BMCB 658A EXAM 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:51 AM on 3/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
1
New cards
Which of the following is most directly related to the speed of a reaction?
The ΔG0‡ of the reaction
2
New cards
Why can the breakdown of A T P power cellular processes?
As an exergonic reaction, it releases energy to spare.
3
New cards
∆G < 0
Spontaneous exergonic
4
New cards
∆G > 0
Nonspontaneous endergonic
5
New cards
_____ is a measure of a system’s instability, its tendency to change to a more stable state.
Free energy
6
New cards
During a spontaneous change free energy ….. and the stability of a system ….
decreases, increases
7
New cards
∆G = 0
Equilibrium
8
New cards
What conditions are necessary for the free energy change to predict the spontaneity of a reaction?
Free energy change can be used to predict spontaneity of reaction under the conditions of constant TEMPERATURE and PRESSURE
9
New cards
Gibbs free energy equation
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
10
New cards
If the ∆G is negative than the ….
reaction is spontaneous
11
New cards
Standard states
Standard set of conditions used for comparisons of chemical reactions
12
New cards
If \[H+\] = 1 M then
pH=0
13
New cards
Standard state for \[H+\] is
\[H+\] = 10-7 M and pH = 7.0
14
New cards
Modified standard state for free-energy change is
∆G°ʹ
15
New cards
Spontaneous reaction occurs without
added energy
16
New cards
How to make endergonic reactions proceed?
Couple endergonic reaction to an exergonic reaction
17
New cards
Enzymes do not affect the change \n in free energy (ΔG); they only …..
speed up reactions that would eventually occur without them
18
New cards
Standard free energy change (ΔG°)
Difference between energies of reactants and products \n under standard conditions
19
New cards
Reaction rate depends on its …
activation energy (ΔG°‡),which is the energy input required to initiate a reaction
20
New cards
Lock-and-key model
Substrate binds to that portion of the enzyme with a \n complementary shape
21
New cards
Induced fit model
Binding of the substrate induces a change in the conformation of the enzyme that results in a complementary fit
22
New cards
Proximity and orientation of the substrate …..
speed up the reaction
23
New cards
Once enzyme and substrate bind (ES) and attain the transition state \n complex (EX‡) …..
catalysis can occur
24
New cards
The active site can lower activation energy and speed up reactions by
* Orienting substrates correctly
* Straining substrate bonds
* Providing a favorable microenvironment
* Non-covalent bonding to the substrate
* Straining substrate bonds
* Providing a favorable microenvironment
* Non-covalent bonding to the substrate
25
New cards
The rate of catalysis can usually be sped up by
Increasing the substrate concentration
26
New cards
Enzyme is saturated when …..
all enzyme molecules in a solution are bonded with substrate
27
New cards
Competitive Inhibition
\n Decrease in enzymatic activity caused by binding of \n a substrate analogue to the active (catalytic) site \n
Inhibitor competes with the substrate for the active \n site on the enzyme
Inhibitor competes with the substrate for the active \n site on the enzyme
28
New cards
Noncompetitive Inhibition
Form of enzyme inactivation in which a substance binds \n to a site other than the active site but distorts the \n active site to inhibit reaction
\
Involves two distinct binding sites, one for the substrate \n and one for the inhibitor
\
Involves two distinct binding sites, one for the substrate \n and one for the inhibitor
29
New cards
Increasing substrate concentration cannot ….
overcome noncompetitive inhibition
30
New cards
Uncompetitive Inhibition
Inhibitor can bind to the ES complex but not to the free E
31
New cards
Allosteric enzyme
Oligomer whose biological activity is affected by other substances binding to it
32
New cards
Allosteric effector
Substance that modifies the behavior of an allosteric enzyme by binding to it
33
New cards
Binding of O2 to hemoglobin exhibits
positive cooperativity
34
New cards
Instead of relying on heat, organisms carry out _____ to selectively speed up reactions
catalysis
35
New cards
Enzymes are biological catalysts that are usually
globular proteins
36
New cards
Enzyme and substrate must bind to form the
ES complex
\
E + S -→ ES
\
E + S -→ ES
37
New cards
First order
Description of a reaction whose rate depends on the first power of the concentration of a single reactant
38
New cards
Second order
Description of a reaction whose rate depends on the product of the concentrations of TWO reactants
39
New cards
Zero Order
rate of reaction does NOT depend on concentration of substrate, it instead relies on the presence of catalysts
40
New cards
Steady state
Condition in which the \[ES\] remains constant in spite of continuous turnover
41
New cards
KM – Michaelis constant
describes the affinity of enzyme for substrate
42
New cards
Vmax
maximum velocity of reaction
43
New cards
When \[S\] << KM
• First-order kinetics \n • Double \[S\], Vinit doubles
44
New cards
When \[S\] = KM
Vinit = Vmax/2
45
New cards
When \[S\] >> KM
Vinit= Vmax \n • enzyme is saturated with substrate \n • Zero-order kinetics
46
New cards
Inhibitors
substances that decrease the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
47
New cards
Reversible Inhibitors
Substances that bind to an enzyme and subsequently are released
48
New cards
Irreversible inhibitors
Substances that react with enzymes to produce proteins that are not enzymatically active and from which original enzymes cannot be regenerated
49
New cards
Competitive Inhibition
Decrease in enzymatic activity caused by binding of a substrate analogue to the active (catalytic) site DOESNT AFFECT CATALYSIS
50
New cards
In the presence of a competitive inhibitor:
* Vmax is unchanged
* apparent increase in KM
\
Because substrate and inhibitor are competing for the same location, a sufficiently high amount of substrate will outcompete inhibitor
* apparent increase in KM
\
Because substrate and inhibitor are competing for the same location, a sufficiently high amount of substrate will outcompete inhibitor
51
New cards
Noncompetitive Inhibitor
Form of enzyme inactivation in which a substance binds to a site other than the active site but distorts the active site to inhibit a reaction
\
Involves two distinct binding sites: one for the substrate and one for the inhibitor
\
Involves two distinct binding sites: one for the substrate and one for the inhibitor
52
New cards
Increasing substrate concentration cannot
overcome noncompetitive inhibition causing the Vmax to decrease and the value of kM to stay unchanged
53
New cards
A biologist working in a lab adds a compound to a solution that contains an enzyme and its substrate. This compound binds to the enzyme and decreases the rate at which the enzyme converts substrate to product. However, this decrease can be overcome by increasing the concentration of substrate in the reaction mix. Therefore, which of the statements is true of the compound?
The compound is a competitive inhibitor
54
New cards
Under steady state conditions the ES …..
remains constant
55
New cards
____ can be used to compare the relative affinity of an enzyme for a substrate if the Vmax values for the enzymes are similar.
KM
56
New cards
Regulation of Enzyme Activity can
Alter enzyme concentration \n
\-rate of synthesis \n -rate of degradation \n
Alter enzyme activity \n
\-allostery (activation, inhibition) \n -phosphorylation \n -post-translational processing \n -sequestration
\-rate of synthesis \n -rate of degradation \n
Alter enzyme activity \n
\-allostery (activation, inhibition) \n -phosphorylation \n -post-translational processing \n -sequestration
57
New cards
____ describes allosteric behavior
sigmoidal curve
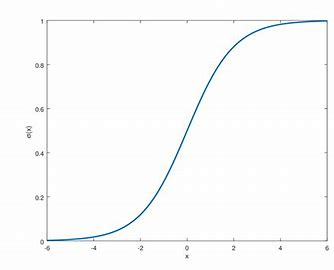
58
New cards
Types of Inhibition
K systems
V systems
K 0.5
V systems
K 0.5
59
New cards
K systems
Enzyme for which the substrate concentration that yields \n one-half Vmax is altered by the presence of inhibitors or activators
60
New cards
V systems
Enzyme in which the presence of inhibitor/activator \n changes the maximal velocity of the enzyme but not the substrate level that yields one-half Vmax
61
New cards
K0.5
Substrate level at one-half Vmax in a K system
62
New cards
Homotropic effects
Allosteric effects that occur when several IDENTICAL molecules are bound to a protein
63
New cards
Heterotropic effects
Allosteric effects that occur when DIFFERENT substances are bound to a protein
64
New cards
Binding of O2 to hemoglobin exhibits
positive cooperativity
65
New cards
Concerted Model
Description of allosteric activity in which the conformations of all subunits change simultaneously
66
New cards
Zymogen
Inactive protein that can be activated by specific hydrolysis of peptide bonds
67
New cards
Negative Cooperativity
Cooperative effect whereby binding of the first ligand \n to an enzyme or protein causes the affinity for the next ligand to be lower
68
New cards
Transition-state analog
Synthesized compounds that mimic the form \n of the transition state of an enzyme reaction
69
New cards
Abzymes
Antibodies that are produced against a transition-state analog and that have catalytic activity similar to that of a naturally occurring enzyme
70
New cards
Coenzymes
Nonprotein substances that take part in enzymatic reactions and are regenerated at the end of the reaction
71
New cards
Amphipathic
Molecule that has one end with a polar or charged, water-soluble group and another end with a nonpolar hydrocarbon group that is insoluble in water
72
New cards
Fatty Acids
Unbranched chain carboxylic acids
* Amphipathic compounds
* 12–20 carbons long
* Unsaturated fatty acids - Contain \n carbon–carbon double bonds
* Saturated fatty acids - Contain only \n single bonds
* Amphipathic compounds
* 12–20 carbons long
* Unsaturated fatty acids - Contain \n carbon–carbon double bonds
* Saturated fatty acids - Contain only \n single bonds
73
New cards
Triacylglycerols
Lipids formed by the esterification of \n three fatty acids to glycerol
\
Ester groups form the polar part of the molecule, and the tails are nonpolar
\
Ester groups form the polar part of the molecule, and the tails are nonpolar
74
New cards
Phosphatidic Acid
Compound in which two fatty acids and phosphoric acid are esterified to the three hydroxyl groups of glycerol
75
New cards
Phosphoacylglycerols
•Polar head group is charged \n
•Phosphate group is ionized at \n neutral pH \n
•Positively charged amino group is \n contributed by an amino alcohol \n esterified to the phosphoric acid
•Phosphate group is ionized at \n neutral pH \n
•Positively charged amino group is \n contributed by an amino alcohol \n esterified to the phosphoric acid
76
New cards
Waxes
•Complex mixtures of esters of long-chain carboxylic acids and long- \n chain alcohols \n
•Serve as protective coatings for plants and animals
•Serve as protective coatings for plants and animals
77
New cards
Sphingolipids
•Contain sphingosine, a long- \n chain amino alcohol \n
•Found in plants and animals and \n are abundant in the nervous \n system
•Found in plants and animals and \n are abundant in the nervous \n system
78
New cards
Glycolipids
•Lipid to which a sugar moiety is bonded
79
New cards
Steroids
•Lipids with a characteristic fused-ring structure •Three six-membered rings (the A, B, and C rings) \n •One five-membered ring (the D ring)
\
Four fused rings in total
\
Four fused rings in total
80
New cards
What are important steroids?
Cholesterol is an important steroid, it acts as a precursor for other steroids
81
New cards
Interaction between lipid bilayers and membrane proteins determines….
membrane function
82
New cards
Lipid Bilayer
Aggregate of a lipid molecule in which the polar head groups are in contact with water and the hydrophobic parts are not that is held together by noncovalent interactions (van der waals and hydrophobic interactions)
83
New cards
When considering the Lipid Bilayer and cholesterol it is important to remember …….?
That the hydrocarbon interior of saturated and unsaturated fatty acid chains and the fused-ring system of cholesterol
84
New cards
Which of the following lipids is not \n found in biological membranes?
triacylglycerols
85
New cards
What is important regarding the OUTER layer of the lipid bilayer?
Sphingolipids, gangliosides, cerebrosides have larger hydrophilic groups and are more likely to be found on the outer layer of a curved bilayer
86
New cards
What is important regarding the INNER layer of the lipid bilayer?
phosphoacylglycerols with smaller hydrophilic groups are more common on the inner layer.
87
New cards
The most abundant open-chain lipids found in typical membranes are
phosphoacylglycerols such as phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine
88
New cards
Membrane fluidity can differ due to the composition of the bilayer for instance …..
Saturated fatty acids have a LINEAR arrangement of hydrocarbon chains leading rigidity
\
Unsaturated fatty acids have a KINKY arrangement that causes disorder in its packing and leads to greater fluidity
\
Unsaturated fatty acids have a KINKY arrangement that causes disorder in its packing and leads to greater fluidity
89
New cards
With membrane fluidity and cholesterol …….
The presence of cholesterol can enhance order and rigidity due to the fused ring structure of cholesterol
90
New cards
Receptor proteins in the membrane ….
detect extracellular signals and trigger intracellular signaling pathway
91
New cards
Peripheral proteins are …
Loosely bound to the outside of a membrane