Chemical kinetics
1/43
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Chemical kinetics definition
Chemical kinetics is a branch of chemistry which deals with the rate of chemical reaction and factor those affect them
Definition of rate of reaction
The rate of reaction describe how rapidly the reactants are consumed or the products are formed.
Average rate of reaction
Average rate of reaction= change in concentration of speci/change in time = ∆c/∆t
For rate of consumption it is minus sign
For rate off formation it is Plus sign
Average rate of reaction is equal to rate of formation is equal to rate of consumption.
Dimension is mol dm⁻³ sec⁻¹.
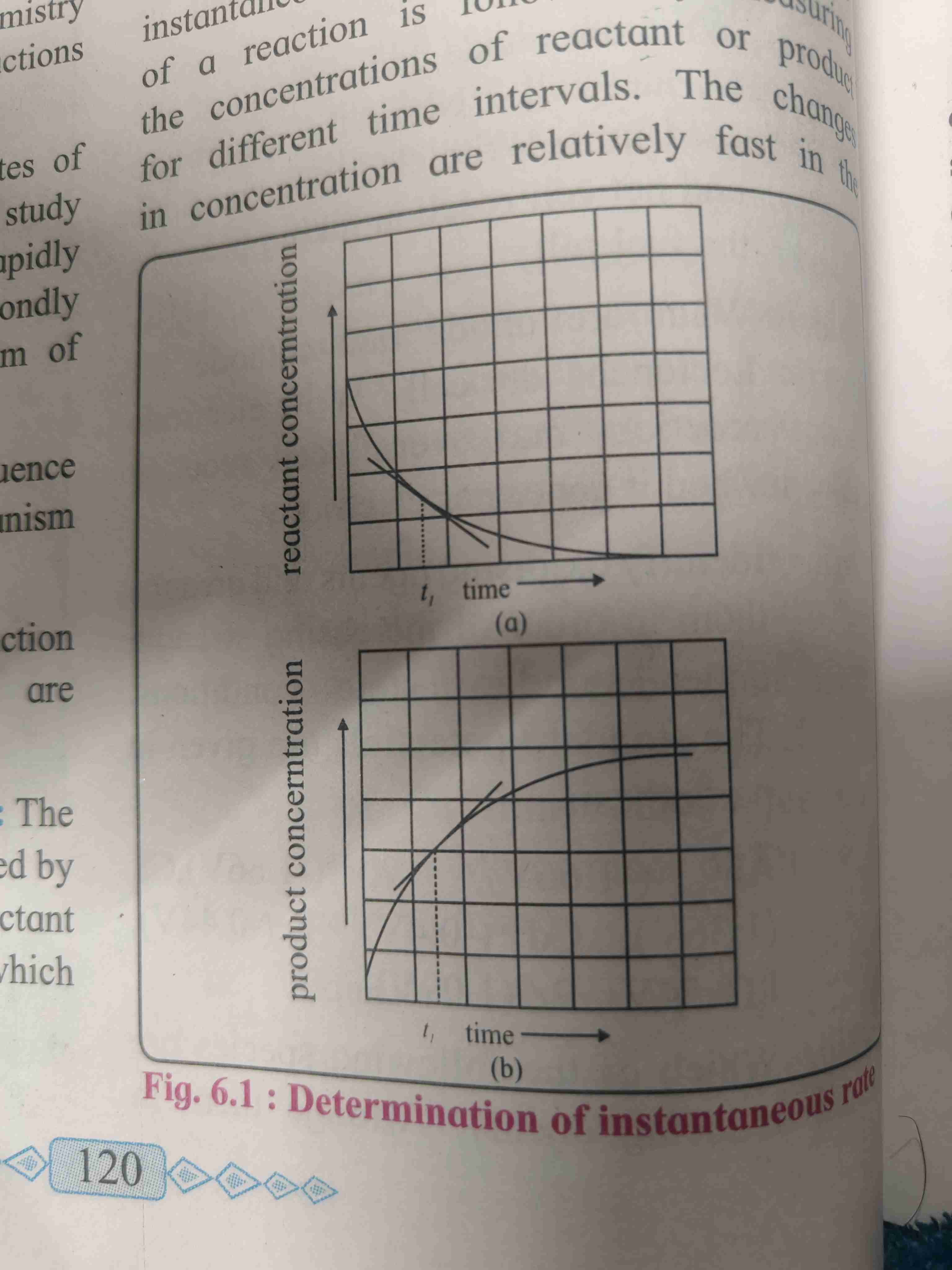
Instaneous rate of reaction
It is used to do determine the rate of reaction for specific time interval
Rate consumption at any time =.-d[A]/dt.
With coefficients the rate of reaction is aA+bB→cC+dD
-1/a d[A]/dt = -1/b d[B] / dt =1/c d[C]/dt = 1/d [D].
Definition of rate law
Rate of reaction at given temperature for a given time instant depend on concentration of reactant . Such rate concentration relation is rate law
Rate law
Rate=K[A]^x[B]^y. Differential rate law
X and y maybe simple whole number zero OR fraction they are experimentally determined
For X and y = 1 , rate = k(A)(B). If concentration of x or y is double rate will be doubled
For x=2 &y=1 , rate =k(A)²(B). If concentration of a is doubled keeping that of B constant the rate will be increased by factor of 4.
X<0 the rate decrease as [A] increse
x=0 rate is independent of concentration of A
Writing rate of law
2H2O2—— 2h20 + 02
If rate of reac is proportional to concentration of h2o2 rate law is
Rate =K[h2o2].
Order of reaction
Addition of X and y powers.
Rate =K[A]^x[B]^y. , x+y.
K(h2)(i2) , x+y = 1+1 = 2 order of rec
Order of reaction is experimentally determine d
It can be integer or fractional.
If order of reaction is zero, means the rate of reaction is independent from concentration of reactant.
Only few reaction of third order has been found.
Complex reaction
Complex reaction are those which constitute a series of elementary chemical reactions
Elementary reaction
Reaction occurs in single step and cannot be broken down further into simple reactions .
Molecularity of reaction
The number of molecules involves in reaction is the number of molecularity of the reaction
02— O+, 1 molecurity , NO2 — two
Order and molecularity of elementary reaction
For elementary reaction in 2N0—-2NO+O2
K[NO]². It is BIOMOLECULAR AND SECOND ORDER.
Rate determination step
Some reactions are multi step reactions
Hence the slowest step is taken as the rate determining step .
Reaction intermediate
Any compound which is formed in first step and then consumed in any step, if it is not present in overall course of reaction it is called reaction intermediate
It is not present in rate law
Distinction between order and molecularity
Order
It is experimentally determined
It is sum of power of concentration of terms of reactant those appear in equation
Maybe an integer fraction or zero
Molecularity
It is theoretically identity
It is number of molecules or moles taking part in elementary reaction
It is integer.
Definition of integrated rate law
These tells us the concentration of reactant for different time
Integrated rate law for first order reaction in solution
Refer page for derivation and laws

Units of rate constant for first order reaction
Unit of K will be s^-1, min^-1, hr^-1.
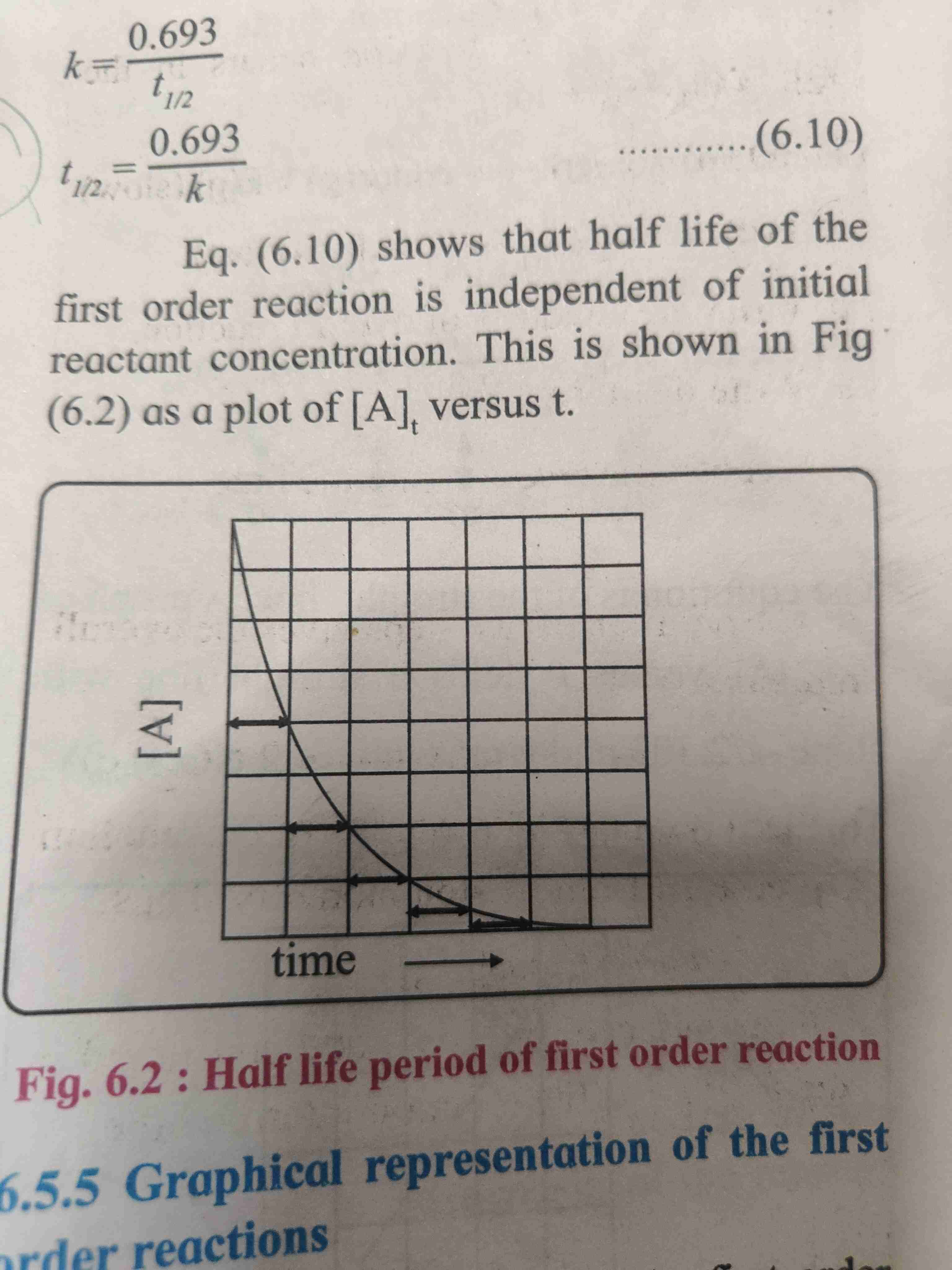
Half life of first order reaction
Half life of a reaction is time required for the reactant concentration to fall to half of its initial value
Half life and rate constant for first order reaction
Half life of first order reaction is independent of initial reactant concentration
Formula K=0.693/t₁/₂ , t₁/₂= 0.693/K.
Derivation refer page

Integrated rate law for gas phase f reaction formula
Formula refer page
Where initial pressure of a is Pi , P is total pressure of reaction mixture at time T.
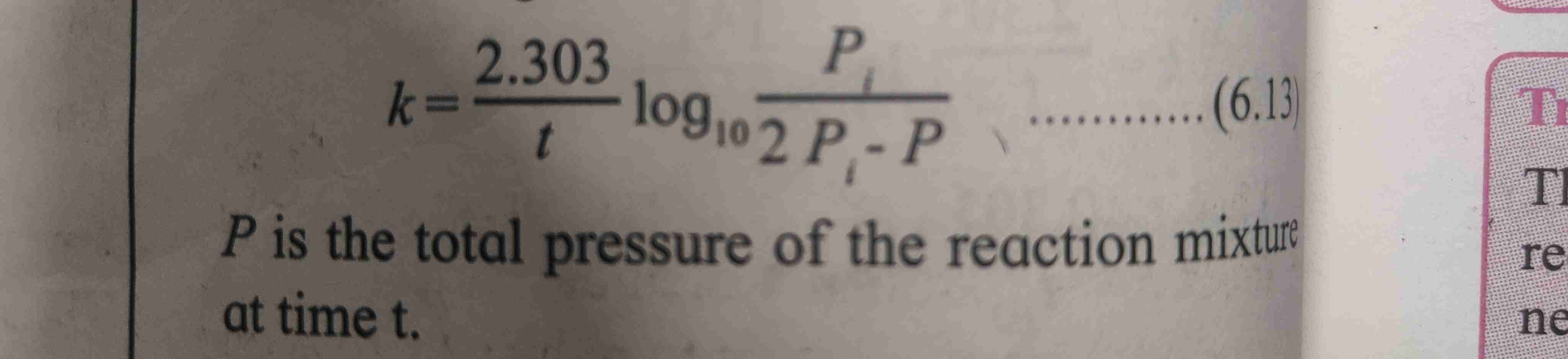
Integrated rate law for gas phase reaction derivation
Refer page for derivation

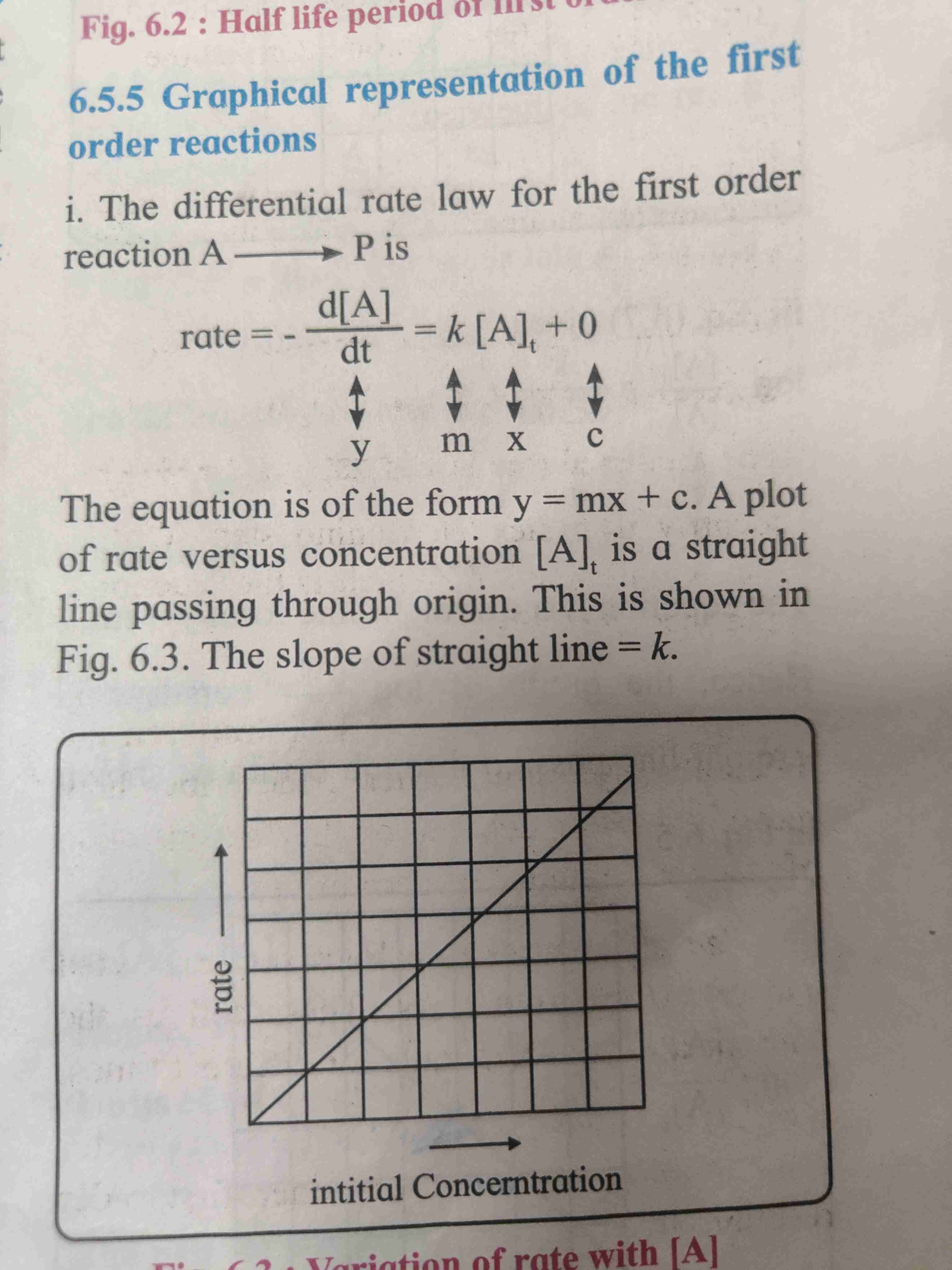
Zero order reaction
The rate of zero order reaction is independent of reactant concentration.
Formula - kt = (A)0-(A)t
Concentration of A = (A)0 at t=0 , concentration of A=(A)t at t=t
Unit of rate constant for zero order reaction is mol dm⁻³ t⁻¹.
For derivation refer page
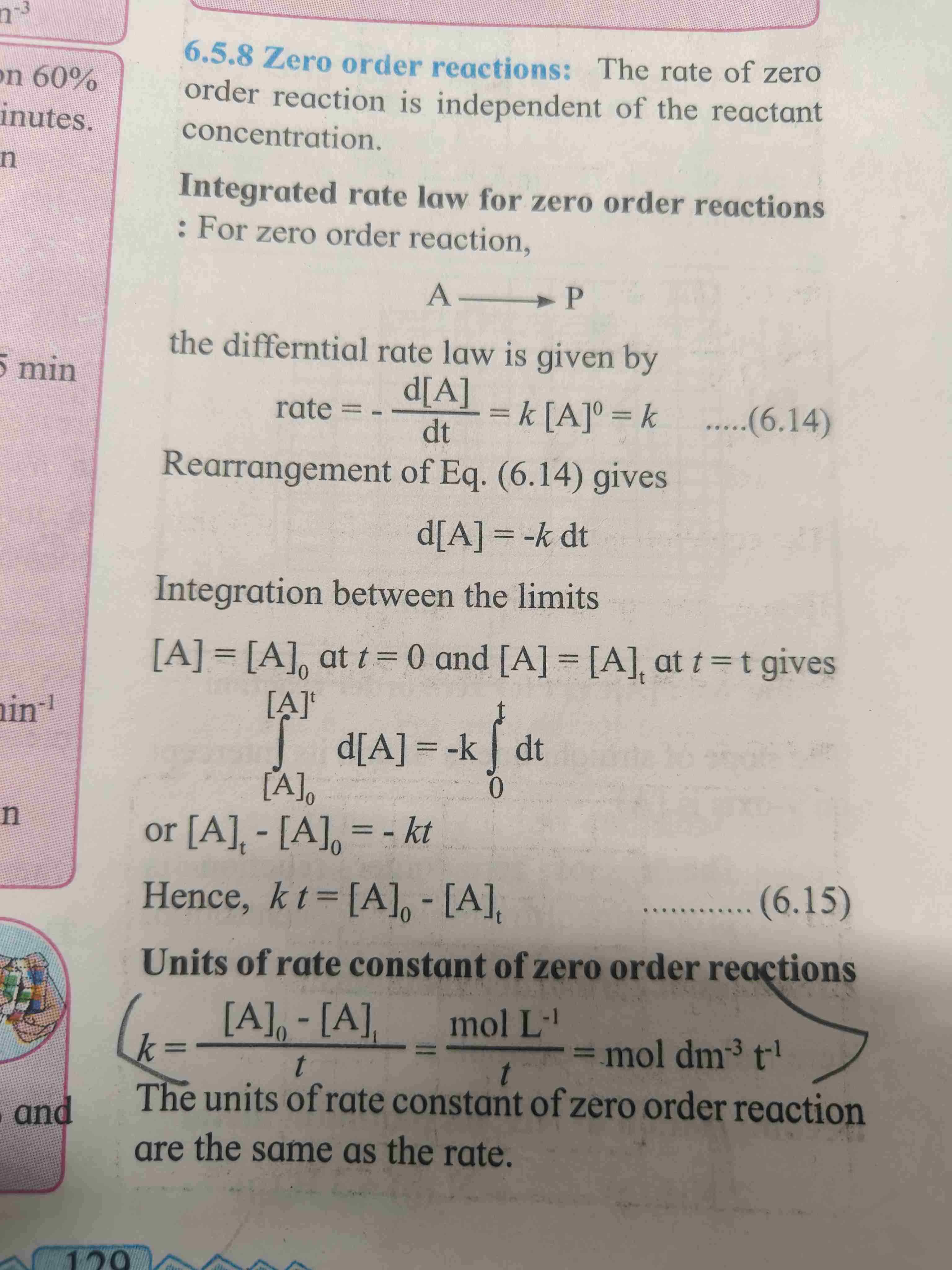
Half life of zero order reaction
The half life of zero order reaction is proportional to the initial concentration of reactant.
Formula t₁/₂ = [A]₀/2k. [A]₀ is initial concentration of reactant.
For derivation refer page
![<ol><li><p>The half life of zero order reaction is proportional to the initial concentration of reactant. </p></li><li><p>Formula t₁/₂ = [A]₀/2k. [A]₀ is initial concentration of reactant.</p></li><li><p>Fo<span style="color: var(--color-neutral-black)">r derivation refer page</span></p></li></ol>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cb3c8b25-f0c5-49de-8b68-21b10f1f0d66.jpg)
Pseudo first order reaction
The reactions which are higher than first order reaction but follows the rules of first order reaction are called pseudo first order reactions.
It happens because one compound is present in very high concentration and amount than other so the change in concentration when added another compound is negligible.
For rate law refer photo
Collision between reactant and molecules
Chemical reaction occur as a result of collision between reactants speci
Hence rate of reaction is expected to be equal to rate of collision.
For gas phase number of collision is far more and typically many powers of 10 compared to the observed rate.
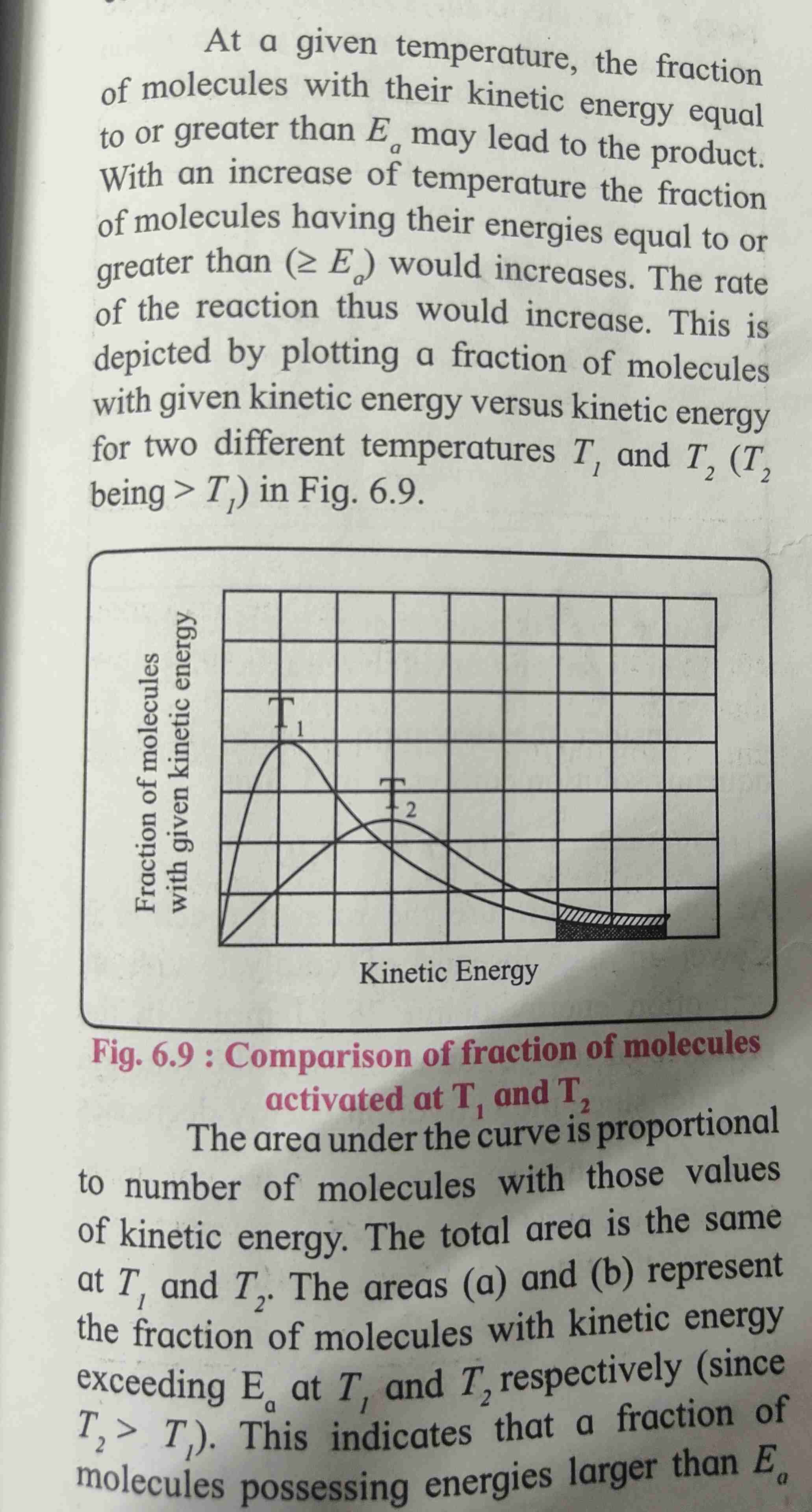
Activation energy
For reaction to occur colliding reactant must poses minimum of kinetic energy [KE] this energy is called as activation energy
When reactant molecules KE gets equal or greater than activation energy the reaction occurs.
Orientation of react and molecule
Beside collision they should also have proper orientation to form reaction
Refer page for orientation.

Activated complex
A configuration in which all three atoms are weakly connected together is called activated complex.
Arrhenius equation
Arrhenius equation suggest that rate of reaction varies with temperature
For formula refer page

Determination of activation energy
Refer page for formula and derivation

Abababa
Rate of reaction increases with temperature.
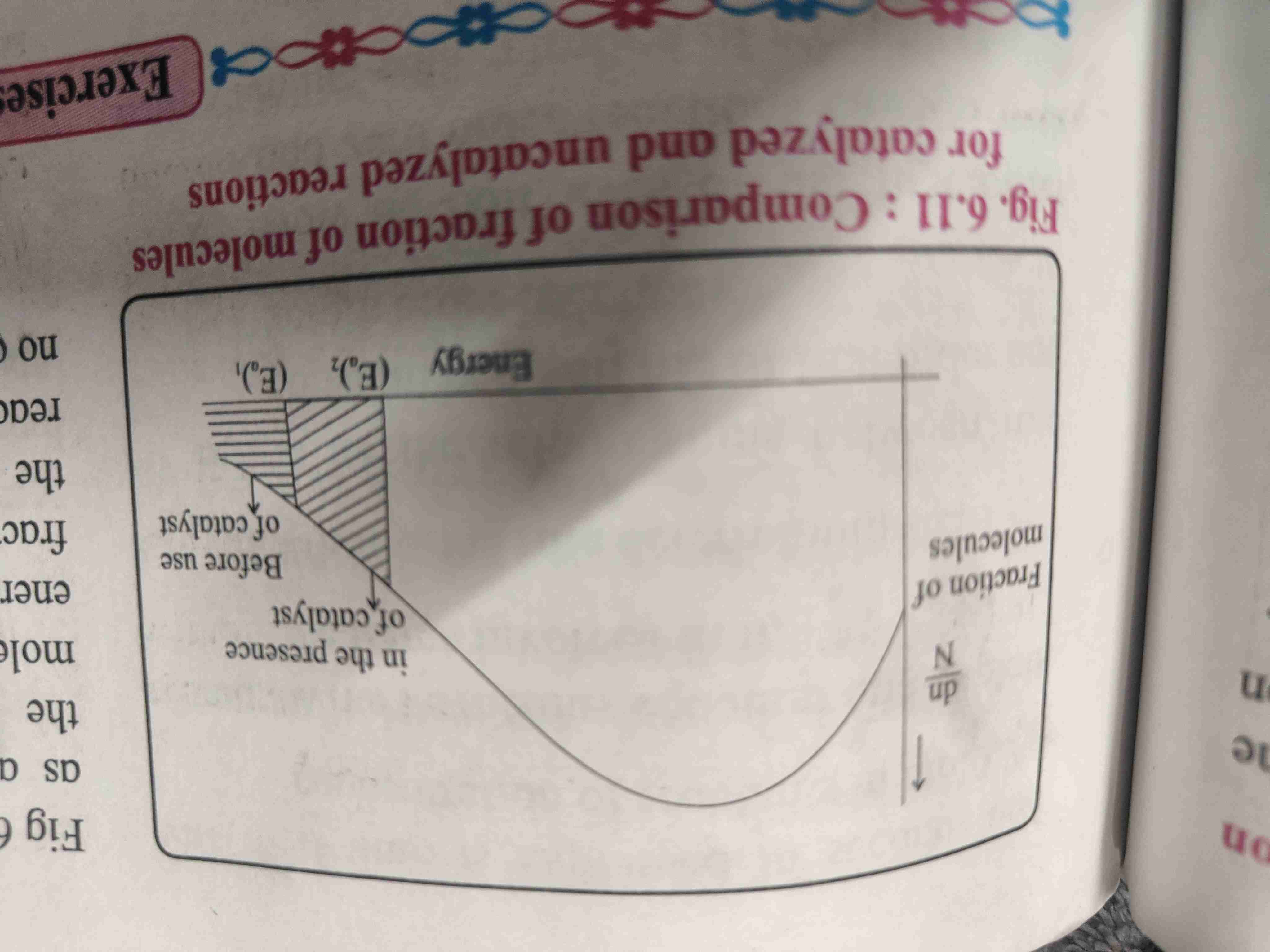
Effect of catalyst on rate of reaction
A Catalyst is a substance added to reactant that increases rate of reaction without itself being consumed in reaction.
It provides alternate pathway with lower activation energy.
A catalyst lowers the threshold energy consequently more molecules acquire the minimum amount of energy and tend to cross the energy barriers
A fraction of activated molecules is greater in the catalyzed reaction .
Rate of reaction is larger of catalyzed reaction compared to uncatalyst reaction
**graphs.
10
Graph of Instantaneous rate
The tangent drawn to the curve at time t gives the rate of reaction
The slope gives the instantaneous rate of reaction
Graph of half life period of first order reaction
It shows that half life of first order reaction is independent of initial reactant concentration .
Graphical representation of first order reaction.
Graphical representation of first order reaction

Graphical representation of zero order reaction
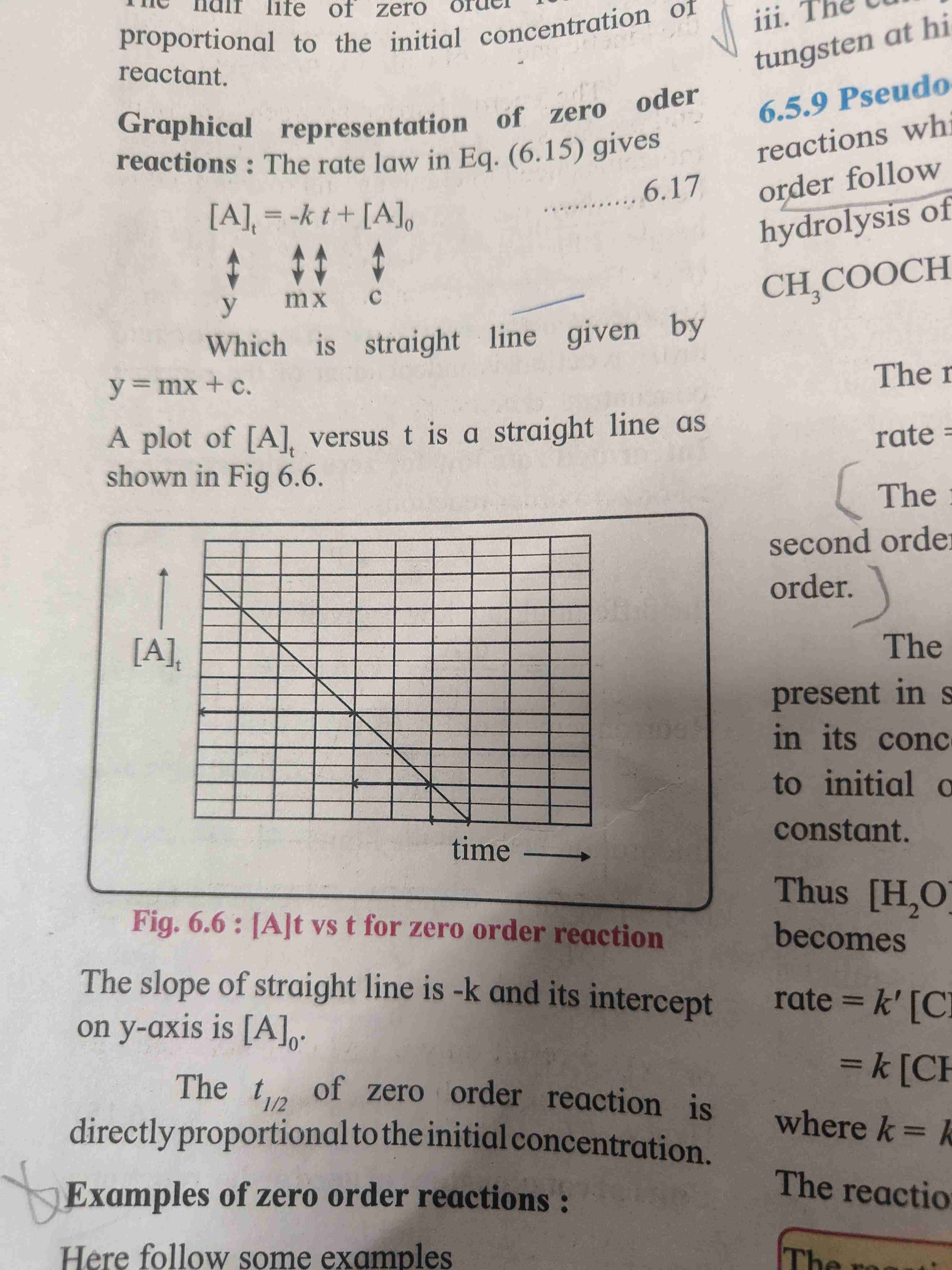
Graphical representation of potential energy barrier
Graphical determination of activation energy
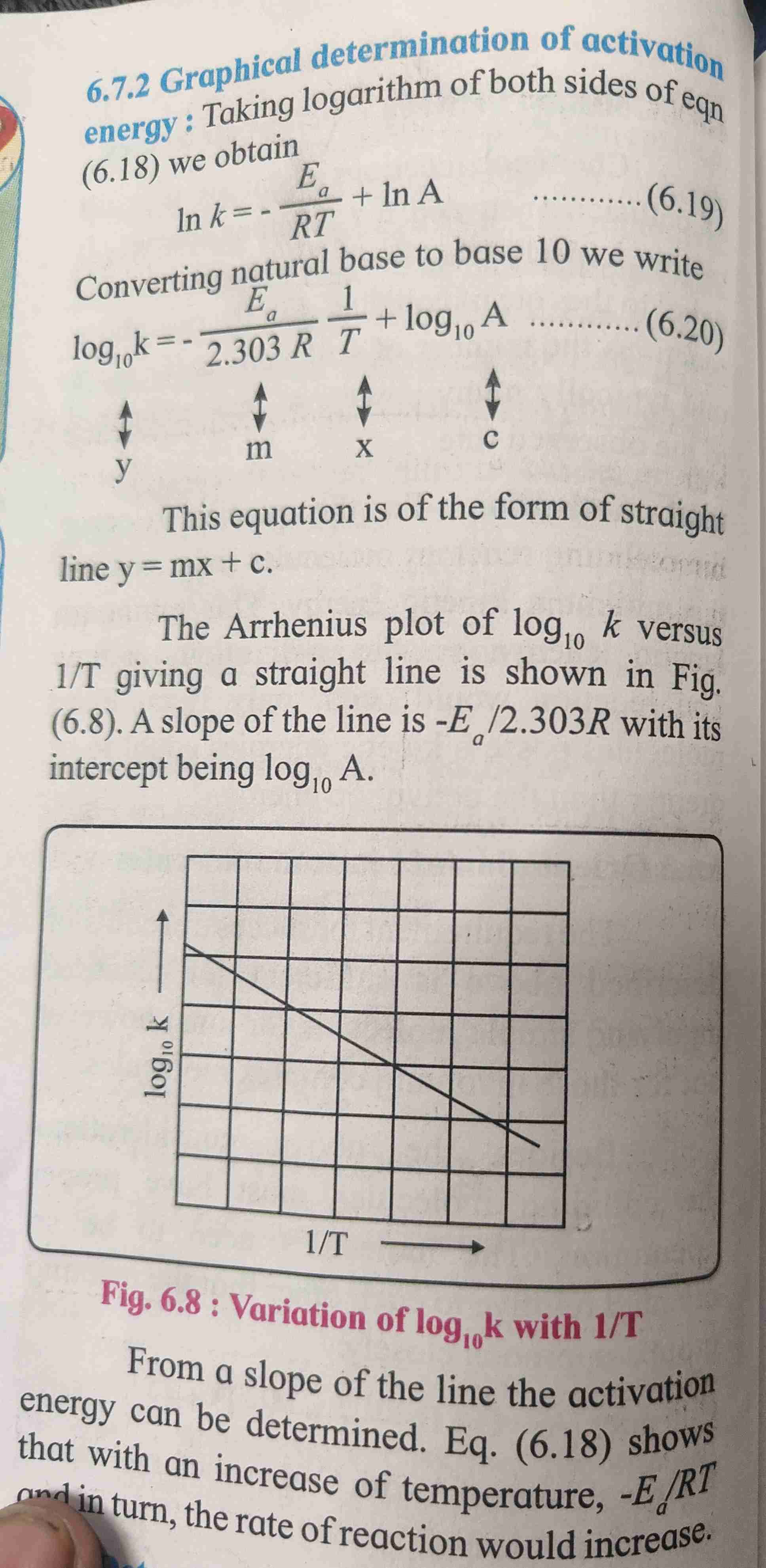
Graphical description of effect of temperature
Graphical representation of potential energy barriers for catalyzed and uncatelised reaction
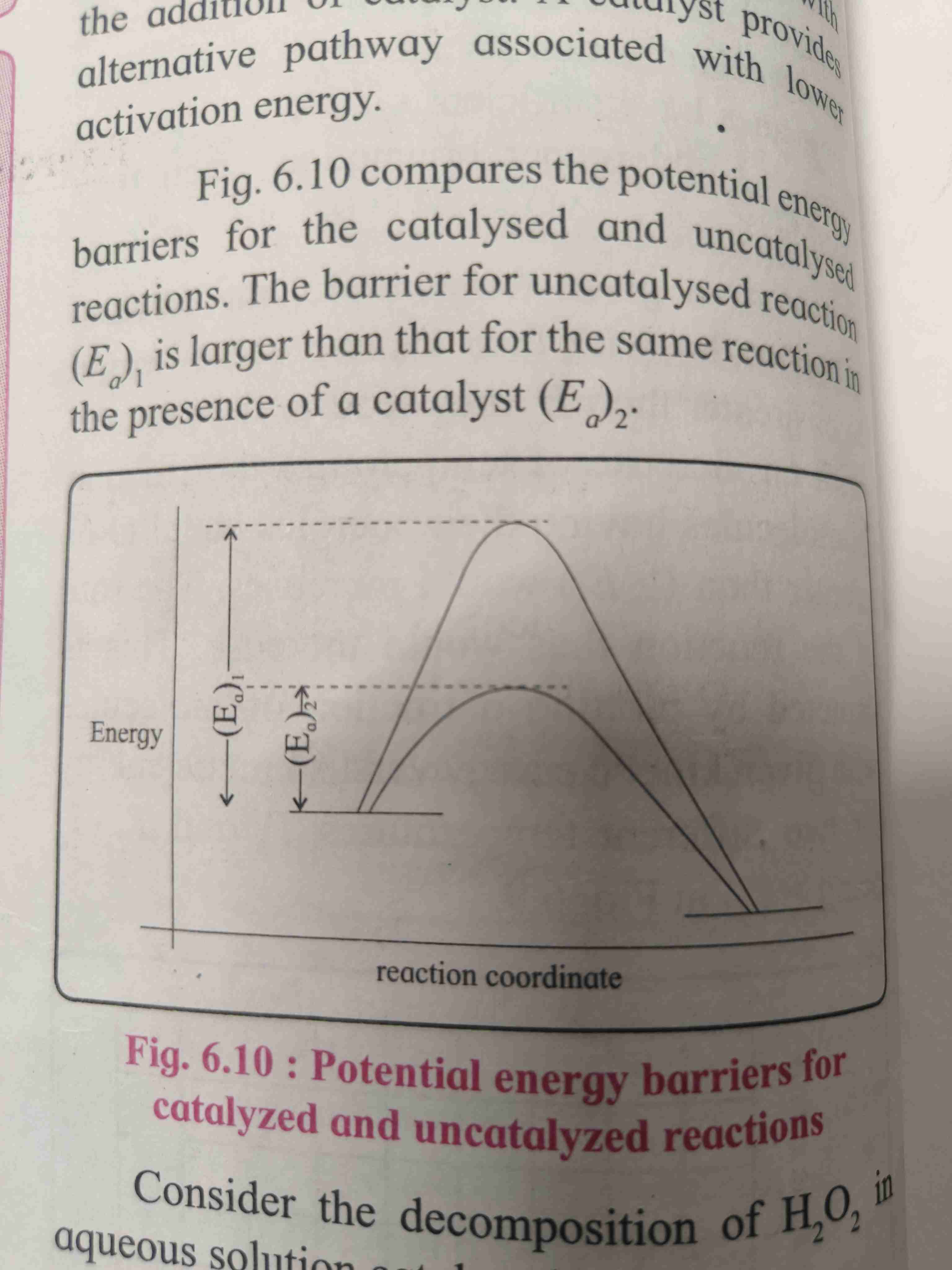
Comparison of fraction of molecules for catalyzed and and catalyzed reactions