[Bio HL1, Fall Semester Final]
1/265
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
266 Terms
Polarity
The property of molecules having a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on another atom.
Hydrogen bonds
The weak bonds formed between the positive hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the negative oxygen atom of another water molecule
Cohesion
The ability of water molecules to stick together, allowing them to form a continuous stream
Surface tension
The property of water that allows small organisms to move along its surface and live around it as a habitat
Adhesion
The ability of water molecules to stick to other polar molecules, allowing water to flow through narrow paths and against gravity
Capillary action
Movement that results when water flows through a narrow path without help from gravity.
Solvent properties
The ability of water to dissolve substances that are charged or polar, creating solutions
Hydration shell
The sphere of water molecules around a dissolved ion using opposite charges
Amphipathic
Having both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region
Metabolism
The sum of all chemical reactions that occur in an organism, facilitated by water as a medium
Buoyancy
The property of water that describes the upward force exerted by a fluid on an object immersed in it, allows organisms to float in water
Viscosity
The stickiness of a fluid, influenced by the internal friction created when the fluid moves
Thermal conductivity
The property of water which describes the rate at which heat passes through a substance, with water being higher than that of air
High specific heat
The property of water that requires a large amount of energy to raise its temperature, resulting in a stable environment
Origin of Water
The theory that water on Earth was delivered by colliding asteroids during the early years of the planet
Retention of Water
The ability of Earth to retain water due to its distance from the Sun and its strong gravity
Goldilocks Zone
The region around a star where conditions are just right for the presence of liquid water and the potential for extraterrestrial life
Goldilocks Zone
The region around a star where conditions are just right for the presence of liquid water and the potential for extraterrestrial life
Pre-biotic Earth
[O2] was low therefore no ozone; [CH4] and [CO2] was high; temp was high due to greenhouse gases; there was much lighting
Abiogenesis
Spontaneous origin of cells from non-living sources
Catalysis, self-assembly, compartmentalization, self-replication
Four requirements that must have happened for abiogenesis to occur
Miller-Urey's Experiment
Demonstrated abiogenesis; boiled vapors; added H2, CH4, NH3, removed O2; added electrical discharge; produced 20AAs
Significance of Vesicles
Separated "self" from environment; created unique internal chemistry
Significance of RNA
Self-replicating; can work as an enzyme
Ribozymes
RNA molecules that work as catalysts
LUCA
Last Universal Common Ancestor; microbe that existed ~4 to ~4.5 BYA
Estimation of Dates
Using isotope ratios and genomic analysis
Cell Theory (Robert Hooke)
Cells are the smallest unit of life;
all living organisms are composed of cells;
cells come from pre-existing cells
Structures No Longer Considered Organelles
Cell wall, Cytoskeleton, Cytoplasm
Universal Structures (3)
Plasma Membrane, Cy DNA, Ribosomes
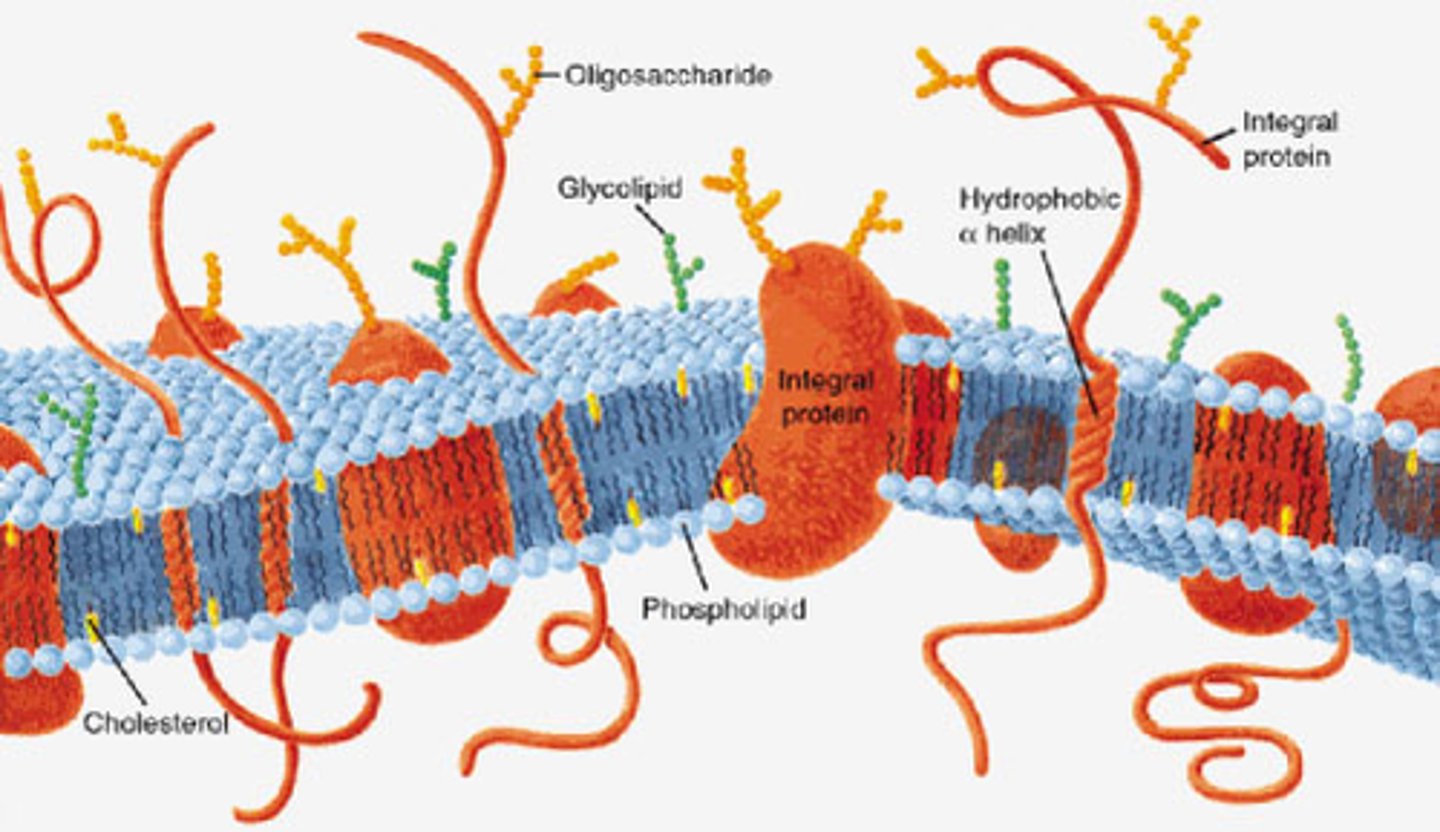
Plasma Membrane (Universal Structure)
Structure: phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins and cholesterol
Function: Semi-permeable barrier that separates internal/external environment; controls entry/exit of substance
DNA (Universal Structure)
Structure: double helix made of nucleotides
Function: contains instructions for all cell functions, specifically making proteins
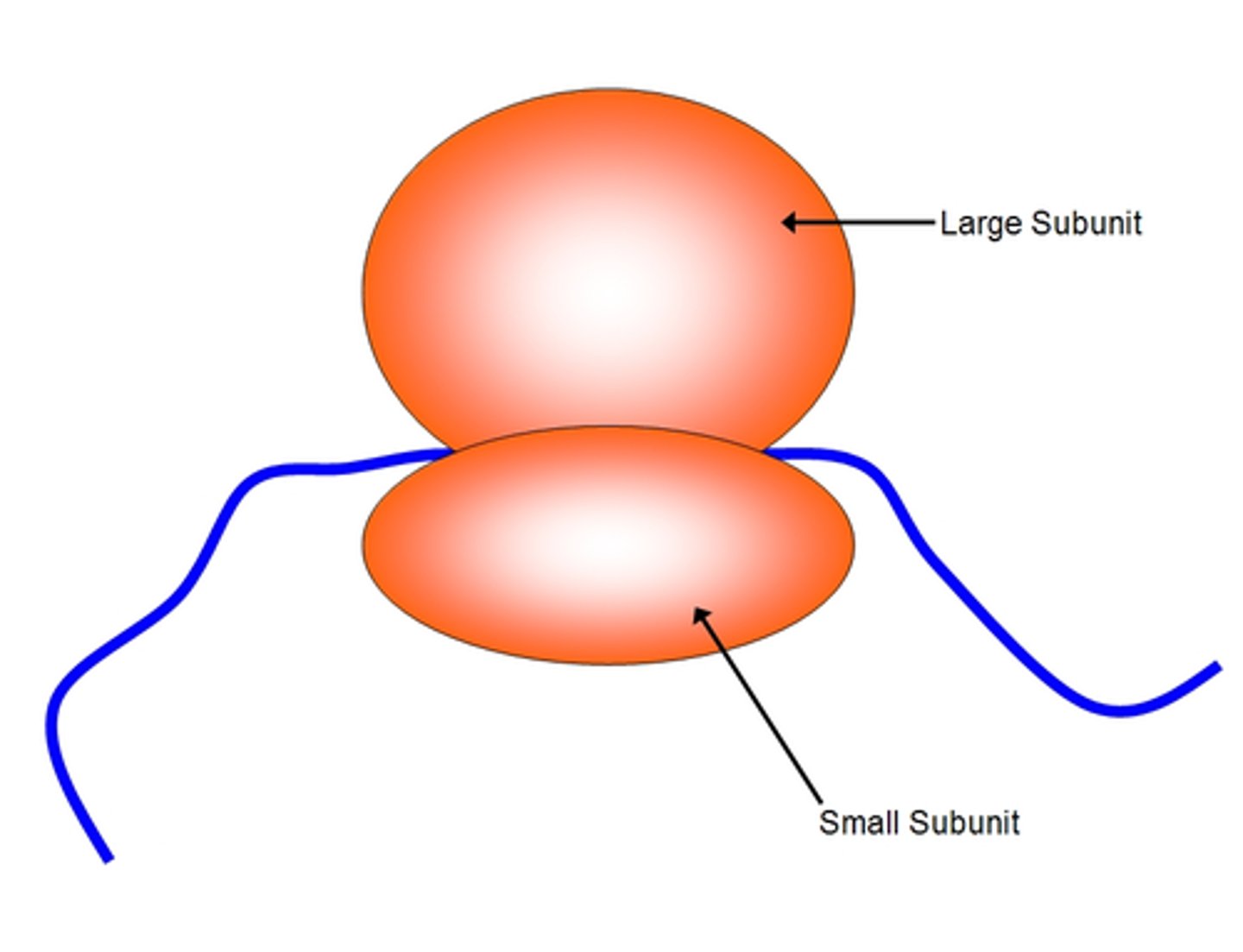
Ribosomes (Universal Structure)
Structure:
2 subunits (large and small) made of rRNA and proteins
no membrane
two different sizes
Function: Protein synthesis
70S vs. 80S
Prokaryotes have 70S, Eukaryotes have 80S (larger)
Svedberg units (Ribosomes)
Measurement of the relative size of cell parts through sedimentation during centrifugation
Free vs Bound Ribosomes
Free ribosomes make proteins to be used in cytosol (In Cell)
Bound ribosomes make secretory proteins, like hormones
*ribosomes structurally identical and interchangeable*
**every ribosome initially free, then when needs to make secretory protein, becomes bound to ER**
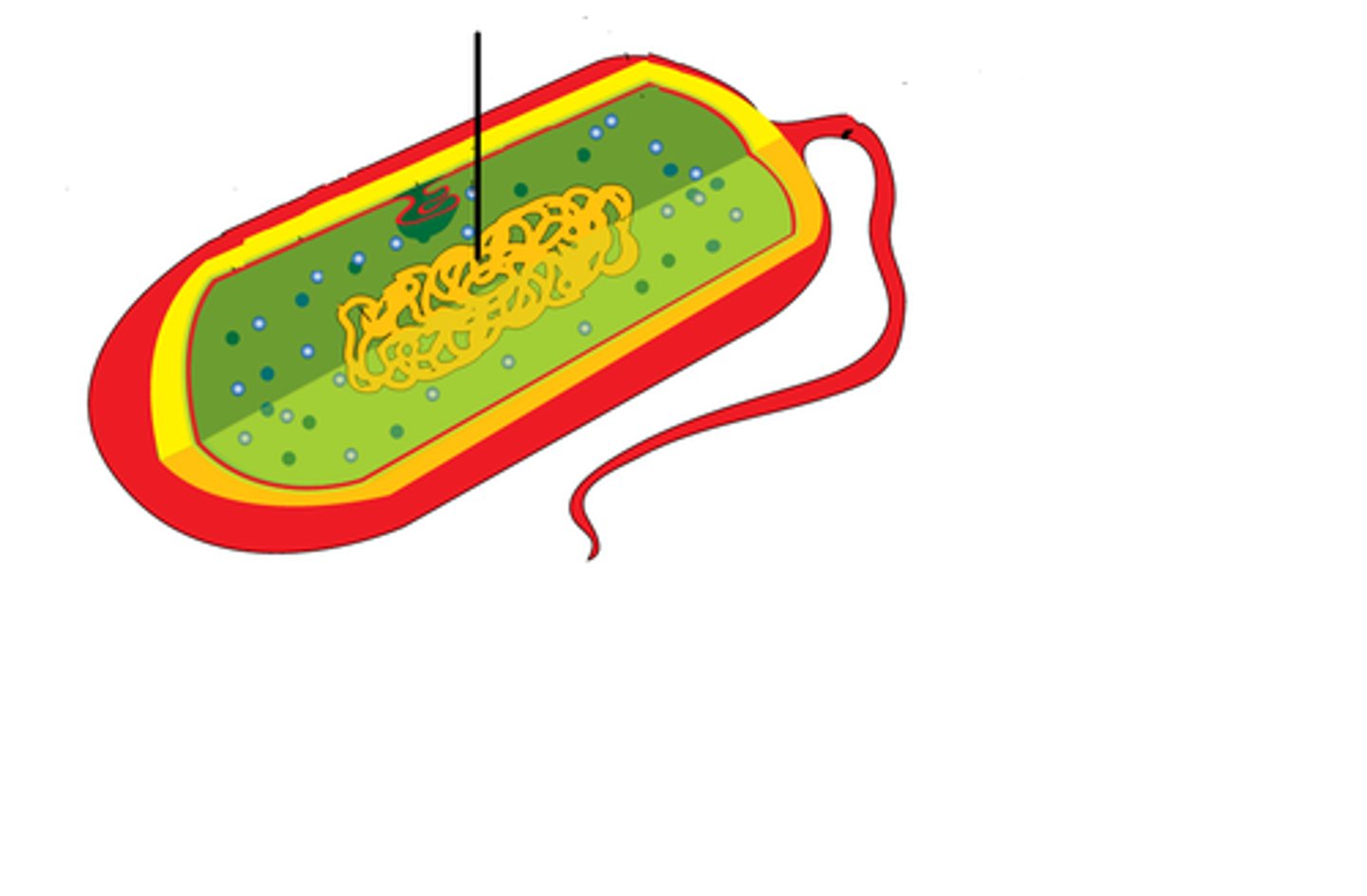
Prokaryote Structure
nucleoid, naked DNA, 70S ribosomes, cytoplasm, plasma membrane, cell wall (thicker), pili/cilia, flagella
*shape is more rod-shaped, length 2x width*
Nucleoid (Prokaryotes only)
Area where circular DNA is found
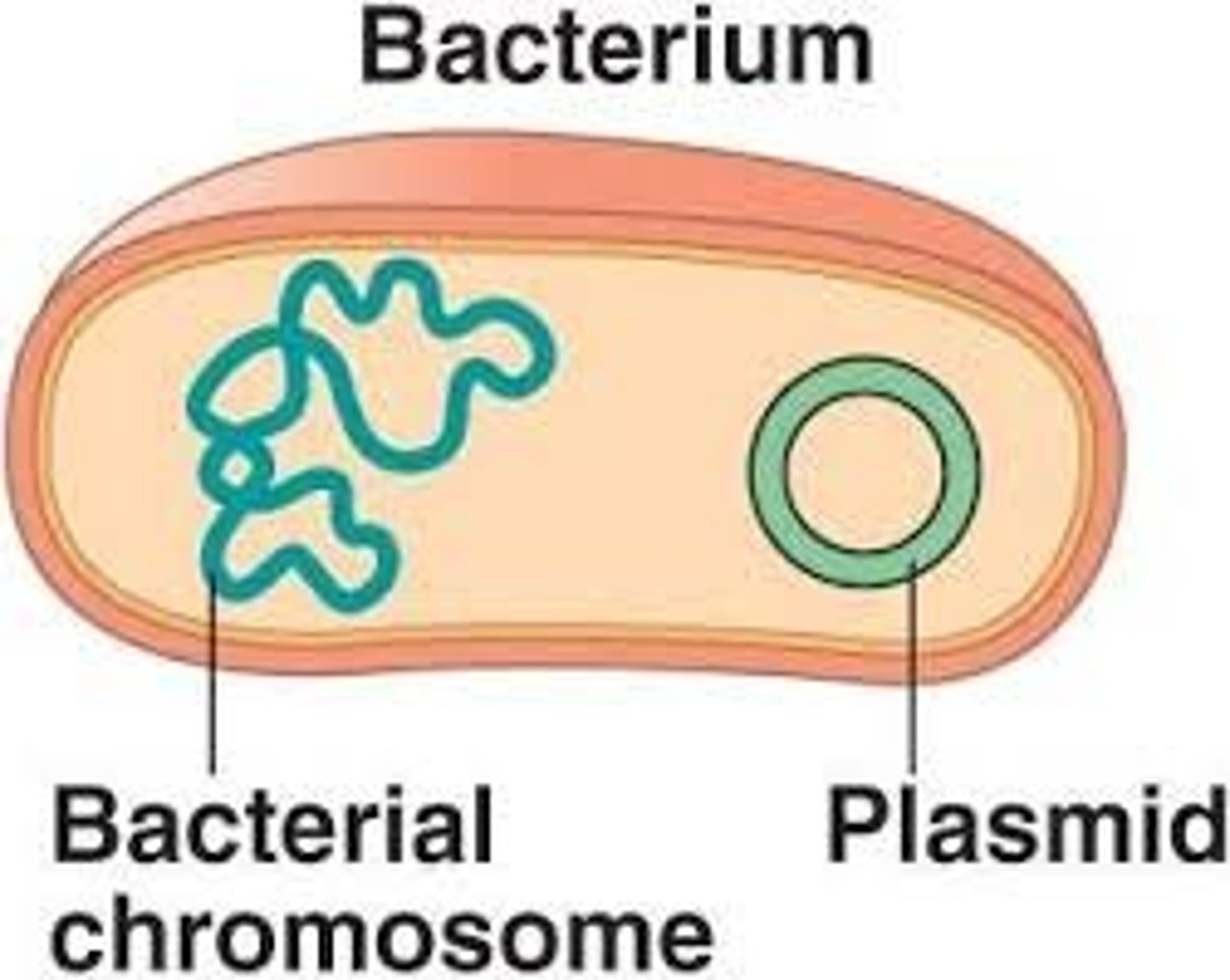
Genophore (Prokaryotes only)
Single, main DNA of prokaryotes
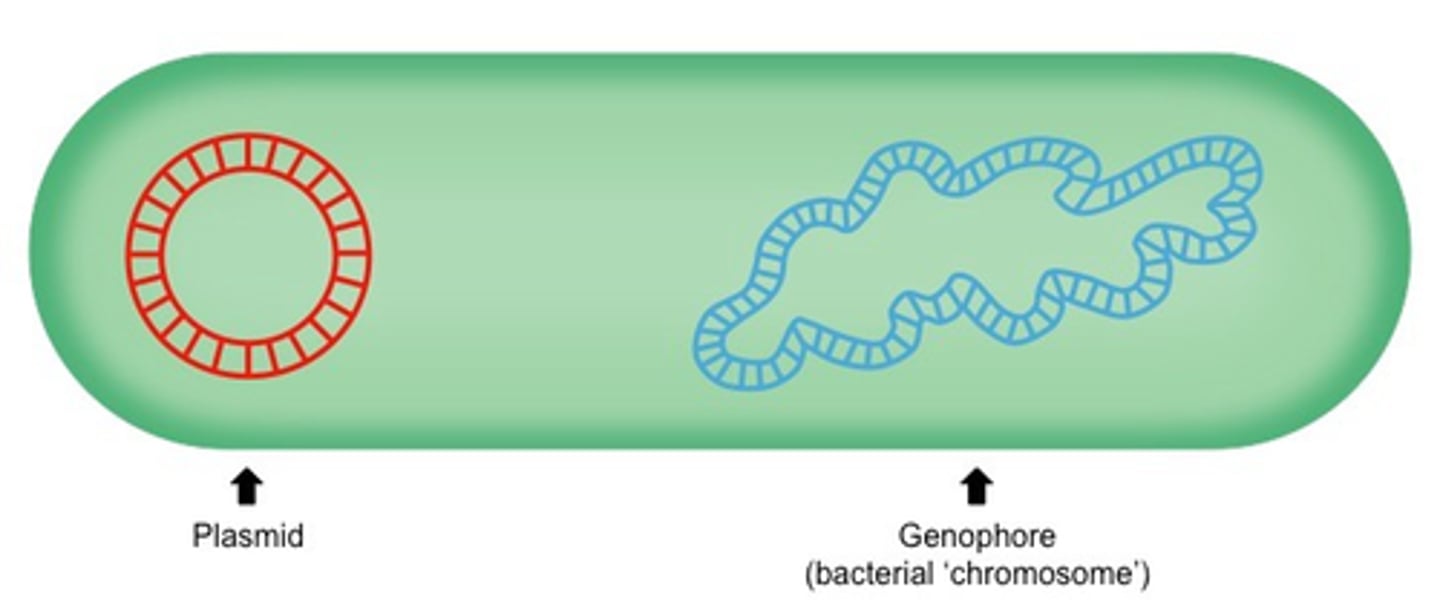
Plasmids (Prokaryotes only)
Extra circular DNA w/ additional info
Prokaryote Ribosome Size
70S
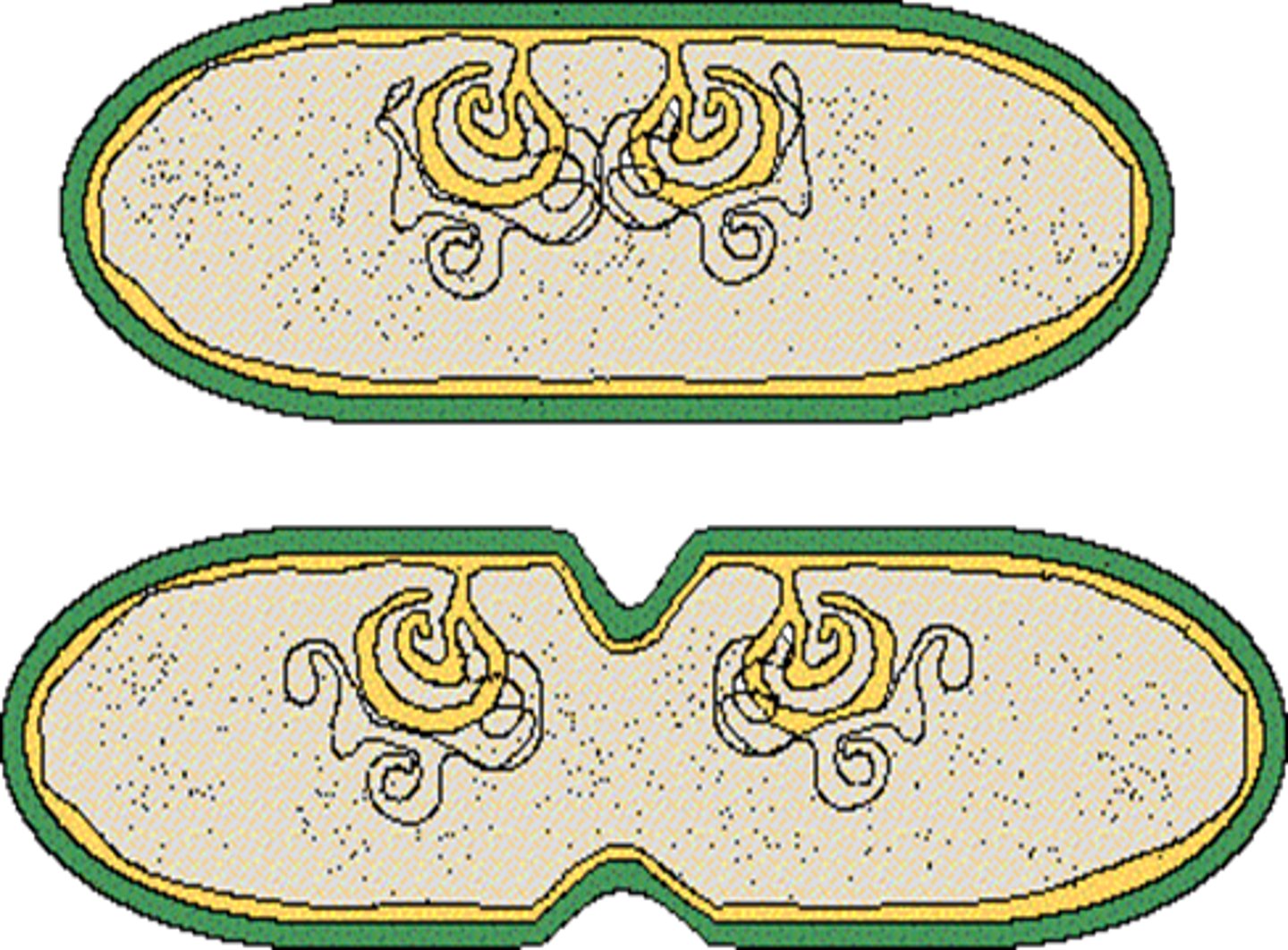
Mesosomes (Prokaryotes only)
Infoldings that increase surface area and act as sites for cellular respiration
Cell Wall (Prokaryote)
Made of peptidoglycan, protects cell, maintains shape, prevents bursting (prokaryote cell wants to be a bit turgid)
Flagella
Long, slender extensions used for movement
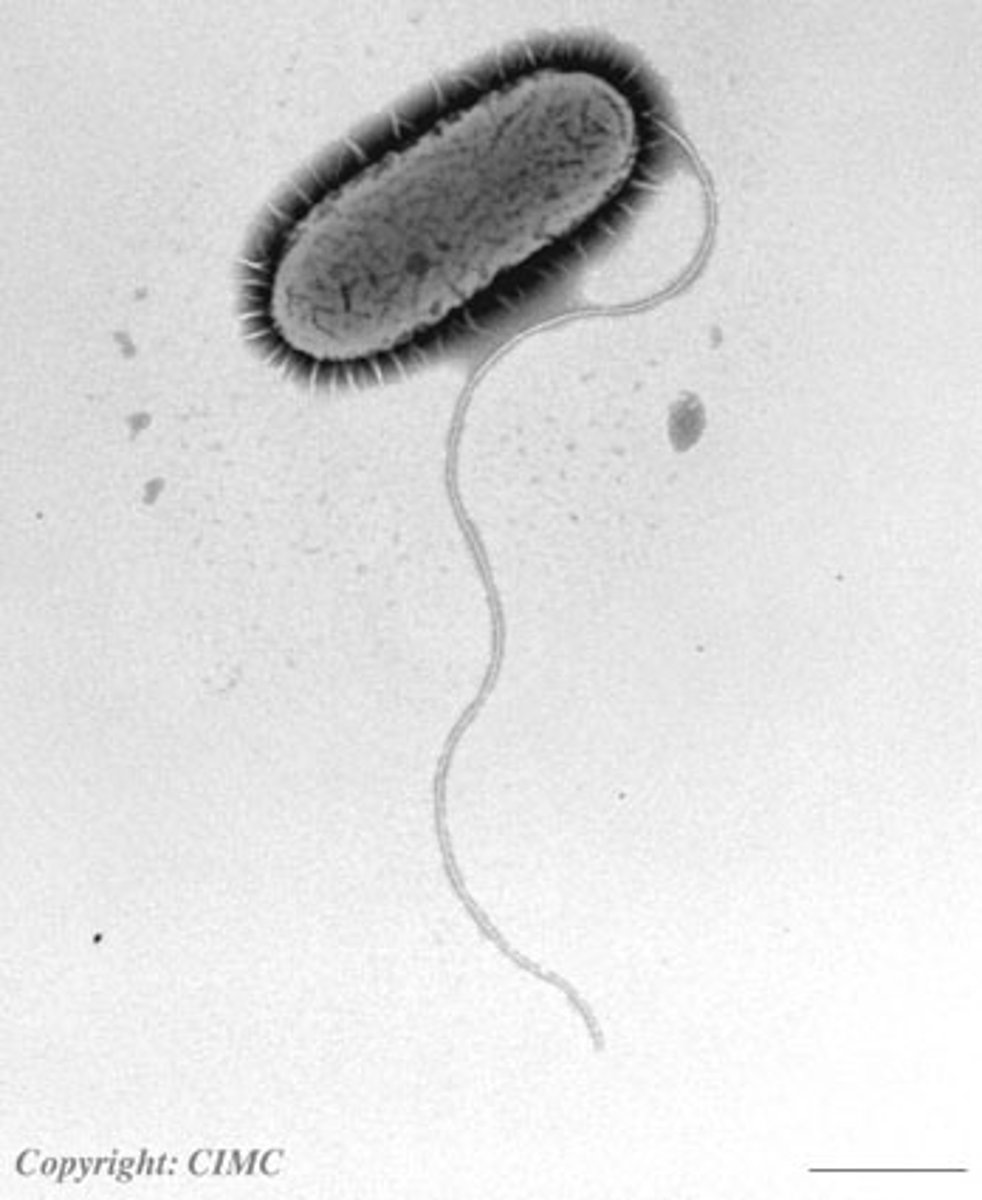
Cilia (Sex pili)
Hair-like, sticks to surfaces, used in bacterial conjugation
Nucleus
Structure: nuclear envelope is double membraned (2 phospholipid bilayers) with pores; contains nucleolus
Function: stores genetic info as chromatin (DNA + Histones)
Nucleolus (Both)
Region in nucleus for ribosome synthesis (proteins for ribosomes synthesized outside of nucleus, travel in to join w/ rRNA)
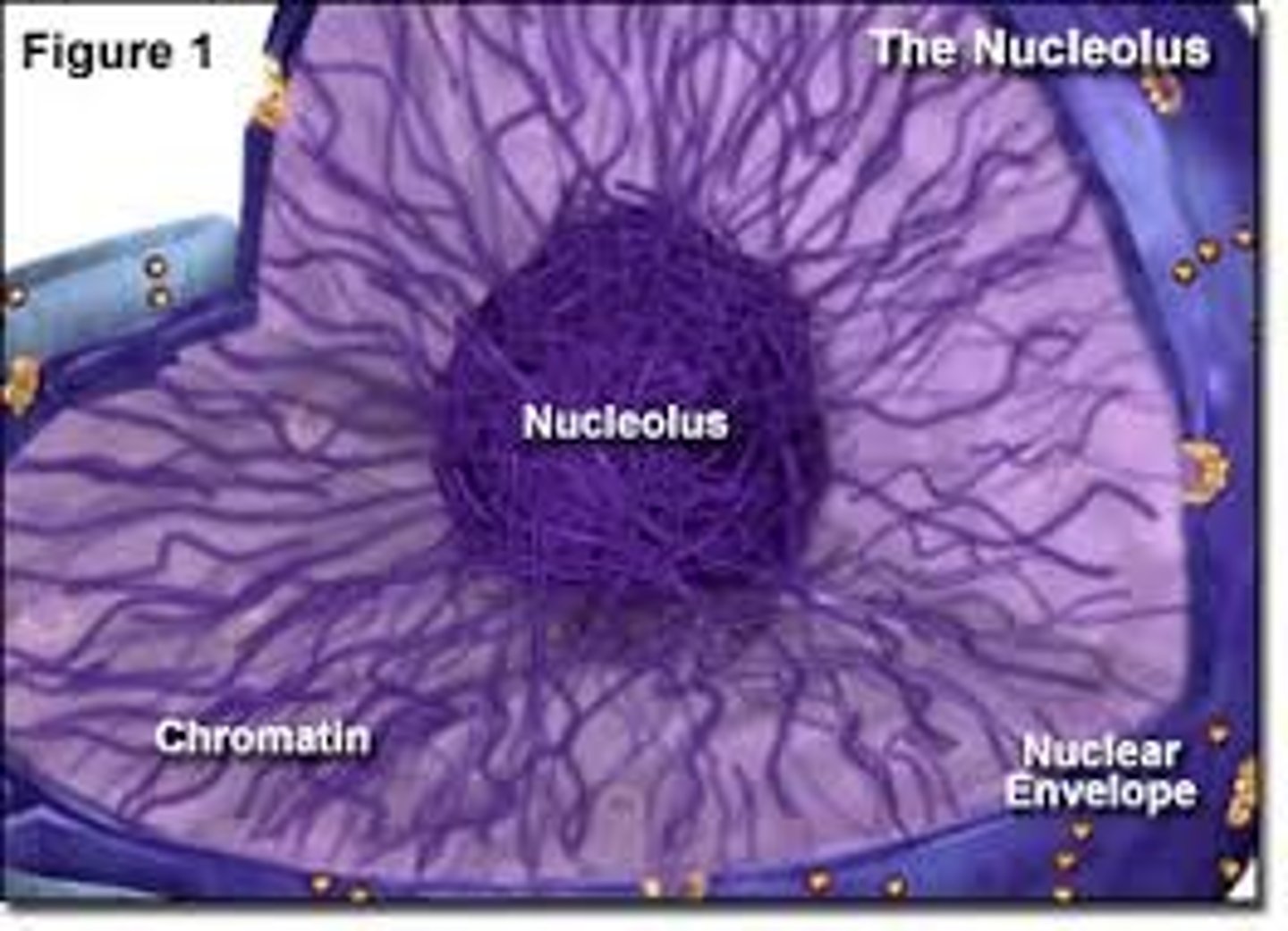
Chromatin
Form in which genetic information is stored in cells (DNA + histone proteins)
Benefits of Double Nuclear Membrane
Hydrophobic core is never exposed to water (if punctured, it seals itself), transportation of materials in & out of nucleus; allows membrane break down and chromosomes to move to opposite poles of the cell
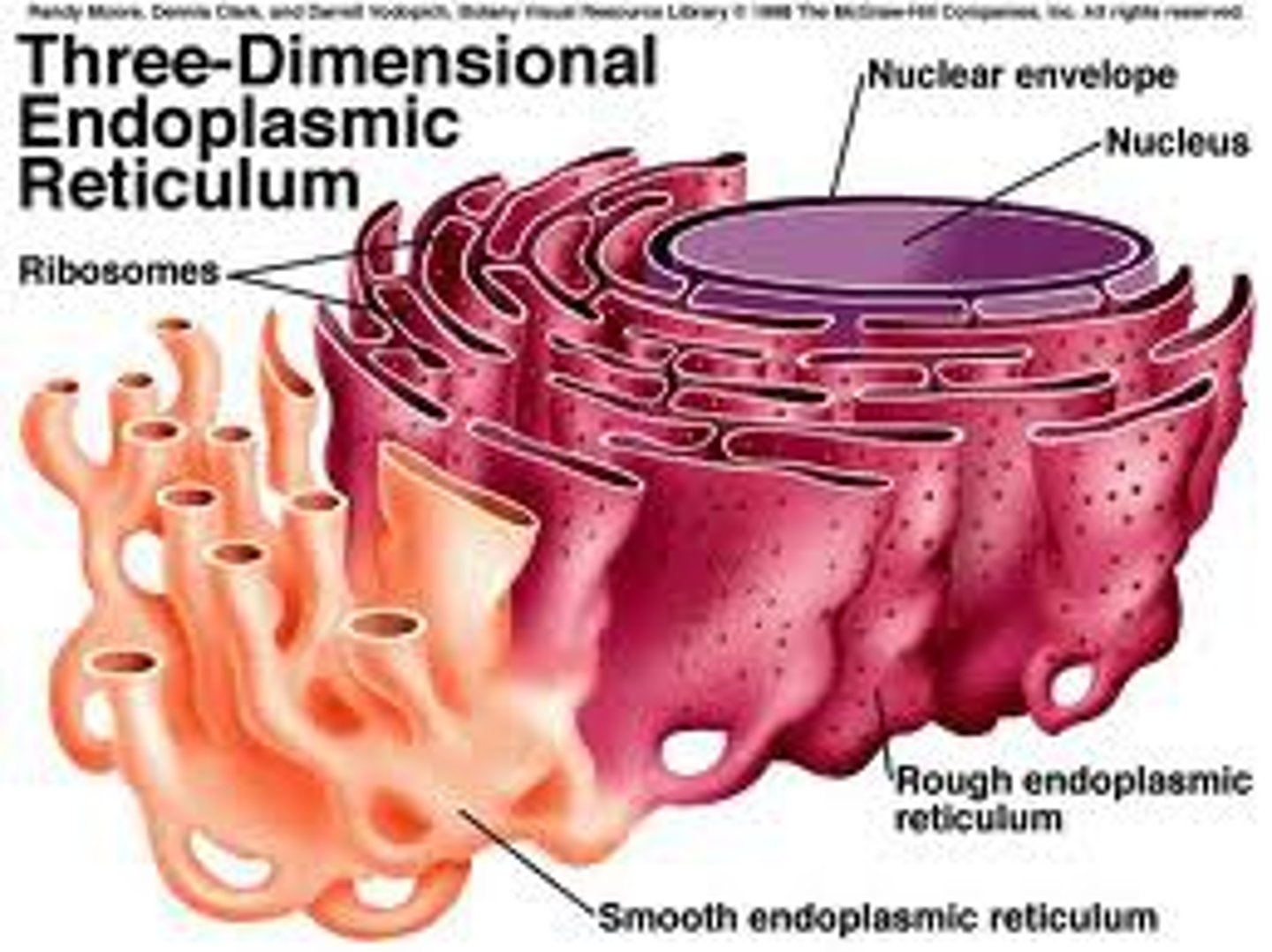
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (rER) (Both)
Structure: made of cisternae, has 80S ribosomes attached
Function: folds/packages secretory proteins (typically hormones)
Cisternae
Flattened membrane sacs (folds)
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (sER) (Both)
Structure: made of branched, tubular membranes;
NO RIBOSOMES
Function: makes lipids (phospholipids/hormones), detoxifies drugs, stores calcium ions for muscles
Golgi Apparatus (Both)
Structure: consists of cisternae
Function: receives vesicles from the rER (cis face); modifies and ships most to plasma membrane for secretion (trans face)
*cis face always faces the nucleus*
Vesicle Transport Model
Cisternae remains static, vesicles move proteins between them
Cisternal Maturation Model
Vesicles from rER coalesce to from new cisternae on cis side which matures and moves to trans side, which then breaks into vesicles
Lysosomes (Only animal cells)
Structure: membrane sacs filled with hydrolytic enzymes from Golgi
Function: digests food, organelles, and sometimes entire cell (apoptosis)
Mitochondria (Both)
Structure: Double membrane, like nucleus (outer membrane is smoother, inner contains cristae); matrix (fluid) inside; has own DNA and ribosomes, makes own proteins
Function: cellular respiration, makes ATP
Cristae
Infoldings of the inner membrane of a mitochondrion that houses the electon transport chain for synthesis of ATP.
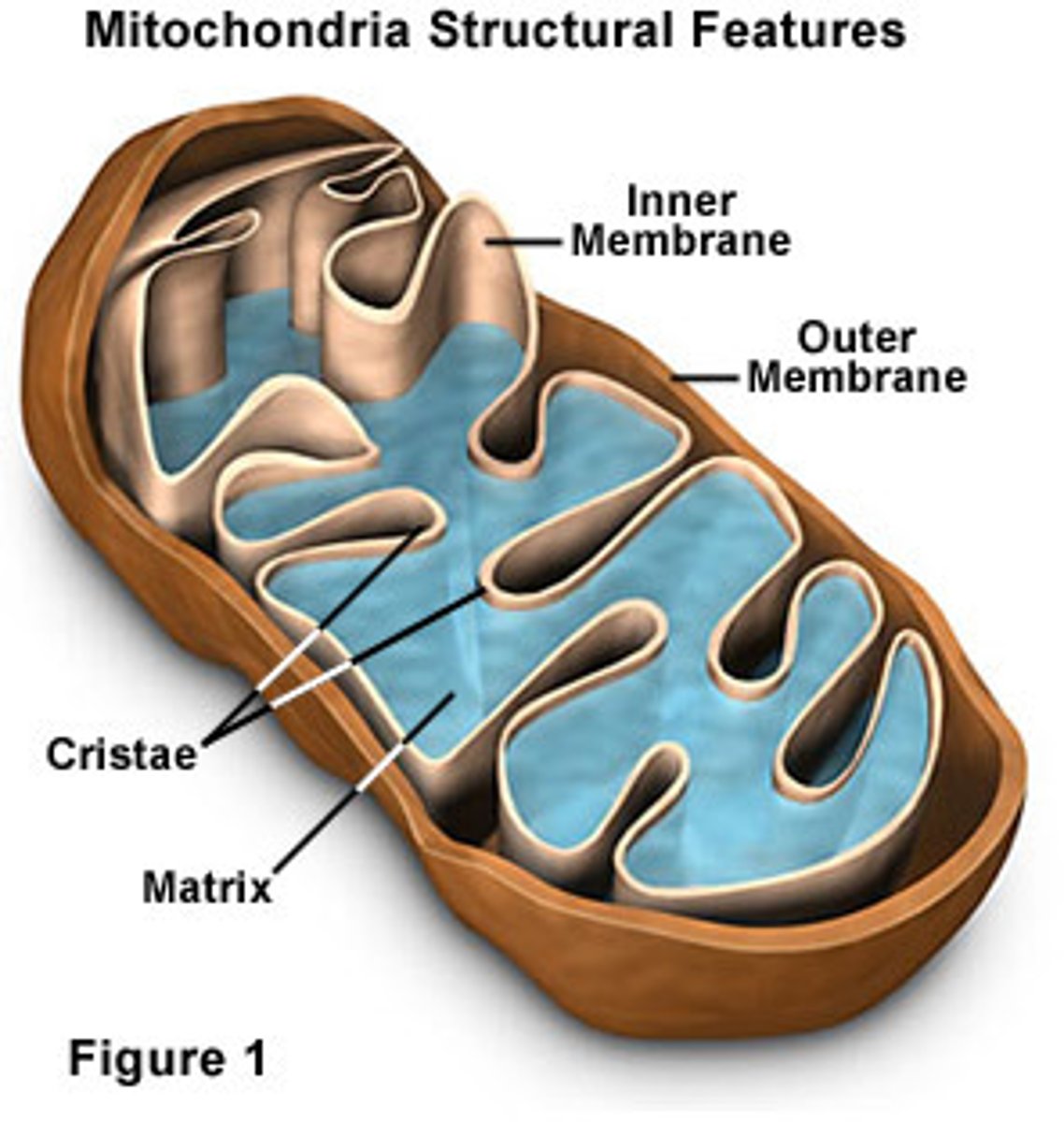
Matrix
Center compartment of the mitochondrion that contains dissolved enzymes in fluid
Sap Vacuoles (Both)
Structure: single membraned sack filled with fluid, contains dissolved materials
Function: store food (animal cells), store poison, pigments (plant cells), expel water (contractile vacuole in paramecium)
Central Vacuole (Only plant cells)
Found only in plant cells, stores water, pigments, poison, and maintains hydrostatic pressure
Vacuole vs. Vesicle
Large vs. small;
permanent vs. temporary
Adaptations of Vesicles
Moves contents within;
moves membrane or proteins that makeup vesicles
Clathrin
Three-legged protein that positions itself on the surface of membranes which then forms vesicles
Cytoskeleton (Both)
Microtubules (largest) and microfilaments (smallest)
Microtubules
Structure: made of tubulin protein
Function: found in mitotic spindle fibers; cilia/flagella;
moves organelles within cell (ex. vesicles)
Microfilaments
Structure: made of actin protein
Function: cytoplasmic streaming (when you circulate cytosol to transport food/enzymes); muscle contraction;
helps animal cells maintain shape
Centrosome (Only animal cells)
Structure: contains 2 paired centrioles;
each centriole made of 9 triplet microtubules
Function: used as spindle fibers in mitosis/meiosis
Chloroplast (Only plant cells)
Structure: double membrane;
contains stacks of thylakoids inside (in stacks called granum)
Function: photosynthesis;
makes glucose, stored as starch grains
Cell Wall
Structure: rigid outer layer made of cellulose
Function: provides support, protection, prevents excess water uptake, lets plant cell remain upright
Differences between Animal/Plant/Fungi
plastids, cell wall, vacuole, centrioles, undulipodia
Plastids differences in eukaryotic cells
organelle w/ 2 outer membranes and internal sacs;
not in animal/fungi;
in plant cell in chloroplasts and amyloplasts (starch storage)
Cell Wall differences in eukaryotic cells
not in animal cell;
made of chitin in fungi;
made of cellulose in plant cells
Vacuole differences in eukaryotic cells
animal cell, small/temporary;
in plant/fungi, large/permanent
Centrioles differences in eukaryotic cells
in animal cell, microtubule spindles and cilia/flagella;
not in plant/fungi except in swimming male gametes
Undulipodia differences in eukaryotic cells
cilia/flagella to generate movement;
present in animal cells, including male gametes;
absent in plant/fungi except in swimming male gamete
Cell wall differences (one more time)
prokaryotes - made of peptidoglycan;
fungi - made of chitin;
plant cells - made of cellulose
Atypical Cell Structures
Red blood cell, skeletal muscles, aseptate fungal hyphae
Red Blood Cell
no nucleus;
lets cell be smaller/more flexible/carry more O2;
cannot repair itself (live ~3 months)
Skeletal Muscles
cells fuse together and become large & multinucleate (more than one nucleus);
a muscle fiber (bunch of cells fused together w/ many nuclei); can be as long as 30 cm
Aseptate Fungal Hyphae
nucleus divides first w/o cell division;
produces cell walls;
results in some cells w/out a nucleus and some with multiple
"aseptate" = w/out nucleus
Magnification Formula
Magnification = size of image/size of specimen
1 mm
= 1,000 micrometers
=1,000,000 nanometers
Electron Microscopy
utilizes wavelengths of electrons focused by electromagnets;
has higher magnification (x1 Million) and good resolution (clear image);
kills specimen and only in black/white
Freeze Fracture
-produces images of surfaces within cells
-rapidly freeze sample in liquid propane
-use steel blade to fracture sample
-etch - remove ice crystals via vaporization
-coat - pour vapors of platinum/carbon to form replica (like a mold)
Cryogenic Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM)
-captures how proteins change form to carry out function
-flash freeze thin layer of protein solution
-place in electron microscope
-take many images, due to random orientation of protein in solution, use algorithms to produce 3D image of proteins
Fluorescent Stains
sample absorbs light & re-emits at longer wavelength, producing color that can be detected
Immunofluorescence
method of tagging antibodies with a fluorescent markers to detect specific proteins (antigens)
Endosymbiosis
Eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotes engulfing other prokaryotes via phagocytosis;
developed a symbiotic relationship;
larger provided protection, smaller provided energy
Endosymbiont
a cell that lives within another with mutual benefits
Evidence of Endosymbiosis
Mitochondria & Chloroplasts have:
• own DNA - circular & naked like prokaryotes
• own ribosomes - 70S in size like prokaryotes
• double membrane - outer may initially have been a vesicle
• reproduces through a fission-like process
• affected by antibiotics - suggests bacterial origins
Functions of life in unicellular organisms (8)
Nutrition, metabolism, growth, response to stimuli, excretion, homeostasis, movement, reproduction
Nutrition
Supply of food & gasses from environment for energy, growth and repair
Metabolism
Sum of all biochemical rxns in organism (ex. cellular respiration)
Growth
Increase in size or number of cells over time
Response to Stimuli
Perception of internal/external stimuli and responding appropriately
Excretion
Removal of waste (CO2, urea, feces)
Homeostasis
Maintenance stable, internal conditions
Movement
Change in physical location or position from rest to motion & vice versa
Reproduction
Production of offspring and passing on genes