Kinesiology of the Knee: Structure and Function
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
Medial Tibia-Femoral Compartment
- Medial Femoral Condyle
- Medial Aspect of Tibial Condyle
Lateral Tibia-Femoral Compartment
- Lateral Femoral Condyle
- Lateral Aspect of Tibial Condyle
Patello-Femoral Compartment
- Posterior Aspect of Patella
- Anterior Aspect of Femur

Knee Stability
- less osseous stability
- Primary = soft tissue (ligamentous/tendinous)
Knee Movement
- mostly sagittal (flexion/extension)
- some transverse (can move Tibia in IR/ER)
- frontal (passive)
Knee Function
- flexion/extension for running/walking/etc.
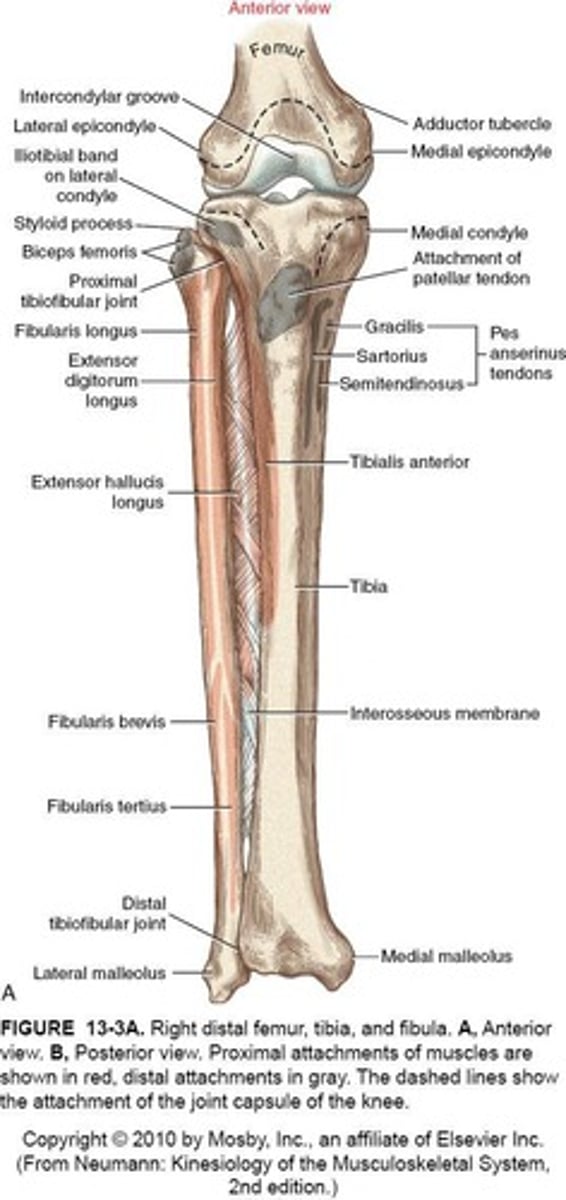
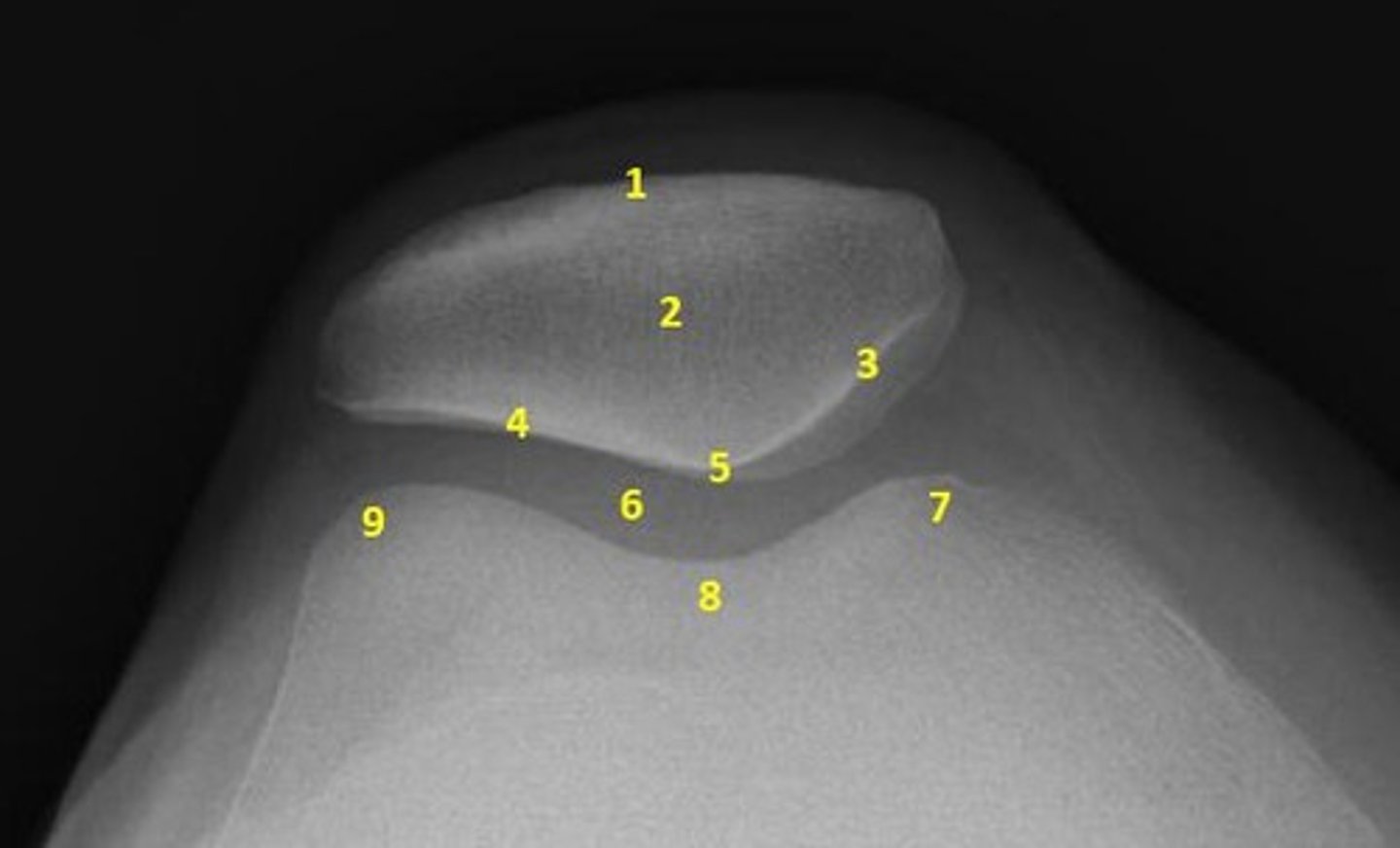
Distal Femur
large lateral & medial condyles for joint articulation
Femoral Epicondyles
projections from each condyle providing elevated sites for collateral ligaments
Intercondylar Notch
- passage for cruciate ligaments
- narrowing = increased risk of ACL injuries
Trochlear Groove
- anterior fusing of the condyles
- pathway for patellar movement
- concave M-L, slightly convex A-P
Lateral & Medial Facets
- sides of Trochlear Groove
- Lateral = much larger
- provides congruency & stability to prevent excessive lateral excursion of Patella
Medial Facet of Trochlear Groove
- more oval shaped
- much longer A-P than M-L
- matches with articular surfaces of Tibia
Patella's Natural Pull
Supero-lateral direction during movement.
Tibial Plateau
Flat surface for weight acceptance from femur.
Intercondylar Eminence
Attachment site for cruciate ligaments & meniscal attachments
Tibial Tuberosity
- Common palpable landmark
- site for quadriceps tendon insertion.
Fibula's Role
Aids in weight dispersion, indirect transfer via Interosseous Ligament
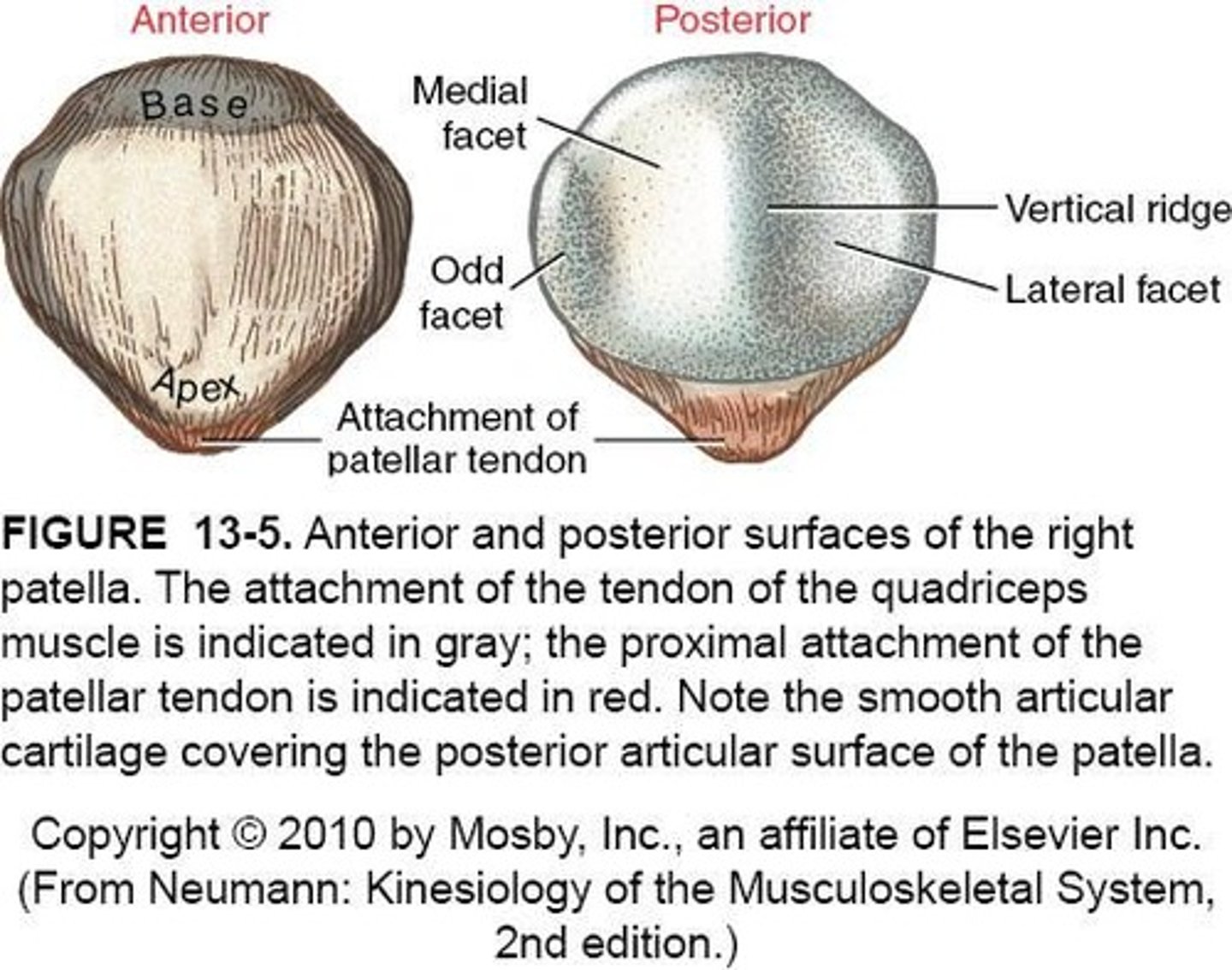
Patella
- Largest sesamoid bone
- embedded in quadriceps tendon
Posterior Surface of Patella
- covered with 4-5mm. of articular cartilage (absorb forces from knee flexion & WB)
- articulates with femur forming Patellofemoral Joint
Apex of Patella
- inferior end
- where patellar tendon inserts
- extends down to Tibial Tuberosity
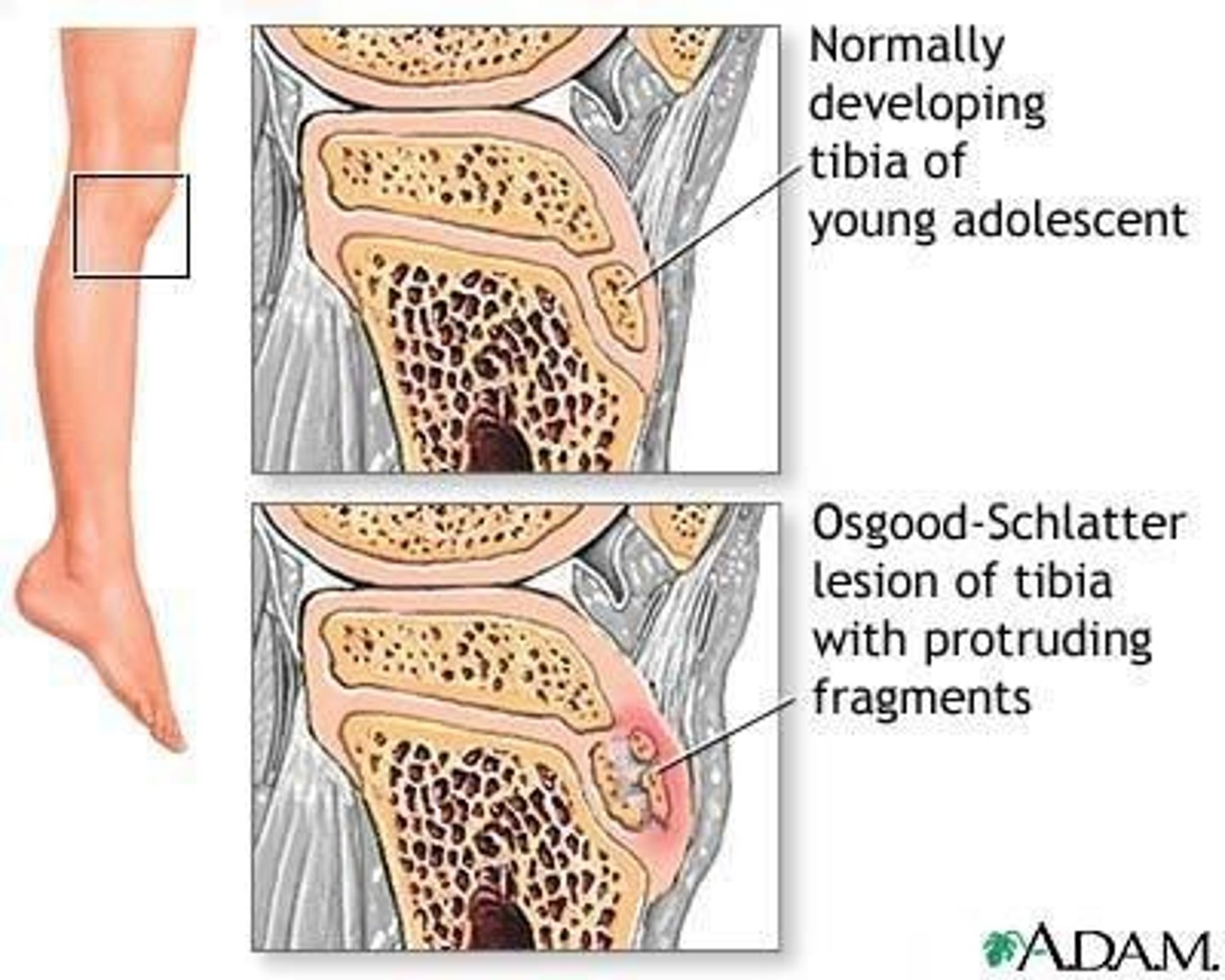
Osgood-Schlatter Disease
- Inflammation at growth plate in adolescents
- more in males than females
- running/jumping increase quads demand & tendon pulls on bone at insertion
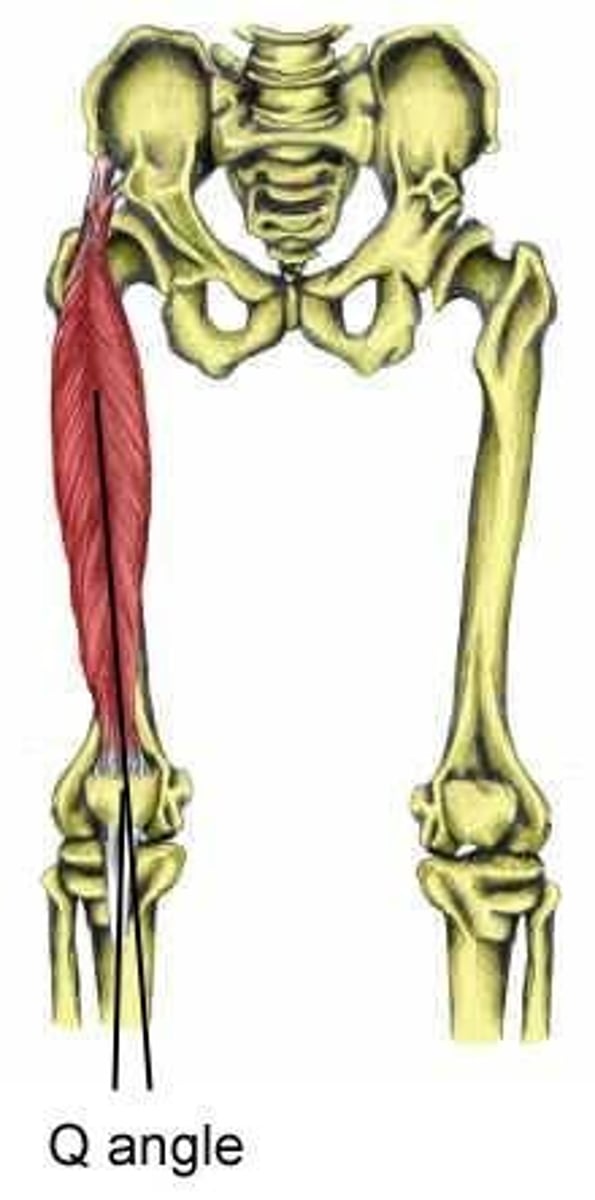
Q Angle
- angle between ASIS & patellar tendon
- average for men = 11.2
- average for women = 15.8
- greater genu valgum = larger Q angle
Genu Varum (knock-knee)
- feet are more lateral than the knees
- angles less than 165
Genu Valgum (bow-leg)
- feet more medial than knees
- angles greater than 180
Genu Recurvatum
- sagittal plane deformity - Hyperextension at knee.
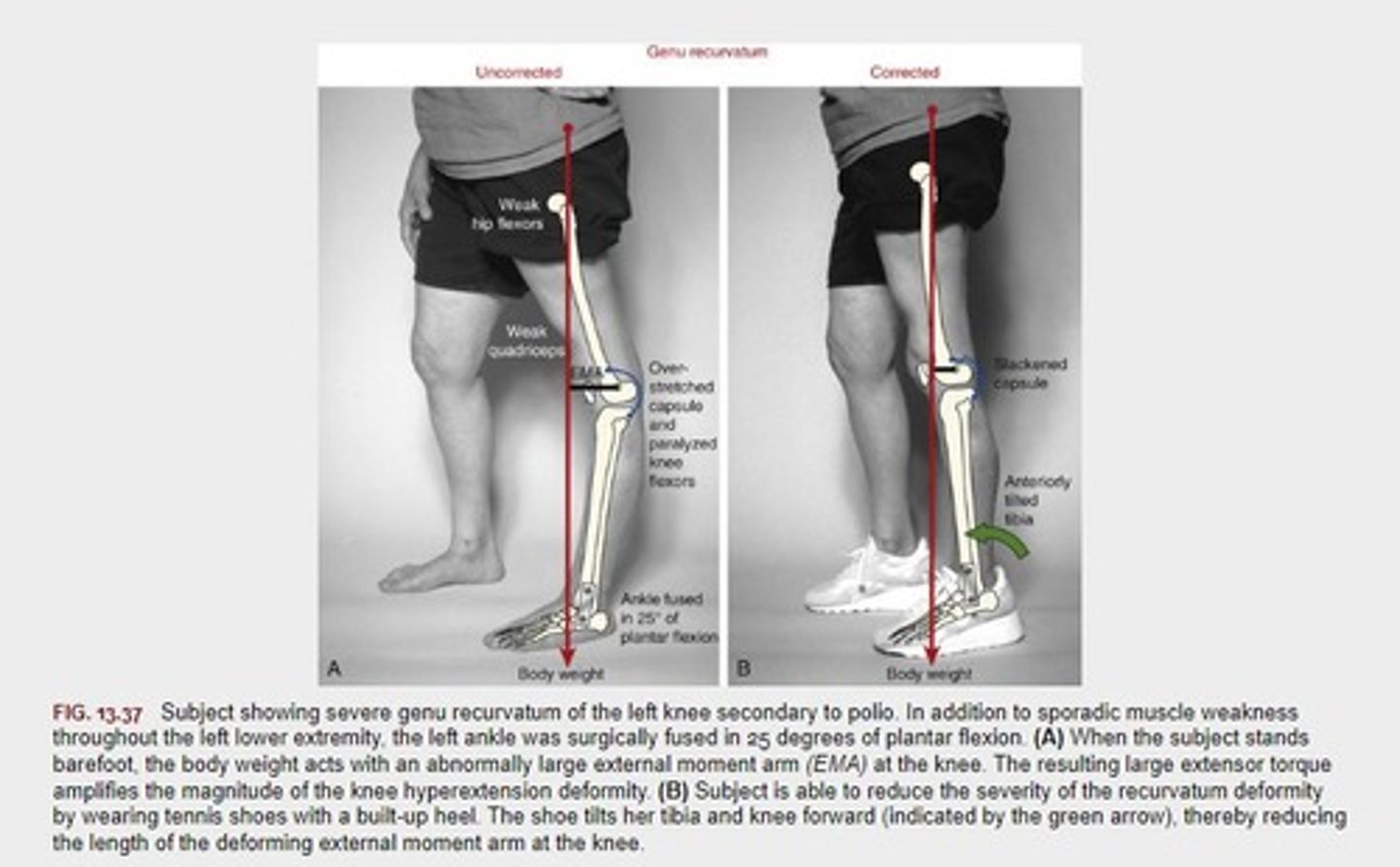
Excessive Plantar-Flexion leads to...
Excessive extension at the knee
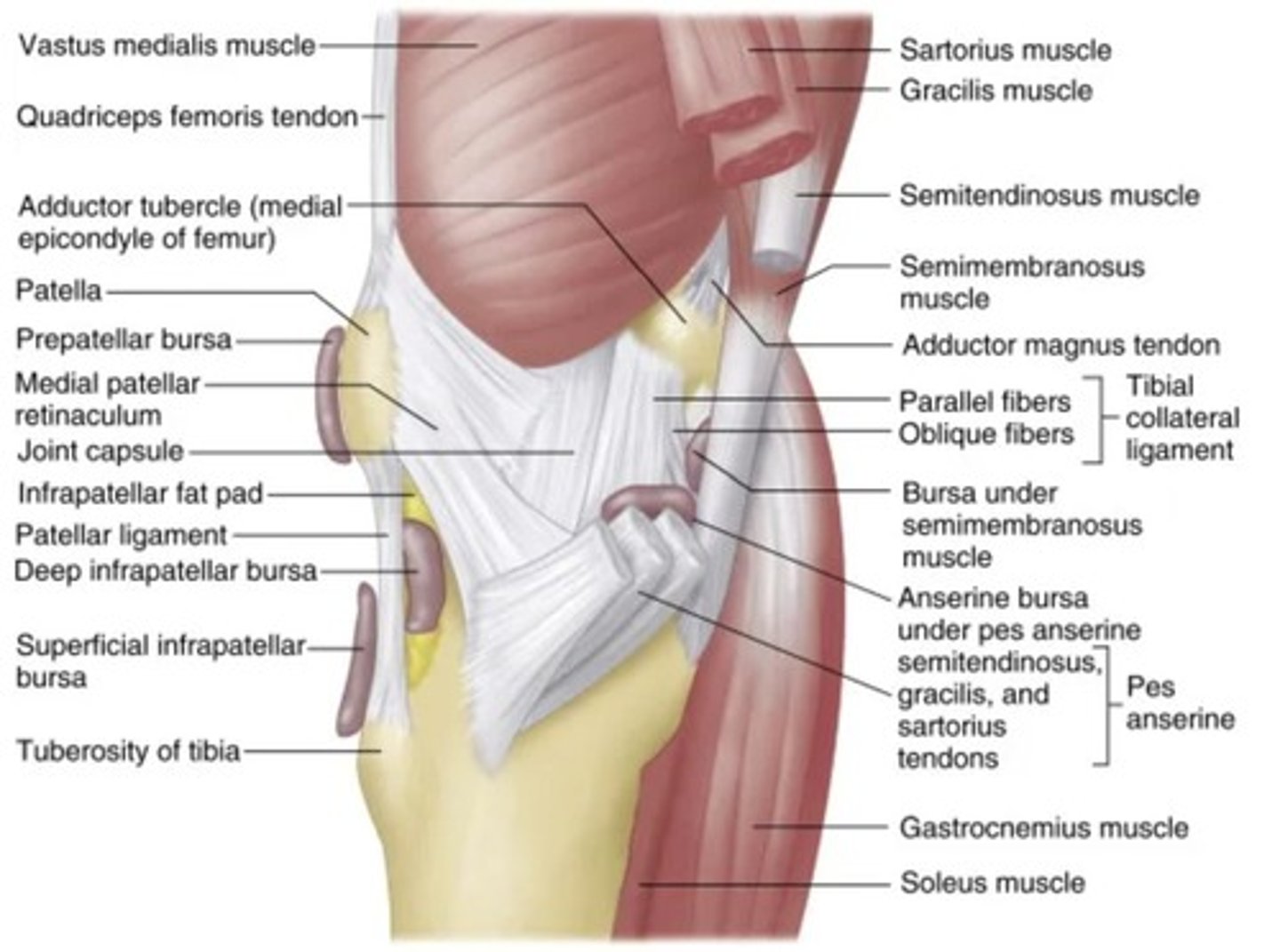
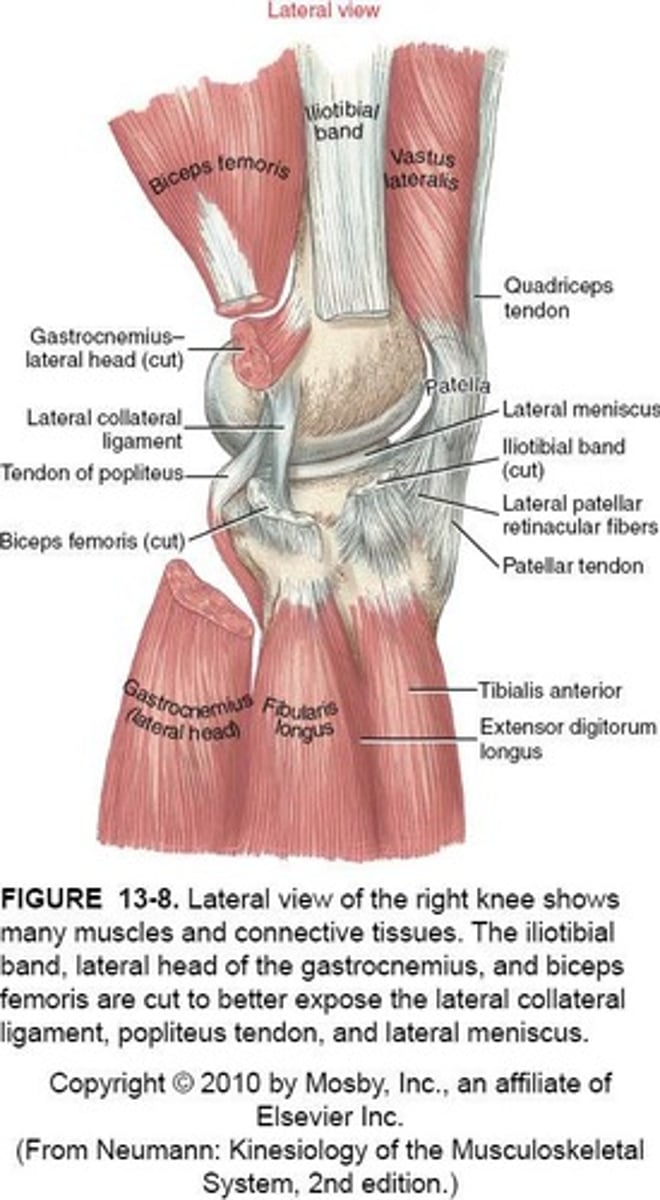
Joint Capsule
- Encloses tibiofemoral and patellofemoral joints
- ligaments blend in with capsule to provide support
Arcuate Complex
- Arcuate Popliteal L.
- LCL
- Popliteus M.
- reinforcement of the Postero-Lateral capsule of the knee
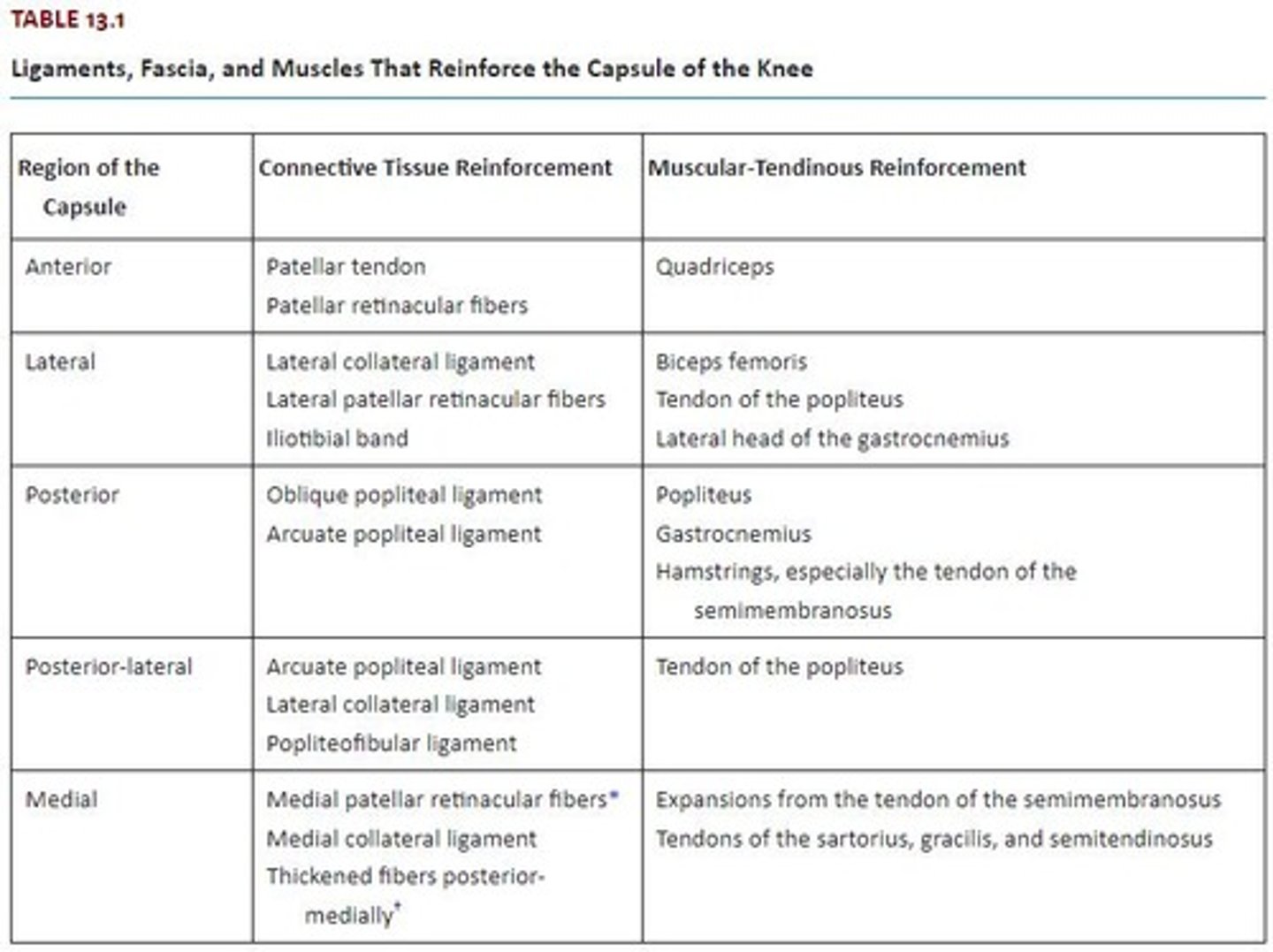
CT Reinforcement of Anterior Capsule
- Patellar Tendon
- Patellar Retinaculum
Muscular-Tendinous Reinforcement of Anterior Capsule
Quadriceps
CT Reinforcement of Lateral Capsule
- LCL
- Lateral Patellar Retinaculum
- IT Band
Muscular-Tendinous Reinforcement of Lateral Capsule
- Biceps Femoris
- Popliteus Tendon
- Lateral Gastrocnemius
CT Reinforcement of Posterior Capsule
- Oblique Popliteal L.
- Arcuate Popliteal L.
Muscular-Tendinous Reinforcement of Posterior Capsule
- Popliteus
- Gastrocnemius
- Hamstrings (SemiMem)
CT Reinforcement of Postero-Lateral Capsule
- Arcuate Popliteal L.
- LCL
- Popliteofibular L.
Muscular-Tendinous Reinforcement of Postero-Lateral Capsule
Tendon of Popliteus
CT Reinforcement of Medial Capsule
- Medial Patellar Retinaculum
- MCL
- Thickened Fibers Postero-Medially
Muscular-Tendinous Reinforcement of Medial Capsule
- Expansions from SemiMem Tendon
- Sartorius, Gracilis, SemiTen tendons
Postero-Lateral Knee Compartment
accounts for about 16% of all knee injuries
Synovial Membrane
- Lines internal capsule of the knee
- secretes synovial fluid
- can be a pain generating structure
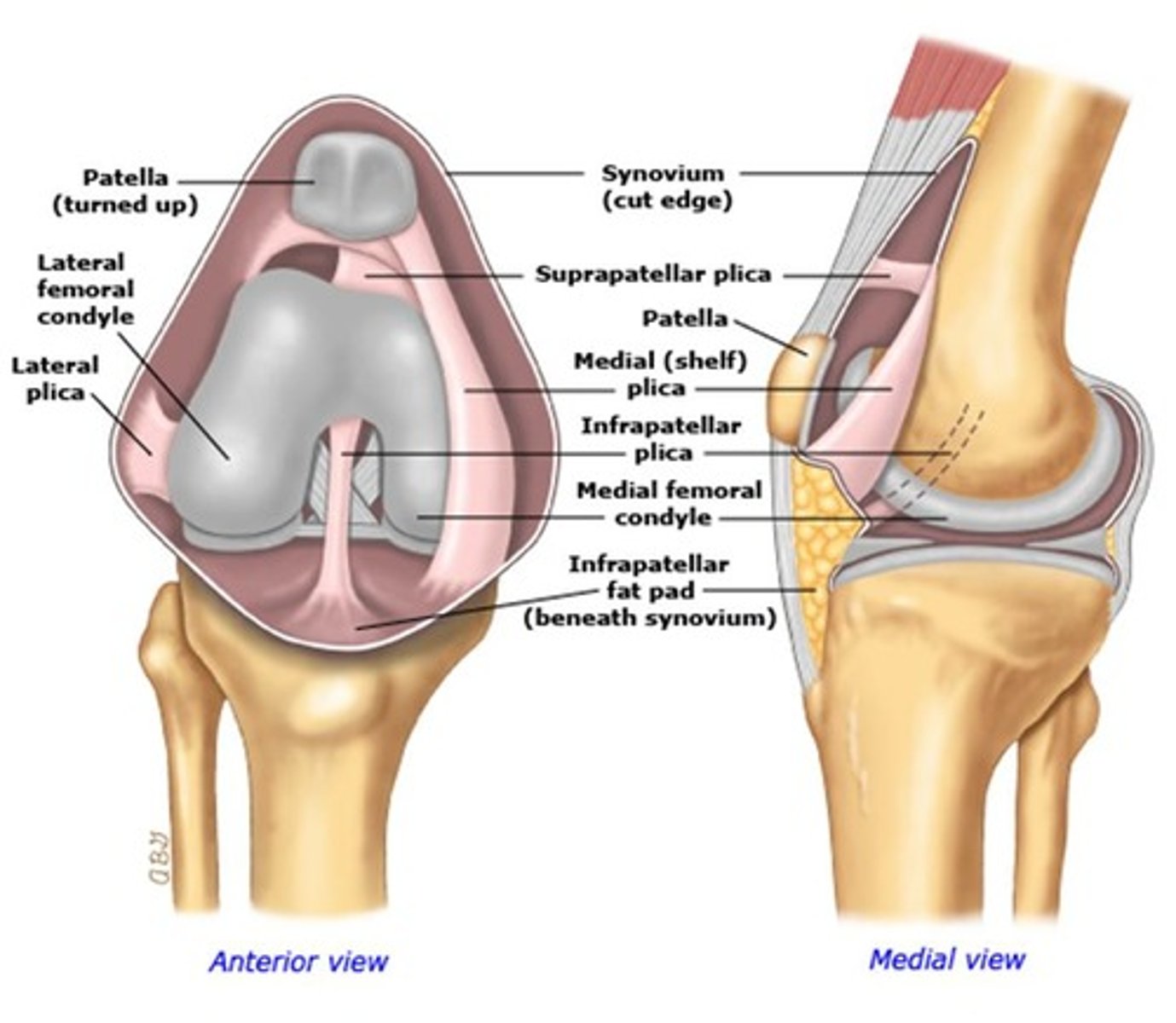
Plicae
- Folds in synovial membrane
- incomplete resorption of this mesenchymal tissue during development
Fat Pads
- Reduce friction between friction & contractile structures
- can be source of knee pain
Bursae
Fluid-filled sacs reducing friction in joints.
Most prominent Bursa
- Suprapatella
- Deep Infrapatella
Menisci
- Crescent-shaped fibrocartilage in knee joint
- create "seats" for femoral condyles
Functions of Menisci
- improve congruency between tibia & femur
- reduce compressive stress acros Tibiofemoral Joint (70% of load)
- increase stabilty
- provide proprioception
- guide knee arthrokinematics
Characteristics of Menisci
- thick centers & thin inner edges
- anchored to intercondylar region of tibia via Ant. & Post. Horns
Medial Meniscus
C-shaped cartilage on inner knee.
Lateral Meniscus
O-shaped cartilage on outer knee.
Passive Support for Menisci
- Coronary/Meniscotibial Ligaments
- Transverse L. (anterior)
- Mesnicofemoral L. (posterior)
Coronary/Meniscotibial Ligaments
Attach menisci to tibial plateau.
Meniscofemoral Ligaments
- attaches posterior horn of lateral meniscus to the lateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle
Functions of Meniscofemoral Ligaments
- Keeps posterior root of lateral meniscus in place
- prevent excessive posterior translation of tibia
- limits meniscus movement to keep contact
Transverse Ligament
connects the anterior portions of the medial and lateral menisci
Dynamic Support for Menisci
- Quadriceps (anteriorly) - SemiMem (medial- posterior)
- Popliteus (postero-lateral)
Screw Home Mechanism
Knee locking mechanism during extension.
Hoop Stress
- menisci deform peripherally as they are compressed
- allows part of the compression force at the knee to be absorbed as circumferential tension
- tear of the meniscus especially the posterior horn, loses its ability to resist
Compression Forces
- 2.5-3x BW while climbing stairs
- menisci 3x area of joint contact & reduce pressure on cartilage
- complete lateral meniscectomy increases peak contact pressure by 230%
Meniscectomy
Surgical removal of meniscus, increases pressure.
Red Zone
- outer edge of meniscus
- tears heal quicker due to better blood supply
White Zone
- innermost edge of menisci
- bad blood supply, injured portion must be removed
White-Red/Pink Zone
- middle area between white & red zones
- intermediate blood supply
ACL Injury Association
50% of acute ACL injuries involve meniscal damage.
Mechanism of Injury (MOI) for ACL
Forceful axial rotation with partially flexed knee while WB
Medial Meniscus Injury
- 2x as likely to be injured compared to lateral
- attachment to MCL
Peak Contact Pressure
Increases to 230% with complete meniscus removal.
Meniscal Repair Criteria
Repair considered with good blood supply.
Meniscal Debridement
Used when blood supply is poor.
Articular Cartilage Type
Hyaline cartilage covering diarthrodial joint surfaces.
Cells composing Articular Cartilage
- Chonrdrocytes
- Extracellular Matrix (water & type 2 collagen/chondroitin sulfate)
Articular Cartilage Layers
- superficial (10-20%)
- middle (40-60%)
- deep (30%)
Superficial Layer of Articular Cartilage
- cells are parallel to articulating surface
- provides resistance to shear forces
Middle Layer of Articular Cartilage
- haphazard arrangement of cells & fibers
- provides resistance in any direction
Deep Layer of Articular Cartilage
- cells/fibers are perpendicular to surface
- resists compressive forces
Osteoarthritis Cause
Biochemical breakdown of articular cartilage.
Chondroitin Sulfate
- important structural component of cartilage
- provides a majority of resistance to compression
- dietary supplement used to treat OA
MCL Characteristics
- Flat, broad ligament with superficial and deep parts
- resists Valgus forces
- Superficial Fibers = stressed in 20-30 of knee flexion
- Deep Fibers = in full extension
LCL Characteristics
- Short, cord-like ligament from femur to fibula
- blends with biceps femoris tendon
Secondary Restraint to Valgus Forces
- Postero-Medial Capsule
- ACL & PCL
- Lateral Joint Contact
- Lateral Meniscus Compression
- Medial Patellar Retinaculum
- Pes Anserinus
- Medial Gastrocnemius
Secondary Restraint to Varus Forces
- Postero-Lateral Corner of Knee
- IT Band
- Bicep Femoris Tendon
- Medial Joint Contact
- Medial Meniscus Compression
- ACL & PCL
- Lateral Gastrocnemius
Cruciate Ligaments
- Cross-shaped ligaments providing knee stability
- poor blood supply, Medial Genicular Artery
- together, resist extremes of all knee motion
ACL Function
Resists anterior translation of the tibia.
Posterolateral Bundle
- taut in extension
- greatest restraint to Ant. translation until about 20 degrees of flexion
Anteromedial Bundle
- tight throughout flexion (more in higher degrees of flexion)
- anteromedial bundle increases tension from 20-90 degrees
Anterior Drawer Test
- Tests anteromedial bundle at 90 degrees flexion
Positive Anterior Drawer Test
Excursion > 6mm with empty end feel.
Lachman's Test
Tests posterolateral bundle near extension.
Antagonist for ACL
Quadriceps
Pivot Shift Test
Assesses overall knee stability.
PCL (posterior cruciate ligament)
- most taut in 90-120 degrees of flexion
- prevents posterior translation of Tibia on Femur
2 sets of PCL
- larger, antero-lateral
- smaller, postero-medial
PCL MOI
- knee flexion
- dashboard injuries
Osteokinematics of Knee
- 2 DOF
- Flexion/Extension (0-150 degrees)
- frontal plane motion, only passive
Evolute
- Migrating axis of rotation in knee movement
- Instantaneous Axis of Rotation moves due to large femur surface
Effects of Evolute movement
- alters length of internal moment arm of flexors/extensors
- causes increased Shear
Tibia on Femur (OKC) Extension
- Concave on Convex
- Roll & Slide = Anterior
Femoral on Tibia (CKC) Extension
- Convex on Concave
- Roll = Anterior
- Slide = Posterior
Factors guiding "Screw-Home" Mechanism
1. shape of medial femoral condyle
2. tension in ACL
3. lateral pull of quads
Ligaments relatively slack in Flexion
- ACL
- MCL
- PMC (Posterior-Medial Capsule)
- OPL (Oblique Popliteal Ligament)
Open Pack Position
25 degrees of knee flexion