BIOL116 Lecture #21 (11/24/25) (11/26/25)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What formula captures the impact (I) of a human population on the environment ?
The formula is I = P A T, where:
P is the number of people
A is average income
T is level of technology
Habitat destruction fragmentation, modification, degradation
anthropogenic stressor
Change in nutrients and resource availability
anthropogenic stressor
Chemicals (pollution)
anthropogenic stressor
Eutrophication
anthropogenic stressor
pathogens
anthropogenic stressor
Overexploitation
anthropogenic stressor
Invasive species
anthropogenic stressor
Climate change
anthropogenic stressor
Ranking of ecological footprint by country
China
USA
India
Russia
Japan
What does the ‘Human ecological footprint’ measure?
It measures the amount of land area (global hectares) and energy needed to support an average citizen of a nation
According to the provided material, what is the greatest threat to the world’s species?
Habitat destruction is the greatest threat, followed by overexploitation
What term describes the process where a large continuous habitat is reduced in area and divided into two or more fragments?
habitat fragmentation
In habitat fragmentation, the area of different vegetation or land use introduced between fragments is known as the ___
matrix
What is ‘effective population size’ (Ne)
It is the size of the population estimated by the number of its breeding individuals, which is usually lower than the total population size (N)
What is the term for the process where toxic chemicals in water become successively more concentrated at higher trophic levels?
Biomagnification
The accumulation of a substance, such as a toxic chemical, in various tissues of a living organism is known as ___
bioaccumulation
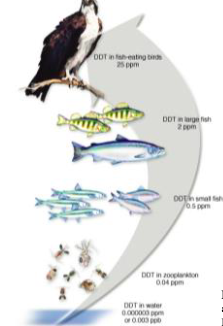
What does this image show?
An example of biomagnification (not bioaccumulation)
What is eutrophication?
It is the increase in nutrient levels in a water body, which has significant effects on aquatic communities, often leading to algal blooms
During eutrophication, wat is the direct consequence of the massive increase in phytoplankton like cyanobacteria and algae?
They cover the upper sunlit layer of the water, which can block light to organisms below.
What environmental problem is produced when industries release large quantities of nitrogen and sulfur oxides that combine with atmospheric moisture?
Acid rain, which is a combination of nitric and sulfuric acids
ON the pH scale, a substance with a pH less than 7 is considered ___, while a substance with a pH greater than 7 is considered _
acidic; alkaline
What is definition of overexploitation or overharvesting?
It is a harvest that exceeds the productive capacity of a species, causing its population to decline over time
What Latin American tree species, also known as caoba, is mentioned as being overexploited for its wood?
Broad leaf mahogany (Siwetenia macrophylla)
Why was the American bison (Bison bison) hunted almost to extinction by European colonizers and who
native Americans
What is the ‘Tens Rule’ regarding invasive species?
Roughly 10% of imported species escape, 10% of those establish populations, and 10% of established species become problematic.
What are the five defining characteristics of an invasive species listed in the material?
not native
established
abundant
spreading
has negative effects on local species or ecosystems
has negative effects on local species or ecosystems
defining characeristic of invasive species
spreading
defining characteristic of invasive species
established
defining characteristic of invasive species
abundant
defining characteristic of invasive species
not native
defining characteristic of invasive species
A disease-producing pathogen that moves from an animal species to humans is known as a __
zoonosis
According to the source, what percentage of emerging pathogens are zoonotic
75%
The HIV virus, which causes AIDs, is an example of a zoonosis that jumped to humans from what type of animal?
Nonhuman primates, such as chimpanzees.
What term is used to describe the human introduction of pathogens or hosts into new areas?
Pathogen pollution
Why did vulture populations (Gyps spp.) decline in India, Pakistan, and Nepal?
They were consuming cattle carcasses containing the anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac, which is a toxin to them and caused kidney failure.
What is the purpose of inserting a gene from the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) into corn?
The gene produces proteins that are toxic to certain insects, making the corn resistant to pests.

For what purpose were cane toads (Rhinella marina) organically produced to Australia?
They were introduced as a form of biological control to combat beetles that were damaging sugar cane crops.
How do activities like deforestation and mining create environments suitable for disease-transmitting mosquitoes?
These activities create more spots that collect rainwater, providing ideal breeding grounds for mosquito larvae.
The Black Death, which killed over a third of Europe’s population in the 14th century, was caused by what bacterium?
The bacterium Yersinia pests
What environmental impact related to plastic waste was a consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic?
The widespread use of masks, gloves, and other single-use medical supplies led to a significant increase in plastic pollution
How can air pollutants form industrial processes cause water bodies to become more acidic?
Pollutants like nitrogen and sulfur oxides combine with moisture in the atmosphere to form nitric and sulfuric acids, which then fall as acid rain.
As acidity in water bodies increases, there are __ effects on fish, tadpoles, etc.
lethal
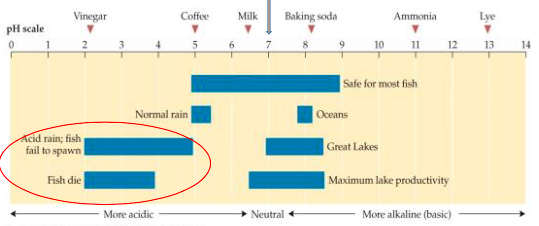
What should I takeaway from this graph about pH in aquatic environments?
Most aquatic life thrives in pH from 6.5 - 9; survival drops outside of range
Acid rain lowers pH, which prevent fish from spawning or fish death
Human activities and pollution an shift pH, affecting lake productivity and ecosystem health
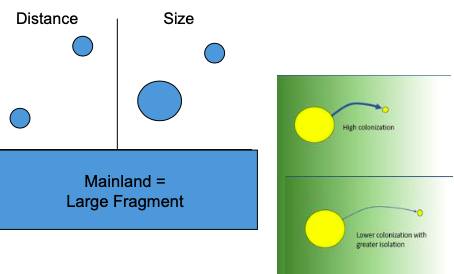
What should I takeaway from this slide about habitat fragmentation?
Habitat fragments act like islands - small size and greater isolation reduce species colonization
Closer and larger fragments = more biodiversity (easier for species to move and survive)
Number of isolated patches
habitat fragmentaiton depends on this
size of patches
habitat fragmentation depends on this
connectivity
habitat fragmentation depends on this
nature of matrix between patches
habitat fragmentation depends on this
ecology of individual species
habitat fragmentation depends on this
What happens when birds, marine mammals, and many other ocean animals when they are covered by crude oil following spills?
They sicken and die.
More reproductive individuals of a species are better for __
conservation
Why is the effective population size Ne lower than the total population size (N):
inability to find a mate
being too old or too young
poor health
sterility
malnutrition
mating system: polygyny, polyandry, etc.
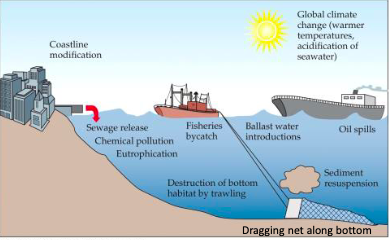
What should I takeaway from this slide about marine environments facing multiple threats?
Pollution: sewage, chemicals, and excess nutrients cause eutrophication and degrade water quality.
Fishing impacts: trawling damages seafloor habitats; bycatch harm non-target species.
Shipping: ballast water introduces invasive species oil spills pollute marine environments
Coastal development: alters shorelines and disrupts natural habitats
Sediment resuspension: reduces light penetration and affects aquatic life
Climate change: warms oceans and increases acidification, stressing marine ecosystems

Eutrophication (Oligotrophic)
clear water
low productivity
very miserable fishery at large game fish

Eutrophication (mesotrophic)
increase produciton
accumulated organic matter
occasional algal bloom
good fishery

Eutrophication (eutrophic)
very productive
more experience oxygen depletion
rough fish common
High reproductive rate + ___ rate = successful invasive species
high dispersal
Generalist diet + ___ and pathogens = successful invasive species
lack of predators
Tolerates disturbance and human presence and __ plastic = successful invasive species
phenotypically
Tolerance for wide range of conditions + ___ diet = successful invasive species
broad
Good competitors + __ or fast life cycle = successful invasive species
asexual
What parasitic flea, discussed in the lecture, can penetrate he skin of pigs and humans, often under the nails?
tunga penetrans
What do we have to know about tuna penetrates (flea) (extra)
there are males and females
this is a parasitic-like interaction
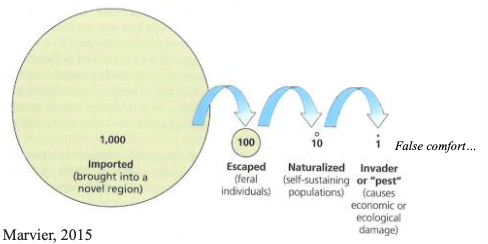
What phenomenon does this image show?
The tens rule
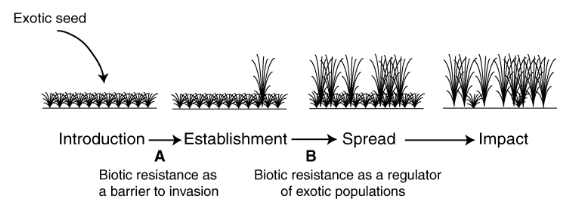
What should I takeaway from this side about species introduction and invasion?
Invasive species go through stages: introduction → establishment → spread → impact
Biotic resistance from native species can either block invasions or limit their growth after arrival
What is the difference between biomagnification and bioaccumulation?
Bioaccumulation is the buildup of substances in a single organism over its lifetime, while biomagnification is the increasing concentration of these substances at successive trophic levels in a food chain.