BIOL 1406 - Lecture Exam 2
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Eukaryotic cytoskeleton
network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. functions in structural support for the cell and in motility and signal transmission
components are made of protein: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules
Microfilaments
thin rods made of actin that function in muscle contraction , amoeboid movement, cytoplasmic streaming, and support of microvilli
Intermediate filaments
support cell shape and fix organelles in place, made of keratin proteins
Microtubules
shape the cell, guide organelle movement, and separate chromosomes in dividing cells
form core structure of cilia and flagella
Extracellular matrix
a non-cellular network of proteins and polysaccharides that surrounds and supports cells in tissues and organs
Composed of mostly collagen
Plasmodesmata
microscopic channels in plant cell walls that connect the cytoplasm of adjacent cells, allowing for the movement of water, ions, and molecules
Tight junctions
this junction establishes a barrier that prevents leakage of extracellular fluid across a layer of epithelial cells
the plasma membranes of neighboring cells are very tightly pressed against each other, bound by specific proteins
Desmosomes
fasten cell membranes together into strong sheets
a type of anchoring junction
Gap junctions
provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to an adjacent cell, allowing cells to communicate
also called communicating junctions
Plasma membrane fluidity
Unsaturated fatty acid tails prevent packing
Cholesterol reduces membrane fluidity at moderate temps but at low temps hinders solidification
Movement
all directions, all the time
Net movement
NEVER all directions all the time
Diffusion
Net movement that follows concentration gradient (high to low)
Cellular membranes
____________ are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins
Passive transport
Net movement follows concentration gradient (simple + facilitated)
No energy is used
Simple diffusion
net movement follows concentration gradient
small and uncharged molecules (gases, steroids, H2O but difficult)
Facilitated diffusion
net movement follows concentration gradient
diffusion with help from protein channels or carriers (aquaporins)
ions, biomolecules, and H2O
Osmosis
diffusion of water molecules
[water] is hidden, so use [solute] to find net movement
Tonicity
the ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
Isotonic
What type of solution is this?
same [solute]
no net movement of water
Hypertonic
What type of solution is this?
higher [solute]
net movement of water out of the cell
Hypotonic
What type of solution is this?
lower [solute]
net movement of water into the cell
Active transport
uses energy to move solutes against their gradients
ex: Na+/K+ pump
Exocytosis
the cell secretes certain molecules by the fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane
Endocytosis
the cell takes in molecules and particulate mater by forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane
First law of thermodynamics
the amount of energy in the universe is constant
Second law of thermodynamics
energy conversion increases the disorder (entropy) of the universe
Chemical energy
the potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction
Gibbs free energy
the portion of a system’s energy that can perform work when temperature and pressure are uniform throughout the system (G)
Exergonic reaction
G change is negative; reactants have more free energy
Breaking covalent bonds releases energy (chemical energy, heat, light)
catabolic reaction
Endergonic reaction
G is positive; products have more free energy
Forming covalent bonds stores chemical energy
Energy coupling
the use of an exergonic process to drive an endergonic one
Enzymes
speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers (activation energy)
reusable catalyst
Activation energy
the amount of energy needed to push the reactants to the top of an energy barrier
Substrate
describes reactant molecules that bind to the active site of an enzyme
Cofactors
a non-protein chemical compound that is required for an enzyme to function, a coenzyme
Competitive inhibitors
reduce the productivity of enzymes by blocking substrates from entering active sites
Noncompetitive inhibitors
impede enzymatic reactions by binding to another part of the enzyme cause it to change its shape
Feedback inhibition
a metabolic pathway is halted by the inhibitory binding of its end product to an enzyme that acts early in the pathway
Allosteric regulators
inhibit or activate enzymes with quaternary structure
bind to regulatory site and keep enzyme in a specific shape
Induced fit
substrate binding to active site causes temporary change in enzyme’s 3D shape
Adenosine triphosphate
what molecule is this?
3 phosphate groups
1 sugar ribose
1 nitrogenous base (adenine)
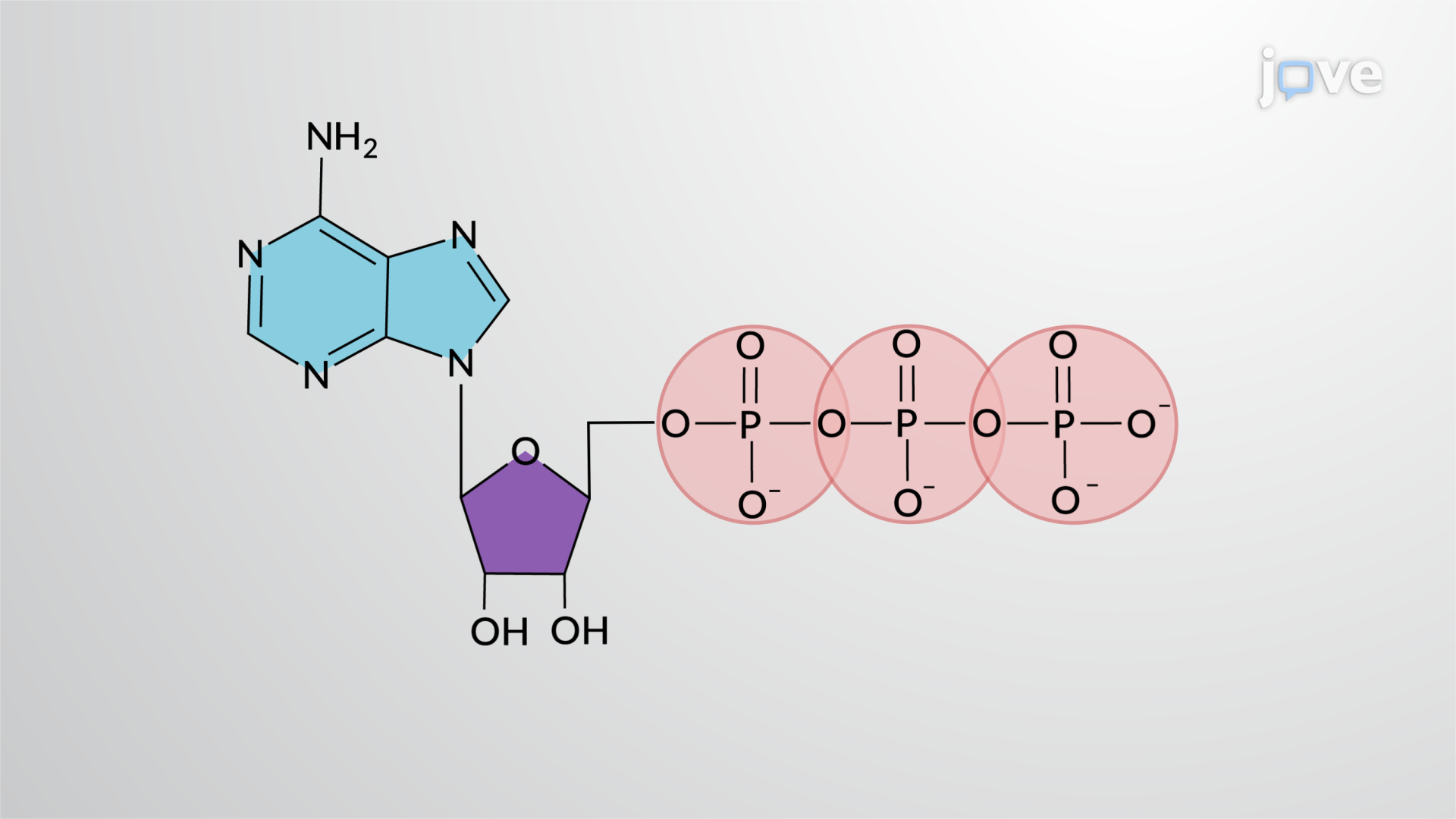
ATP hydrolysis
reaction of ATP and water that yields inorganic phosphate and ADP and releases energy (chemical and heat)
powers cell work
Cellular respiration
an aerobic (O2) and catabolic (breaking down glucose) pathway
Pathway
a series of chemical reactions giving the cell control over ATP yield
Cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6+6O2—>6CO2+6H2O+Energy(ATP, heat)
Redox Reaction
in cellular respiration:
glucose loses electrons (oxidized)
O2 gains electrons (reduced)
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
NAD+ —> NADH
can carry 2 electrons
NADH function
delivers electrons to the mitochondrial electron support chain
Electron transport chain
series of molecules that pass electrons to O2, maintains proton gradient
built into the inner membrane of the mitochondria
Glycolysis
occurs in cytosol
break down glucose to extract electrons
some ATP synthesis (substrate level phosphorylation)
Pyruvate oxidation
occurs in mitochondrial matrix
produces acetyl coenzyme A
Citric acid cycle
occurs in mitochondrial matrix
starts with acetyl coenzyme A
extracts many more electrons
some ATP synthesis (substrate level phosphorylation)
Oxidative phosphorylation
involves mitochondrial inner membrane, matrix, intermembrane space
produced 90% total ATP
Energy investment phase
glucose split to form glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
2 ATP used per glucose
part 1 of glycolysis
Energy payoff phase
In what phase does this occur?
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate converted to pyruvate
per glucose: net 2 ATP, 2 NADH, H+, H2O, 2 pyruvate
Glycolysis products
per glucose:
2 pyruvate
net 2 ATP
H2O
H+
2NADH
Pyruvate oxidation products
per glucose:
2 acetyl coenzyme A
2 NADH
H+
CO2
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
a coenzyme that acts as an electron carrier in cellular respiration
FAD+ —> FADH2
Citric acid cycle products
Per glucose:
6 NADH
2 FADH2
2 ATP
2 oxaloacetate
H+
CO2
Chemiosmosis
an energy-coupling mechanism that uses energy stored in the form of an H+ gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work.
NADH
What singular electron carrier yields 2.5 ATP?
FADH2
What singular electron carrier yields 1.5 ATP?
30 or 32
How much ATP is produced in total?
Oxidative phosphorylation products
Per glucose:
26 or 28 ATP
H2O
Fermentation
anaerobic ATP production
glycolysis produces net 2 ATP, 2 NADH per glucose
NAD+ regeneration: NADH —> NAD+
Alcohol fermentation
pyruvate is converted to ethanol
Per glucose:
net 2 ATP
2 NAD+
2 ethanol
CO2
Lactic acid fermentation
pyruvate is reduced directly by NADH to form lactate as an end product
Per glucose:
net 2 ATP
2 NAD+
2 lactic acid
Qualities of semi-permeable membrane
phospholipid bilayer
biomolecule mosaic
fluid mosaic bc of cholesterol and phospholipids