Macroeconomics MIDTERM
0.0(0)Studied by 4 people
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:54 PM on 3/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
Circular Flow Model
2
New cards
What is GDP
Gross Domestic Product
\
the market value of the final goods and services a country produces within a fixed period of time
\
the market value of the final goods and services a country produces within a fixed period of time
3
New cards
What is the formula for GDP
Y = C+I+G+(X-M)
4
New cards
Monetary Policy
the actions of central banks to achieve macroeconomic policy objectives such as price stability, full employment, and stable economic growth
\
The fed conducts the nations monetary policy by changing interest rates and adjusting the quantity of money
\
The fed conducts the nations monetary policy by changing interest rates and adjusting the quantity of money
5
New cards
Final Goods
An item that is bought by its final user during the specified time period
6
New cards
Intermediate Goods
An item that is produced by 1 firm and bought by another firm to produce a different final product
7
New cards
Federal Reserve
The central bank of the United States, a public authority whose main role is the regulation of banks and money (to achieve stable prices and full employment)
8
New cards
Federal Funds Rate
The interest rate that the banks each other on overnight loans
9
New cards
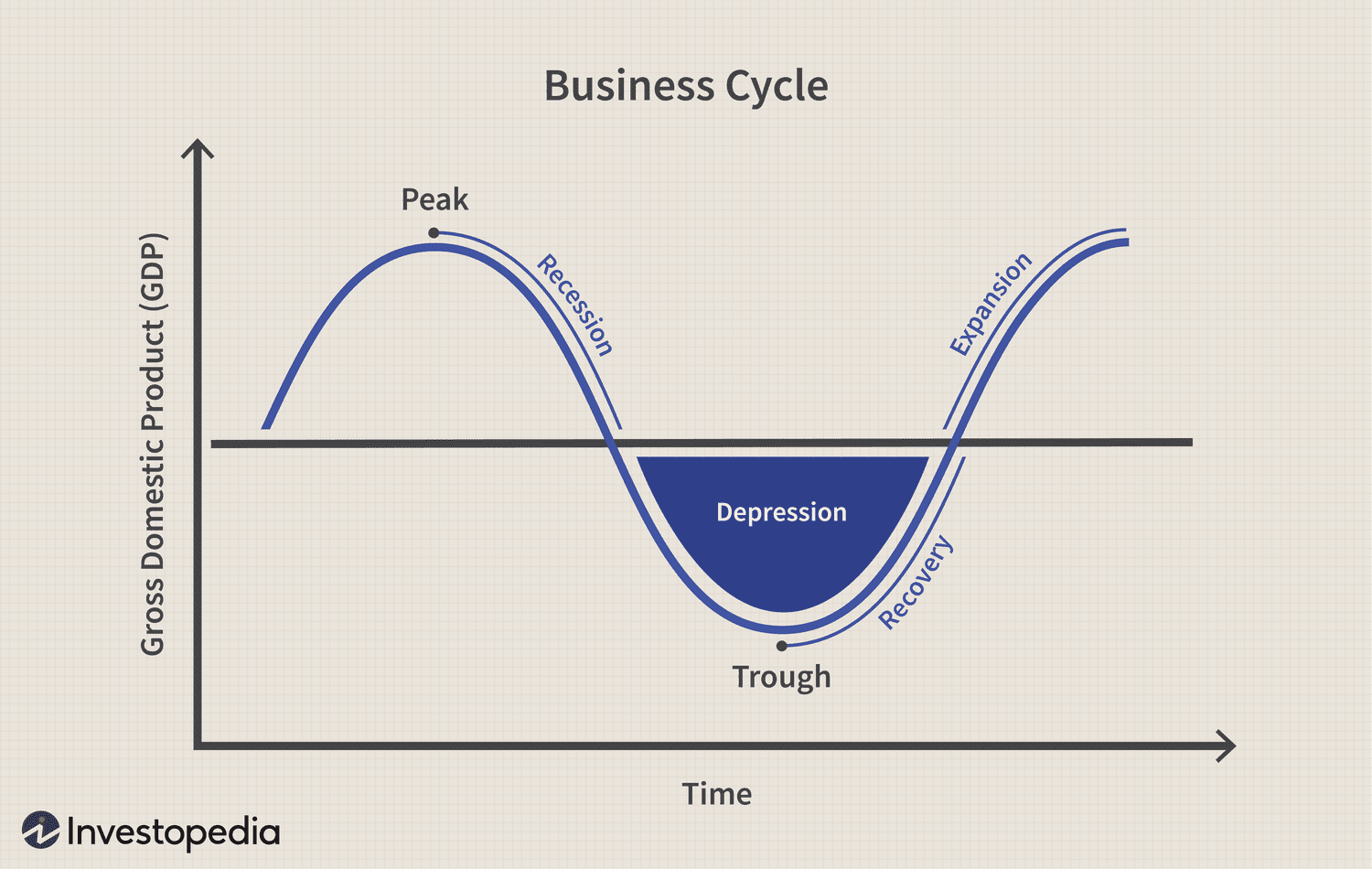
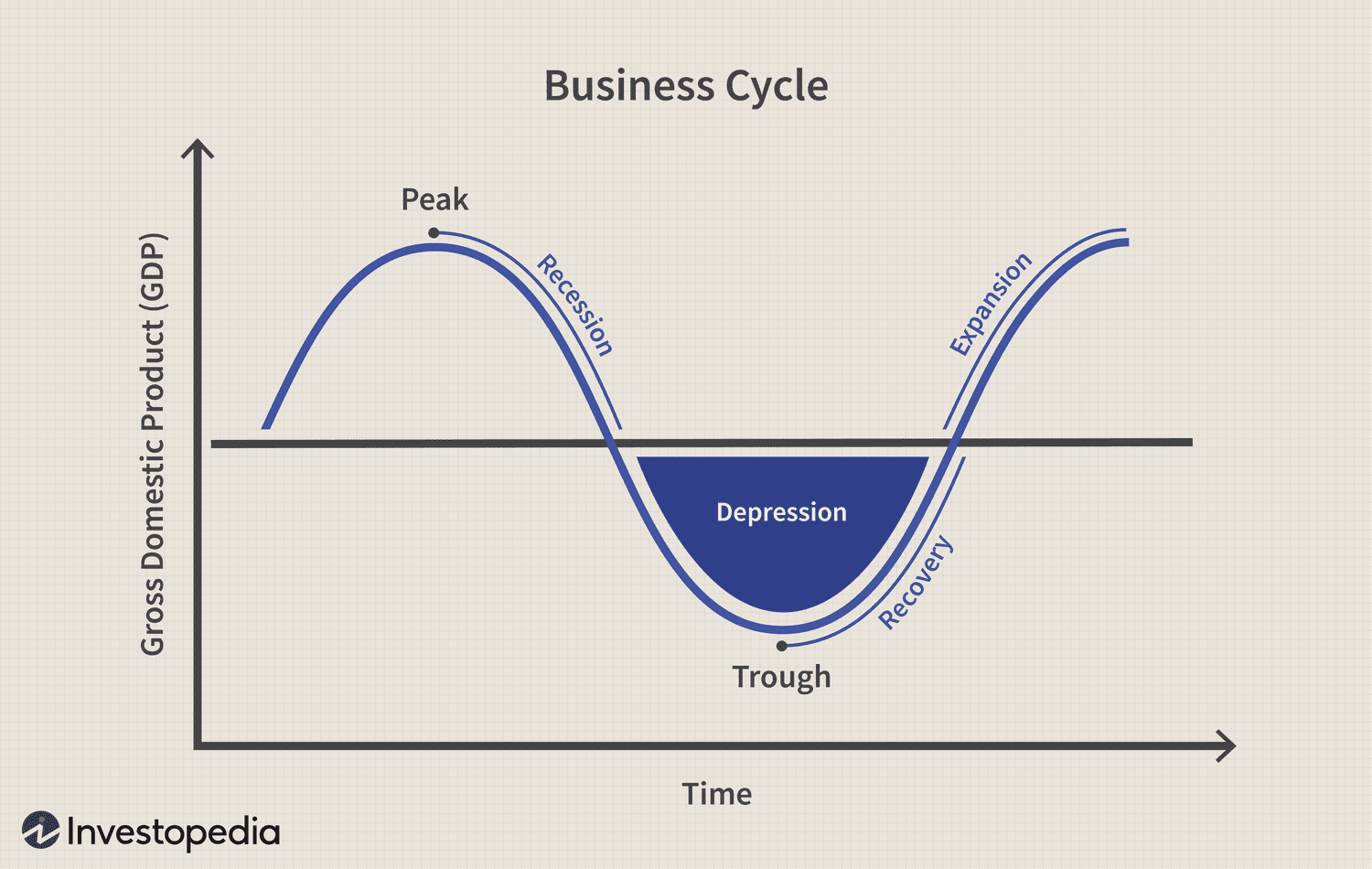
Economic Cycle
the overall state of the economy as it goes through four stages in a cyclical pattern: expansion, peak, contraction, and trough. Factors such as GDP, interest rates, total employment, and consumer spending can help determine the current stage of the economic cycle.
10
New cards
Inflation
a period of persistently rising price levels
11
New cards
Recession
A business cycle phase in which real GDP decreases for at least two successive quarters
12
New cards
CPI
CONSUMER PRICE INDEX
An index that measures the average of the prices paid by urban consumers for a fixed basket of consumer goods and services
\
MEASURES INFLATION
An index that measures the average of the prices paid by urban consumers for a fixed basket of consumer goods and services
\
MEASURES INFLATION
13
New cards
Working Age Population
The total number of people aged 16 years and over who are not in jail, hospital, or some other form of institutional care
14
New cards
Stagflation
1. high inflation
2. slow economic growth
3. high unemployment
INFLATION + RECESSION
15
New cards
Labor Force Participation Rate
The percentage of the working age population who are members of the labor force
\
(Labor Force ÷ Civilian Noninstitutional Population) x 100
\
(Labor Force ÷ Civilian Noninstitutional Population) x 100
16
New cards
Fiscal Policy
The use of the federal budget, by setting and changing tax rates, making transfer payments, and purchasing goods and services, to achieve macroeconomic objectives such as full employment, sustained economic growth, and price level stability
17
New cards
What is the most costly type of unemployment
Long term unemployment
18
New cards
Prime Rate
the current prime rate is 7.75%
\
the current interest rate that financial institutions in the U.S. charge their best customers (Large corporations/wealthy families)
\
the current interest rate that financial institutions in the U.S. charge their best customers (Large corporations/wealthy families)
19
New cards
Economic Growth
The expansion of production possibilities frontier (***an increase in the production of economic goods and services in one period of time compared with a previous period)***
20
New cards
Basis Point
a unit of measurement that denotes a change in the interest rate of a financial instrument and is equal to 1/100th of 1% or 0.01%
21
New cards
Rule of 70
A rule that states that the number of years it takes for the level of any variable to double is approximately 70 divided by the annual percentage growth rate of the variable (like an investment)
22
New cards
FOMC
Federal Open Market Committee
1. minimize inflation
2. maximize employment
1. minimize inflation
2. maximize employment
23
New cards
Jobs Report
the U.S. Department of Labor provides a useful snapshot of how many jobs the economy created the previous month, how many people were unemployed, and what kind of wage hikes workers received. It also delivers an excellent snapshot of overall economic health.
24
New cards
Equilibrium
The price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied
25
New cards
Demand for Labor
QUANTITY OF LABOR DEMANDED AND REAL WAGE RATE
(# OF LABOR HRS. HIRED) INVERSELY RELATED
(# OF LABOR HRS. HIRED) INVERSELY RELATED
26
New cards
Things that can cause a shift in DEMAND or SUPPLY
Consumers tastes, wages
Suppliers costs, productivity
Suppliers costs, productivity
27
New cards
Influences of Labor Productivity:
1. Physical Capital Growth
2. Human Capital Growth
3. Technological Advances
28
New cards
ETF’s
EXCHANGE TRADED FUND
basket of securities that can be structured to track anything traded on exchange like stock
basket of securities that can be structured to track anything traded on exchange like stock
29
New cards
Mutual Funds
let you pool your money with other investors to "mutually" buy stocks, bonds, and other investments. They're run by professional money managers who decide which securities to buy (stocks, bonds, etc.) and when to sell them.
30
New cards
Financial Statements
**Balance Sheet-**reports a company's assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity. It provides a snapshot of a company's finances (what it owns and owes) as of the date of publication. (assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity)
**Income Statement-**report a company's financial performance over a specific accounting period. It indicates how the revenues are transformed into the net income or net profit. (revenue, expenses, and net income)
**Statement of Cash Flows-**summarizes the amount of cash and cash equivalents entering and leaving a company. (net cash flow)
\
convey the business activities and the financial performance of a company
**Income Statement-**report a company's financial performance over a specific accounting period. It indicates how the revenues are transformed into the net income or net profit. (revenue, expenses, and net income)
**Statement of Cash Flows-**summarizes the amount of cash and cash equivalents entering and leaving a company. (net cash flow)
\
convey the business activities and the financial performance of a company
31
New cards
EBITDA
**Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization** and is a metric used to evaluate a company's operating performance. It can be seen as a loose proxy for cash flow from the entire company's operations
\
=**Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization**
E=net income
I=interest
T=taxes
D=depreciation
A=amortization
\
=**Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization**
E=net income
I=interest
T=taxes
D=depreciation
A=amortization
32
New cards
Market Capitalization
the total value of all a company's outstanding shares of stock. DETERMINES THE VALUE OF A COMPANY
**Micro-cap-**less than $250 million
**Small Cap-**between $250 million and $2 billion
**Mid-cap-**$2 billion and $10 billion
**Large Cap-**between $10 billion and $200 billion
**Mega Cap-**$200 billion or more
**Micro-cap-**less than $250 million
**Small Cap-**between $250 million and $2 billion
**Mid-cap-**$2 billion and $10 billion
**Large Cap-**between $10 billion and $200 billion
**Mega Cap-**$200 billion or more
33
New cards
Stock Market Indices
**S&P 500-**500 of the largest companies traded on either the NYSE, Nasdaq, or Cboe
**Russell 2000-**2000 small cap companies
**Dow Jones-**30 large-cap American companies
**NASDAQ 100**-100 largest, most actively traded U.S companies listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange. The index includes companies from various industries except for the financial industry, like commercial and investment banks
**Russell 2000-**2000 small cap companies
**Dow Jones-**30 large-cap American companies
**NASDAQ 100**-100 largest, most actively traded U.S companies listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange. The index includes companies from various industries except for the financial industry, like commercial and investment banks
34
New cards
Where is all the money?
Wealthy families, Pension Funds, Endowments, Foundations, Sovereign Wealth Funds, Insurance Companies
35
New cards
Largest Asset Managers by AUM (Assets Under Management)
Blackrock, Vanguard, Fidelity, UBS, State Street Global, Capital Group, T. Rowe Price, AllianceBernstein, etc.
36
New cards
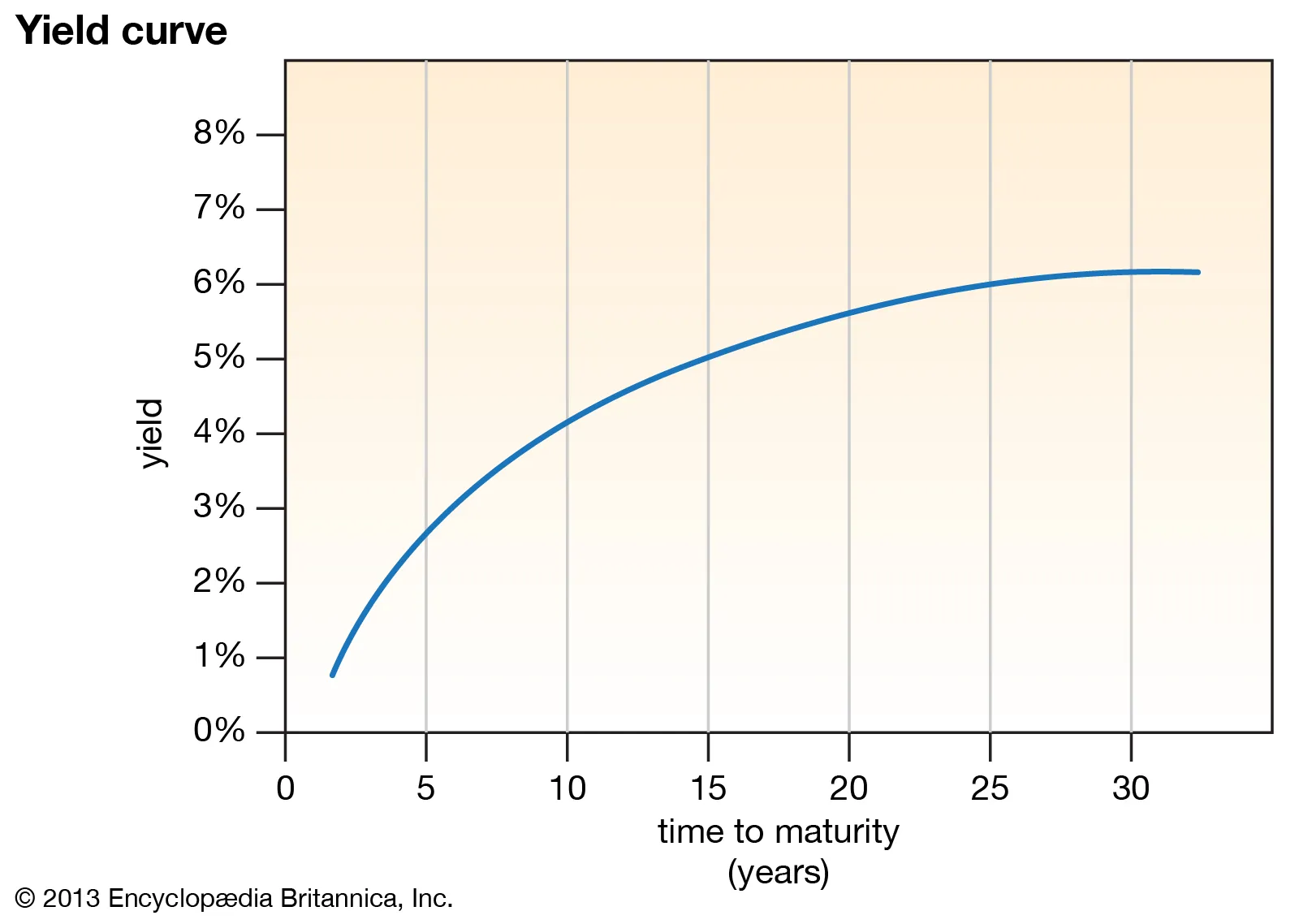
US Treasury Yield Curve
a graphical representation of the interest rates on debt for a range of maturities. It shows the yield an investor is expecting to earn if he lends his money for a given period of time.
37
New cards
Industry Groups and Market Sectors
a way of grouping individual companies or stocks based on common business lines. GICS categorizes stocks into 24 industry groups and 11 sectors.
38
New cards
Commercial Banks
A commercial bank is a financial institution which accepts deposits from the public and gives loans for the purposes of consumption and investment to make profit
\
These institutions make money by lending loans to individuals and earning interest on loans
\
EXAMPLES-
JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, Wells Fargo, and Citibank.
\
These institutions make money by lending loans to individuals and earning interest on loans
\
EXAMPLES-
JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, Wells Fargo, and Citibank.
39
New cards
Investment Banks
a special segment of banking operation that helps individuals or organisations raise capital and provide financial consultancy services to them
advise businesses and governments on how to meet their financial challenges
\
EXAMPLES-
* **JPMorgan Chase**.
* **Goldman Sachs**.
* BofA Securities.
* **Morgan Stanley**.
* **Citigroup.**
* UBS.
* Credit Suisse.
* Deutsche Bank.
advise businesses and governments on how to meet their financial challenges
\
EXAMPLES-
* **JPMorgan Chase**.
* **Goldman Sachs**.
* BofA Securities.
* **Morgan Stanley**.
* **Citigroup.**
* UBS.
* Credit Suisse.
* Deutsche Bank.