Economics - 1.2
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What does rational decision making mean?
Rational decision making is when economic agents are able to consider the outcome of their choices and recognise the net benefits of each one. Rational agents will select the choice which presents the highest benefits
Consumers try to maximise their utility
Producers try to maximise their profit
The government try to maximise their welfare
What is the definition of utility
The amount of satisfaction gained from consuming a good or service
What is marginal utility
The additional satisfaction gained from each unit of consumption
What is diminishing marginal utility
As more units of a good is consumed, additional units will provide less additional satisfaction
What is the equation for profit
Total revenue - Total costs
Why might consumers and other economic agents not make rational decisions
Peer pressure
Habits
Emotions
Altruism
Herd mentality
What is demand
Demand is the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at a given time
What is the law of demand
When the price of a good rises, the quantity demanded will fall
Income effect
When the price of a good increases, the real income falls, meaning purchasing power decreases. People therefore feel poorer, and buy less, so quantity demanded decreases
What is the substitution effect
The price of a good is more expensive relative to another good and the consumer switches to the cheaper good
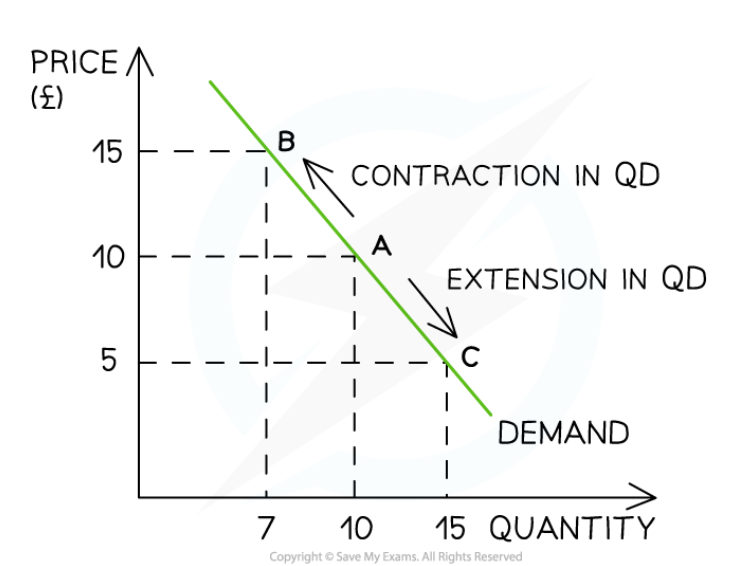
Demand curves
Price only moves along the demand curve, it does not shift demand.
An increase in price is a contraction and and decrease is an extension
Factors that effect demand
Population
Advertising
Substitutes
Income
Fashion and trends
Interest rates
Complimentory goods
Why does a demand curve slope downwards
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility helps to explain the reason why the demand curve is downward sloping
When the first unit is purchased, the utility is high and consumers are willing to pay a higher price
When subsequent units are purchased, each one offers less utility and the willingness of the consumer to pay the initial price decreases
Lowering the price makes it a more attractive proposition for the consumer to keep consuming additional units
This is one reason why firms offer discounts such as '50% off the second item.'
What is PED
The responsiveness to quantity demanded of a good given a change in price
Interpreting PED values
<1 - inelastic
0 - perfectly inelastic
0-1 - relatively elastic
1 - Unitary
>1 - Perfectly elastic
Factors effecting PED
Availability of substitutes
Addictiveness of the product
Time period
Percentage of income
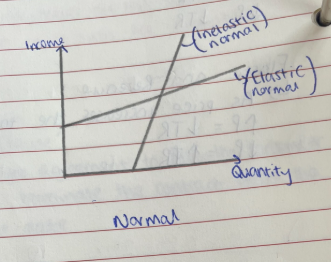
What is YED
Responsiveness to quantity demanded of a good given a change in income
Interpreting YED values
<0 - Inferior good - As income increases, demand decreases.
0-1 - Normal necessity good - As income increases, demand increases. Income is inelastic
>1 - Normal luxury - As income increases, demand increases. Income is elastic
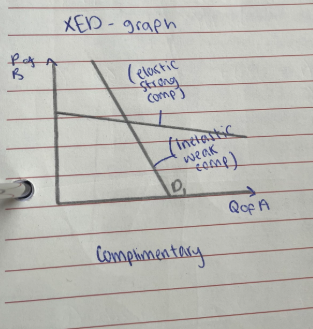
What is XED
Responsiveness of quantity demanded of Good A, given a change in price of Good B
YED graphs
What are the types of goods
Substitutes - Positive relationship between price of other good and quantity demanded of main good
Complimentary good - Negative relationship between price of other good and quantity demanded of main good
Interpreting XED Values
<1 -inelastic
>1 - elastic
0 - No relation in goods
XED graphs
What is supply
Supply is the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to pay for at a given time
Law of supply
As price increases, quantity supplied will also increases
Reasons for the law of supply
Firms want to maximise profit
Higher prices gives firms an incentive to produce more
Cost of production goes up eg wages, capital cost, raw materials
Higher prices attracts more entrants
Why do lower prices reduce the quantity supplied
Reduces profit and therefore reduced incentive to produce
Reduced the number of possible entrants into the market
Factors effecting the supply curve
Productivity
Indirect tax
No of firms
Technology
Subsidy
Weather
Cost of production
Price elasticity of supply
The responsiveness of quantity supplied given a change in price
Factors effecting price elasticity of supply
Production log
Stocks
Spare capacity
Substitutability of FOP’s
Time period
What is equilibrium
This is when supply meets demand, meaning there is no excess demand or supply
AKA. The market clearing price
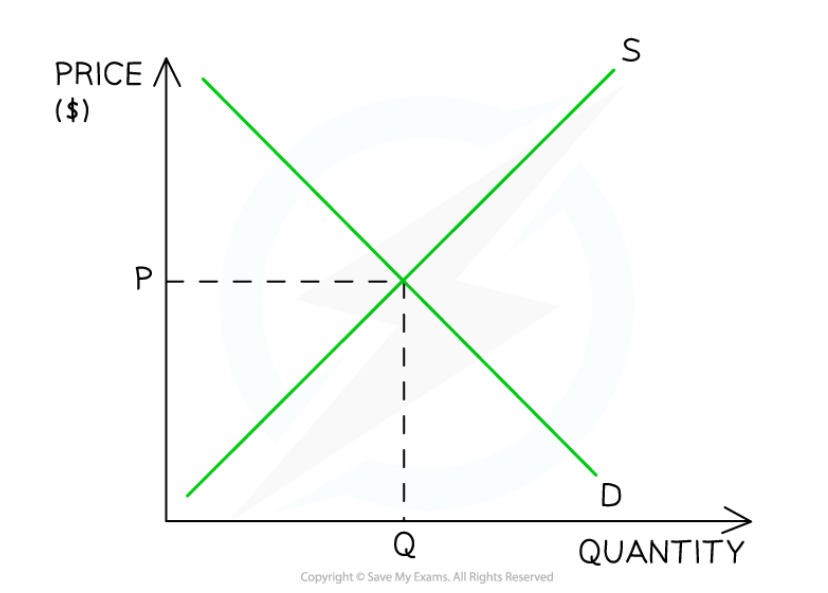
When the price is above the equilibrium price
1) Consumers are less willing and able to spend
2) Producers are unable to sell all they are willing anf able to supply at the current price
3) There is excess supply (which worsens the basic economic problem)
When the price is below the equilibrium price
1) Consumers are unable to obtain all they demand and are willing to pay a higher price
2) Producers are unwilling o supply at the current price being offered by the market. They are willing to accept a higher price.
3) There is a shortage in the market and this drives up the market price, leading to excess demand

What is allocative efficiency
Where resources are distributed to produce the combination of good most desired by society
What is disequilibrium
A situation in the market where supply is no longer equal to demand
What causes disequilibrium in the market?
Price change
Change in demand and supply
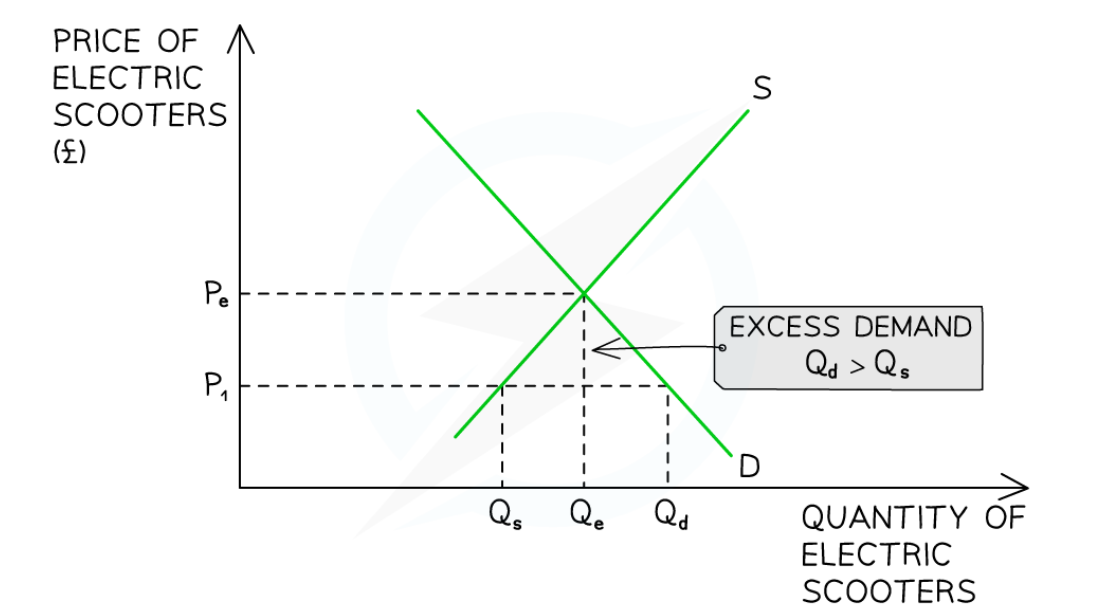
Excess demand
Quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied
This causes a shortage in the market
Sellers realise they can raise prices
Sellers gradually raise prices, which leads to a decrease in quantity demanded, as buyers are less willing to pay higher prices.
This also leads to an increase in quantity supplied as buyers are more incentivised to supply at higher prices
This will gradually clear excess demand
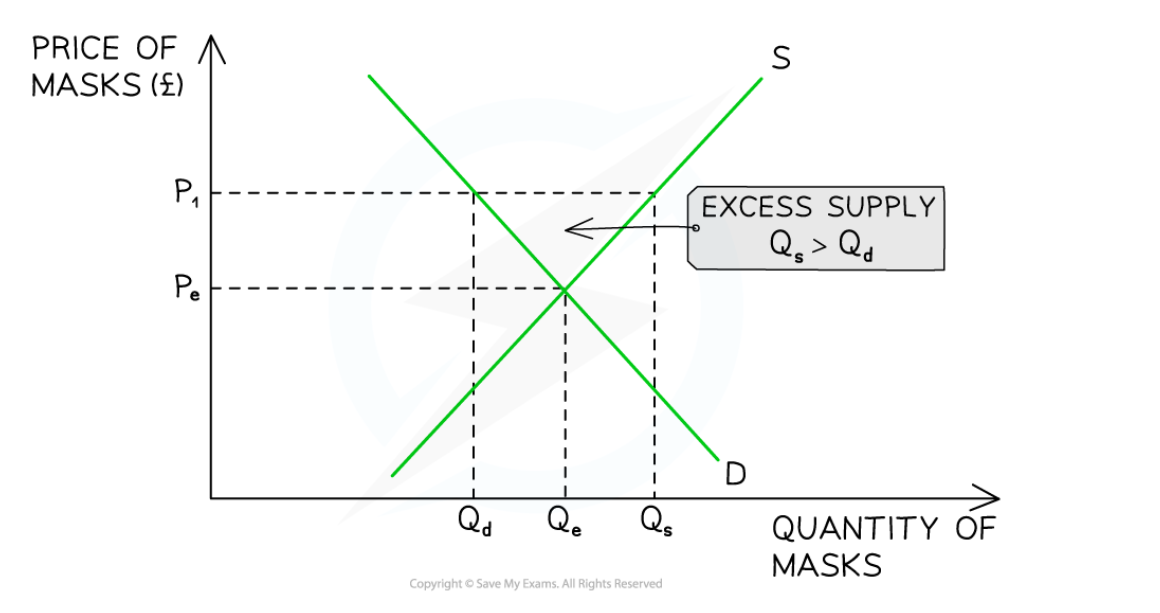
Excess supply
Quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
Sellers will gradually lower prices
This causes a contraction in quantity supplied as sellers are less incentivised to produce supply
This also causes an increase in demand as buyers are more willing and able to pay lower prices
This gradually clears excess supply
What is the price mechanism
The interaction of demand and supply in a free market
Functions of a price mechanism
Signals - Rapid increase in sales, stock levels fall
Incentives - Maximise profit - raise price. Higher prices incentivises producers to allocate more FOPs to produce
Rationing - Prices increase over time, excess will be cleared
Allocative efficiency - Supply = Demand
Consumer surplus
This difference between the price that the consumer is willing and able to pay and the price they actually pay
This is the area below the demand curve and above the price line
Higher surplus means that more consumers are willing to pay above the new market price
Producer surplus
The difference between the price the producer is willing to sell at and the price they actually sell at
This is the above the supply curve but below the price line
Community surplus
The total benefit the society receives from an economic transaction
Types of tax
Specific tax - A set tax per unit of a product
Ad valorem tax - Percentages such as VAT, which is added to the unit price
Incidence of tax
The share/burden of tax to be paid
Specific tax

Subsidy
Payment from the government to the producers to lower cost of production
Advantages of subsidy