CS
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Algorithm
An algorithm is a set of instructions for solving a problem or completing a task
Abstraction
Abstraction involves removing unnecessary detail from a problem so that you can focus on the essential components
What are models used for
We often build models that are simplified versions of the real world and will remove unnecessary details
Decomposition
This involves breaking down a large problem into smaller subproblems Then the sub-problems can be broken down further until each small task is manageable
Advantages of decomposition
The problem becomes easier to solve
Some subprograms could be reusable, therefore saving development time
Reduces the amount of code needed
Easier to maintain and have fewer bugs
Arithmetic operators: +, -, /, *, **, %, //
How do you check answers for equations in python
x= (4 + 3)*6
print(x)
Variable
A location in memory in which you can temporarily store a value such as a string
or number
Variable names
When you assign names to variables, like mark1, and mark 2
what is total=total+mark 3
Add the value in the location called mark3, to the value in the location called total
What are the 2 main tools to help write down procedure/steps?
Flowcharts
Pseudocode
Flowchart symbols, pallelogram, rectangle, diamond, arrow, oval, rectangle with lines
When are subprograms used?
Subprograms are used when you wish to call another procedure or function
Sequence, how are they showed in flowcharts
A sequence is a series of steps which are completed one after the other. In a flowchart they are shown as process, input or output symbols shown one after the other.
Selection, how are they showed in flowcharts
Selection is the ability to choose different paths through a program. In flowcharts, decision symbols are used for selection.
What statement is a kind of selection?
An if statement is a kind of selection, the next statement depends on weather the condition is true or false
Repetition / looping/ iteration
Iteration means repeating a part of a program. In flowcharts, iteration is shown by using arrows that repeat a section of the flowchart. A decision will control whether more iterations are required
What are the 2 types of iteration?
For loop
While loop
What is a for loop and what kind of repetition is it
Repeat the loop for a specific number of times
It’s a count controlled repetition
for i in range(5):
Print (“hello”)
What is a while loop and what kind of repetition is it
Repeats a set of instructions as long as a certain condition is true. You don’t have to know how many times it will repeat — it keeps going until the condition becomes false. It checks the condition before each repetition. It’s a condition controlled repetition
The loop keeps running as long as condition is true– e.g.
while score < 10:Keeps on running until the score reaches ten
What happens during iteration over a data structure?
This loop goes through each item in a collection like list or string* – e.g.
for item in list:It stops once it’s done printing, so when there is no more things in the list
What are strings
String is a sequence of characters, like letters, numbers, and symbols that are always enclosed in quotation marks.
Eg. “Hello” “12345”
List 5 data types with definitions
List boolean operators used for comparison, greater than, equal to, greater than or equal to, less than, less than or equal to, equal to, not equal to, exponent
greater than >
greater than or equal to >=
less than <
less than or equal to <=
equal to ==
≠not equal to !=
Pseudocode and it’s benefits
Informal and rough version of real python code (not real)
Helps people focus on logic of the algorithm instead of the exact syntax coding language
How to assign a variable
Name it an use an = sign
cost = adult 2 + child 3
Write a statement of pseudocode to change the value stored in total to include VAT (at 20%)
total = total * 0.2 + total
ORtotal = total * 1.2
What is input and where is it saved
Most programs ask the user to type something in, like their name or age.
The program then saves that input in a variable (a named storage space).
Display a prompt “Press Enter to continue”. When the user presses Enter, continue to the next statement.
input("Press Enter to continue")
Write pseudocode for a program which asks the user to enter the cost of two items, adds the two costs and if the cost is greater than £10.00, displays a message “Sorry, too much”. Otherwise it displays the change due from £10.00
item1 = input("Please enter price of first item:")
item2 = input("Please enter price of second item:")
total ← item1 + item2
if total > 10:
print("Sorry, too much")
else:
change = 10 – item1 - item2
print("Change from £10.00 is £", change)
Arrays and where does it start
Arrays are a data structure that stores many items under one identifier/name.
Each item in the array has a position number called an index (starting at 0).
What is iteration over an array
Iteration over an array means going through each item one by one
What is a 2D array like and how do you iterate through it?
A 2D array is basically like a table
To iterate through a 2D array, you must use nested for loops (a for loop inside another for loop)
Which number does CS always start with
0
Explain the code:
num = int(input("Start number: "))
for i in range(num):
num = num + 1
print(num)
The number starts at 5
Repeats 5 times (0-4)
i is the amount of times it repeats
Each time the loop runs, the number increases by 1
Print end result
How do we determine if an algorithm is fit for purpose?
We measure the efficiency
How is efficiency measured by?
Comparisons – How many items it compares
Loop passes – How many times it loops
Memory used – How much space it takes up
How many input(s) are there in trace tables
1
How does this code work?
num = int(input("Start number: "))
for i in range(num):
num = num + i
print(num)
Add i to current number to make it a new number
What is the algorithm, number of passes through a loop, and use of memory in this code?
num = int(input("Start number: "))
for i in range(num):
num = num + i
print(num)
Algorithm= Version 1
Number of passes through a loop= 5
Use of memory= i, num
What is the algorithm, number of passes through a loop, and use of memory in this code?
num = int(input("Start number: "))
result = ((num + 1) * num) / 2
print(result)
Algorithm= Version 2
Number of passes through a loop= 1 (no loops)
Use of memory: num, result
Why is algorithm 2 more efficient
Far more efficient in loops/processing; same use of memory
Syntax error
program code doesn’t conform to the rules/grammar of the language and won’t run
Logic error
the program runs but doesn’t do what the programmer intended
Runtime error
an error when the program is running – e.g. out of bounds or divide by zero
What does a trcae table do?
It records the values of variables as a program is ‘run’ by a human
What are the 2 different types of search algorithms?
Linear search
Binary search
Linear search
searches each item in the list one by one until it’s found the wanted one
Binary search
searches list by dividing it by 2, then going on to the first one when there’s only 2 left
What are the 2 different types of sorts?
Bubble sort
Binary sort
Bubble sort
Compare two numbers next to each other, and swap them if they’re in the wrong order. Do this again and again until the whole list is sorted in numerical order or alphabetical order
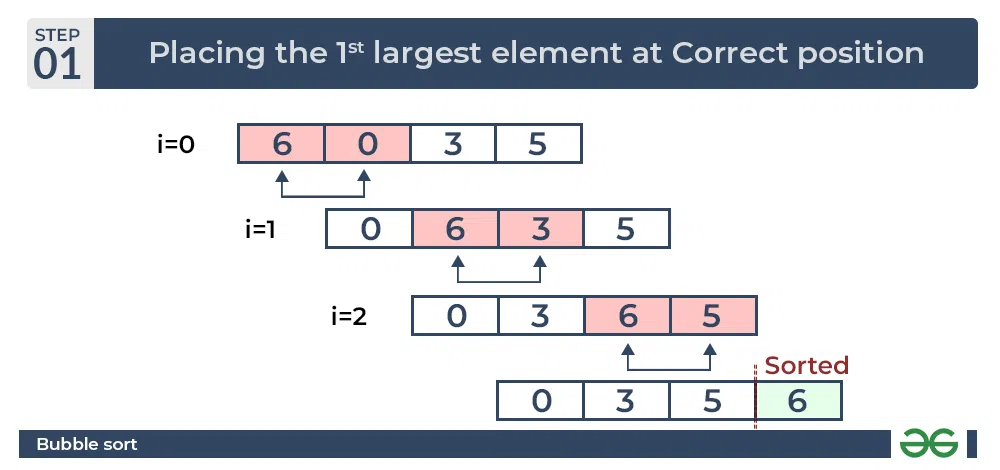
Merge sort
Split the list into smaller pieces (halving) until each piece has 1 item. Then merge those pieces together in the correct order.
What are the 3 different types of logic gates?
And, or, not
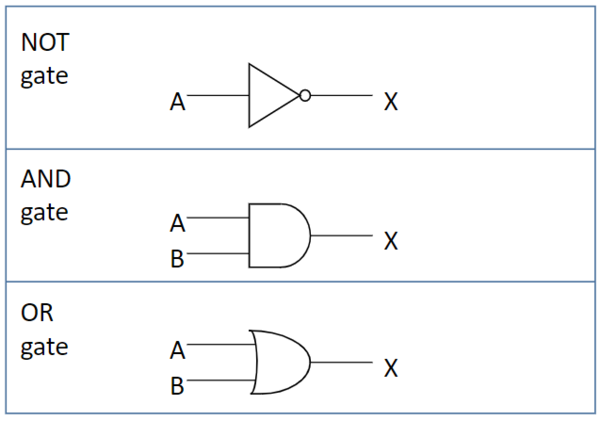
What does an AND logic gate do?
Both inputs must be true for the output to be true, both must be 1.
What does a NOT logic gate do?
At least one input must be true for output to be true. (1)
What does an OR logic gate do?
The output would be opposite the input
What does a truth table show?
It shows all the possible combinations of inputs and outputs they create
Python symbols