HCI Midterms
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Human-Computer Interaction
is a discipline concerned with the design, evaluation and implementation of interactive computing systems for human use and with the study of major phenomena surrounding them.
Design
This is what customers pay us for— to sweat all these details so it’s easy and pleasant for them to use our computers. We’re supposed to be really good at this. That doesn’t mean we don’t listen to customers, but it’s hard for them to tell you what they want when they’ve never seen anything remotely like it. Take desktop video editing. I never got one request from someone who wanted to edit movies on his computer. Yet now that people see it, they say, ‘Oh my God, that’s great!” — Steve Jobs
Human-Computer Inteaction
is a discipline concerned with the design, evaluation and implementation of interactive computing systems for human use and with the study of major phenomena surrounding them.
Albert Einstein
Computers are incredibly fast, accurate, and stupid. Human beings are incredibly slow, inaccurate, and brilliant. Together they are powerful beyond imagination.
Late 1970s and early 1980s
HCI began emerging as a discipline in the _______ alongside advancements in personal computing.
Before this period, computers were primarily used by experts and specialists; user-friendliness wasn’t a priority.
Graphical user interfaces
The introduction of ______ ______ ______ () like those seen in Apple's Macintosh computers marked a turning point, as technology became more accessible to non-expert users.
HCI
Over time, ____ has evolved to accommodate emerging technologies like mobile devices, wearable gadgets, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and artificial intelligence (AI). This evolution continues as HCI adapts to societal needs and technological advancements.
Key Components of HCI
User interface design
Usability testing
Accessibility
Interaction techniques
Importance of HCI
Enhancing user experience
Accessibility
Safety and efficiency
Innovation
Education
User Interface: PC applications, cloud apps, netbooks
Goal: educations, papers, presentations, problem solving, creativity, internet
User: Students
Transportation
User Interface: 747 Jet, MD
11 - Goal: Transport people safety and efficiently
User: Airline Pilots
Exploration
User Interface: Space shuttle
Original cockpit (left), astronaut obtained information from mechanical gauges and CRT (cathode ray tube) displays.
Updated cockpit (right), gauges are replaced by liquid crystal displays (LCDs)
Because the displays are computers driven, they can have a wide range of graphics, colors, and text.
Business
User Interface: Compose Documents
Goal: Communicate via written documents
User: almost every PC users world wide
Healthcare
User Interface: Radiology Software
Goal: Diagnosis
User: Radiologists
Gaming
User Interface: Gaming (wifi, call of duty elite)
Goal: Entertainment
User: Those seeking to be entertained
Communications
User Interface: Email
Goal: Communication to other individuals
User: Everyone
The Arts
User Interface: Music Composition
Goal: Create Music
User: Music Composers
Emergency Management Response
User Interface: Firefighting
Goal: Predict direct and intensity of firewinds
User: Emergency Management Personnel
Telecommunications
User Interface: Mobile Devices
Goal: Communicate (talk, text)
User: Everyone
Finance
User Interface: TurboTax
Goal: File federal, state, and city taxes
User: accountant, taxpayers
Information and Entertainment
User Interface: Browser-Based Applications
Goal: Fulfill Personal Interest
User: Everyone
Energy
User Interface: Nuclear Power Plant
Goal: Generate Electric
User: Plant Operators
Social Networking
User Interface: Facebook
Goal: Communication, sharing content
User: 80 million social network workers
Commerce
User Interface: eBay
Goal: Buy and Sell
User: Buyer and Sellers
Humans
are limited in their capacity to process data.
information is received and responses given via number of input and output channels
Visual Channel
refers to information received visually such as sight, color, dreams and visions.
reading is a function of the ____ channel
Auditory Channel
describes the way vocal signals can be used to produce language
the speaker uses vocal tract to produce speech sounds, and the hearer employs an auditory apparatus to receive and process the speech sound
Haptic Channel
is the science of applying tactile sensation to human interaction with computers.
Haptic device
is one that involves physical contact between the computer and the user, usually through and input/output device
Sensory Memory
is stored in sensory memory just long enough to be transferred to short-term memory.
Sensory Memory
allows individuals to retain impressions of sensory information after the original stimuli have ended.
Short Term Memory
is the capacity to keep a small amount of information in mind in an active, readily available for a short period of time.
Long-term memory
is the phase or type of memory responsible for the storage of information for an extended period
Reasoning
the action of thinking about something in a logical, sensible way.
the process by which we use the knowledge we have to draw conclusions or infer something new about the subject of interest
Problem Solving
use information we have to find solutions in new situations
Skill Acquisition
also refereed to as motor learning and control is the interdisciplinary science of the intention, action, and calibration of the performer-environment relationship
Error
the state or condition of being wrong in conduct or judgement
Types of Error
Slips
Mistakes
Slips
right intention, but failed to do it right
causes: poor physical skill, inattention, etc.
change to aspect of skilled behavior can cause slip
Mistake
wrong intention
cause: incorrect understanding
Computer
a computer system comprises various elements, each of which affects the user of the system.
Text entry
refers to the process of creating messages composed of characters, numbers, and symbols using mobile devices.
can be performed using small physical keys, virtual keyboards presented on touch sensitive screens, gesture or handwriting recognition, speech recognition, and various other technologies.
Computer Keyboard
is one of the primary input devices used with a computer.
it is composed of buttons that create letters, numbers, symbols as well as perform other functions.
most companies use ____ with 104 keys as a de facto standard.
Speech Recognition
also known as voice recognition
a computer software program or hardware device with the ability to decode the human voice.
is commonly used to operate a device, perform commands, or write without having to use a keyboard, mouse, or press any buttons.
Handwriting Recognition
is a technology that allows a computer to recognize and interpret text written by a human hand.
generally used with devices where text has been handwritten, but and needs to be changed over to digital characters.
Pointing
is a gesture specifying a direction from person’s body, usually indicating a location, person, event, thing or idea.
principally the mouse, but also a touchpad, stylus and others
Pointing Device
a generic term for any device used to control the movement of a cursor on a computer screen.
Computer mouse
handheld hardware input device that controls a cursor in a GUI and can move and select text, icons, files, and folders.
Mechanical mouse
a computer mouse that contains a metal or rubber ball on its under side.
Optical Mouse
is a computer mouse first introduced by Microsoft on April 19, 1999, that utilizes LEDs or laser to help track movement.
3D Interaction
a form of human-computer interaction where users are able to move and perform interactions in a three-dimensional space.
Bitmap Display
Different types of screen mostly using some form of _______ ______
Raster Image
an image file format that is defined by a pixel that has one or more numbers associated with it.
are commonly BMP, GIF, JPEG, and PNG files.
Disadvantage of a raster image
inability to resize the image without getting jaggies or another type of distortion
Vector Images
are used for logos, graphics, and text because of the ability to be resized in any direction without distortion.
Raster
is lines inside of the screen traced by electron beam to create an image called a horizontal scan line.
these lines appear on a CRT monitor or a TV screen
VR
is a computer-generated artificial environment that allows a user to view, explore and manipulate the environment and a term popularized by Jaron Lanier.
is a computer-generated reality manipulated and explored using various input devices such as goggles, headphones, gloves, or a computer.
The Computer

The Interaction
is a kind of action that occur as two or more objects influence one another.
3 terms of interaction
Domain - the area of work under the study
Goal - what do you want to achieve
Task - how you go about doing it
Ergonomics
is the process of designing or arranging workplace, products, and systems so that they fit the people who use them
Interaction Styles
refers to all the way the user can communicate or otherwise interact with the computer system.
Command Line Interface
is an interface found on network devices, such as network routers.
allows the management and control of that network device
a user interface that is navigated by typing commands at prompts, instead of using the mouse.
Menus
a list of commands or choices offered to the user through the menu bar.
commonly used in GUI operating systems and allow a user to access various options the software program is capable of performing.
File Menus
commonly accessed using the computer mouse; however, may also sometimes be accessed using shortcuts on the keyboard.
Natural Language
is the idea of creating a programming language that uses the grammar, vocabulary, and syntax of the human language.
Question/Answer and Query Dialogue
commonly used to describe a question or request that is made by a user or another computer or device.
Form-Fills and Spreadsheets
e-form or form is a web page or paper that contains a listing of questions or fields that ask for user input
WIMP
short for windows, icons, menus, pointer
is a term coined by Merzouga Willberts to describe a type of GUI interaction first used with the Xerox Aito computer.
Point and Click
is the action of moving the mouse to a specific location and clicking an object to perform a specific task.
Three-Dimensional Interfaces
is a description of a visual object that has the appearance of height, width, and depth.
Paradigm
refers to a new method of thinking about a problem or situation
Batch Processing/Batch System (Impersonal Computing)
a technique of processing data that occur in one large group instead of individually.
is usually done to help conserve system resources and allow for any modifications before being processed.
Time Sharing (Interactive Computing)
process of giving multiple users access to a system or group of systems at the same time.
with this setup a computer gives users a small portion of its processing power in pieces.
Network (Community Computing)
a collection of computers, servers, mainframes, network devices, peripherals or other devices connected to one another to allow the sharing of data.
Graphics (Direct Manipulation)
is an image or visual representation of an object.
Processor/Central Processor/Microprocessor/CPU
is the central processing unit of the computer.
handles all instructions it receives from hardware and software running on the computer.
World Wide Web (WWW)
is graphical interface for the internet that was first introduced to the public on August 6, 1991, by Tim Berners-Lee. A few days later on August 23, 1991, it was available to everyone.
Ubiquitous Computing
is a paradigm in which the processing of information is linked with each activity or object as encountered.
involves electronic devices, including embedding microprocessors to communicate information.
devices that uses this have constant availability and are completely connected
The Waterfall Model
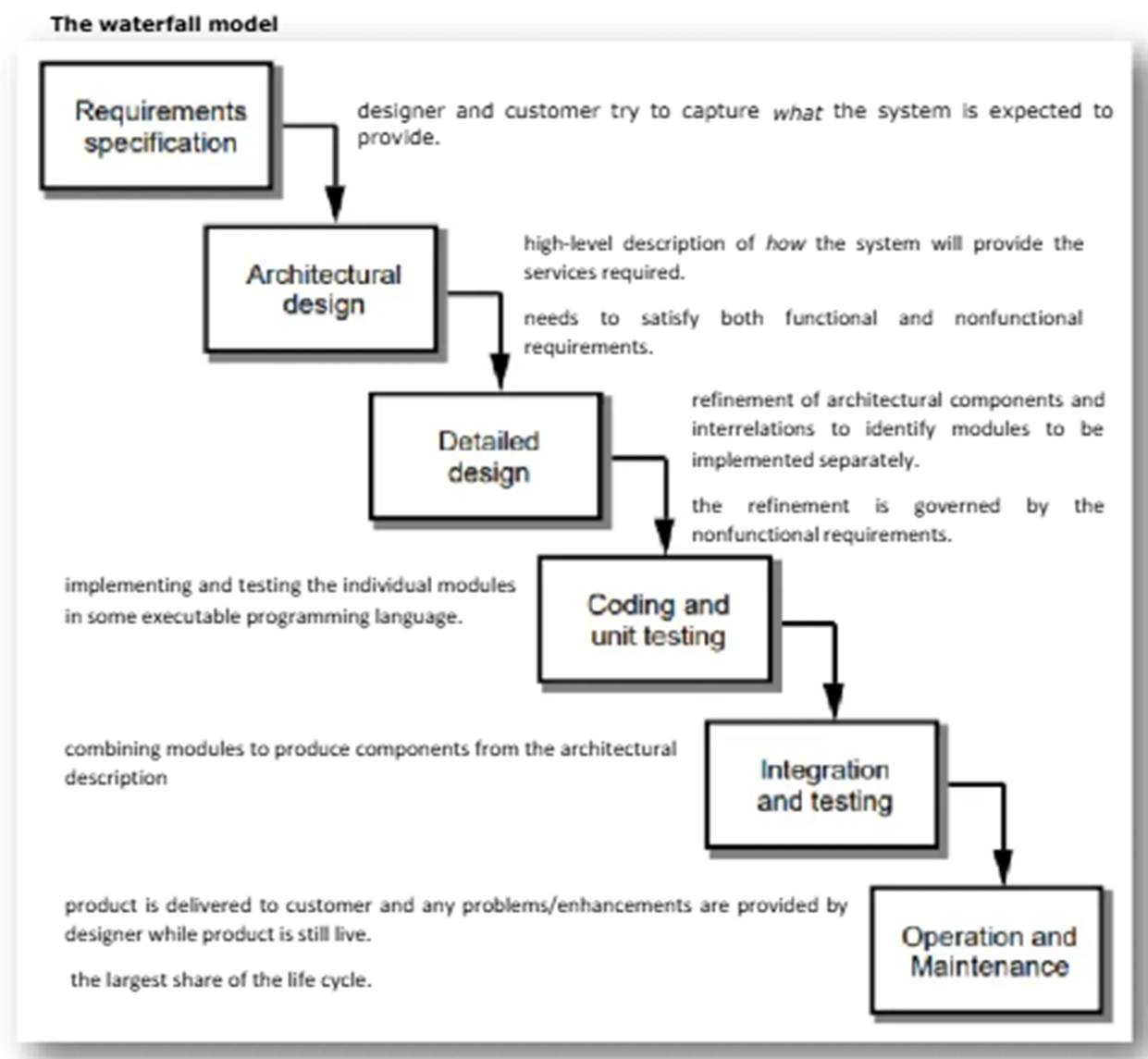
User-centered Design
is a type of user interface design and a process in which the needs, wants, and limitations of end users of a product are given extensive attention at each stage of the design process.
User-centered Design
an approach to design that grounds the process in information about the people who will use the product.
is an approach to interactive system development that focuses specifically on making systems usable. it is a multi-disiplinary activity.
User
Development proceeds with the ______ as the center of focus.
Purpose of UCD
the biggest cost benefit that UCD can provide is by more accurately defining requirements
produce products that have a high degree of usability
the ultimate goal of UCD is to optimize a user’s experience of a system, product, or process.
Users Perspective
Needs and wants
Goals, motivations, and triggers
Obstacles and Limitations
Tasks, activities and behaviors
Geography and Language
Environment, work, life and experience
Important Principles of UCD
a clear understanding of user and task requirements
incorporating user feedback to refine requirements and design
active involvement of user to evaluate designs
integrating user-centered design with other development activties
Typical UCD Methodology
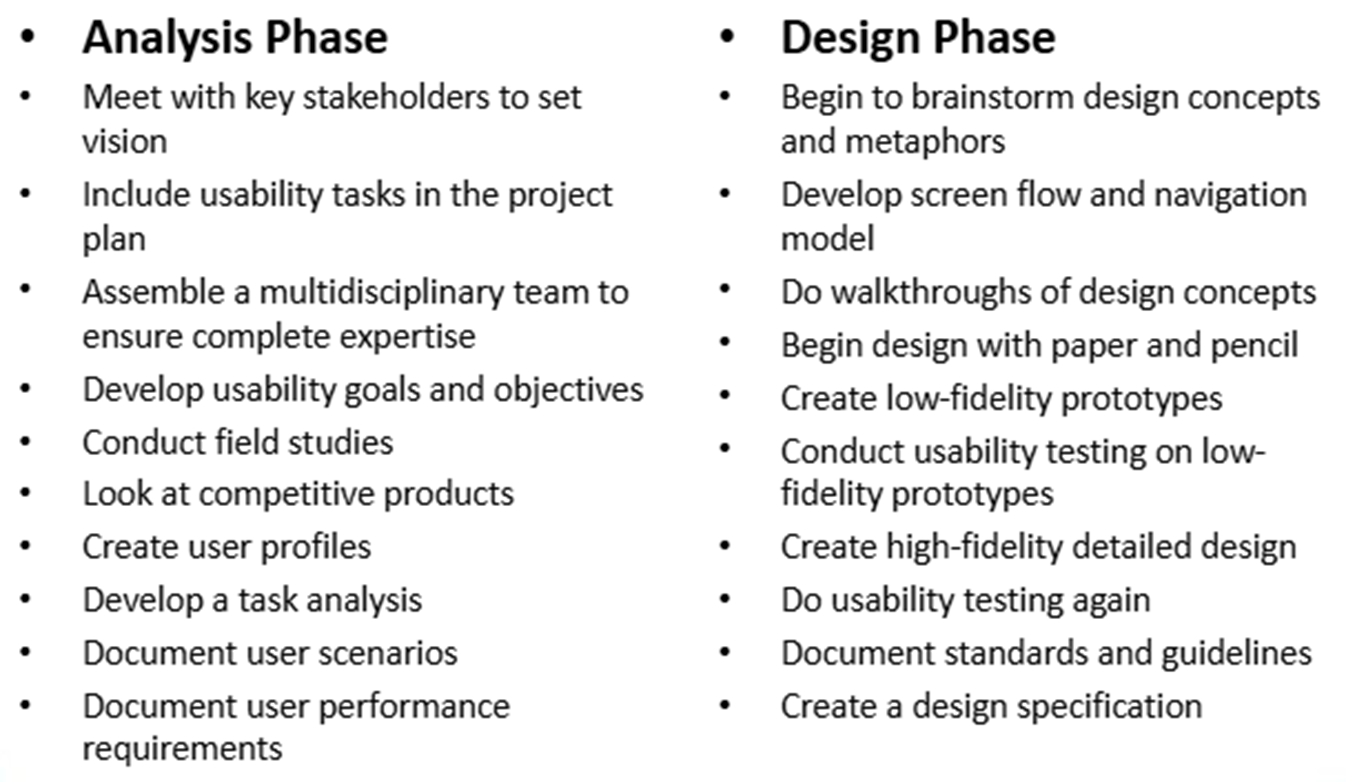
Analysis Phase
Design Phase
Implementation Phase
Deployment Phase
Analysis and Design Phase
Implementation and Deployment Phase
UCD in SDLC
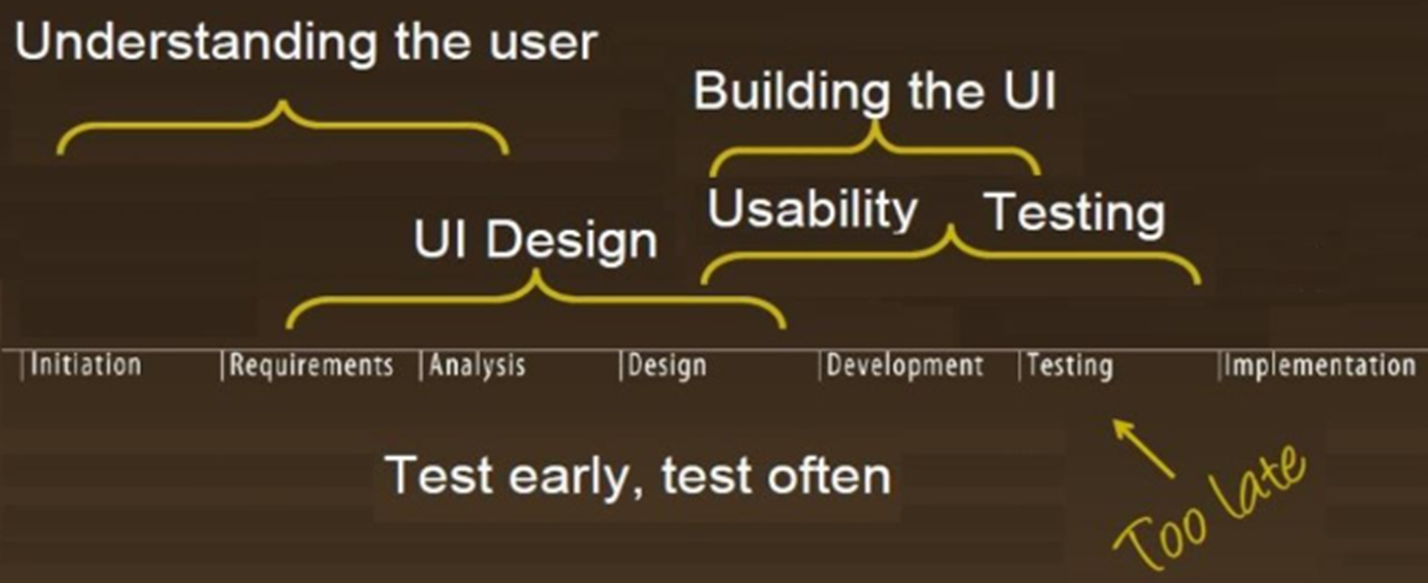
Basic Steps in UCD
Get to know the users
Analyze user tasks and goals
Establish usability requirements
Prototype some design ideas
Usability test and concepts
Repeat as necessary
Waterfall vs Agile vs UCD

Design Thinking
a human-centered approach to problem-solving that integrates the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success.
Design Thinking
a methodology that provides a solution-based approach to solving problems.
It’s extremely useful when used to tackle complex problems that are ill-defined or unknown—because it serves to understand the human needs involved, reframe the problem in human-centric ways, create numerous ideas in brainstorming sessions and adopt a hands-on approach to prototyping and testing.
Core Principles of UCD
Empathy
Collaboration
Iteration
Creativity
Traditional Design
Linear Process
Solution-focused
Expert-driven
Design Thinking
Iterative
Problem-focused
User-centered
Phases of Design Thinking
Empathize
Define
Ideate
Prototype
Test
Empathize
The first stage of the design thinking process focuses on user-centric research.
You want to gain an empathic understanding of the problem you are trying to solve.
Consult experts to find out more about the area of concern and conduct observations to engage and empathize with your users.
You may also want to immerse yourself in your users’ physical environment to gain a deeper, personal understanding of the issues involved—as well as their experiences and motivations. Empathy is crucial to problem-solving and a human-centered design process as it allows design thinkers to set aside their own assumptions about the world and gain real insight into users and their needs
Define
you will organize the information you have gathered during the Empathize stage. You’ll analyze your observations to define the core problems you and your team have identified up to this point. Defining the problem and problem statement must be done in a human-centered manner.