Q4 - Clinical Translations II
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
What is treatment planning?
The planning of the management of a patient's dental and oral problems in a systematic and ordered way that assumes a complete knowledge of the patient's needs, the precise nature of the problems and the prognoses of possible management options under consideration
What are the four basic steps that are followed for every examination done?
1. Information gathering
2. Examination and problem identification
3. Problem list, diagnosis, risk assessment and assessing prognosis
4. Developing a comprehensive treatment plan based on 1-3
What is a chief complaint?
A concise statement describing the problem, condition, etc that is the reason for encounter. Usually stated in patients own words
Why is it good to put the CC in the patient's own words?
So that you avoid adding your own diagnostic interpretation into the CC
What is a common side effect of prescriptions?
Dry mouth
What about the patient's diet should you ask about?
- Refined/fermentable carbs
- Acidic food and drinks
- Sugar intake
If you ask for a diet analysis, how long should they do it and when?
It should be at least 3 days including the weekend
Should you mention the diet analysis on the first appointment?
No, they will just lie to you next time you ask
What are some things to keep in mind when motivational interviewing your patient about their habits?
- Help people find the motivation to make a change (they wont do it for you, they will only do it if they want to)
- Collaboration instead of confrontation
- Evocation versus education
- Autonomy over authority
What are some things to be notes from the extra oral exam that are specific to restorative dentistry?
- Symmetry
- TMJ
- Visible occlusal plane
- Lip line
- Smile line
- Esthetics
What is used to diagnose occlusal caries?
ICDAS 0-6 based on visual examination
What is used to diagnose interproximal caries?
E0-D3 diagnosis based on radiographic presentation
How can you tell whether a lesion is active or inactive?
Color and surface texture
Active = yellow, dull, soft
Inactive = darker, hard, shiny
What are some additional tests and records that could be included in information gathering?
- CBCT
- Medical tests
- Photographs
- Pulp testing
- Alginate impressions
What is a provisional diagnosis?
This is a working diagnosis that needs to be further investigated either by further testing or a specialist
What is a definitive diagnosis?
A diagnosis that you conclude based on presented information ex. caries, periodontal diagnosis, TMD
T or F
There does not have to be a prognosis for every diagnosis.
False; there should be a prognosis for every diagnosis
What is a problem list?
Summary listing the patient's complaints, lesions found, conditions, and all things needing treatment. Should be organized by the priority of problems
Once you have a problem list from the patient's exam, what should be done?
- Determine if further consultations are needed
- Investigate what might cause treatment modifications
- Sequence the proposed treatment plan
What are the phases of a treatment plan?
1st systemic - determine tx modifications
2nd Acute - CC and Emergency
3rd Disease control
4th Definitive - fixed restorations
5th Maintenance
When is the systemic phase of treatment planning needed?
- Presence of systemic disease
- When patients need further evaluation from medical providers
- If you need to alter or limit tx
- Prevention of medical emergencies
What are some categories of patients who need systemic phase of treatment planning?
- Special care patients
- Oral cancer patients
- Pediatric patients
- Geriatric patients
- Substance abuse patients
How does systemic disease impact treatment planning?
- May need to postpone tx
- Consultation with physician
- Stress management
- Prescribing or altering meds
What is acute treatment planning?
A dental problem that needs immediate attention such as an emergency or urgent matter. Could coincide with the CC
What are some examples of problems that are addressed in acute phase of tx planning?
- Complaint of pain
- Complaint of swelling
- Esthetic complaints
- Truama
When planning for acute needs during the acute phase, what should you make sure to think about and discuss with the patient?
- Consent for acute phase
- Range of tx options
- Taking into considerations long term implications
What is minimally invasive oral care?
a contemporary and holistic preventive approach to caries management putting the patient and their oral biology at the forefront
What is minimally invasive dentistry?
Tissue preservation by preventing and intercepting disease and removing as little tissue as possible
What are the main principles that allows minimally invasive dentistry to be successful?
- Modern understanding of disease
- Successful bonding
- Adhesive bioactive materials
When are diseases of the mouth usually addressed?
Phase 3 Disease control
What are some factors that impact the decision for restorative treatment?
- Patient preferences
- Risk level of patient
- dental materials
- Remaining tooth
What is the goal of disease control phase?
Remove etiologic factors of disease and stabilize the patients oral and overall health
What is one part of oral health that MUST be stabilized before restorative treatment?
Periodontal disease will have a significant impact on the prognosis of restorative treatment and must be stabilized prior to the definitive phase
What phase is elective endodontic treatment planned in?
Phase 3 Disease control
What is CAMBRA and what does it do?
Caries Management by risk Assessment addresses the caries risk of the patient including diet, habits, preventive measures, lesions, and overall health. CAMBRA identifies the caries risk of a patient which allows us to reduce the risk via preventive interventions
What should be done with large carious lesions?
- Take into account caries risk
- Check pulpal status
- Determine restorability of tooth
What should be done with small to medium carious lesions?
- Take into account caries risk
- Choose material according to clinical situation
When treating deep carious lesions, how should you plan to treat?
Plan to treat with the least invasive option first, but inform the patient of the possibilities of the caries being deeper
What should be done if there is a deep carious lesion, and the pulp is vital with no apical pathology?
Plan to do a filling first
What should be done if you have to leave affected dentin over the pulp ?
Place an indirect pulp cap
What should be done if you are treating a carious lesion that will be an indirect restoration?
Remove all decay
What should be done if you are treating a carious lesions and the pulp is involved?
Endodontic treatment
How do you manage erosive tooth wear?
- Diagnose
- Prevention
- Monitor
- Treat if neccesary
What are some ways to prevent and help treat erosive wear?
- Reduce acids
- Strengthen defense mechanisms
- Strengthen tissues
- Protect surfaces
- Restore lost tooth structure
What is the holding phase?
The time between disease control and definitive phases that allow for the resolution of inflammation and time for healing. After this phase you reassess before definitive care is began
What happens in the definitive treatment phase?
- Advanced perio therapy
- Ortho
- Definitive restorations
- Esthetic dentistry
- Prosthetic
When is a post and core build up needed?
Endo treated tooth with less than 50% tooth structure remaining
What are ways to replace missing teeth?
- Fixed partial denture
- Bridge
- Removable
- Implant
- no treatment
What happens in maintenance phase?
- Periodic exams
- Prophy or perio maintenance
- Fluoride application
- OHI
What determines the recall frequency?
The patient's oral health and risk for disease and caries
What are advantages of incremental layering?
- Mitigate C factor (volumetric shrinkage of resin)
- Efficient curing
- Reduces post op sensitivity
- Reduces microleakage
- Help build shade
What should the base layer be for incremental layering?
Flowable
How thick should each layer be for incremental layering?
2mm
How should increments be added for incremental layering?
Increment should touch one wall and slope towards the other but NOT TOUCH the other wall.
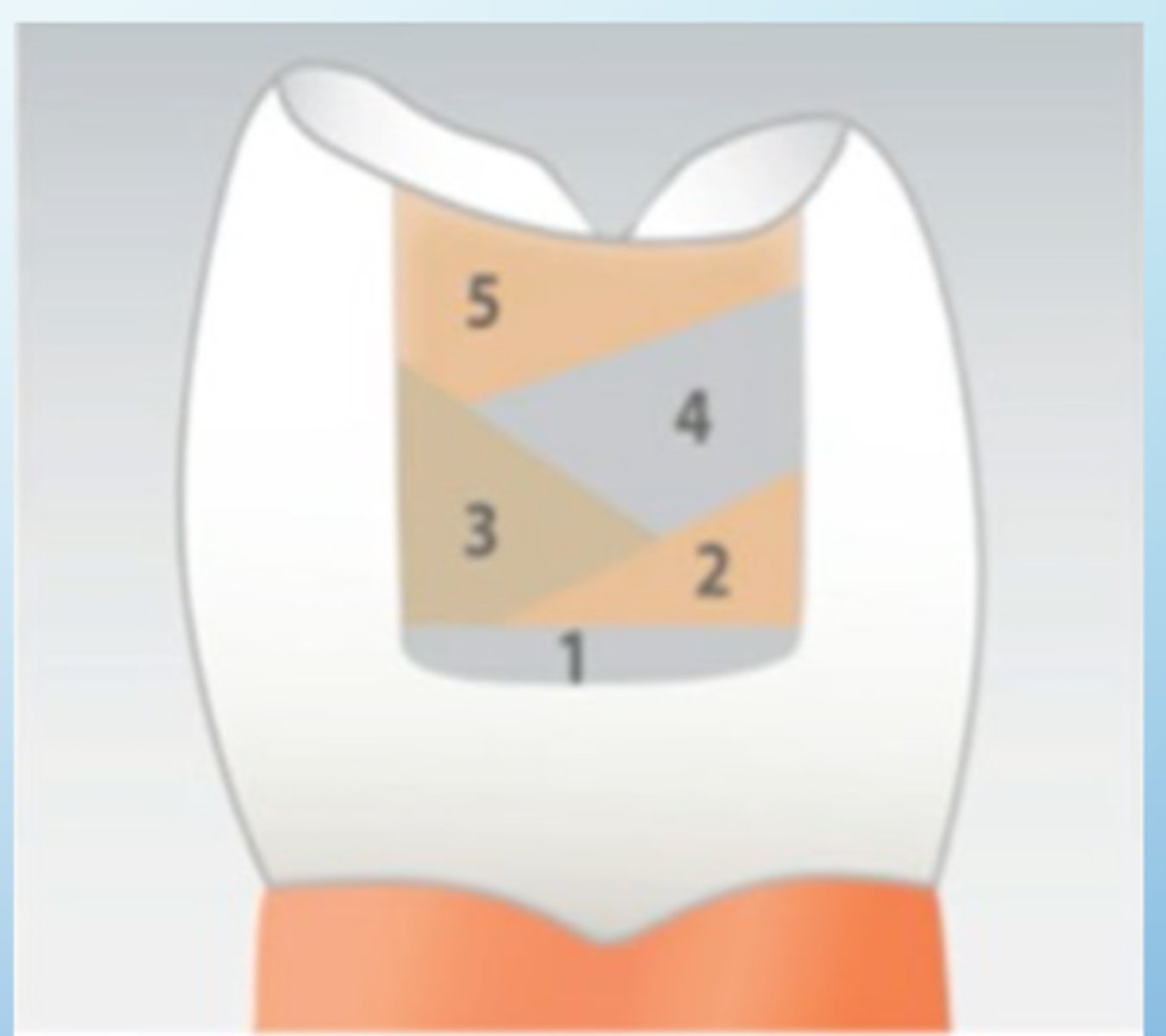
How do you check for flash?
Move the explorer from tooth structure to resin
What direction should the polishing burs move?
From resin to tooth structure
When restoring an anterior tooth using incremental layering, where should enamel shades be placed?
Facial and lingually
Where is opacity more prominent in anterior teeth?
Cervical 1/3 due to thicker dentin
Where is translucency more prominent in anterior teeth?
Incisal 1/3 where dentin is thin and there is almost only enamel
When do you select shade for anterior incremental layering?
Before preparing the tooth so that you can see the color of the hydrated teeth
When shade matching, where should you look for the enamel shade? What about dentin shade?
Dentin shade should be matched at gingival 1/3
Enamel shade should be matched at middle 1/3 where enamel is thickest
What are the two types of hydrocolloid gels?
Reversible and irreversible
What type of hydrocolloid is used for final impressions?
Reversible
What type of hydrocolloid is used for alginate impressions?
Irreversible
What are some advantages and disadvantage to reversible hydrocolloid?
Pro: Accurate, with good detail
Cons: Weaker than VPS, susceptible to changes in moisture and water, technically difficult
What is the structure of alginate?
Mannuronic and glucaronic acid linear polymer
What are some disadvantages of alginate?
- sensitive to temperature
- will distort
-
What sets faster alginate or VPS and what advantage does this have?
Alginate sets faster meaning less distortion however movement during setting can cause distortion and tears
T or F
Upon alginates rapid setting, it can be removed from the patients mouth immediately.
False; it still needs extra set time to achieve strength to be removed from the mouth
Aliginate works best in ____ cross sections.
large
VPS impression material works best in _____ cross sections.
thin; this is due to shrinkage of the material -> thin = less shrinkage
Does VPS shrink?
Yes
What are indications for impressions?
- Study casts
- Working model for wax ups
- Ortho
- Custom trays
When taking impressions for stayplates, what tissue must be captured?
Palate and lingual soft tissue of mandibular arch
How are stayplates retained?
With wire clasps on the facial or undercuts in the lingual gingival embrasures
What do you want to capture in your diagnostic impression?
Teeth, related soft tissues, including vestibules and hard palate
What should you consider if a patient has extremely mobile teeth before taking an impression?
Use vasoline or blockout to ensure there is not premature extraction or plan impression post extraction
What are common difficulties with impressions?
- Limited operator skill
- Teeth not clean
- Unusual arch form
- Deep or cleft palate
- Severe residual ridge resorption
- Huge arch
What are some contraindications of impressions?
- Highly mobile teeth
- Excessive calculus
- Open lesions/wounds
- Less than 1 week post op
- Sensitive teeth
What can you do to help patients that are gaggers when taking impressions?
- Rehearse
- Encourage distraction
- Topical application of anesthetic
Generally, what is the difference between tray sizes for impressions?
5mm difference
What should be done regarding undercuts before taking an impression?
Block out with resin or teflon tape
Are VPS and alginate adhesive the same?
NO they are both blue but they are not the same or interchangable
How do you load a maxillary tray?
1 increment from the back
How do you load a mandibular tray?
3 increments starting at the front then one side and the other
How should you hold a mandibular tray as it sets?
One finger over each molar
How should you hold a maxillary tray as it sets?
One finger in the middle of the palate
Where should the lips be when an impression is getting taken?
Over the tray
When are some times you can use rope wax on an impression tray?
- Posterior border to keep alginate from running
- Tray extension for 3rd molars
- High vaulted palate place rope wax on the palatal part of the tray
How should alginates be stored after they are taken?
They are rinsed, sprayed, and wrapped in a moist towel and placed in a plastic bag until they can be poured up
What are some causes of inadequate impressions?
- Wrong tray size
- Bad tray retention
- Undermixed
- Poor seating
- Distortion
What are characteristics of successful impressions?
- Centered
- Captured all teeth
- Captured vestibule, muscle attachments, palate, floor of mouth
What is the purpose of the kois dento facial analyzer?
Accurately relate in 3D space the condylar relationship between mandible and maxilla
What is the average axis-incisal distance ?
100 mm
What is the best position to take a kois analysis?
Eye to eye with the patient
How should the kois analyzer be set up?
Bow should be parallel to the horizon
Vertical rod should bisect the face
Have the patient open and place the index tray into the mouth until you feel teeth touch. Keep position until material is set
How should you load material into the kois analyzer?
Tripod (one dot at anterior and one dot on each side near molars)
T or F
The facial midline is always related to the dental midline
True
T or F
We an use the interpupilary line to measure parallel to the horizon when using the kois analyzer.
FALSE; their interpupillary line may not be parallel to the horizon
What are three things that are needed for a good outcome with the laboratory and restorations?
- Impression quality
- Model Quality
- Mounting Quality