Ecdysozoans
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A type of proteosome
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
2 groups of Ecdysozoans
Limbless and limbed
Limbless
nematodes
(another that we aren’t going into)
Limbed
tardigrades
velvet worms
arthropods
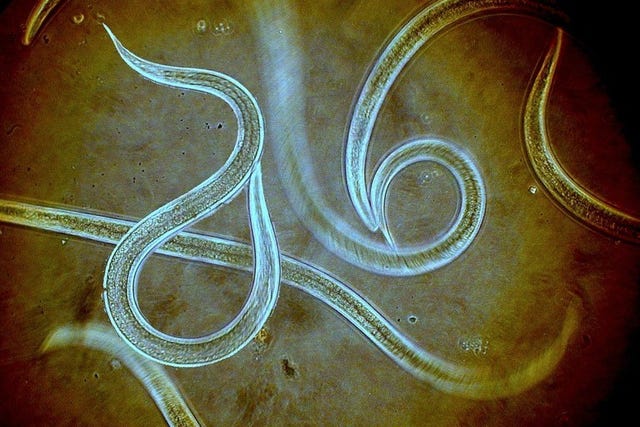
Nematode
unsegmented
thick multilayered cuticle
Gas and nutrient exchange occurs through the cuticle and the gut wall
The pharynx, a muscular anterior organ, moves materials through the gut
lot are microscopic
Modes of nutrition
Scavengers
Predators
Parasites
Arthropods
Has 4 paired jointed appendages
4 groups
Chelicerates
Myriopods
Crustaceans
Hexapods
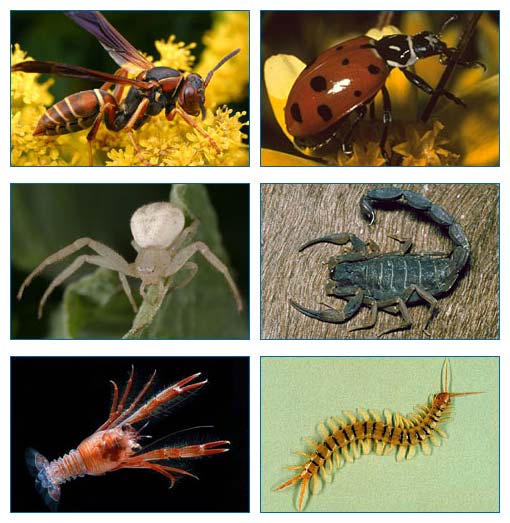

arthropod relatives
Tardigrades, Velvet worms, and Trilobites
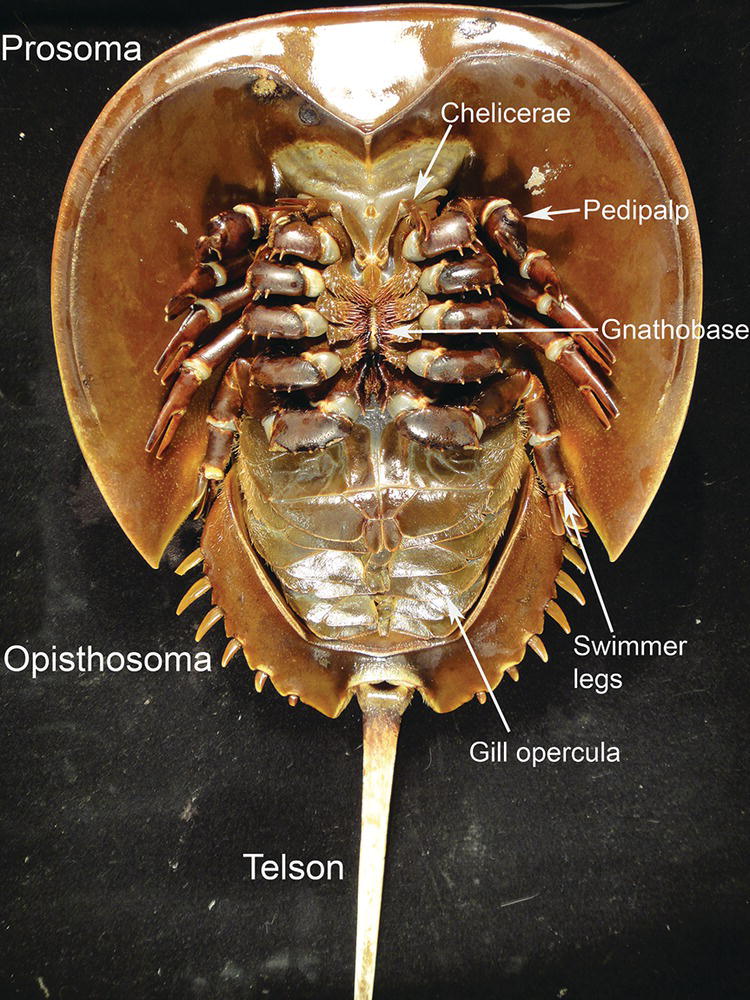
Chelicerates
2 part body
Cephalothorax
Abdoman
Head has two pairs of appendages modified into mouthparts
Most have 4 pairs of walking legs
2 examples
Horseshoe crabs
arachnids

Horseshoe crab
Living fossil
Common in shallow marine waters along eastern North America and Asia.
Come into the intertidal zone in large numbers to mate and lay eggs
Arachnids
Simple life cycle (direct development)
many are parasites of plants and animals (mites and ticks)

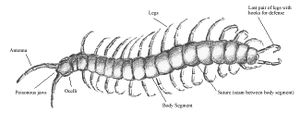
Myriapods
Head and a long, flexible trunk with many pairs of legs
Centipedes—1 pair of legs per segment.
Millipedes— 2 pairs of legs per segment
Mandibulate
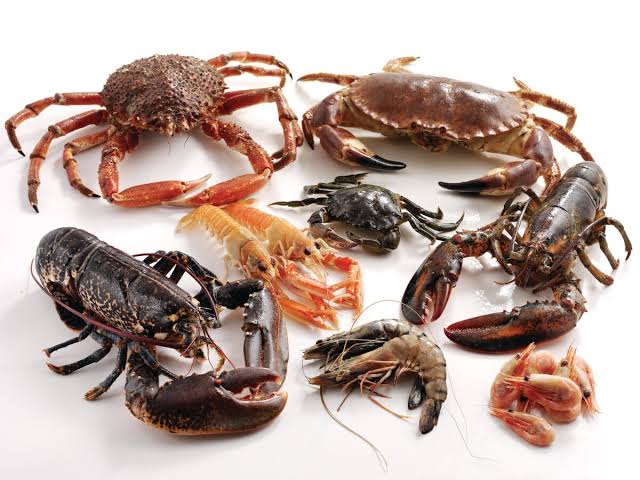
Crustaceans
3 body regions: head, thorax, abdomen
Head segments are fused and have 5 pairs of appendages
Thoracic and abdominal segments usually have 1 pair of appendages each
carapace - exoskeleton that extends over the head and thorax region
Specialized appendages

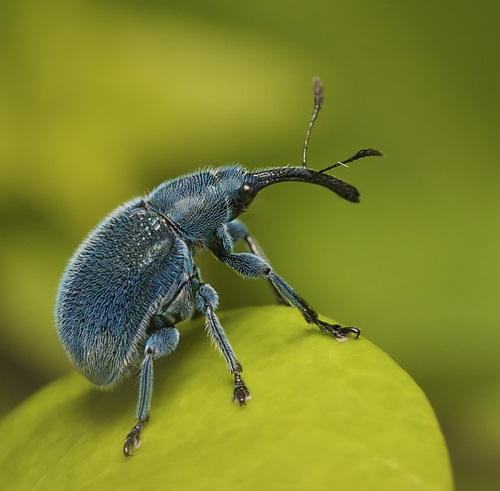
Hexapods
have six legs and include insects

Insects
3 body regions
Head - one pair of antennae
Thorax - three pairs of legs and two sets of wings in most groups
Abdomen - no appendages

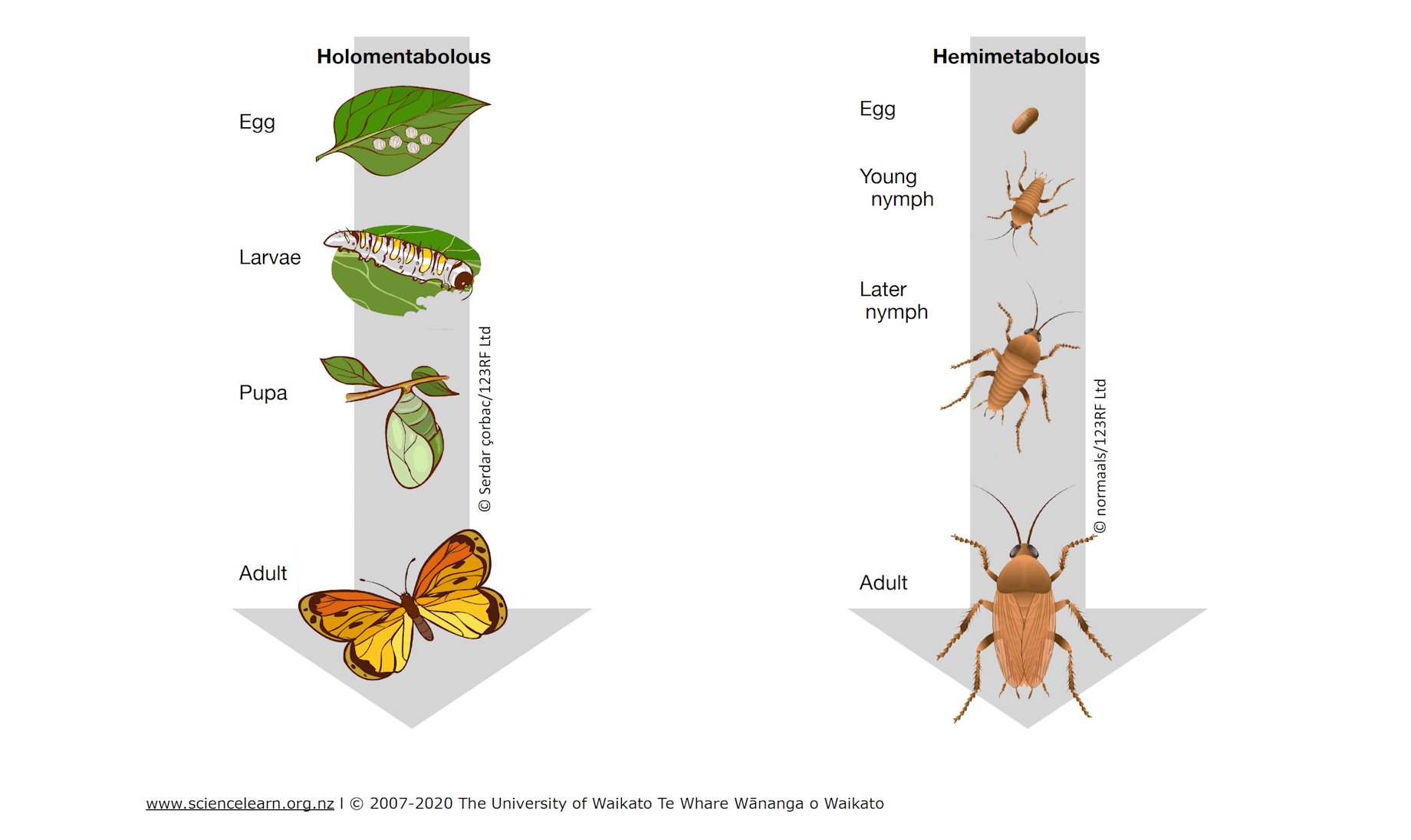
Metamorphosis
substantial physical changes occur between life stages - going from larvae to adult
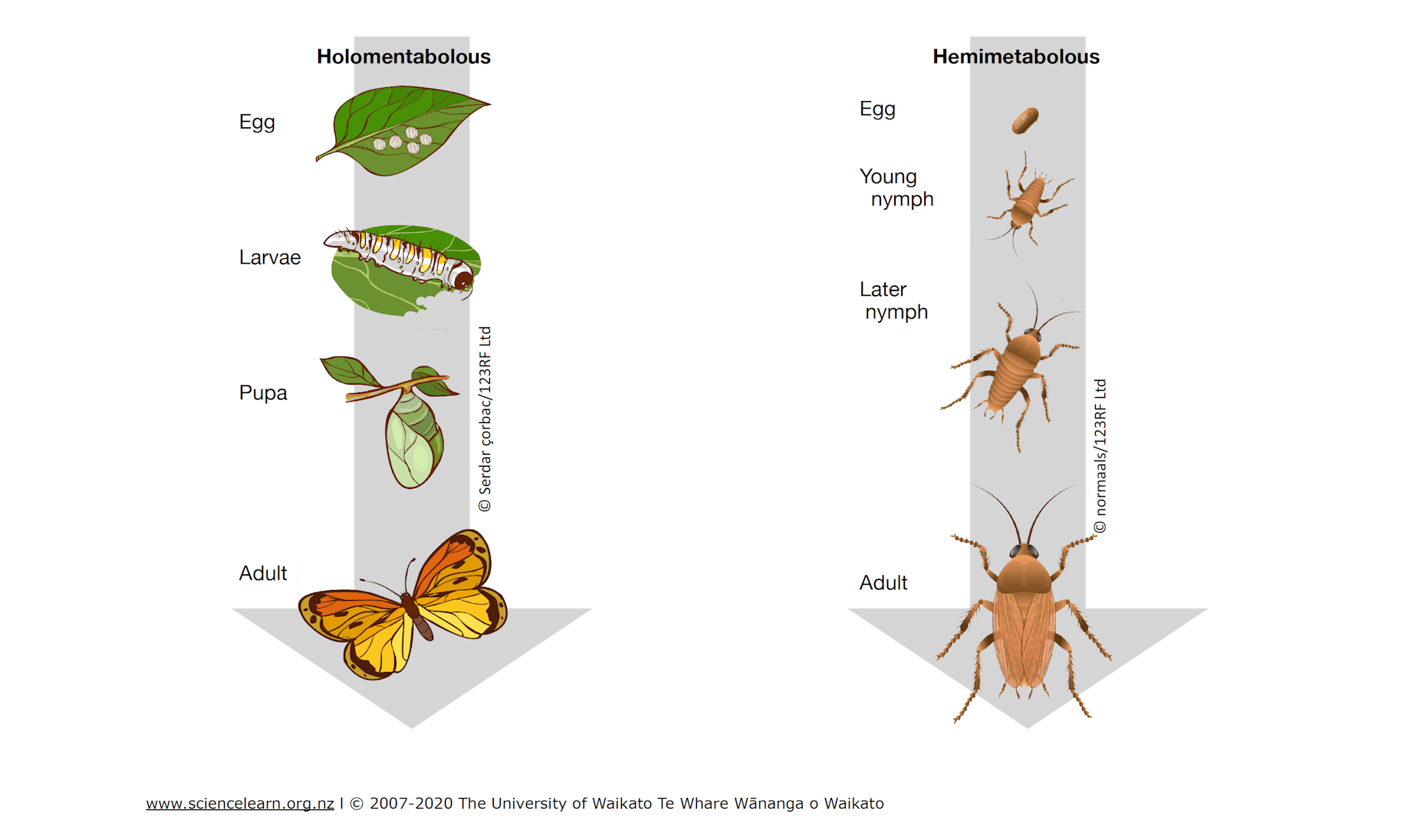
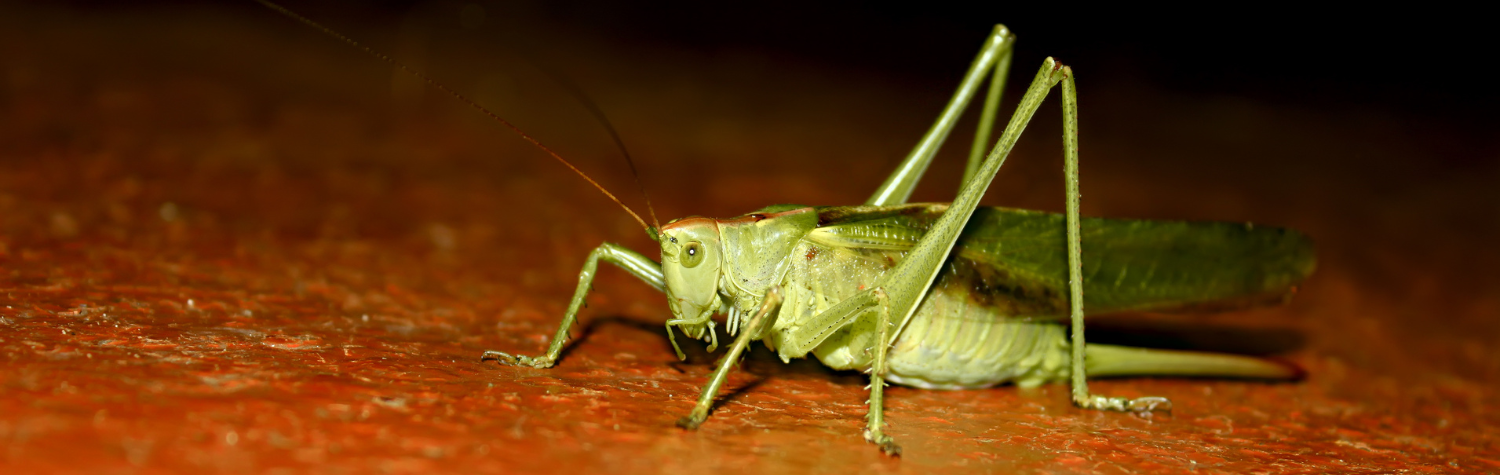
Incomplete metamorphosis
changes are gradual - ex: grasshoppers
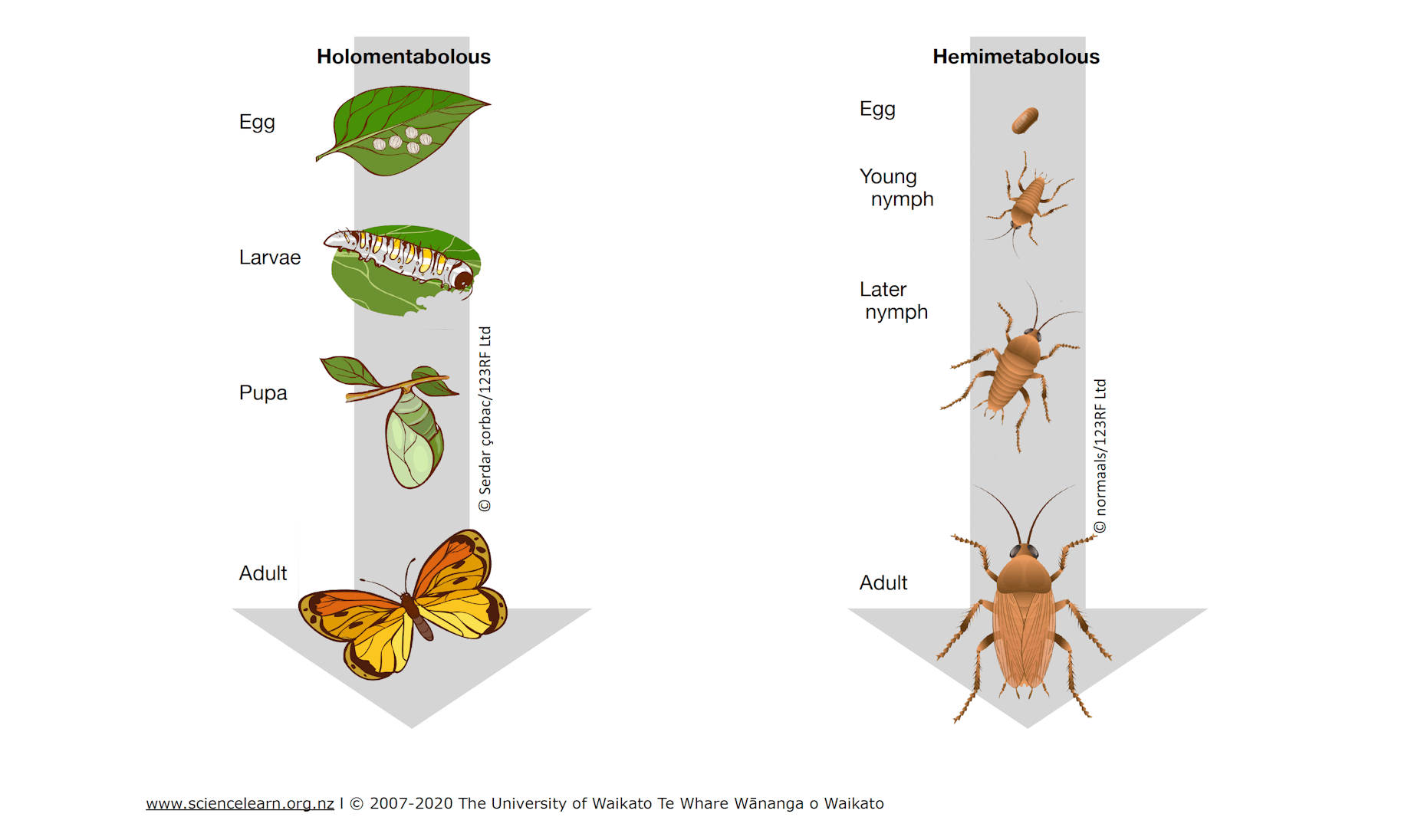
Complete metamorphosis
changes are dramatic - ex: butterflies