AP Government Court Cases
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Engel v. Vitale (1962)
Government-directed prayer in public schools violates the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment, even if the prayer is denominationally neutral and students may remain silent or be excused from the classroom during its recitation.

NY Times v. US (1971)
The court upheld the First Amendment/Freedom of the Press rights of the New York Times and Washington Post to print the Pentagon Papers, without risk of government censorship or punishment.

Schenck v. US (1919)
The defendant, who handed out circulars against war and urged for peaceful action, such as petitioning and the repeal the Conscription Act, was charged with conspiracy to violate the Espionage Act. Authorities argued that he was attempting to cause insubordination in the military and to obstruct recruitment.
During wartime, utterances tolerable in peacetime can be punished because they represent a "clear and present danger" to national security.

Tinker v. Des Moines (1969)
Students in an Iowa school were suspended for wearing black armbands to protest the Vietnam war. The Court ruled that this suspension was unconstitutional, and that public school students do not "shed their constitutional rights at the schoolhouse door." Public school students may engage in symbolic speech, as protected by the First Amendment, when such display does not disrupt classes.

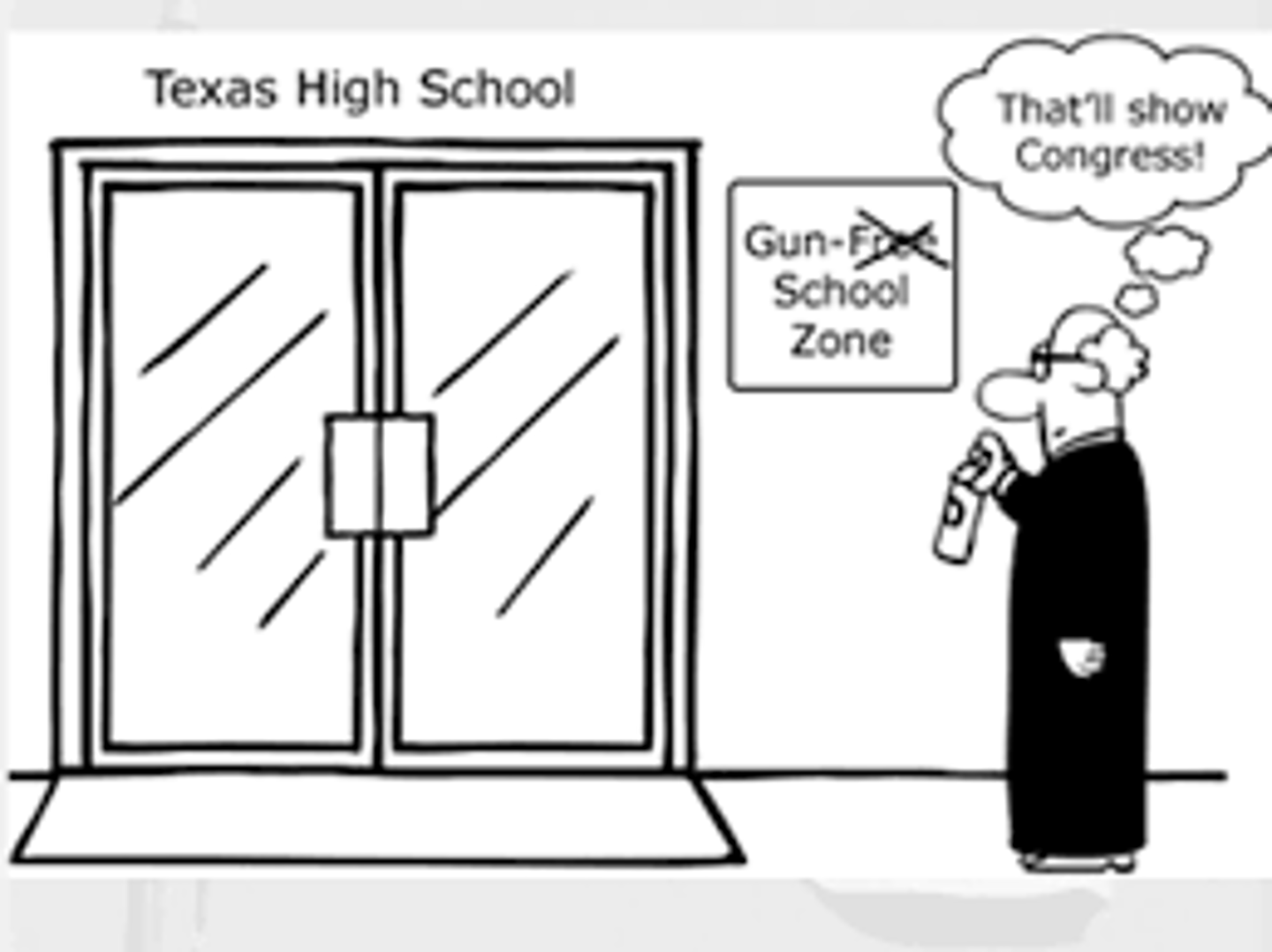
U.S. v. Lopez (1995)
Gun Free School Zones Act exceeded Congress's authority to regulate interstate commerce. The first case to begin reigning in Congress's authority under the Commerce Clause.

Roe v. Wade (1973)
Abortion is a private matter between a woman and her doctor. Women are entitled to the right of privacy (9th and 14th Amendments). As such, women cannot be denied the right to have an abortion.

Brown v. Board of Education (1954)
Ruled for integration of public schools because racial segregation violates the 14th Amendment's Equal Protection clause.

Marbury v. Madison (1803)
Established the Supreme Court as having the power of Judicial Review/Interpret the Constitution.

McCulloch v. Maryland (1819)
Implied powers under the Necessary and Proper Clause: Creation of the national bank was implied based upon the enumerated power of Congress to tax and spend. State of Maryland could not tax federal bank due to Supremacy Clause, because the power to tax is the power to destroy.

Shaw v. Reno (1993)
NO racial gerrymandering; race cannot be the sole or predominant factor in redrawing legislative boundaries; majority-minority districts.
Gideon v. Wainwright (1963)
State courts are required under the Sixth Amendment of the Constitution to provide counsel in criminal cases for defendants unable to afford their own attorneys.

Baker v. Carr (1962)
Established the principle of "one person, one vote". The Court asserted that the federal courts had the right to tell states to reapportion their districts for more equal representation. Ultimately, the Court ordered that state legislative districts to be as near equal as possible in population.

Wisconsin v. Yoder (1972)
Dealt with the Amish community's desire to pull their children from public school before the age of 16 so that they could help with farm and domestic work. The Court sided with the Amish and held that parents may remove children from public school for religious reasons.

McDonald v. Chicago (2010)
The Second Amendment that allows the people to keep and bear arms applies to state governments as well as the federal government.

Citizens United v. FEC (2010)
Corporations have the same 1st Amendment right as individuals to expressly support political candidates for Congress and the White House through campaign contributions.
