Other sensory systems
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
photoreceptors
detection of changes in light
mechanoreceptors
detection of changes in pressure
hair cells
specialized mechanosensory cells
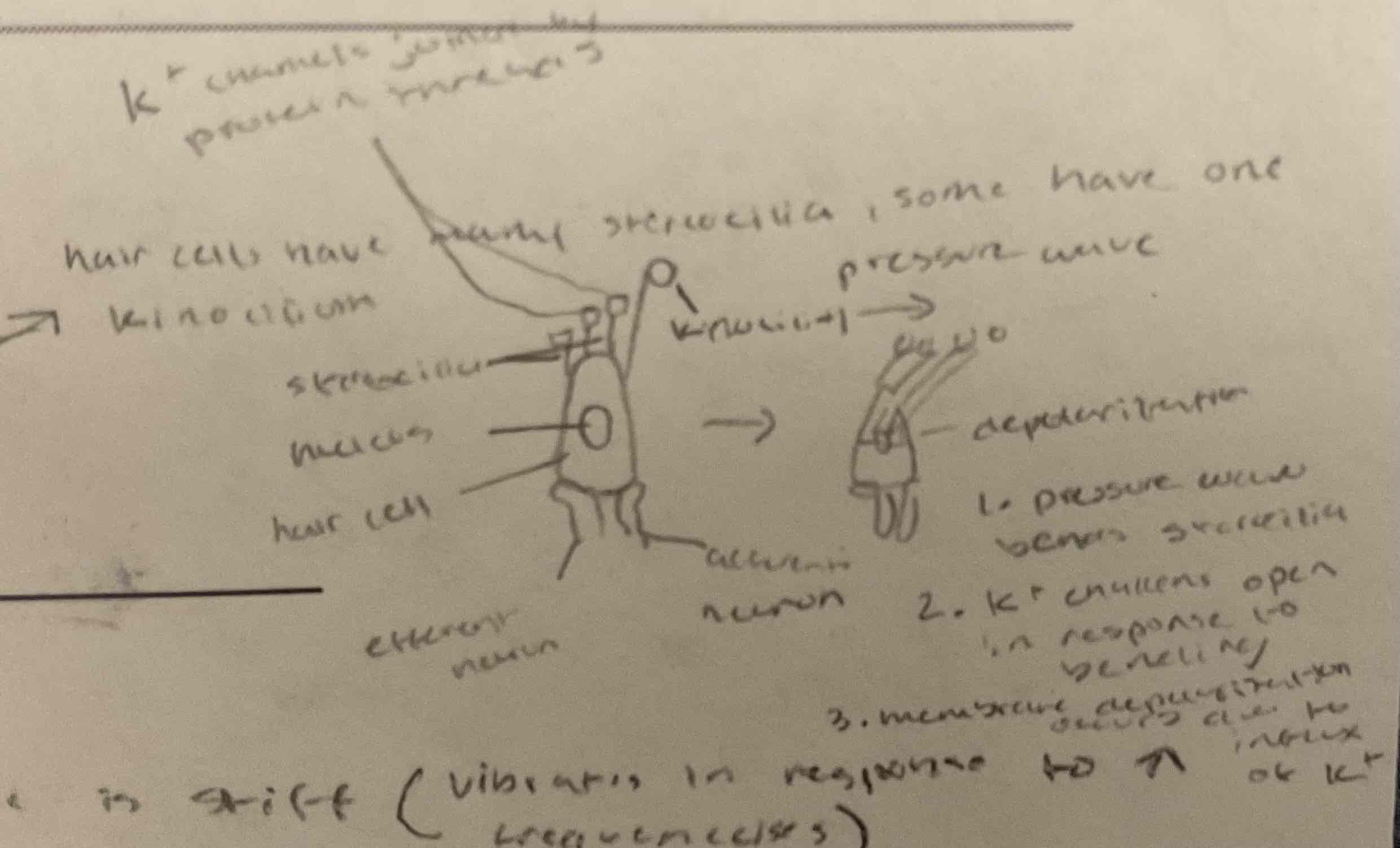
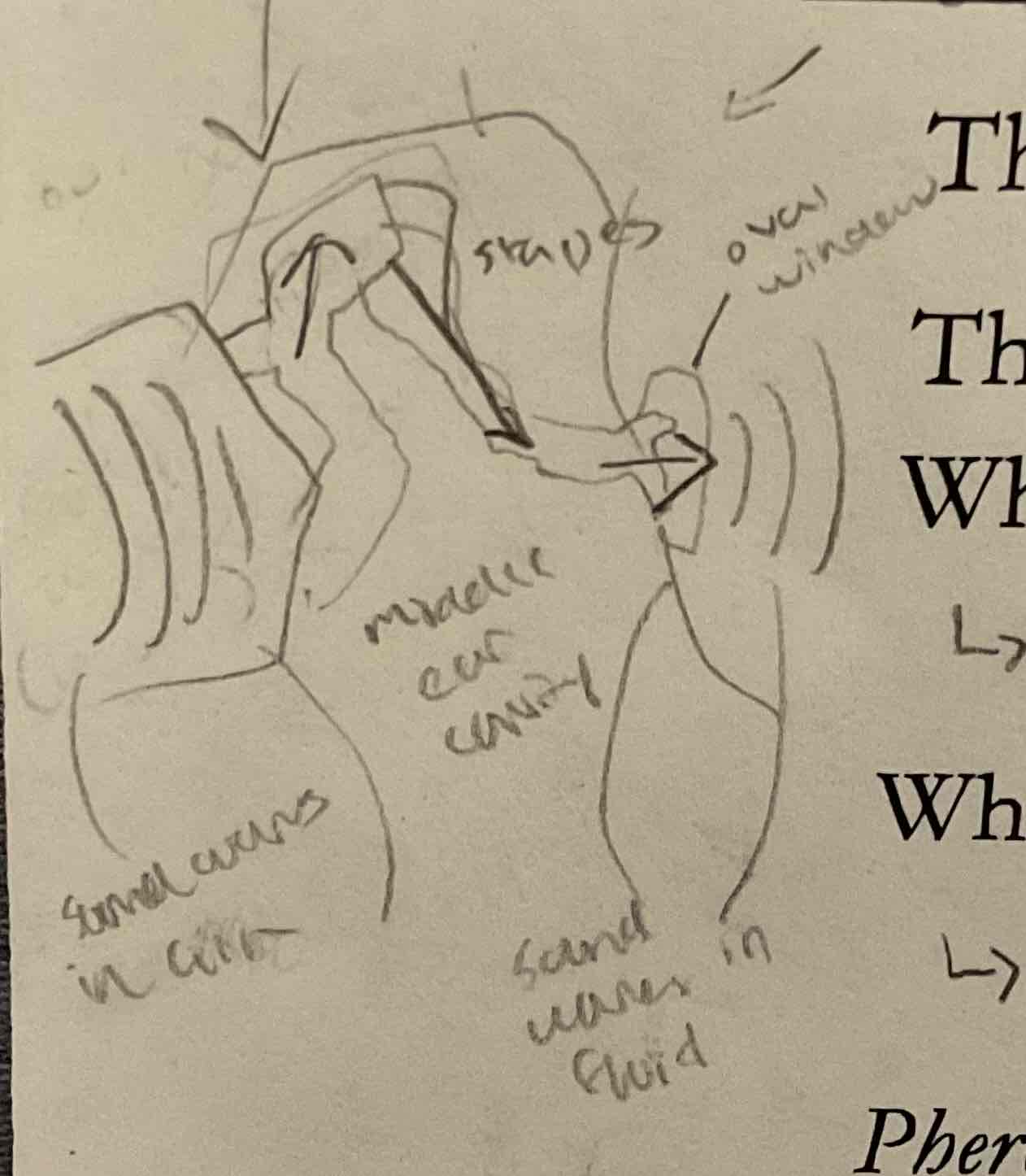
cochlea
allows us to hear diff frequencies; narrow part of basilar membrane is stiff + vibrates in response to high frequencies; wide part of basilar membrane is flexible + vibrates in response to low frequencies
two ranges of sounds humans can’t hear but others can
infrasound, ultrasound
vestibular sense
hair cells in the inner ear are moved by a gel pocket called cupula
specialized system for underwater mechanoreception
lateral line system, statocyst + statolith
lateral line system
series of canals running along head to body and hair cells within canals have kinocilia/sterocilia embedded in cupula; water enters canals via pores bending kinocilia and activating sensory neurons

statocyst and statolith
statocyst contains small, free moving calcium mass called statolith; normally rests at bottom of organ but when tipped, statolith moves and presses against receptors not at bottom, signaling brain to activated muscles to return to normal orientation via action potential
chemoreceptors
detection of specific molecules
two senses of chemoreceptors
taste (gustatory) and smell (olfactory)
why are specific molecules relevant to transduction of chemosensory cues
influences depolarization in action potential
why would so many olfactory receptor genes in mammals be nonfunctional
does not need all senses, sensory overload, filtration
phermones
secreted chemicals affecting behavior/physiology of conspecifics (same species); detected in vomeronasal organ (VNO) - humans have vestigial VNO with no sensory capacity
olfactory receptor neurons..
… bind to specific odorants and strength of signal is proportional to number of molecules
odorants
airbone molecules conveying info about food (environment then enters nose then arrives to olfactory neurons)
thermoreceptors
detection of changes in temperature; in skin + brain (to detect/respond to internal body temp for homeostatis)
vipers
special thermosensitive organ called pits
nocireceptors
detection of harmful stimuli, responds in extreme temperature, pressure, and certain chemicals
three pieces of evidence that fish feel pain
fish have nocireceptors
fish learn to avoid hooks/sharks
BUT nocireceptors are diff from us
umwelt
an organisms experience of the world
electroreceptors
detection of electric fields
electroreceptive
can detect electric fields
electrogenic
can actively produce an electric field
electric organ
made from modified muscle cells
magnoreceptors
detection of magnetic fields
emlen funnel
apparatus used to study bird migration
multimodel signaling
combining two types of sensory signals, enhancing signal (car sickness, VR)
summing multiple action potential…
facilitates continuous variation in response (not just all or nothing)
bird experiment
birds sat at one end of cage at beginning of migration with no visual cues
in circular chambers with artificial magnetic fields birds orientated in reaction to field
when magnetic field disrupted, birds were confused and did not navigate properly
bird beak experiment
hypothesis: sensory neruons in beak have iron deposits
cutting off beak found that these neurons prevented birds from reacting to magnetic fields