesis
CON
no active grasp
limited to specific task
complications of amputations
neuromas: nerve endings adhere to scar tissue
skin breakdown
phantom limb:
syndrome: sensation of presence of limb
pain: painful sensation of presence of limb
infection
contractures
psychological trauma
pre-prosthetic training phase
begin: postsurgical period ends
end: patient receives preparatory or definitive prosthesis
intervention focus:
emotional support
stabilize limb volume
wrapping
distal to proximal
desensitize sensitive areas of residual limb
activities to strengthen motor patterns in preparation to operate the prescribed device
determine optimal type of prosthesis to meet patients goals
prosthetic training phase
begin: delivery of temporary or definitive prosthesis
end: pt demonstrates a successful functional outcome with proper prosthetic use
intervention focus:
control training
balance
repetitive drills
don/doff prosthesis
wear tolerance: start 15-30 min 3x daily
functional training to learn to integrate the prosthesis as an assistive tool in daily activities that align with patient goals
burn levels
1. superficial: dry red, 3-7 days
2. superficial partial-thickness: moist red, 7-21 days
3. deep partial thickness: mottled, 21-35 days, graft
4. full thickness: dry white, months, graft
superficial burns
epidermis only
PRESENTS: dry, crinkle, red, little painful, no blisters
OUTCOME: heal spontaneously in 3-7 days; no scar
EX: sunburn, short flash burns
superficial partial-thickness burn
epidermis & upper level dermis
PRESENTS: blistered, red, weepy, moist; hair follicles intact; very painful
OUTCOME: heals spontaneously within 7-21 days; no grafts; minimal to no scar
EX: scalds, radiation
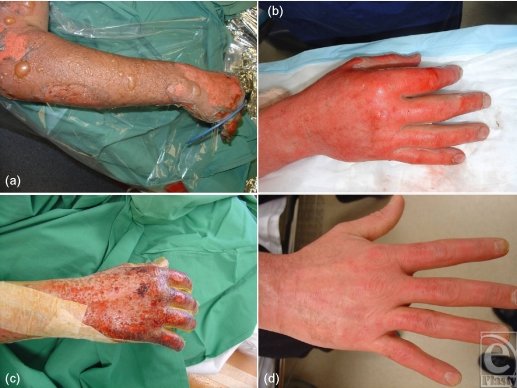
deep partial thickness burn
epidermis & severe damage to dermis, hair follicles, and sweat glands
PRESENTS: blotchy, large pink blisters, mottled white, pink, to cherry red; damage to BV's; painful
OUTCOME: 3-5 weeks to heal (21-35 days); scarring increased; often grafted
EX: immersion scalds, flames
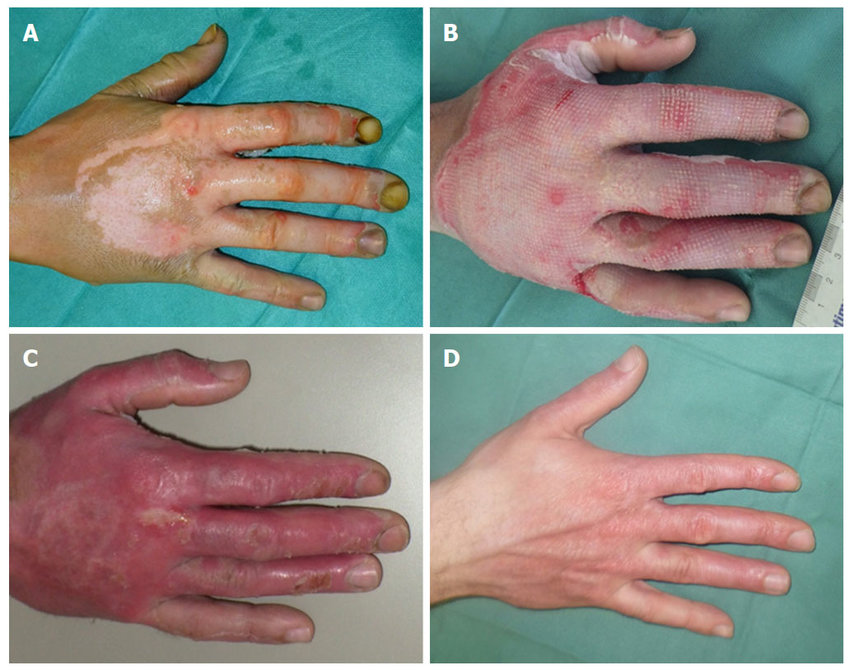
full thickness burn
epidermis & dermis destroyed
may include fascia, muscle, tendon, and bone
PRESENT: white or waxy (adipose showing); dry, leathery, non-pliable until debrided; no sensation
OUTCOME: surgical intervention; can damage underlying structures; months to heal
EX: electrical, chemical, flame, scald
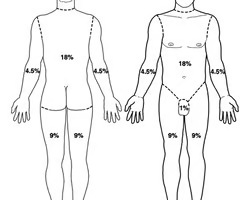
rule of nines
a method used in calculating body surface area affected by burns
HEAD: 9%
ARMS: 9% each
GROIN: 1%
TORSO: 36%
LEGS: 18% each
what is included in the primary survey when assessing a patient with burn injury
- ABCs
Airway with C-spine immobilization
Breathing and ventilation
Circulation and hemorrhage control
Disability and deformity
Exposure and environmental control
Fluids and foley
emergent burn phase
72 hours post burn
focus on stabilization
fluid resuscitation
inhalation injury: possible trach/vent
compartment syndrome
wound care
nutrition: metabolic rate increase with burns; important to increase protein, vitamins, etc
contracture formation
anticontracture positioning for burns
contractures will form in position of comfort
skin will seize up > contracture forms
EX: burn to back of knee will result in knee flexion contractures; burn to anterior neck will result in neck flexion
anterior neck
contracture: neck flexion
position: remove pillows, extend neck with splint or collar
axilla
contracture: adduction
position: 120 abduct with slight ER (gorilla stance)
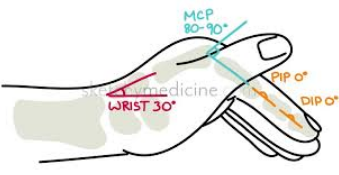
antideformity splint
AKA SAFE POSITION SPLINT
-20 deg wrist ext
-90 deg MCP flex
-PIP/DIP 0 deg ext (full)
for burns to hand or dorsal hand
acute burn phase
after emergent until wounds closed
support and psychosocial adjustment (anxiety, depression, PTSD)
medical management: skin graft
ROM contraindicated following graft
initial eval & interventions
wound care, education, gentle mobility, pain, sensation, splints
rehabilitation burn phase
until scar maturation (6 months to 2 yrs)
intervention focus: general OT burn focuses
sensation, pain, scar, strength
pressure therapy: compression to healed wounds using gloves, bandages, or wraps
2hr > 23hr wear tolerance for 1-2yrs until scars mature
myofascial pain syndrome
persistent, deep aching pain in muscles, nonarticular in origin
well defined, highly sensitive tender spots )trigger points)
fibromyalgia syndrome
musculoskeletal pain and fatigue disorder that can very in intensity
SX:
widespread pain accompanied by tenderness of muscles and adjacent soft tissues
rheumatic disease of unknown origin
low back pain
most common work related injury
causes
poor posture
repetitive bending using poor body mechanics
heavy lifting
poor sleep posture
SX:
pain, difficulty with self-care, difficulty sleeping
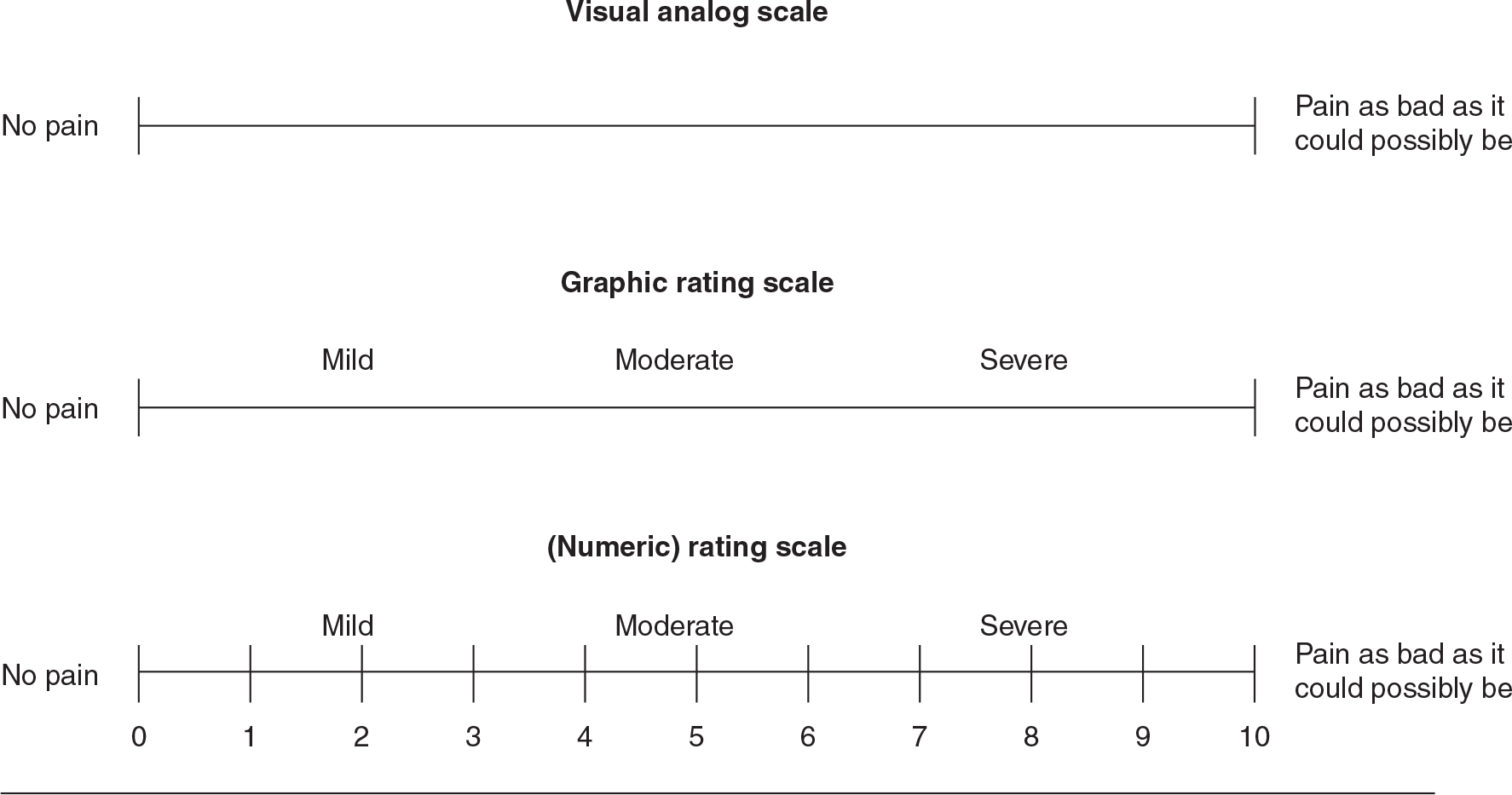
visual analog scale
having individuals mark a point along a straight line that represents a continuum between two extremes