Stem test skeletal system
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Joint
A place where two bones come together
Marrow
two typed of soft connective tissue; red bone and yellow bone
Compact bone
A thick layer behind the membrane; hard and dense but not solid; a dense bone found in the diaphysis; its repeated pattern in arranged in concentric layers of solid bone tissue; can be seen as the layer just under the periosteum
Ligaments
Tough bands of tissue that hold your bones together at your joints
Connective tissue
The connective tissue provides support for your body and connects all its parts
Epithelial tissue
Covers the surface of your body inside and out, some protects the delicate structures that lie beneath it.
Muscle tissue
Carries out movement; makes part of your body move; can contract, or shorten like the muscle cells that form it.
Vertebrae
26 small bones, makes up your backbone; connects to form the backbone or vertebral column
Organ
An organ is a structure that is made up of different kinds of tissue
Nervous Tissue
Directs and controls processes in which the body moves. Carries electrical messages back and forth between the brain and other parts of the body
Cardiac Muscle
Found only in your heart, involuntary
Smooth Muscle
A type of tissue found in the inside of many internal body organs such as the stomach and blood vessels; involuntary
Tendon
A strong connective tissue that attaches the muscle to a bone
Skeletal Muscles
Provide the force that move your bones, appears banded, or striated voluntary
Involuntary muscles
Muscles not under your conscious control, responsible for activities such as digesting your food, breathing and more
Skeleton
your framework, made up of all bones in your body
Spongy Bone
Lighter and less dense than compact bones. A layer at the ends and under the compact bone within long bones.
Cartiledge
Strong connective tissue that is more flexible than bone
Tissue
A tissue is a group of similar cells that perform the same functions
Organ system
An organ system, which is a group of organs that work together cary out major functions
Voluntary Muscles
Muscles under your conscious control, smiling, writing and more
Example of connective tissue
Bone tissue and fat tissue
Examples of epithelial tissue
Skin
Four types of tissue
Muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, epithelial tissue
Examples of connective tissue
Bone tissue and fat tissue
Osteoporosis
a condition in which bones become weak and break easily; causes the spaces in a bone to become larger, reducing its density and strength; caused by mineral loss as you age
Function of a skeletal muscle
Allows your body to react quickly; tires quickly
Function of a smooth muscle
Works to control certain movements inside your body, such as moving food through your digestive system; not striated; muscle reacts and tires slowly
Function of a cardiac muscle
Can contract repeatedly, striated but does not tire
Striated muscle
Muscle cells that appear banded
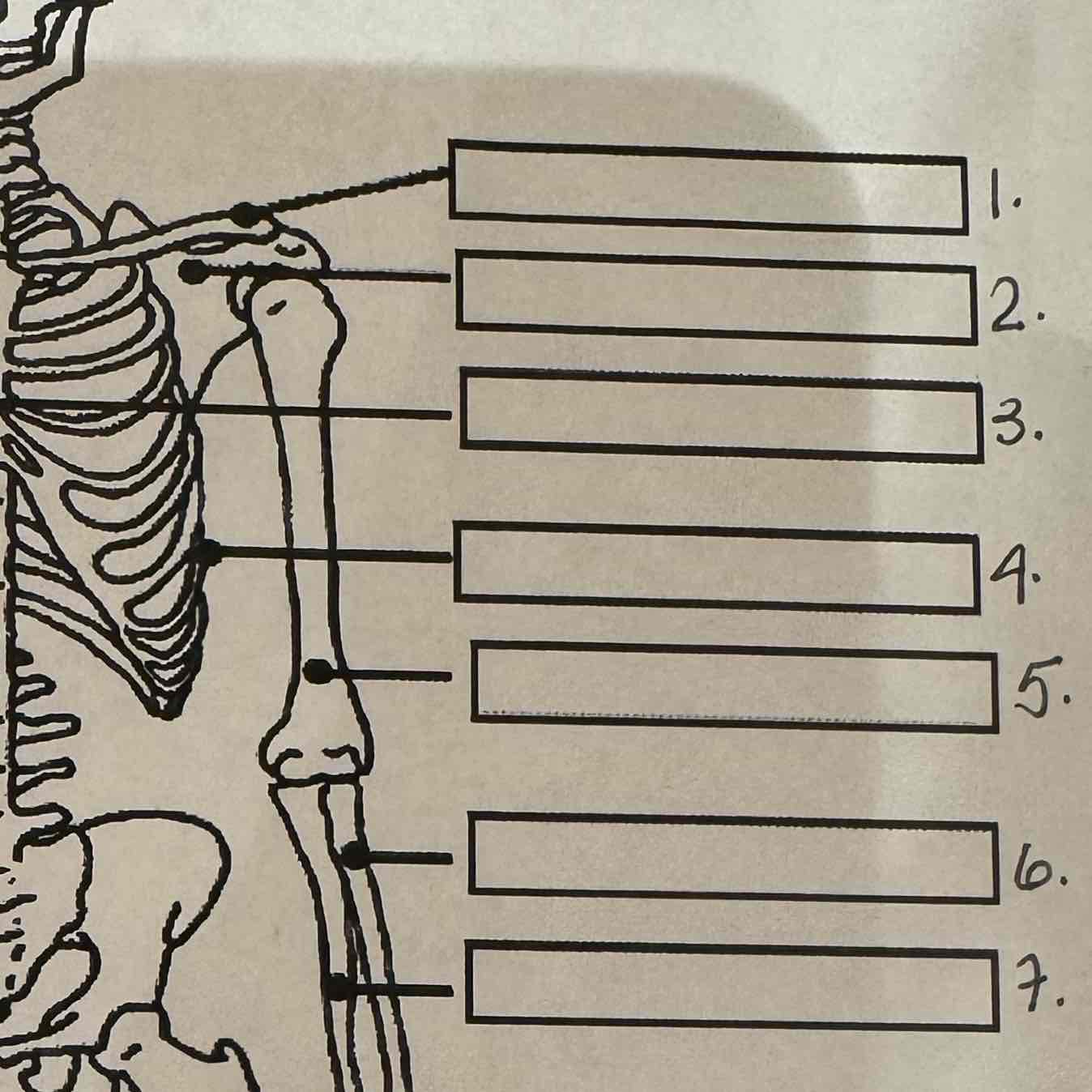
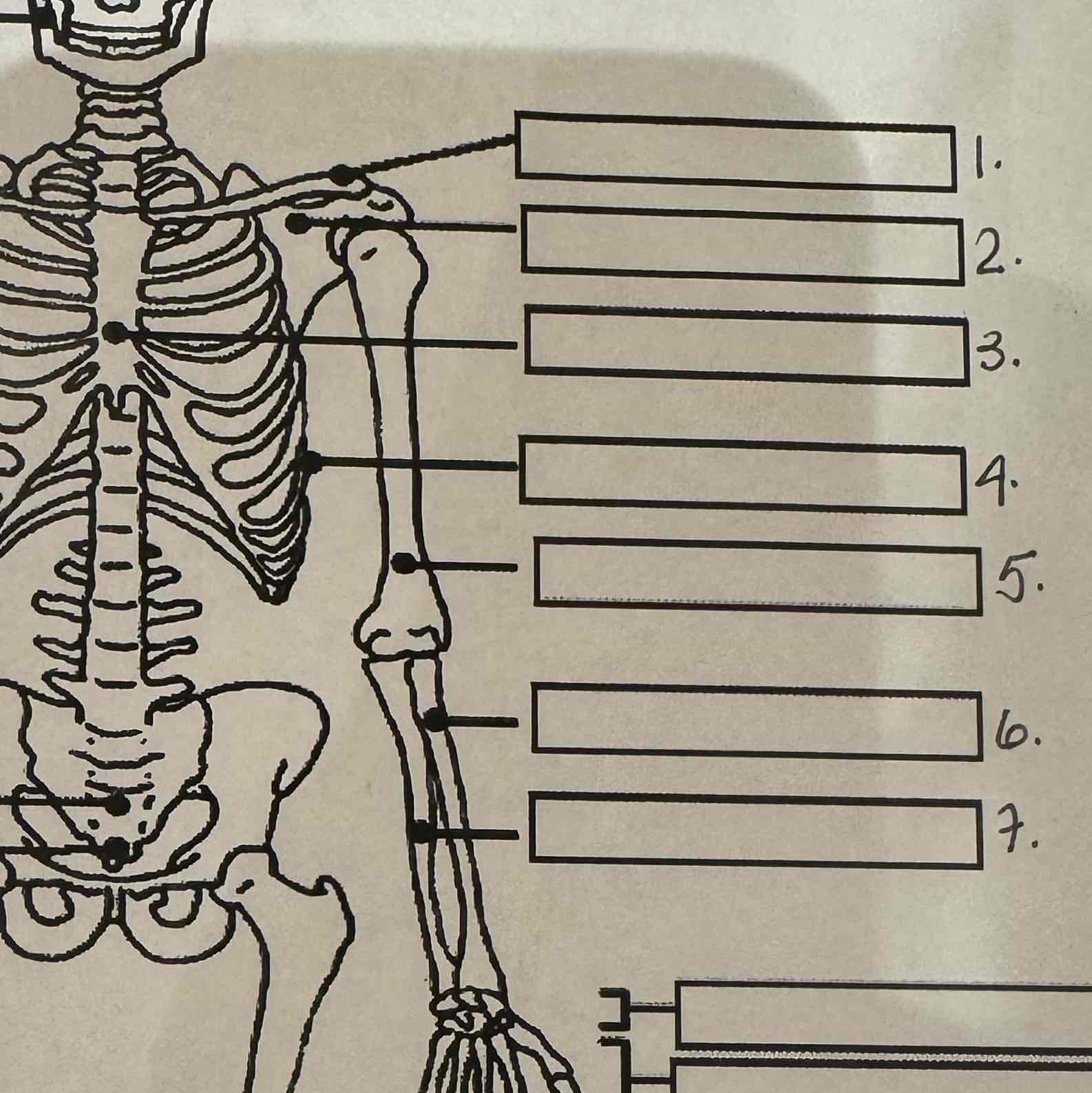
1
Clavicle
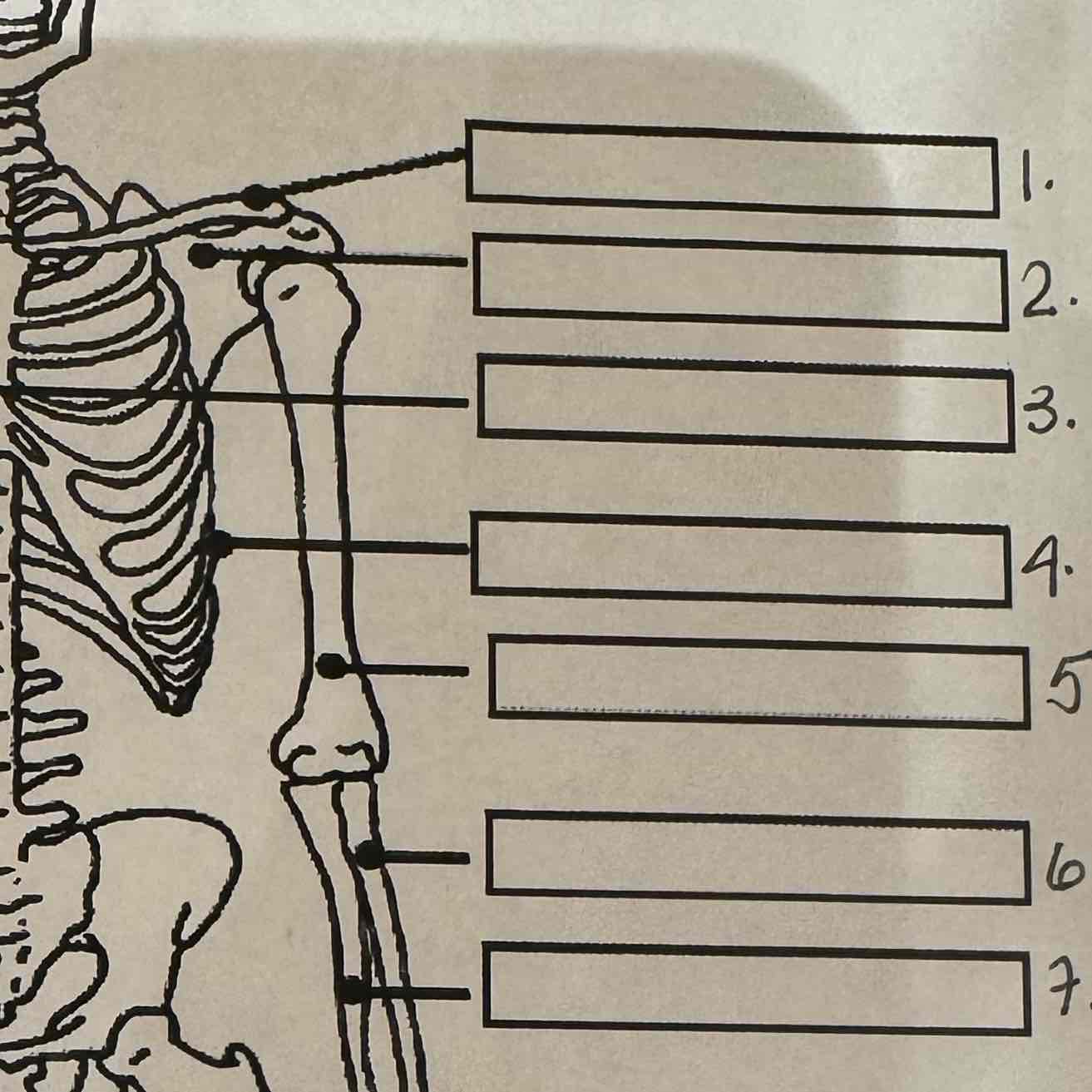
2
Scapula
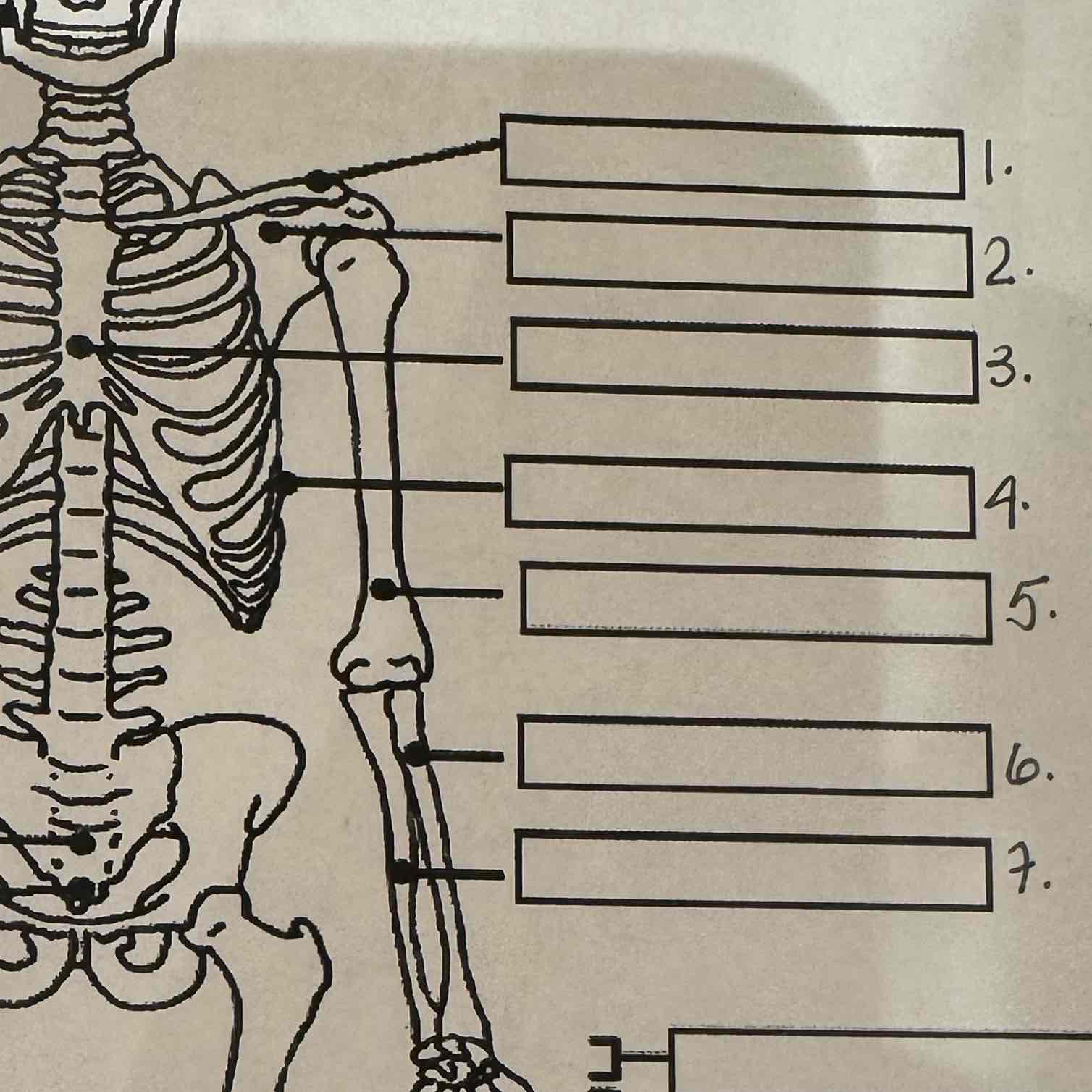
3
Sternum
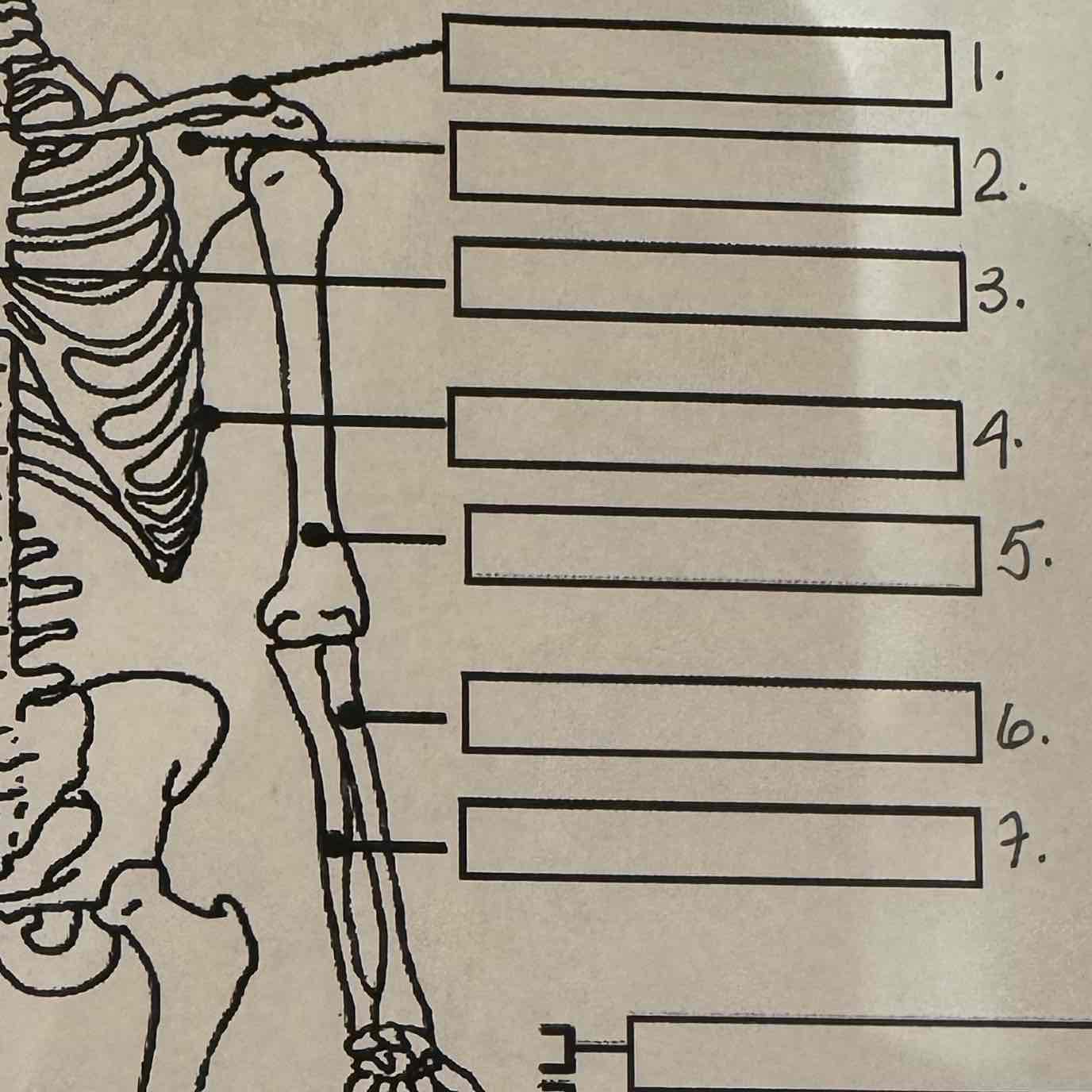
4
Ribs
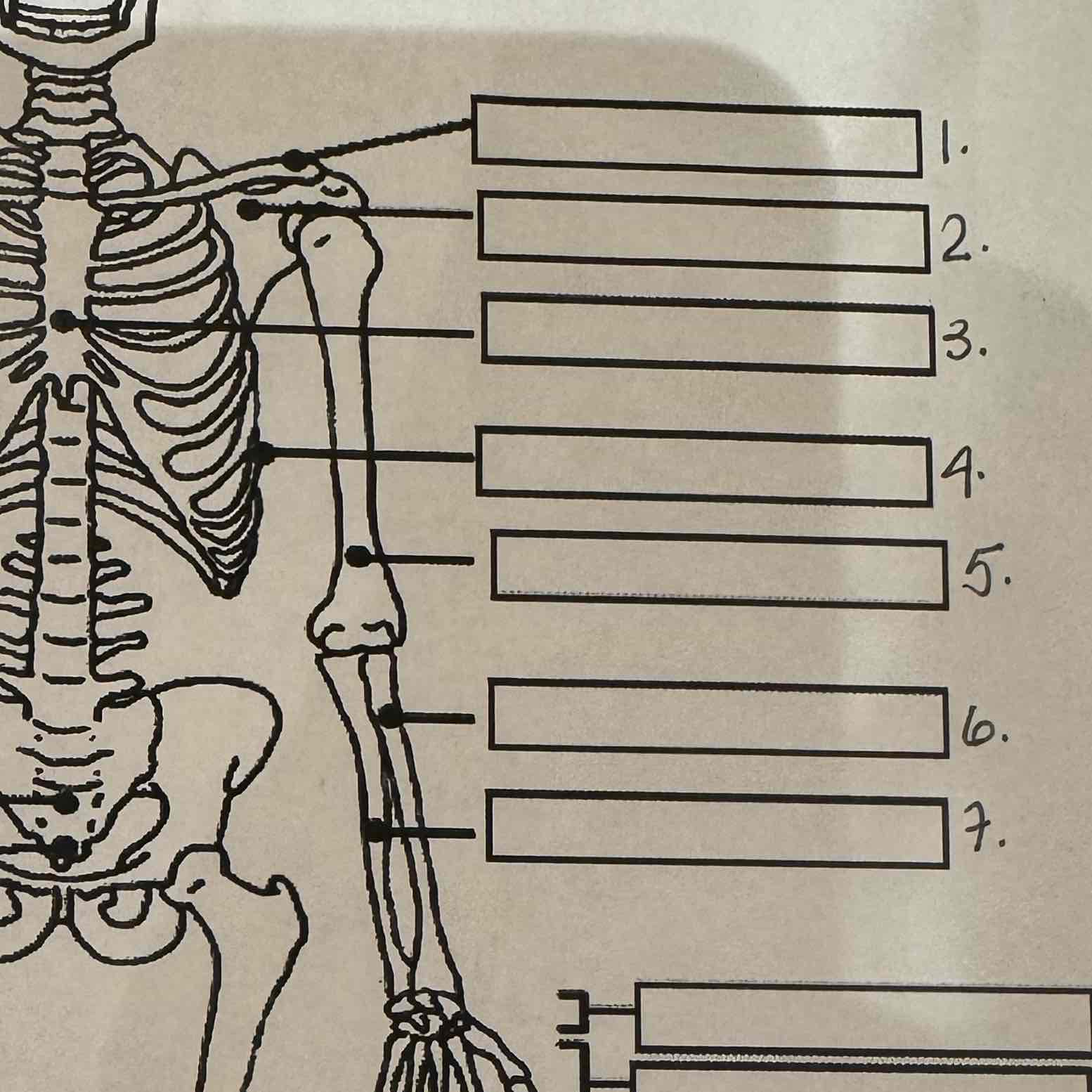
5
Humerus
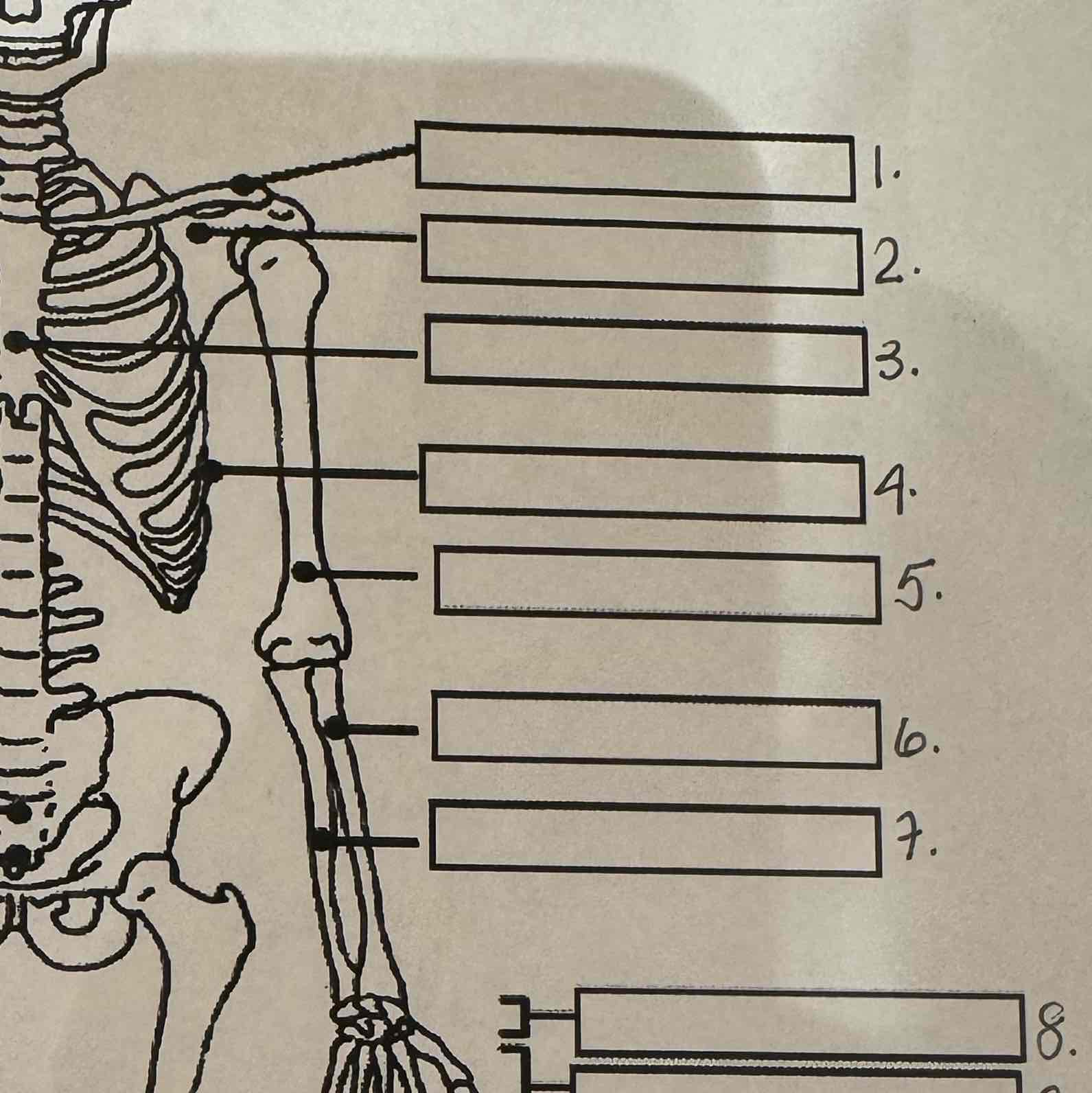
6
Radius
7
Ulna
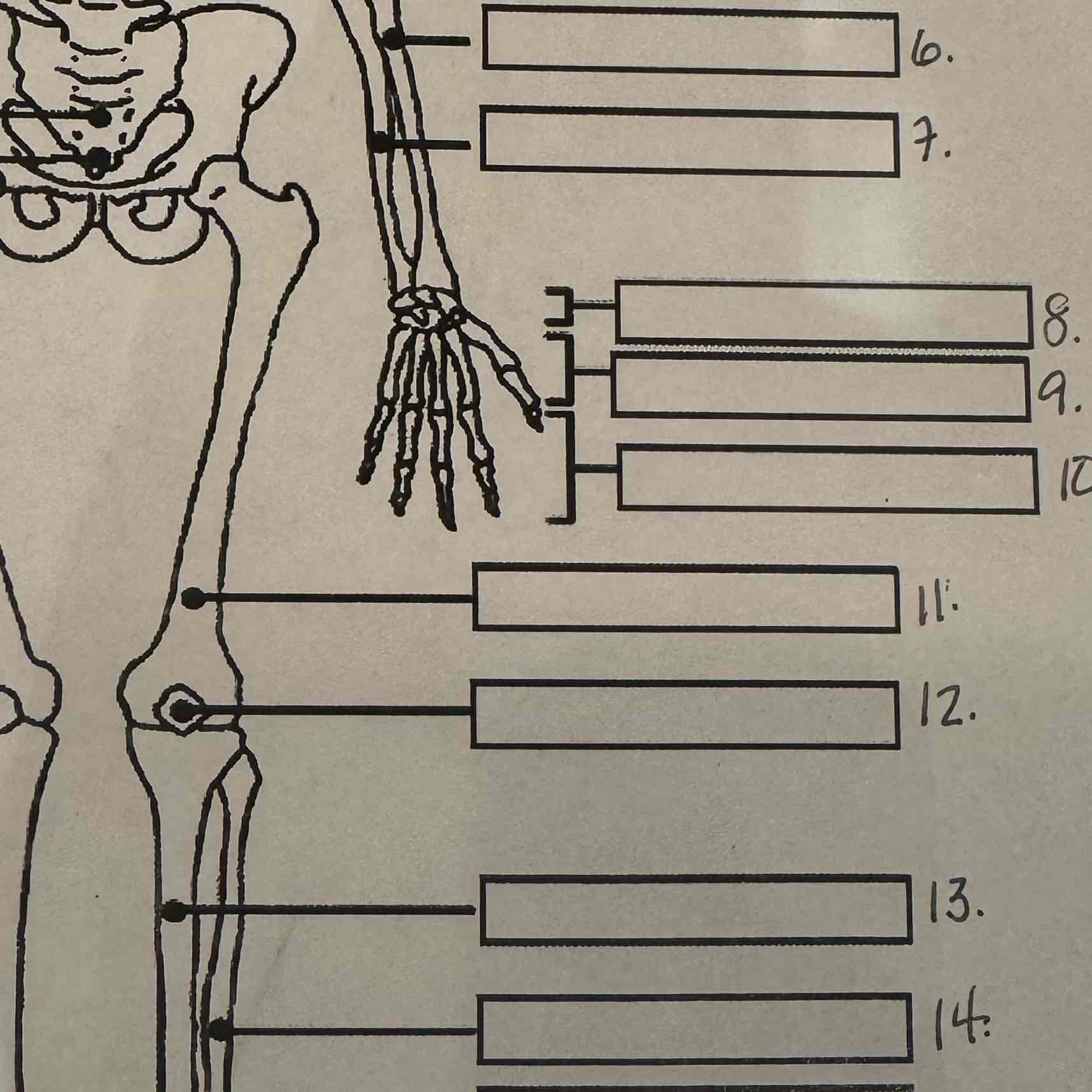
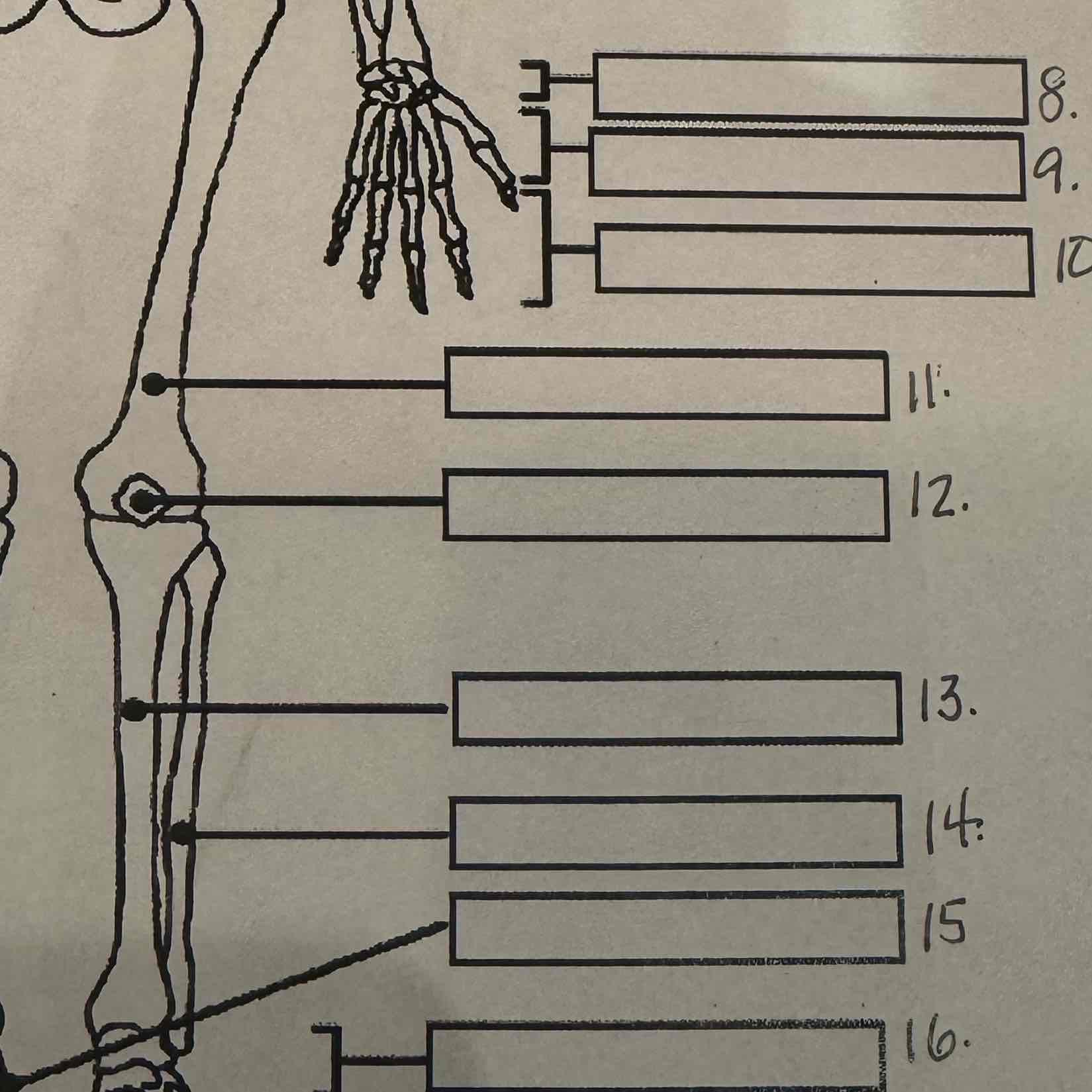
8
Carpals
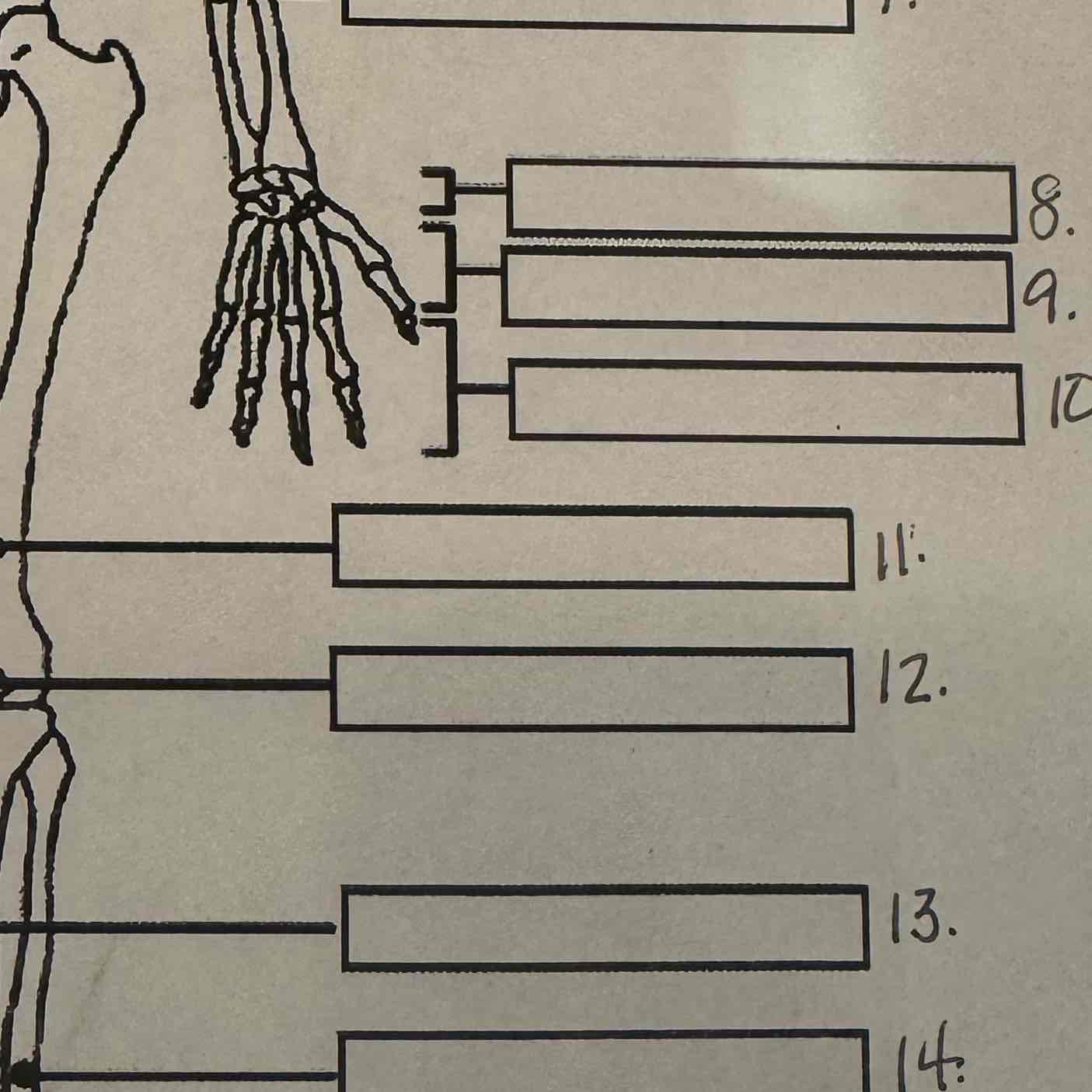
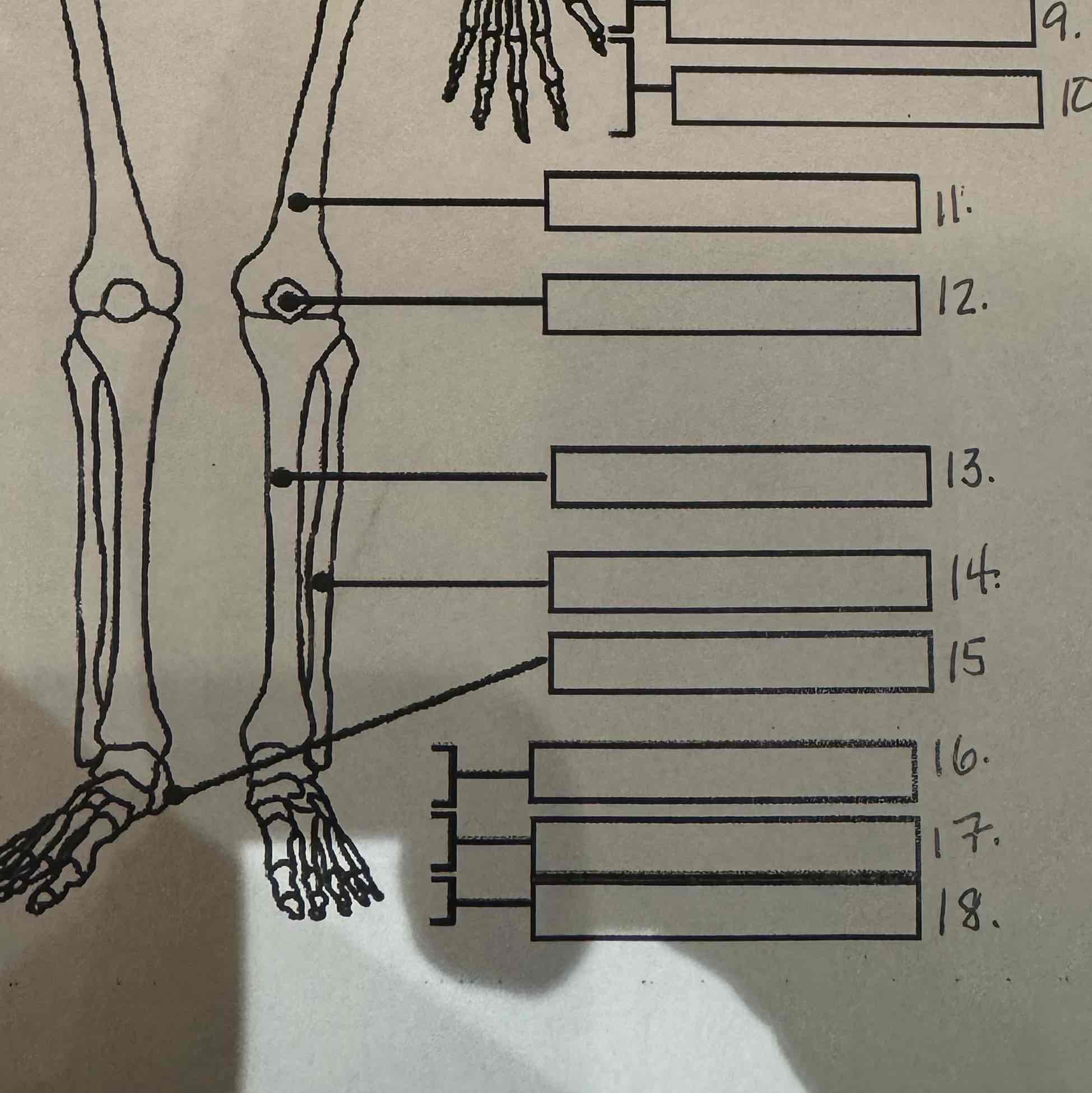
9
Metacarpals
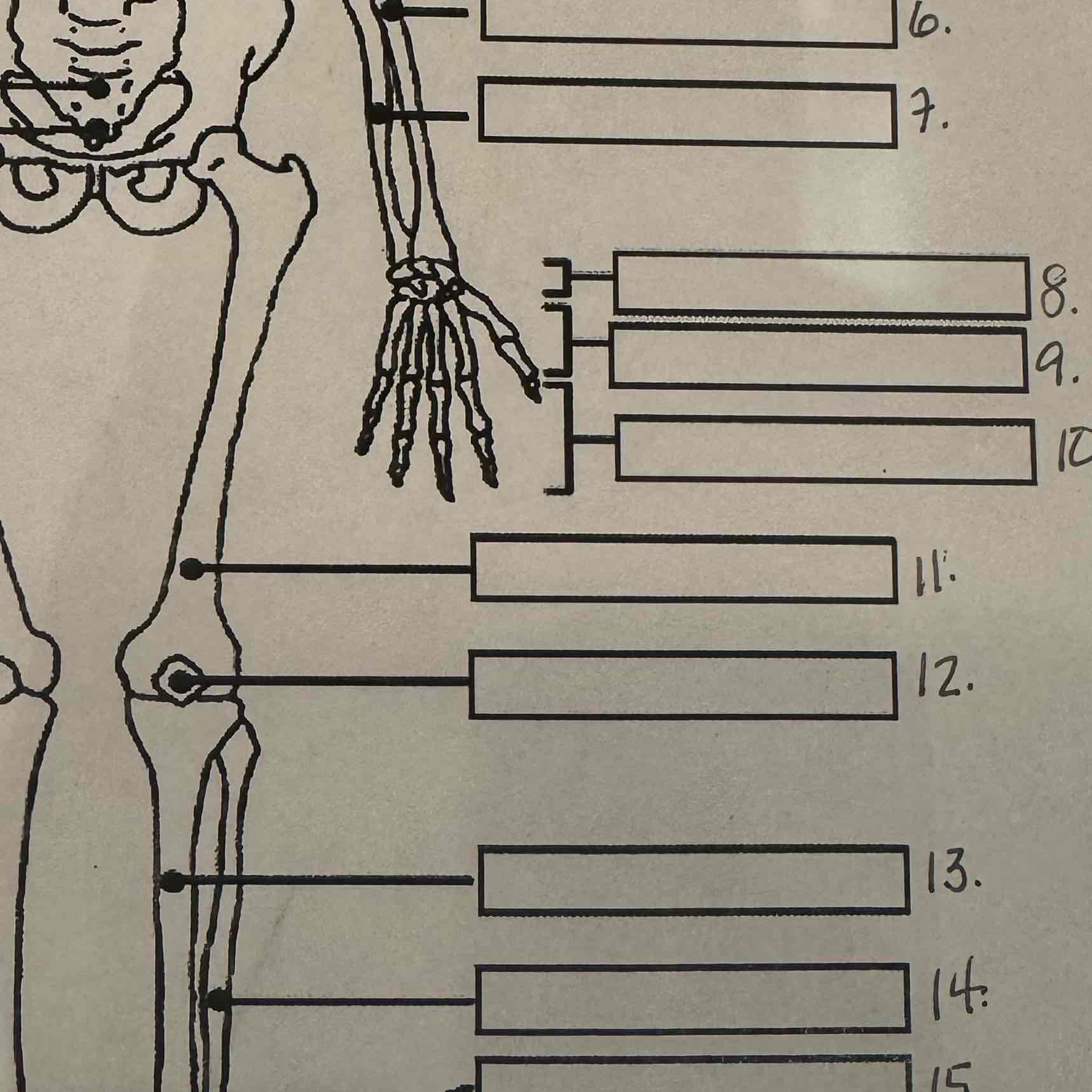
10
Phalanges
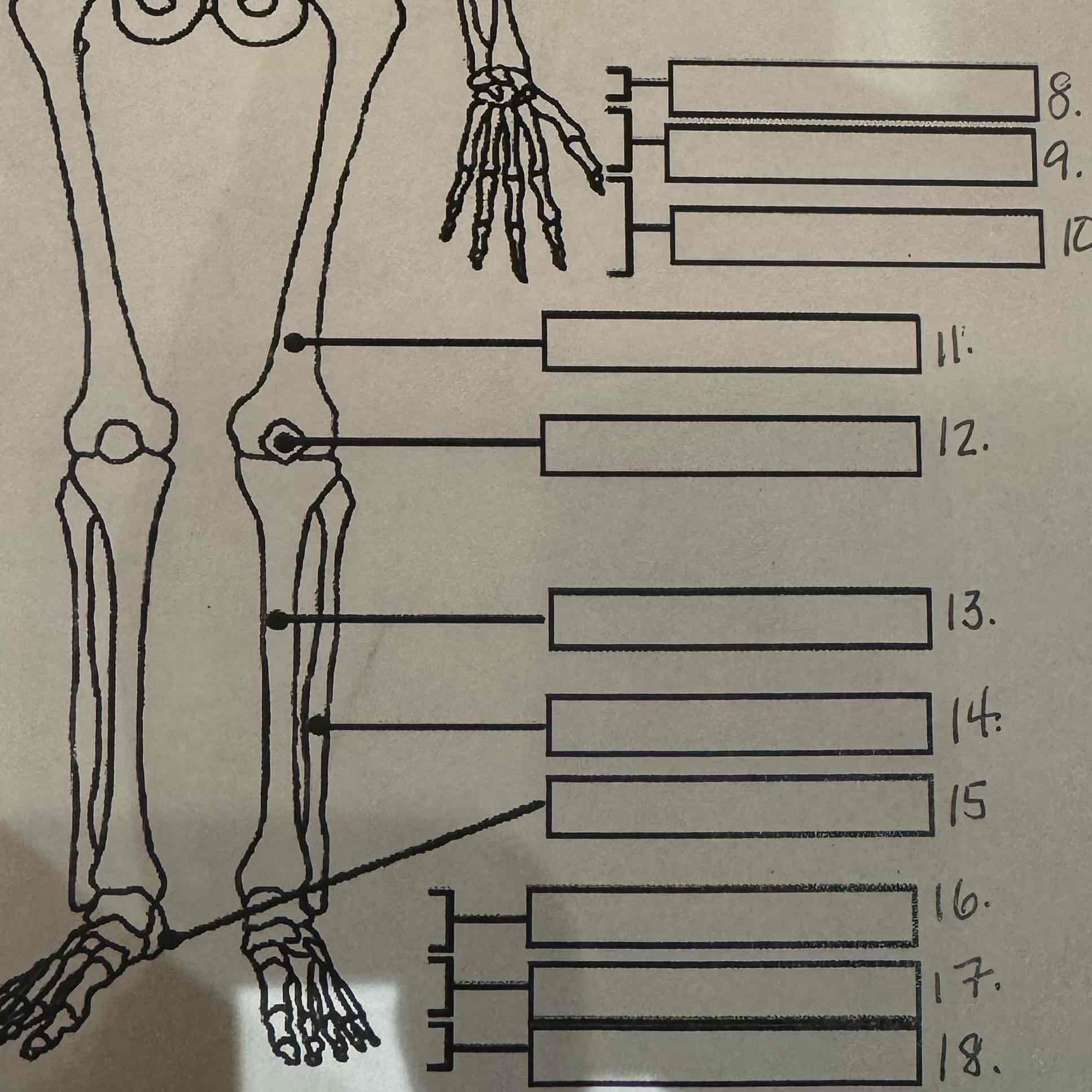
11
Femur
12
Patella
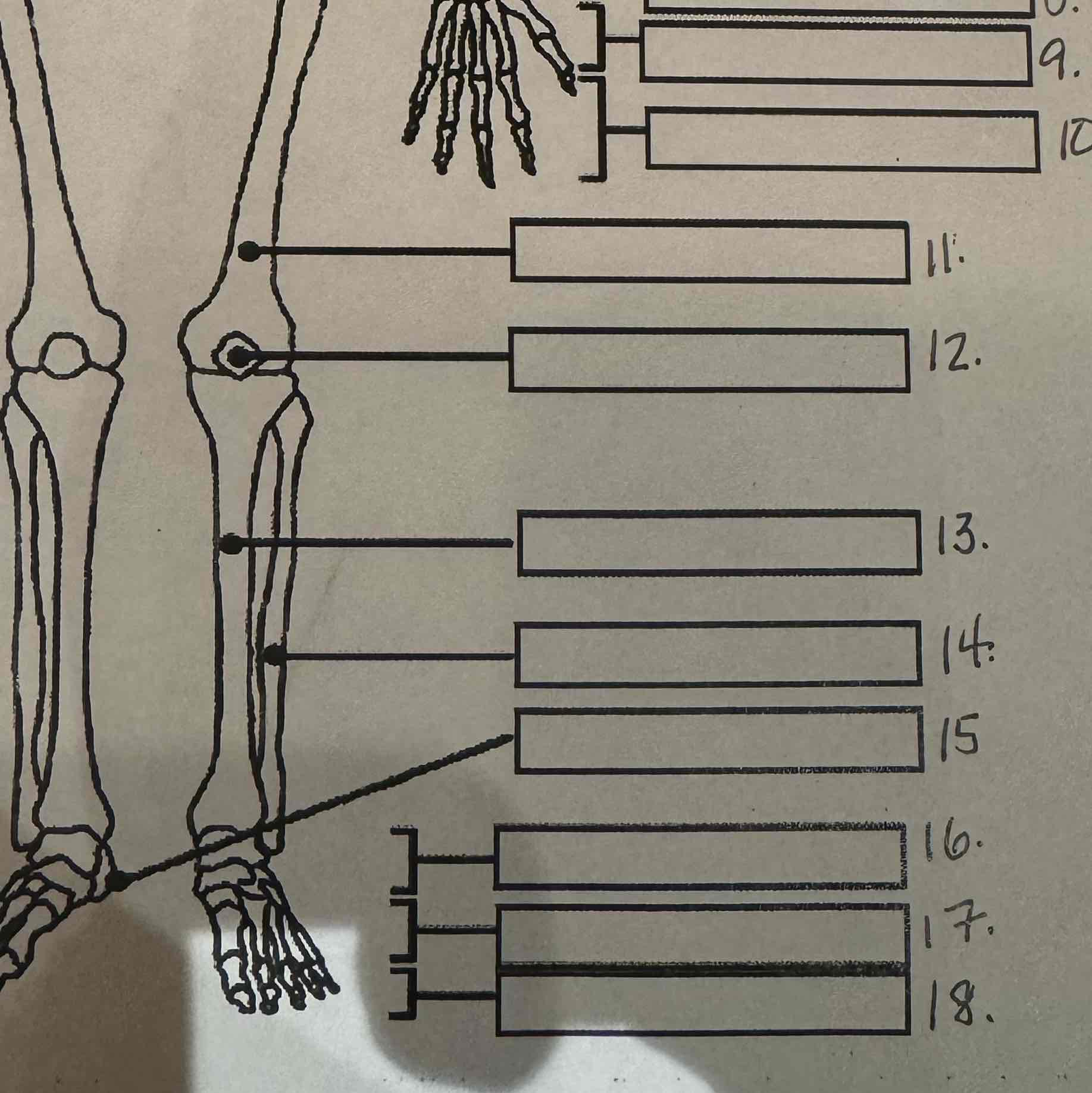
13
Tibia
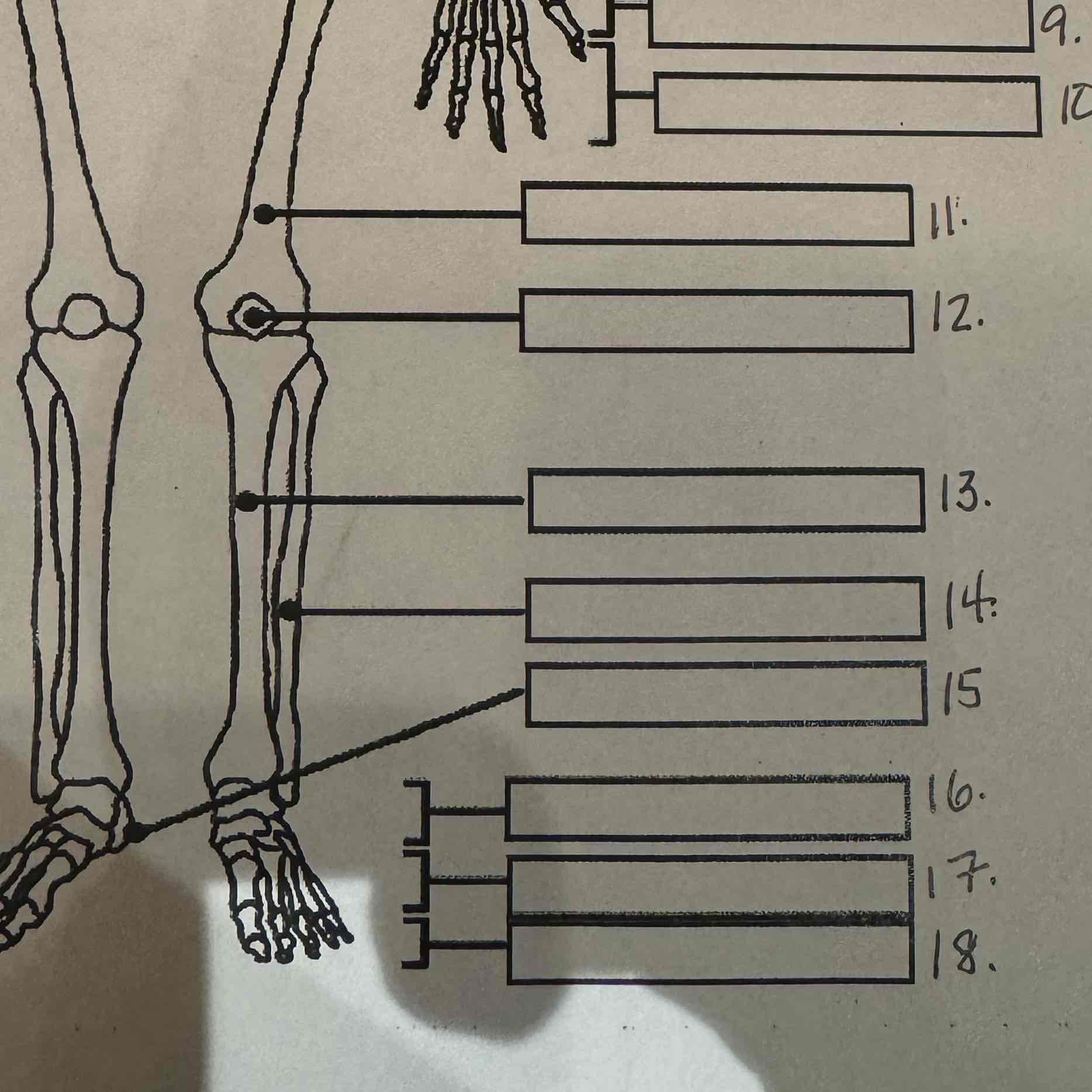
14
Fibula
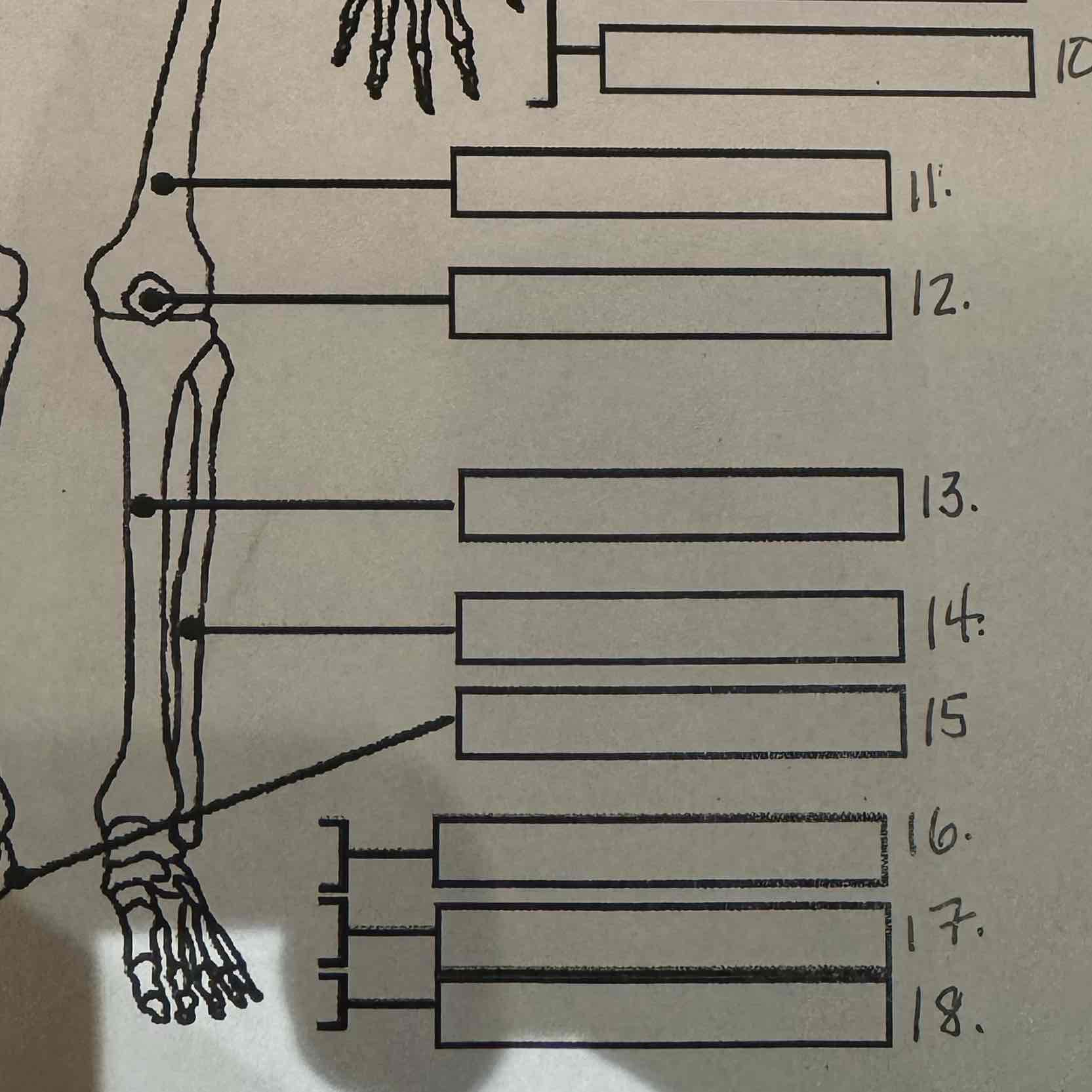
15
Calcaneus
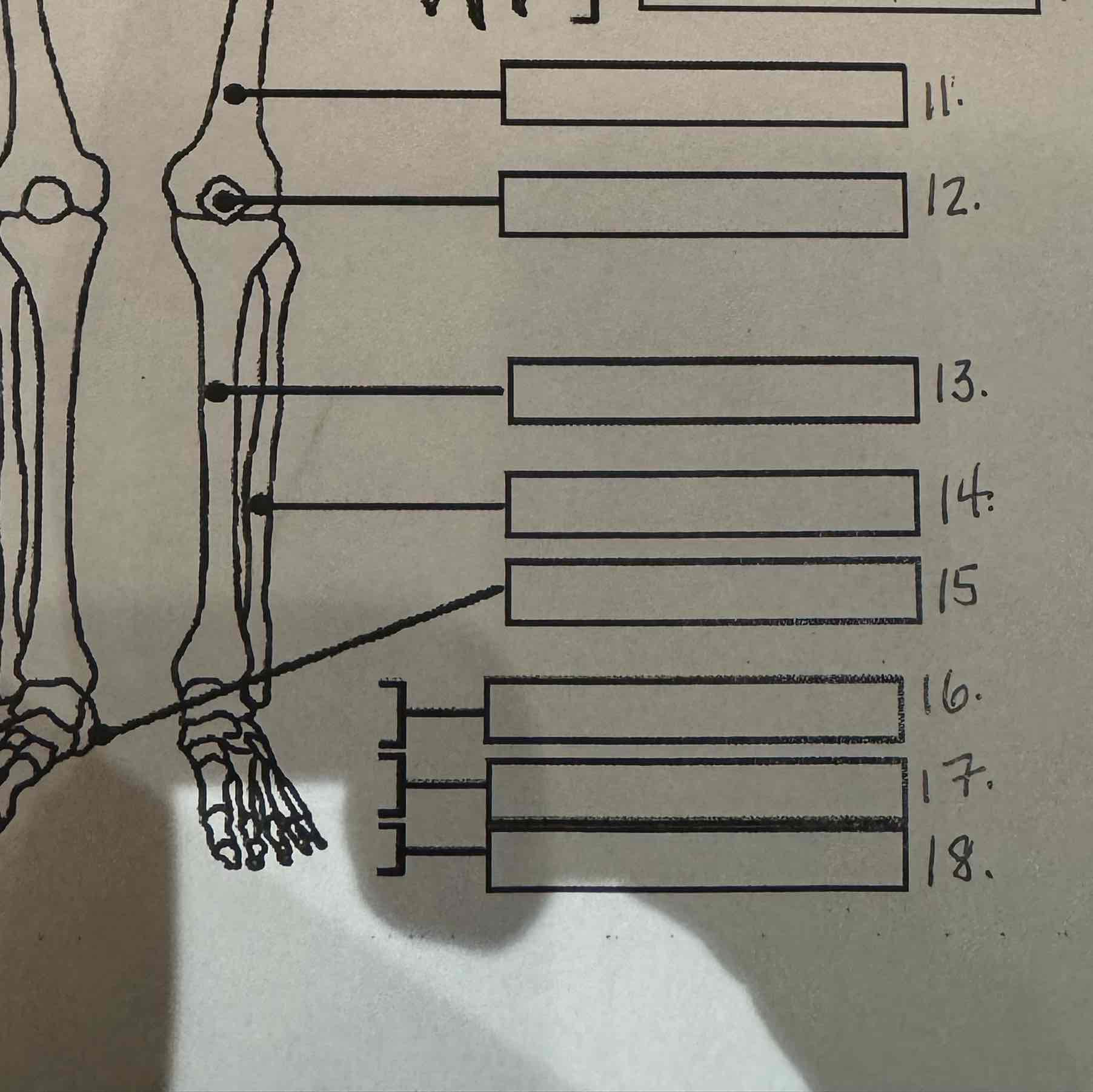
16
Tarsals
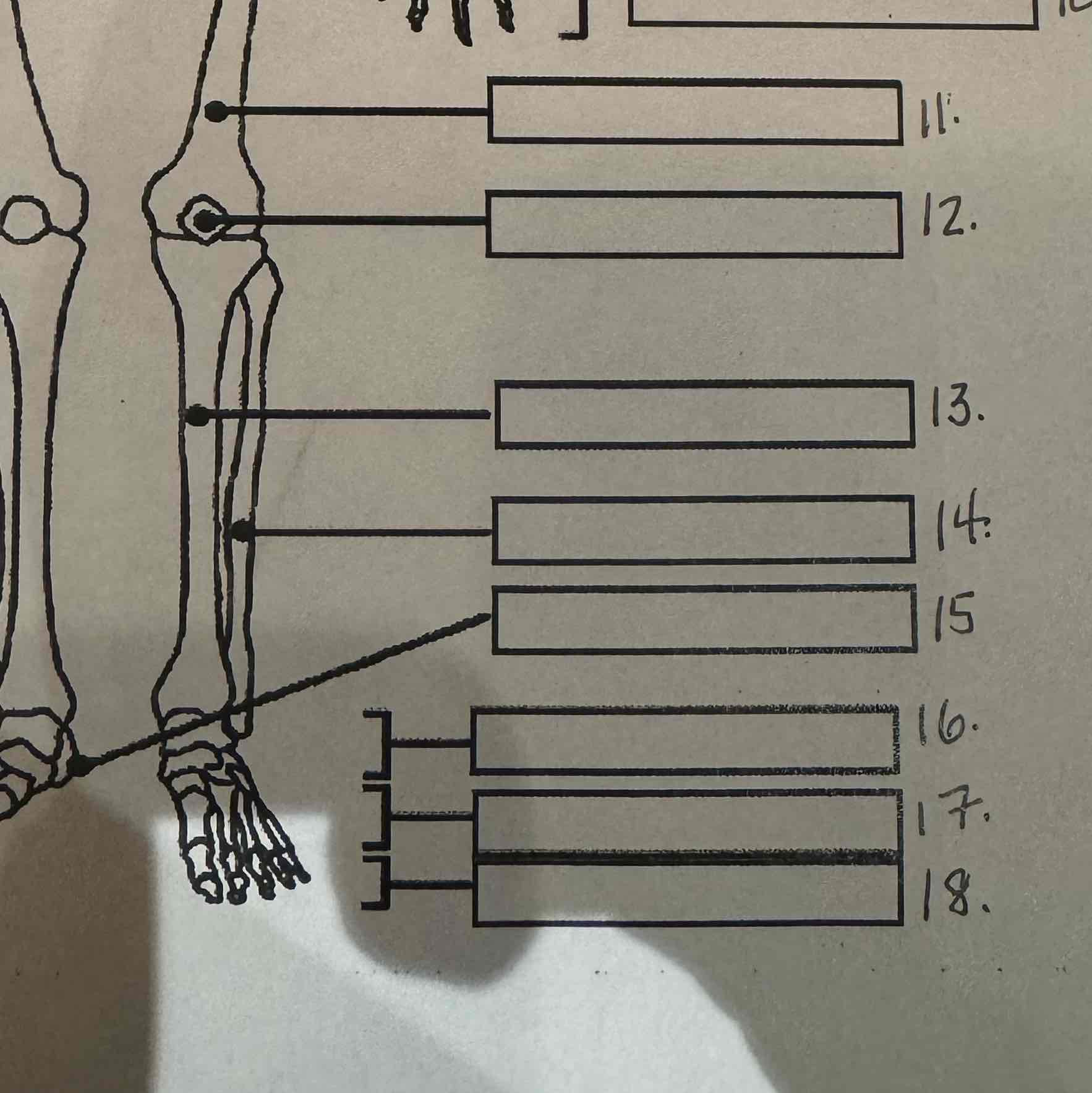
17
Metatarsals
18
Phalanges
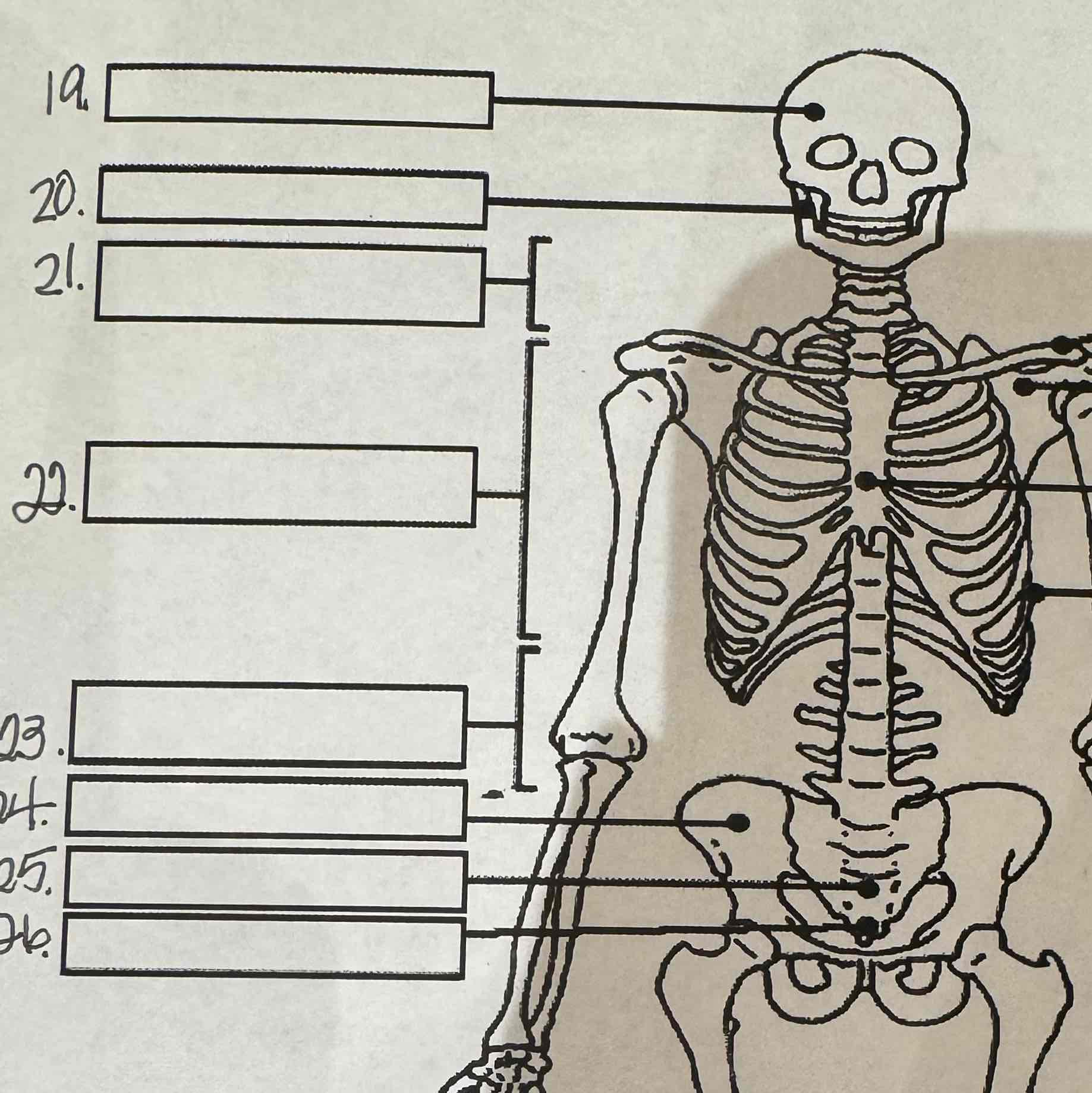
19
Cranium
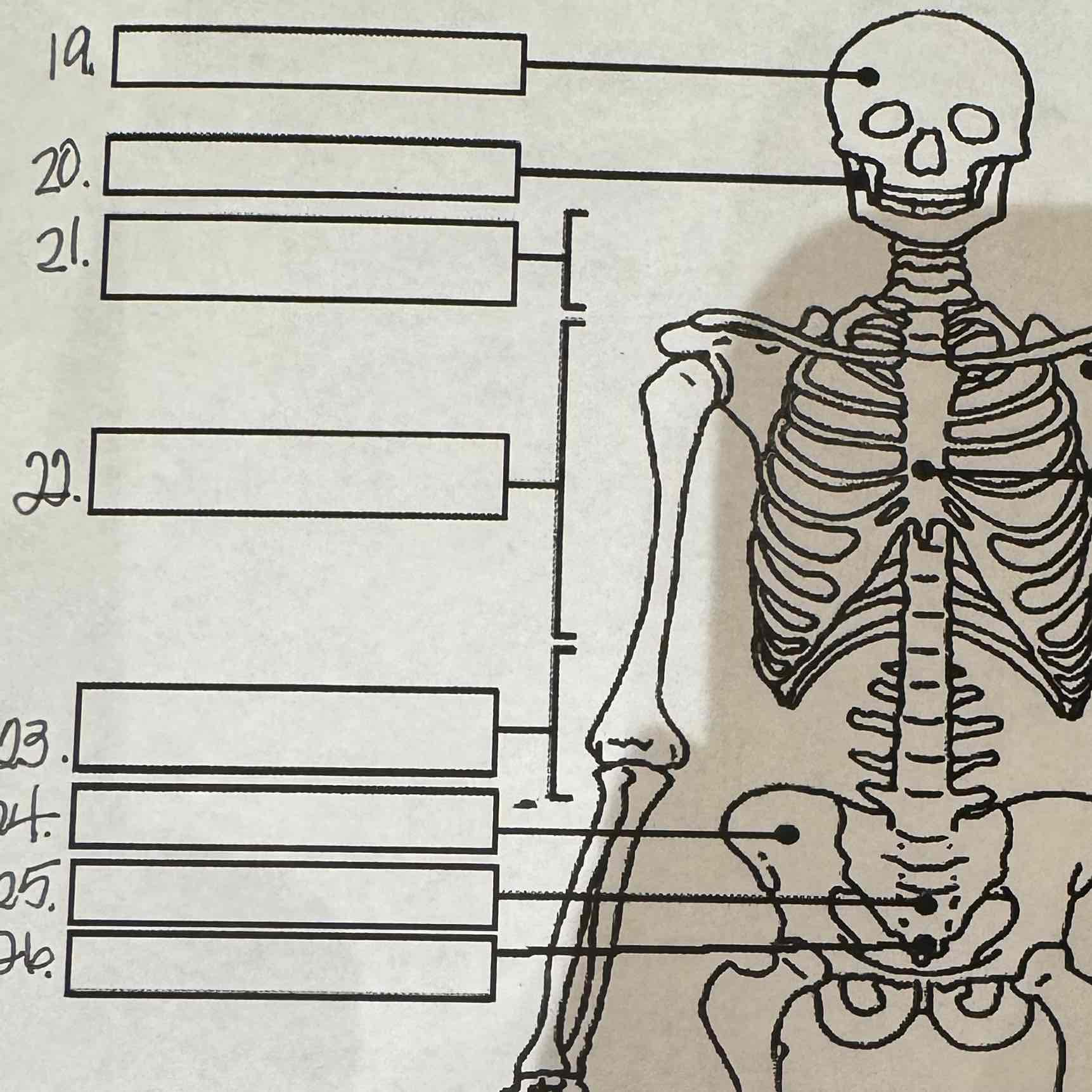
20
Mandible
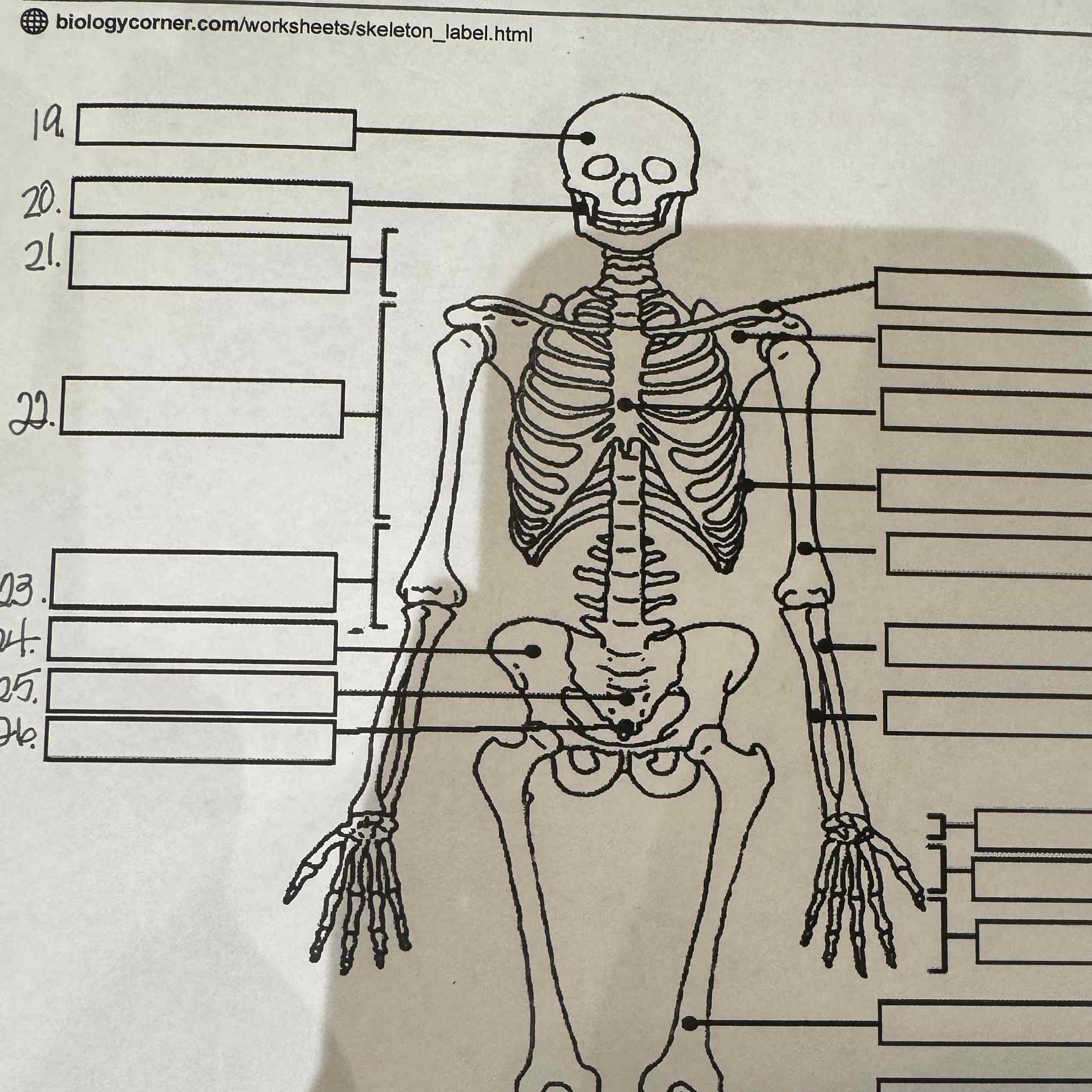
21
Cervical vertebrae
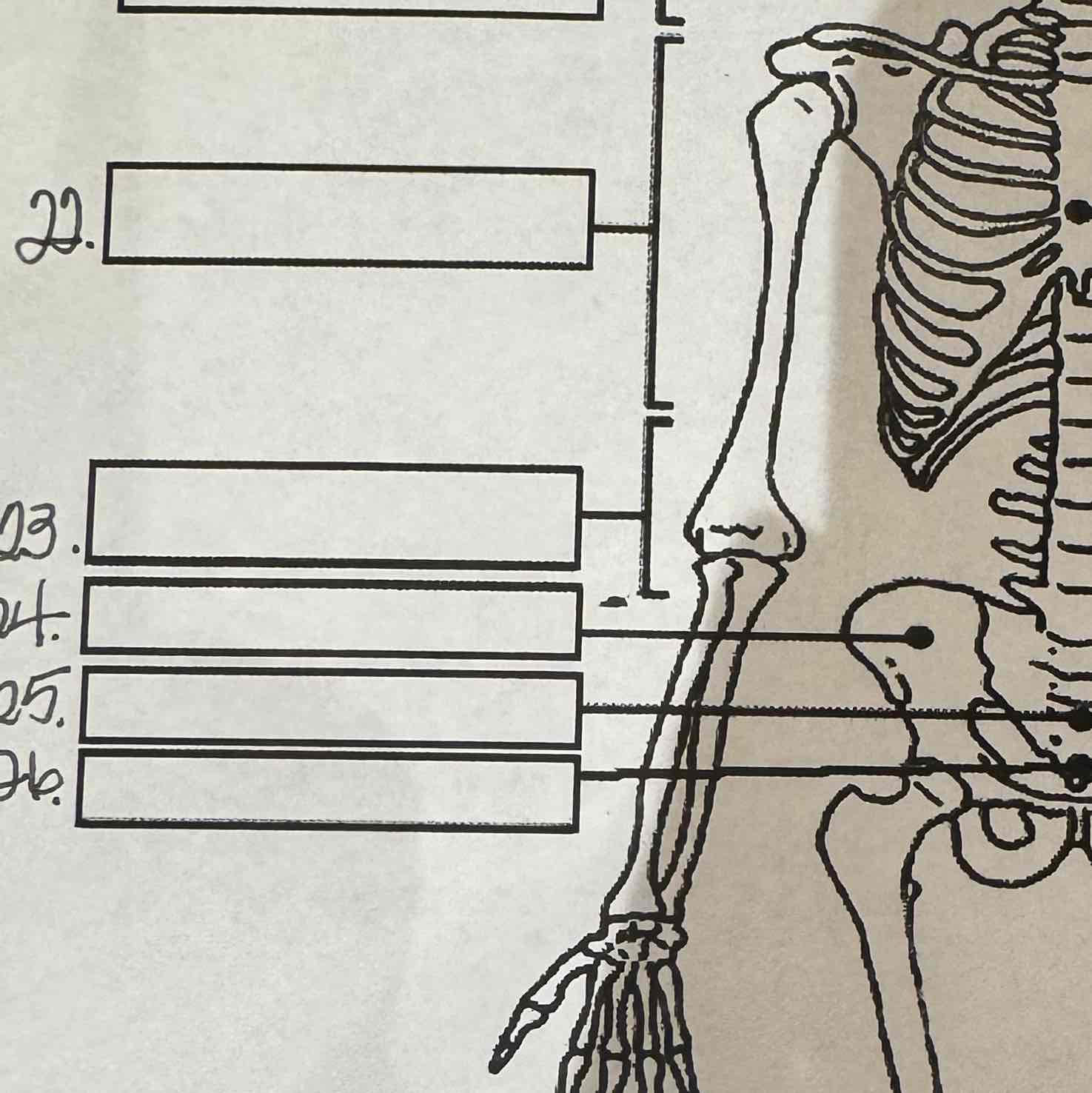
22
Thoracic vertebrae
23
Lumbar vertebrae
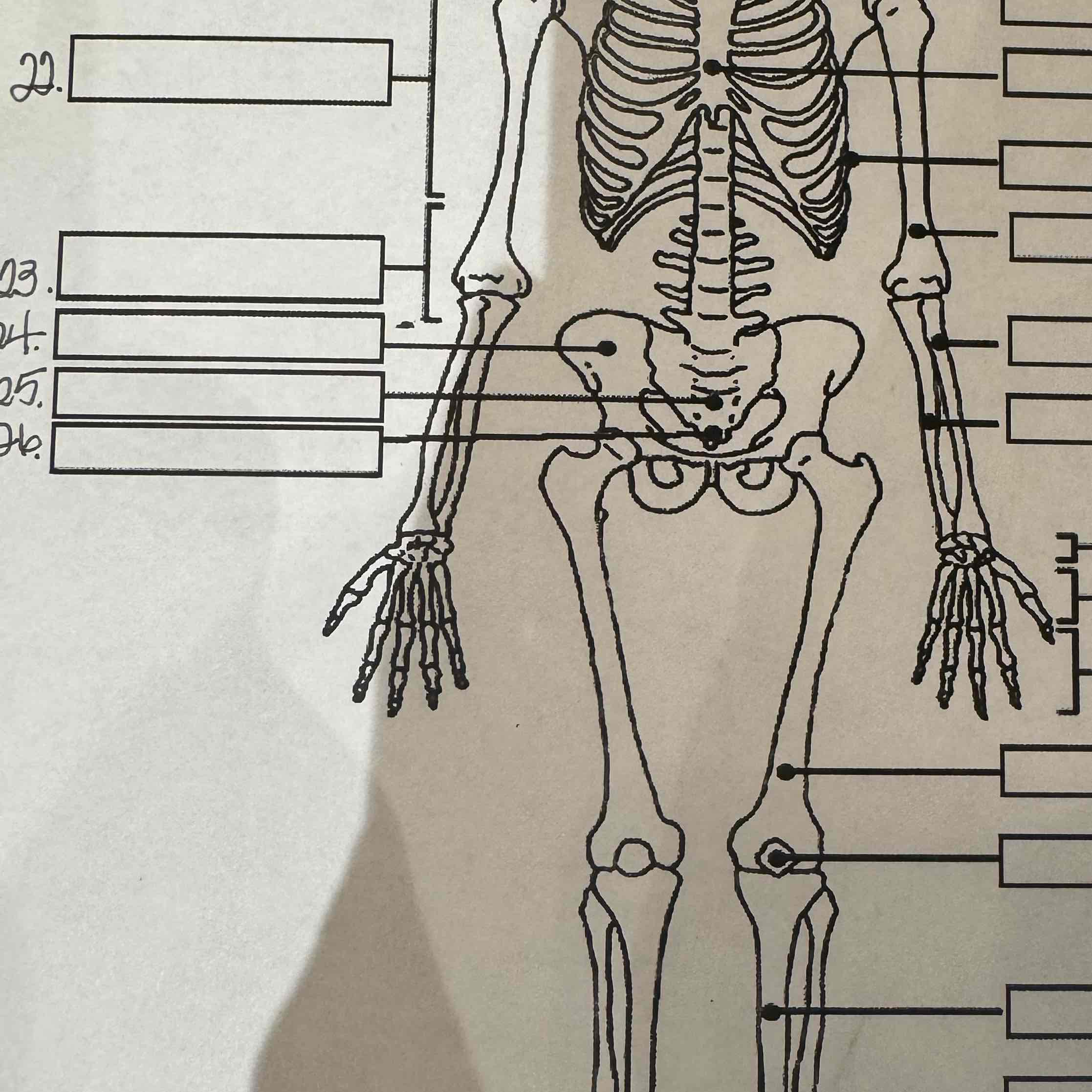
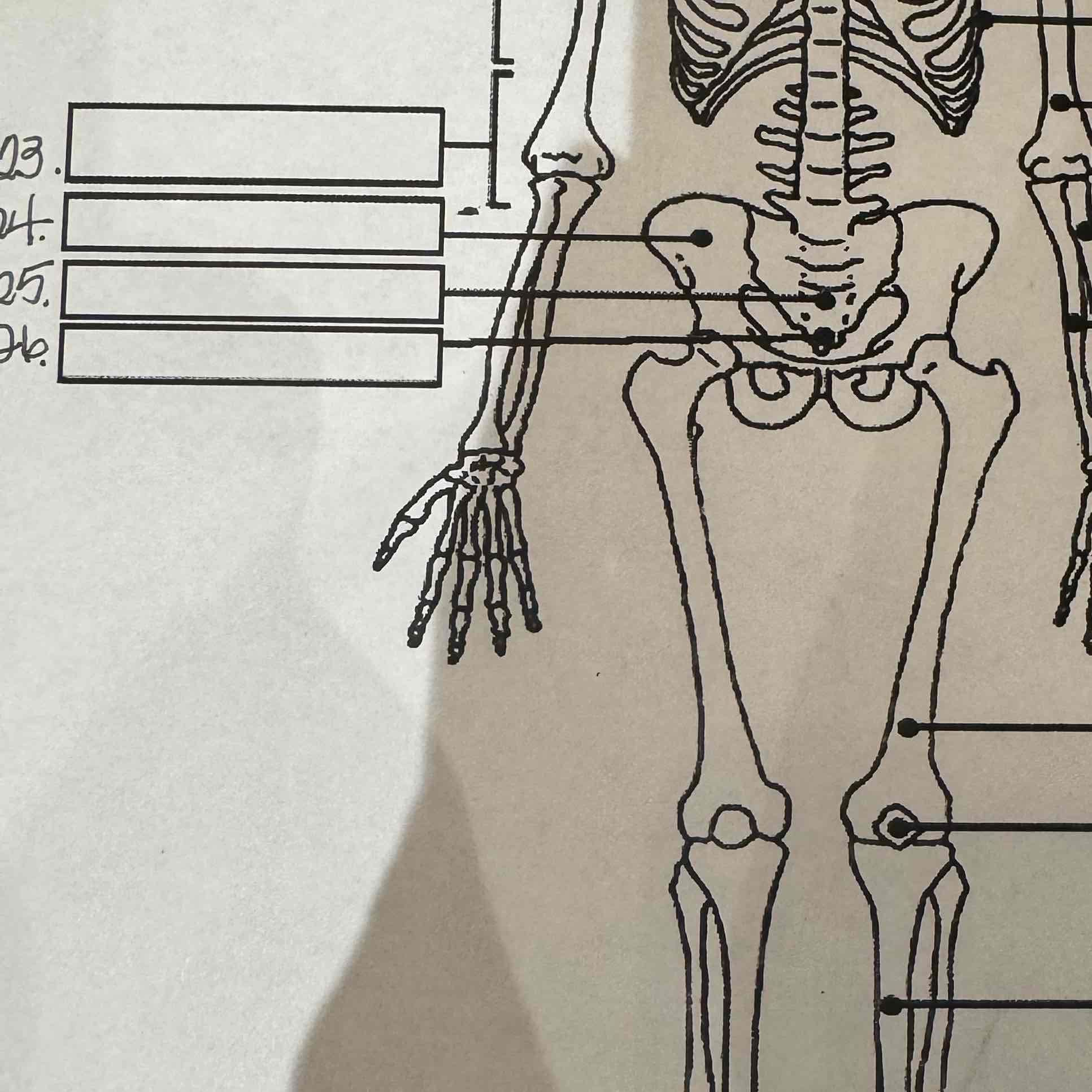
24
Pelvis
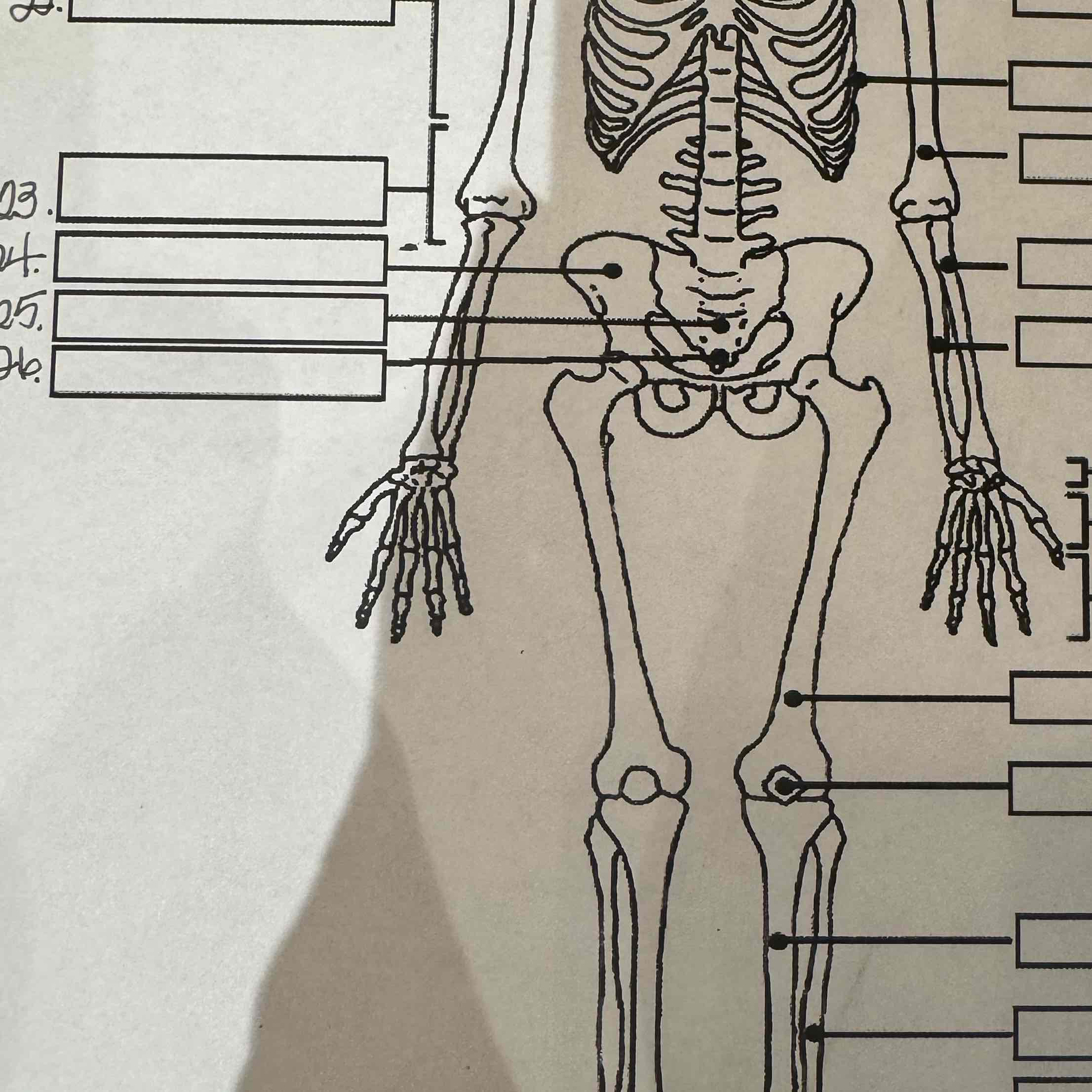
25
Sacrum
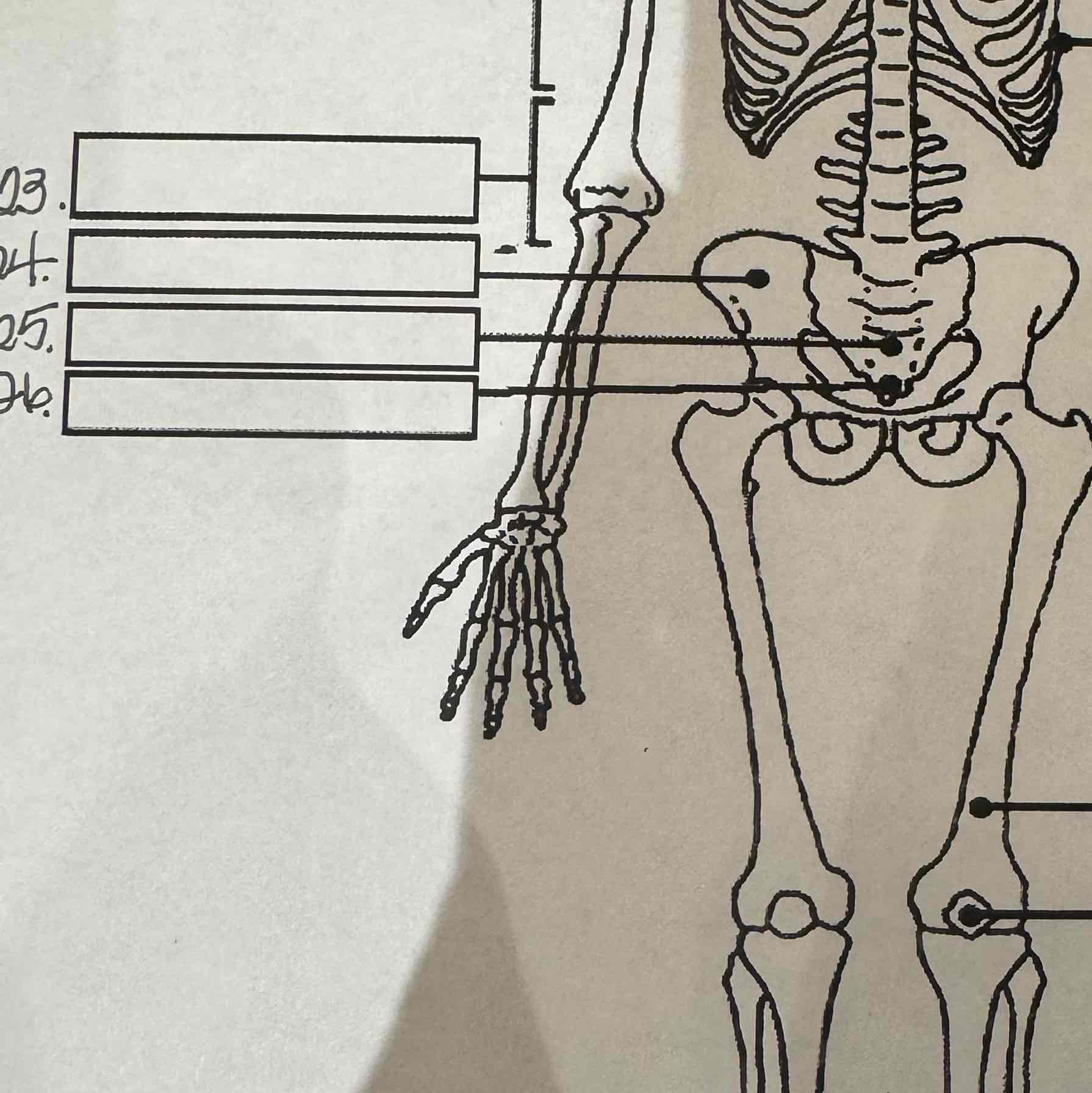
26
Coccyx
Articular cartiledge
Found on the edge of long bones; smooth, slippery, and bloodless; cushions the end of bones at their joints
Cancellous (spongy) bone and marrow
found within the epiphysis and has a textured appereance where it contains red marrow
Medullary Cavity, yellow marrow
Serves to lighten bone weight and provide space for marrow; yellow marrow is associated with fat
Epiphysis
Has a thin layer of compact bone, while internally the bone is cancellous; capped with articular cartilage
Location of yellow marrow
in the medullary cavity; in the middle of the bone.
Location of red marrow
in the spongy bone
Compact bone
a dense bone in the diaphysis; the repeated pattern is arranged in concentric layers of solid bone tissue; can be seen as the layer just underneath the periosteum
Muscle pairs
one muscle contracts while the other relaxes to its original length
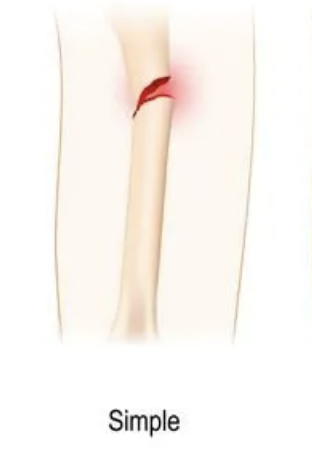
Simple bone fracture
Broken in one place
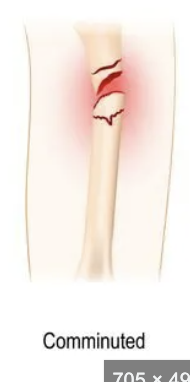
Comminuted bone fracture
Broken 2+ places, crushed.
Complete bone fracture
Broken, 2 separate pieces
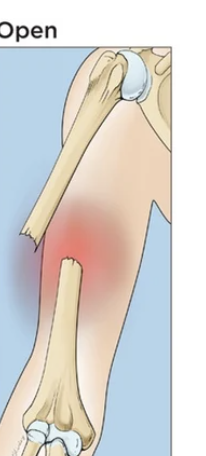
Open bone fracture
broken, sharp piercing muscle and skin
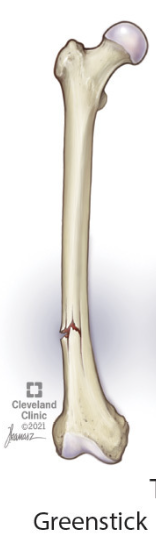
Greenstick bone fracture
not broken completely
Immovable joints
connect bones but allow little to no movement
example of immovable joints
the joints that hold together the bones of a skull
Moveable joints
joints that allow the body to make many different movements; held together by ligaments
Types of moveable joints
hinge, pivot, gliding, ball and socket
hinge joint
allows forward movement or backward motion
ex of hinge joint
knee
pivot joint
allows one bone to rotate around another bone
ex of pivot joint
neck
gliding joint
allows one bone to slide over another
example of gliding joint
wrist
ball and socket joint
allows the greatest range of motion
example of ball and socket joint
hip
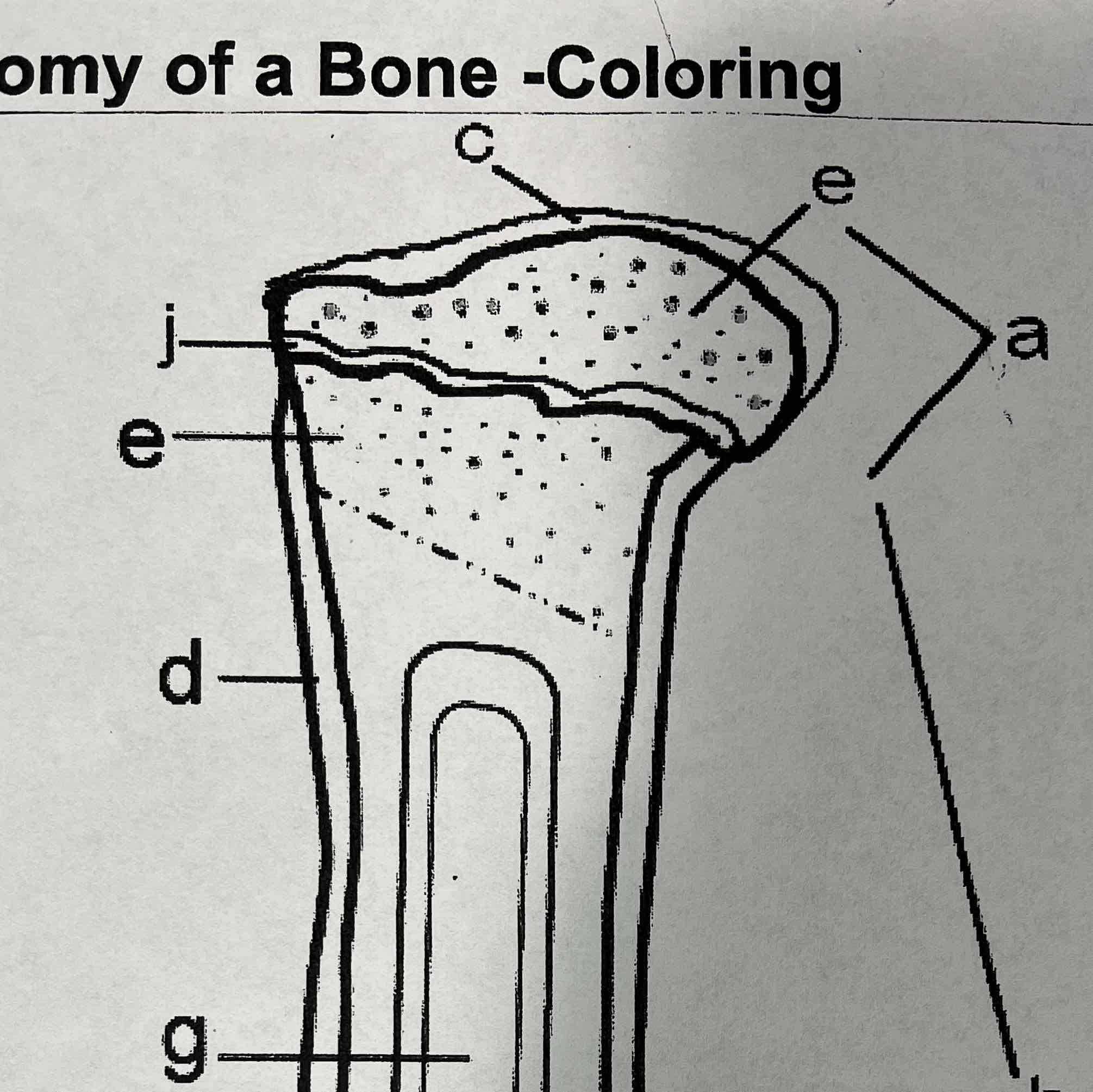
C
Articular cartilage
The articular cartilage is found on the ends of long bones. It is smooth, slippery, and bloodless
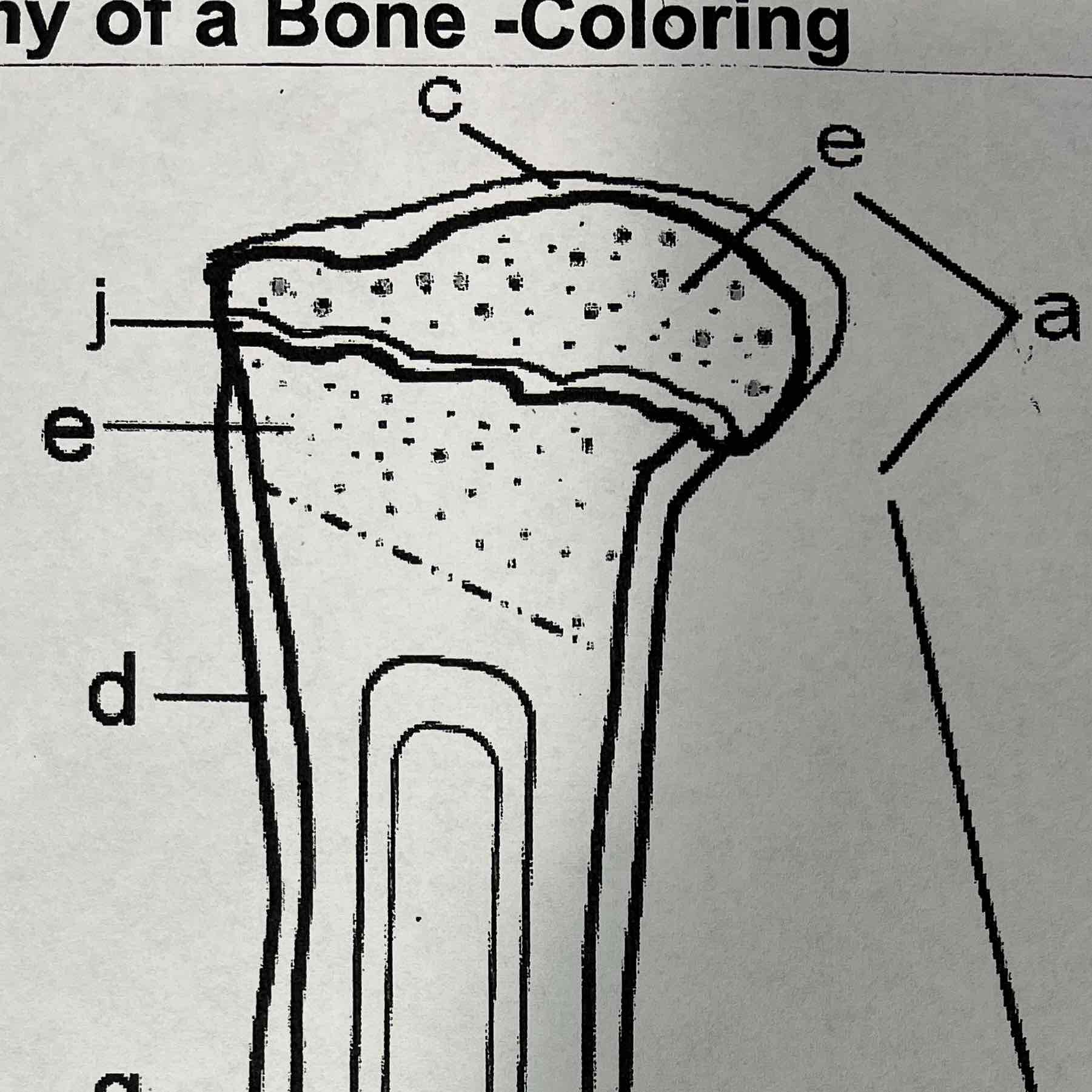
E
Cancellous (spongy) Bone, Marrow
The cancellous bone is found mainly within the epiphysis and has a textured appearance where it contains red marrow.
A
Epiphysis
The epiphysis has a thin layer of compact bone, while internally the bone is cancellous. The epiphysis is capped with articular cartiledge
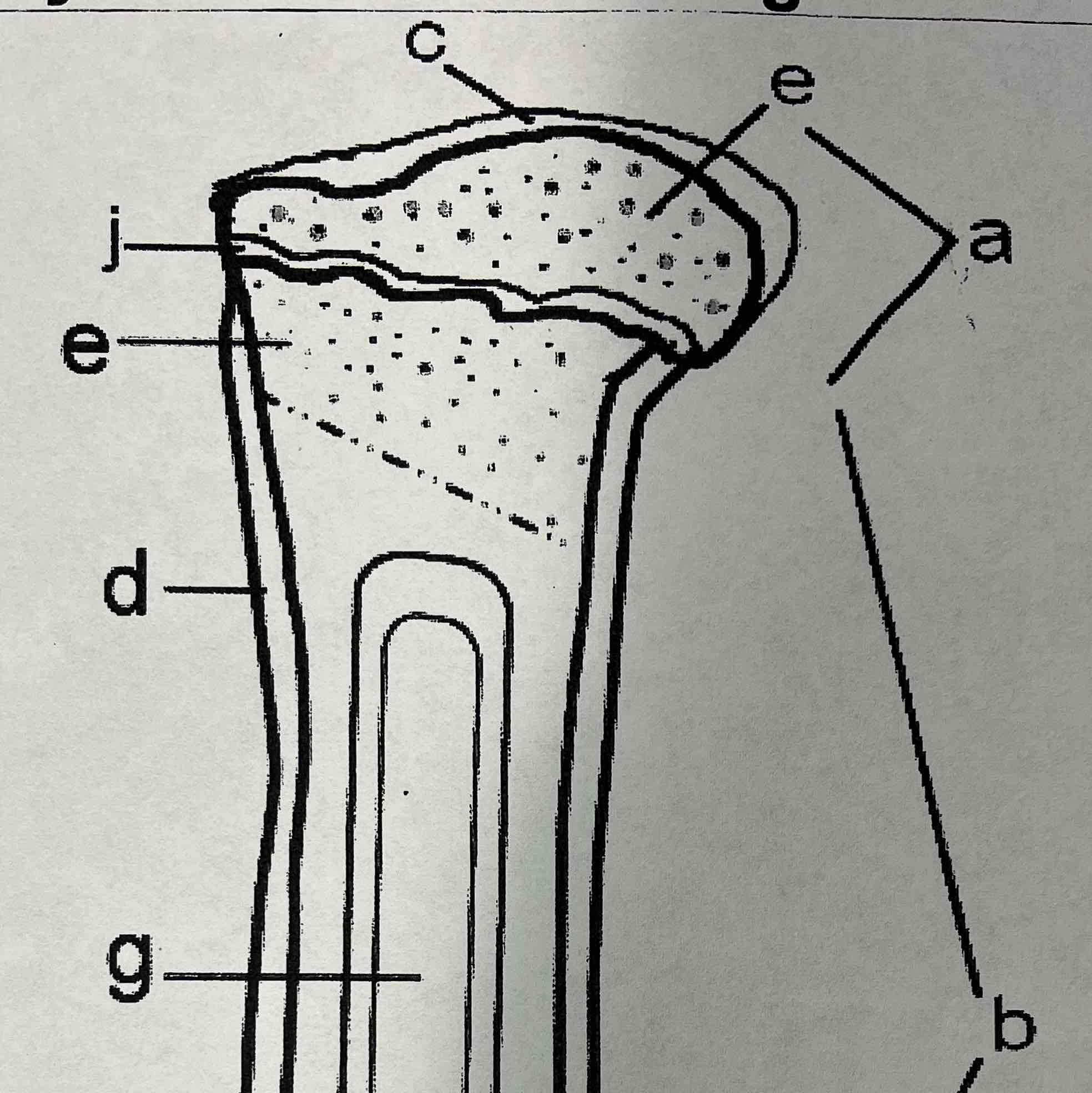
E
Cancellous (spongy) bone and marrow
The cancellous bone is found on the ends of long bones. It is smooth, slippery and bloodless.
D
Periosteum
Periosteum is a vascular, sensitive life support covering for bone. It provides nutrient rich blood for bone cells and is a source of bone developing cells during growth or after a fracture. It is the outer most layer
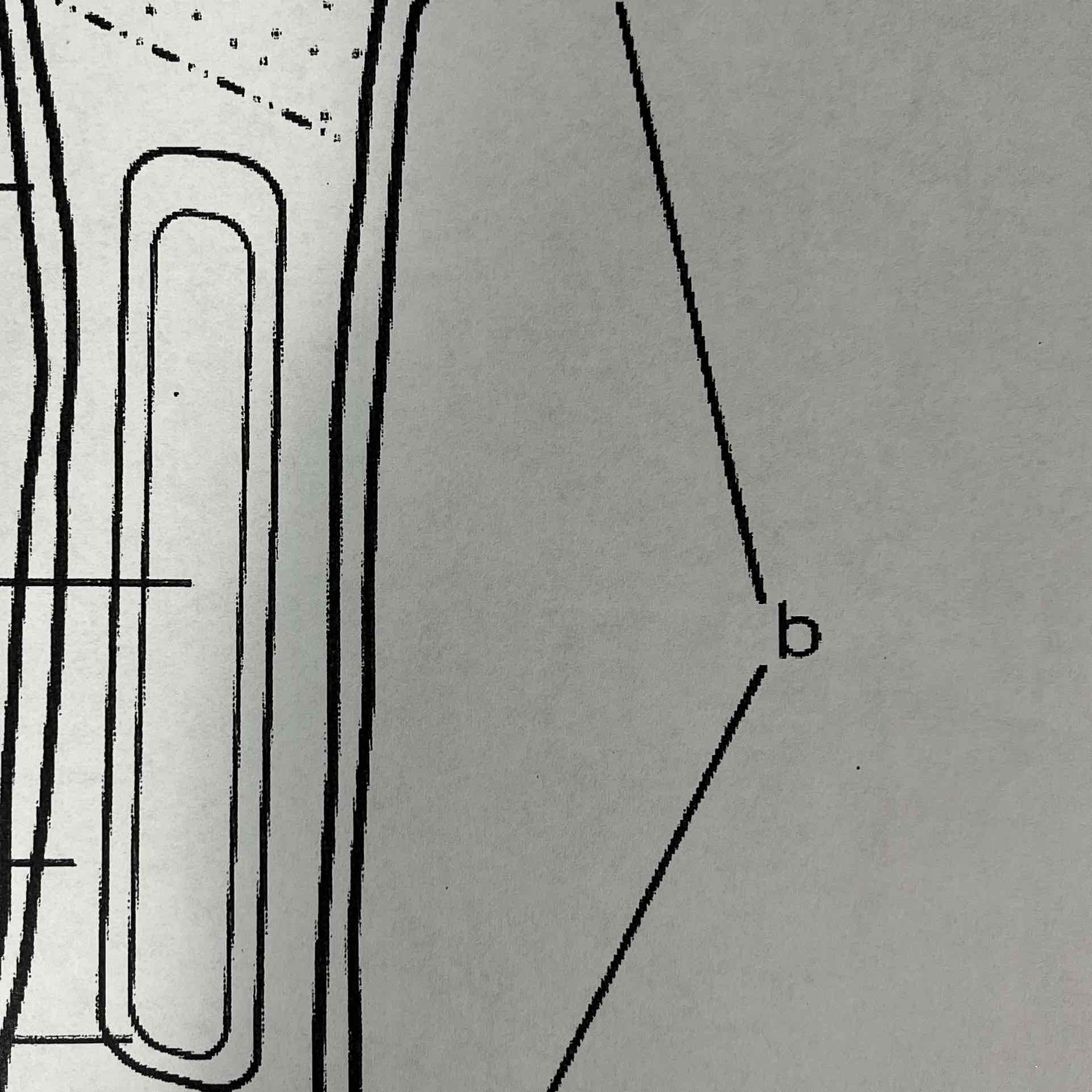
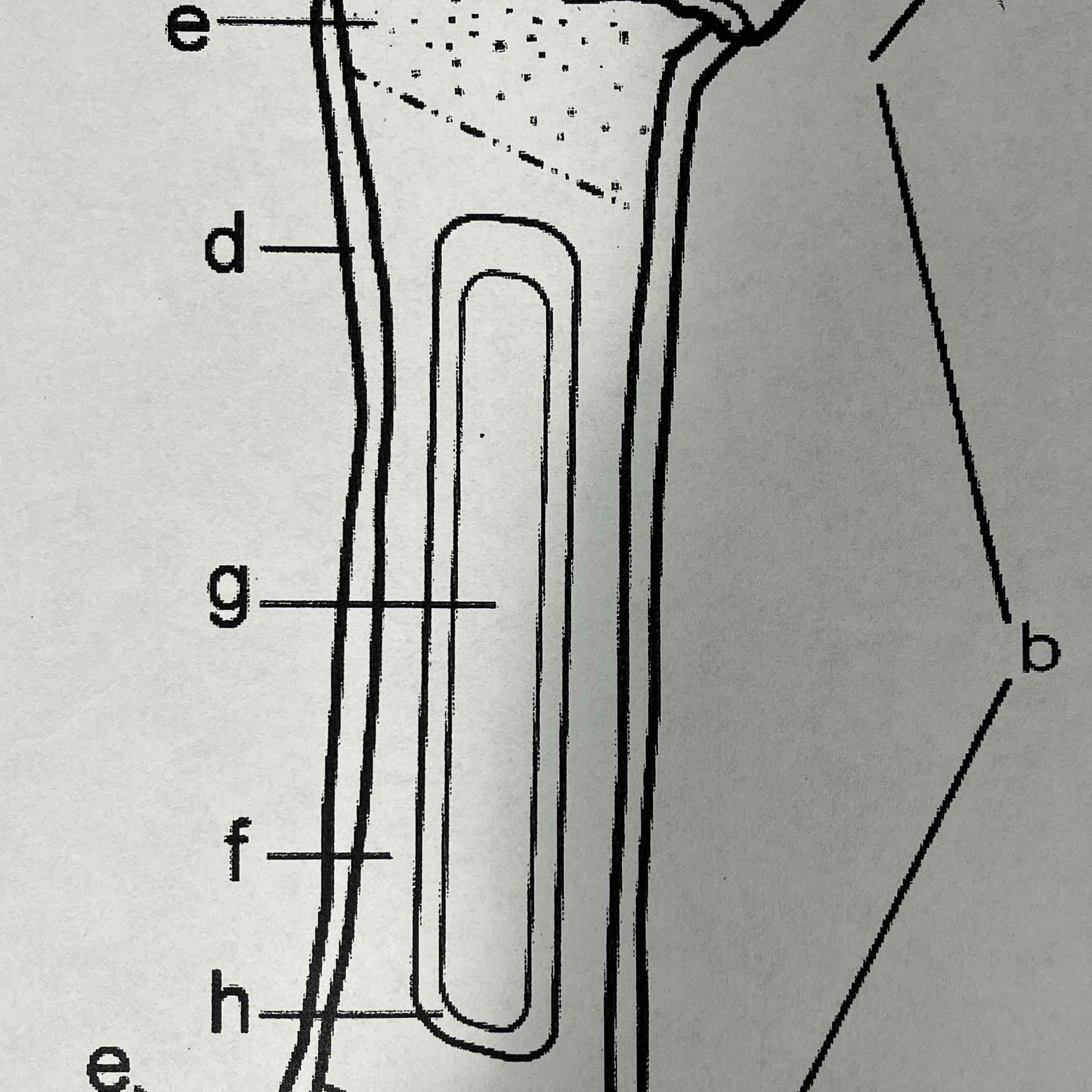
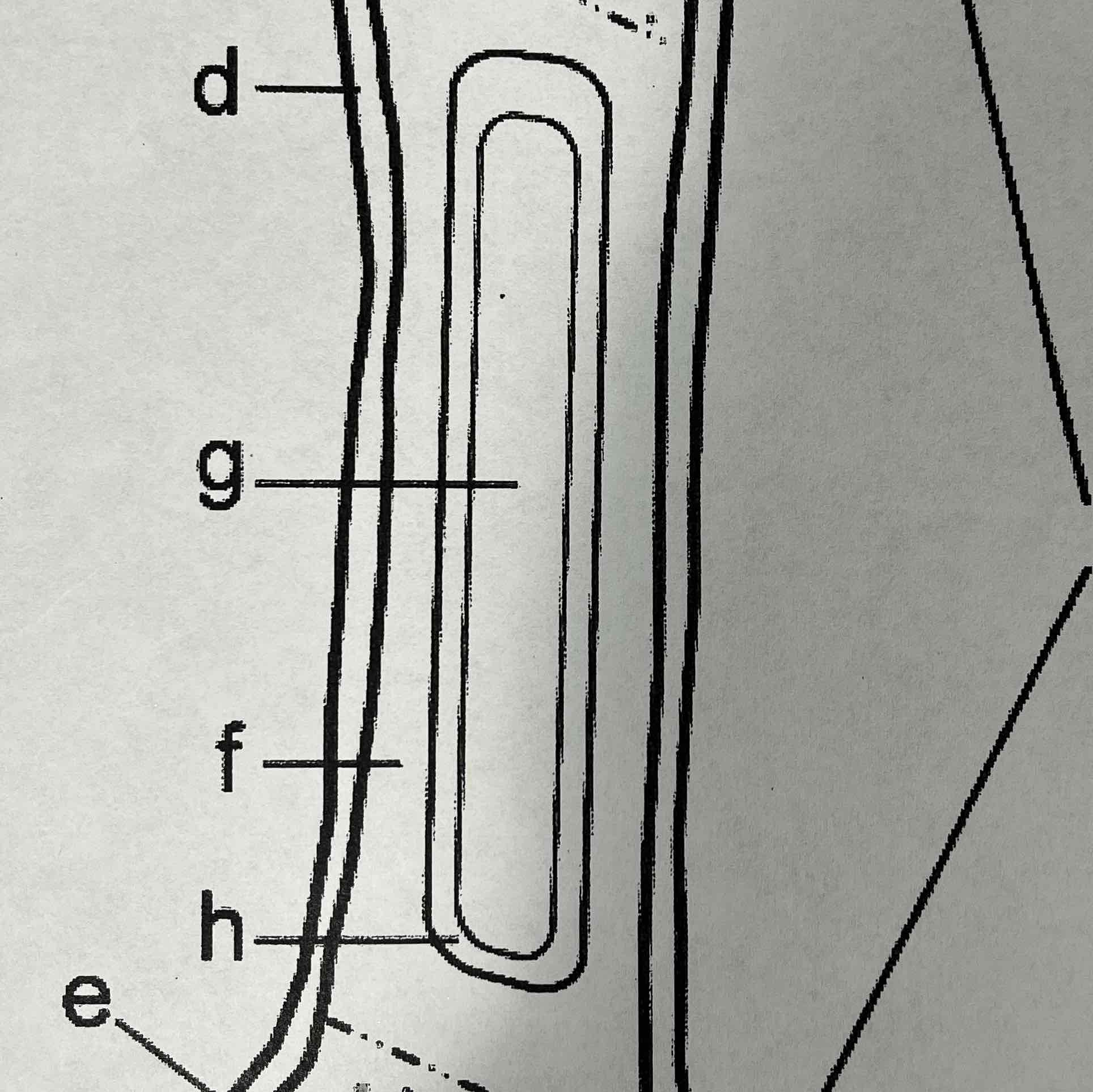
B
Diaphysis (shaft)
The diaphysis is the shaft of the long bone. It has compact bone with a central cavity.
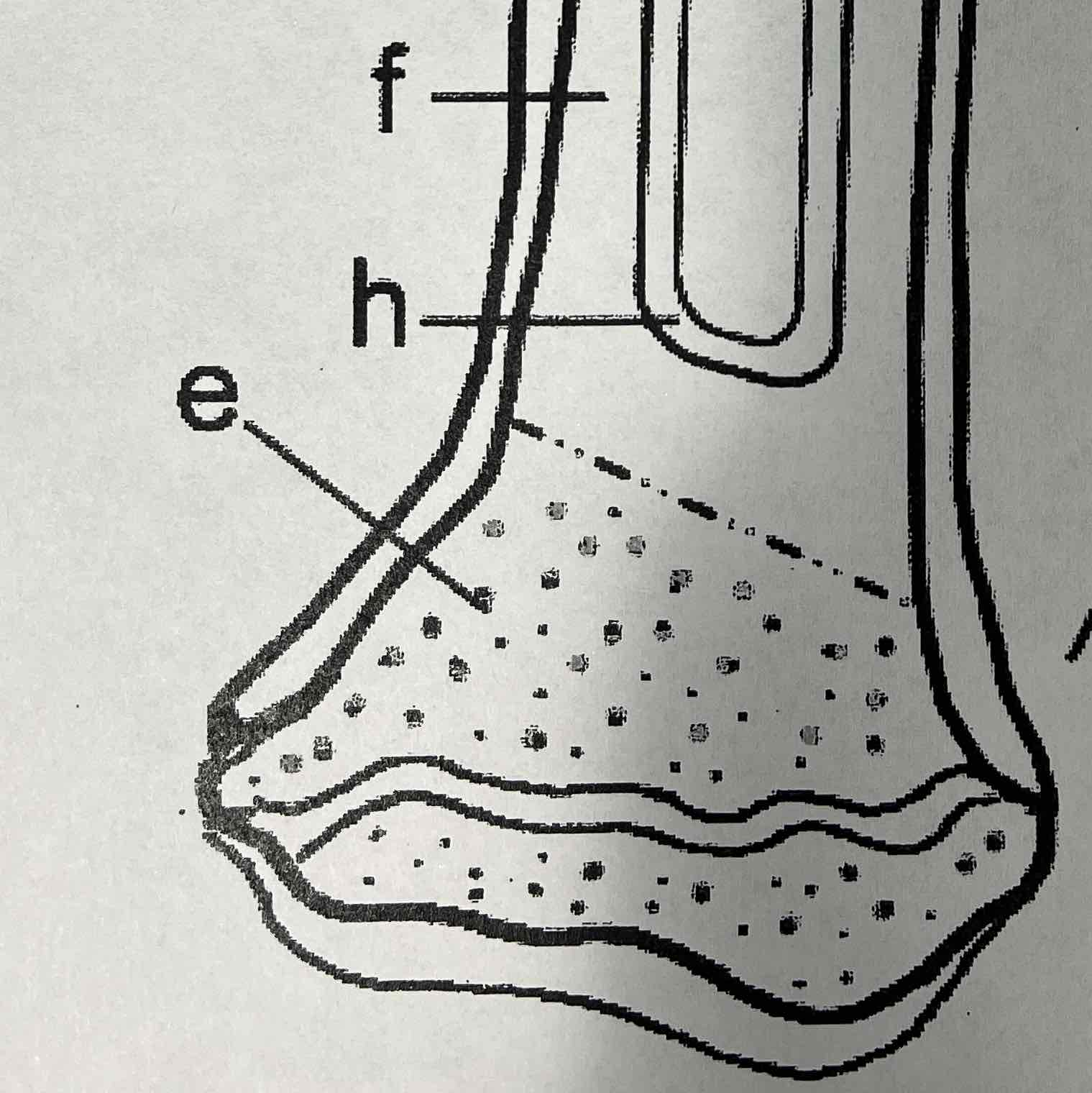
F
Compact bone
The compact bone is a dense bone found in the diaphysis. Its repeated pattern is arranged in concentric layers of solid bone tissue. The compact bone can be seen as the layer just underneath the periosteum.
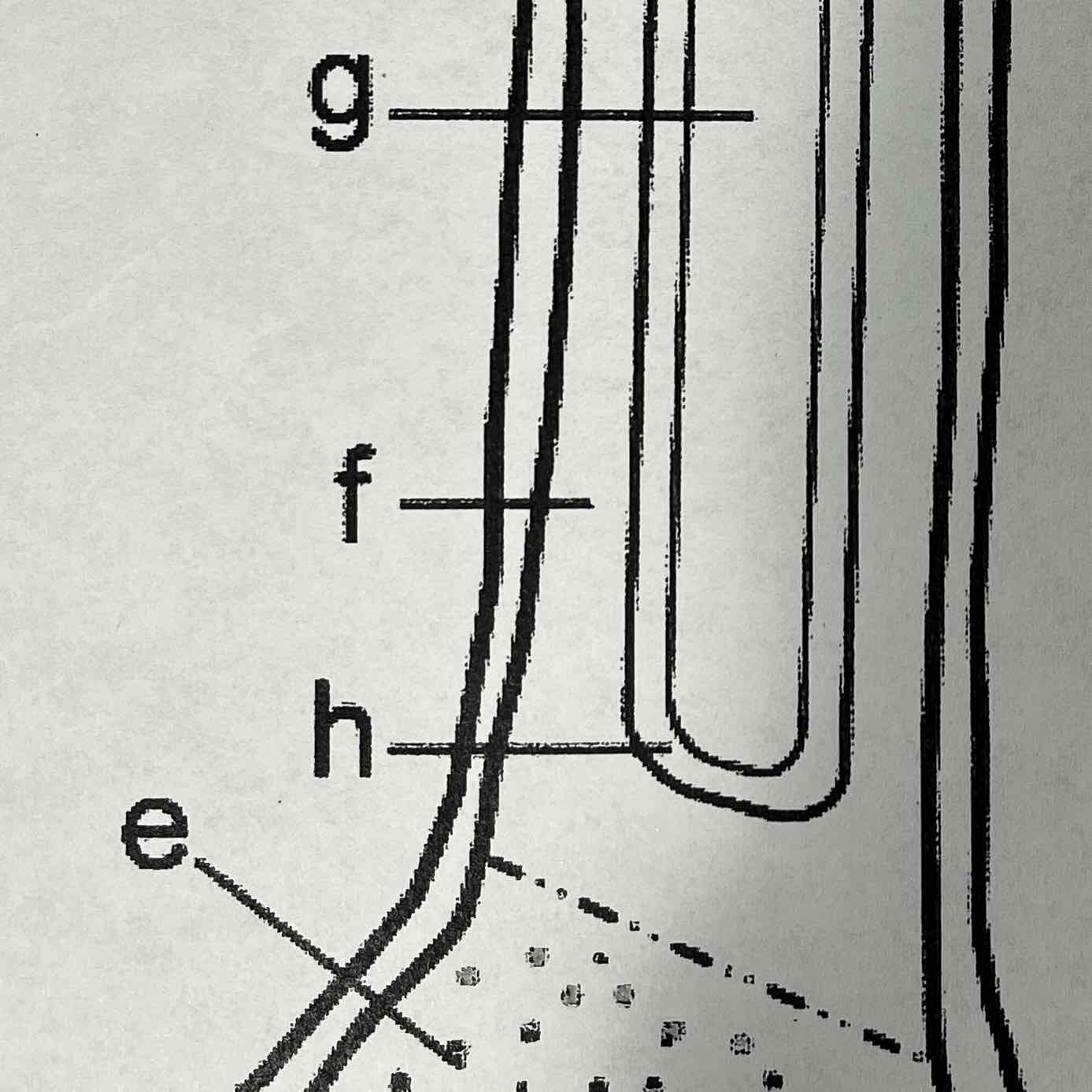
G
Medullary cavity, yellow marrow
The medullar cavity of the diaphysis serves to lighten bone weight and provide space for marrow. Yellow marrow is associated with fat and stores it.
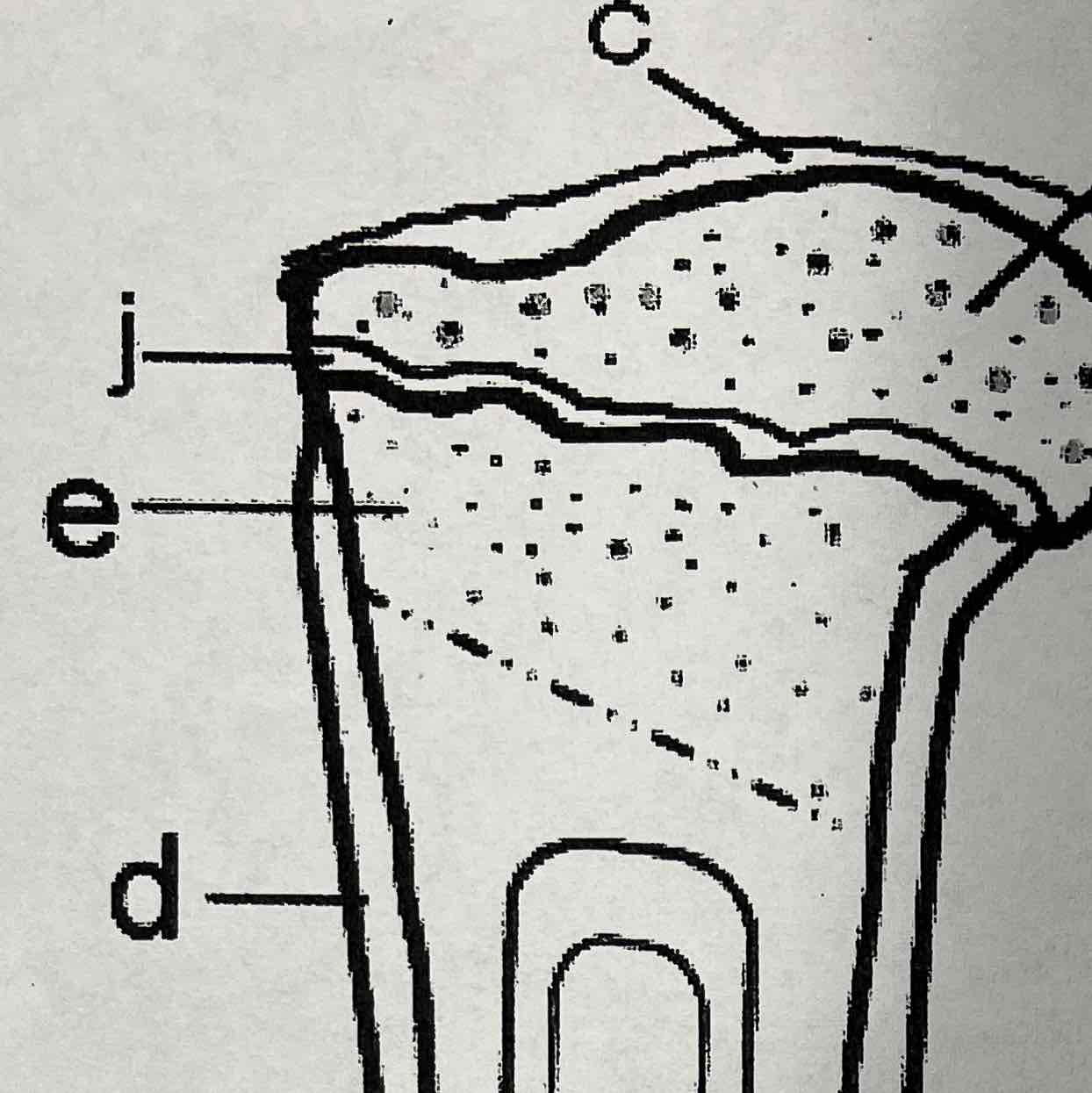
J
Epiphyseal line
The epiphyseal line or disk is also called the growth plate, it is found on both ends of a long Bone
Where do you find yellow marrow
Medullary cavity (core of the bone)
What type of bone is arranged in concentric layers
Compact bone
Where do you find red marrow
Cancellous bone
What is the end of the bone called?
The epiphysis bone
What is spongy bone also called
the cancellous bone
What cushions the ends of bones at their joints
The articular cartilage
What are five major functions of the skeletal system?
The 5 major functions of the skeletal system are movement, shape and support, protects organs, produces blood cells, and stores minerals
What is the function of a ligament? what type of tissue is it made out of
The function of a ligament is to hold your bones together at the joints. It is made of strong connective tissue.
Where is spongy bone found?
spongy bone is found at the end of each bone
cervical vertebrae
all of neck