Unit 2: Population & Migration
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

69 Terms
Overpopulation
a situation in which the number of people in an area exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living
Census
the official count of a population
Nonparticipation (census)
the situation in which homeless people, ethnic minorities, and/or people without proper immigration documents don't fill out census forms
Sampling
a statistical technique used to attempt to get a more accurate census count - the US Supreme Court ruled this cannot be used to determine Congressional district boundaries
Ecumene
permanently inhabited areas of the Earth's surface
Arithmetic Density
the total number of people divided by the total land area
Physiological Density
the number of people per unit of area of arable land (land suitable for agriculture)
Agricultural Density
the number of farmers per unit area of farmland
Developed Country (MDC)
a country that has progressed relatively far along a continuum of development
Developing Country (LDC)
a country that is at a relatively early stage in the process of economic development
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
the percentage growth of a population in a year (the crude birth rate minus the crude death rate)
Doubling Time
the time required for a population to double in size
Crude Birth Rate
the total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society
Crude Death Rate
the total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
the average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years (AKA "children per woman")
Replacement Rate
the total fertility rate needed for a population to replace itself (2.1 for MDCs, 2.4 for LDCs)
Demography
study of population characteristics
Demographic Momentum
the tendency for growing population to continue growing for a time after a fertility decline because it takes time for already born people to reach child-bearing age
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
a process of change in a society's population from a condition of high crude birth and death rates and low rate of natural increase to a condition of low crude birth and death rates with a low rate of natural increase
Medical Revolution
the leap of medical knowledge in stage 2 of the demographic transition
Zero Population Growth (ZPG)
a decline of the total fertility rate to the point where the natural increase rate equals zero
Sex Ratio
the ratio of males to females in a population
Population Pyramid/Age-Sex Structure
A bar graph that represents the distribution of population by age and sex
Dependency Ratio
the number of people who are too young or too old to work, compared to the number of people in the labor force
Elderly Support Ratio
the number of working-age people (15-64) divided by the number of persons 65 and older
Infant Mortality Rate
the total number of deaths in a year among infants under one year old for every 1,000 live births in a society
Epidemiology
the branch of medicine that deals with the incidence, distribution, and possible control of diseases and other factors relating to health
Epidemiologic Transition Model (ETM)
this focuses on identifying and explaining the causes of death in each stage of the Demographic Transition Model
Pandemic
an epidemic that is geographically widespread
John Snow
he mapped the occurrence of cholera in London
Thomas Malthus/ Malthusian Theory
he argued the world's population was increasing faster than the food supplies need to sustain it and reasoned that food supplies grow linearly (arithmetically), whereas population grows exponentially (geometrically)
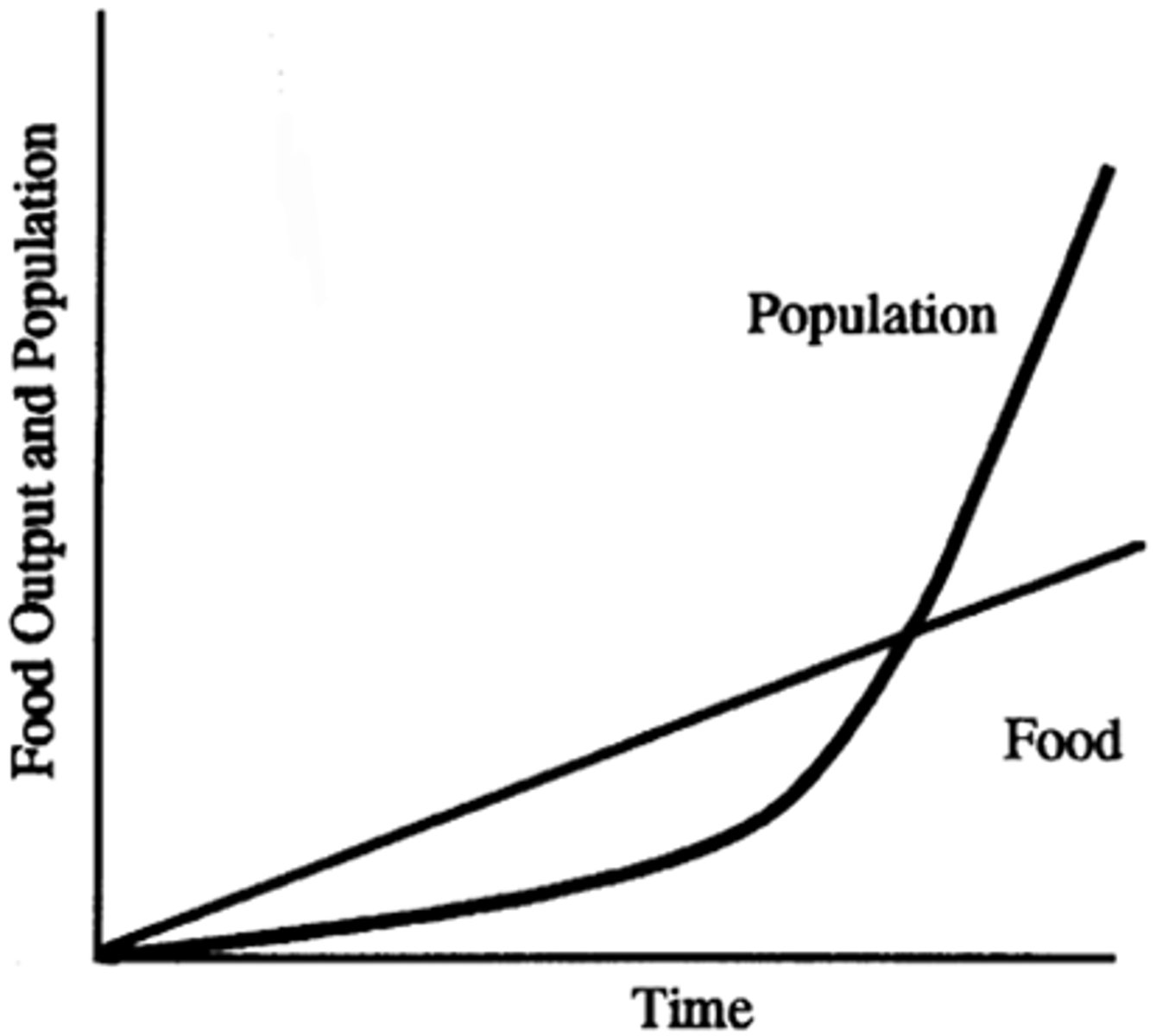
Carrying Capacity
the largest population that an environment can support at any given time
Antinatalist Policy
a government plan to decrease the birth rate

Pronatalist Policy
a government plan to increase the birth rate

Transhumance migration
nomadic migrants that move following the seasonal migration of livestock (goats, sheep, cattle etc.) between mountains and lowland pastures for grazing
Wherever the livestock need to go to get grass to eat - the people follow! The livestock are their main source of food & income