Prelab Questions BIO206L
1/211
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
Bacteria cell wall function
protect cell from lysis
Gram - has, + doesn’t
outer membrane
crystal violet binds to
peptidoglycan
adding iodine solution produces
large crystals
Gram - bacteria turn pink/red when you stain with
safranin
gram staining, hot plate at:
2.5
slide removed from hot plate when:
water evaporates
post-evaporation heat-fixing time on hot plate
1 min
all dyes absorb for
1 min
decolorizer drips over sample for
up to 15 secs
gram staining procedure
crystal violet stain, iodine, alchohol, safranin
alcohol washing turns gram - bacteria _____
colorless
safranin turns gram - bacteria
pink
E. Coli is gram _ and morphology __
-, bacillus
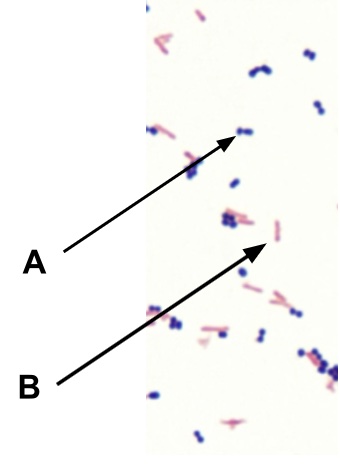
ID the gram + Enterococcus
A
Morphology and Gram status
+, bacillus
MacConkey agar grows Gram
-
Gram-stained bacteria growing on MacConkey agar should be ____
pink
Why is gram staining differential
peptidoglucan cell wall
counterstaining in gram staining is for
enhancing contrast of stained bacteria
after crystal violet, if you forget iodine, what would happen?
gram + and - bacteria appear pink
align 10X objective with:
nosepiece
total magnification =
objective*10
better resolution is with 200 nm or 1000nm?
200 nm
micrometers per reticle unit and magnification are _______ related
inversely
biggest field of view with ___ objective
4X
biggest depth of field in focus with ___ objective
4X
can use coarse knob with ___ objective
4X
immersion oil for ___ objective
100X
100X objective has direct contact with immersion oil?
no
cleaning the objective lens/immersion oil:
use lens cleaner and lens paper
colors: gram - is ____, gram + is ______
red/pink, purple/violet
gram + bacteria are purple after staining because
bacteria retains the crystal violet-iodine complex
L-form/no cell wall bacterium is stained, what color?
pink
why do you gram stain bacteria
ID cell wall characteristics to help classify bacteria into broader taxonomic groups
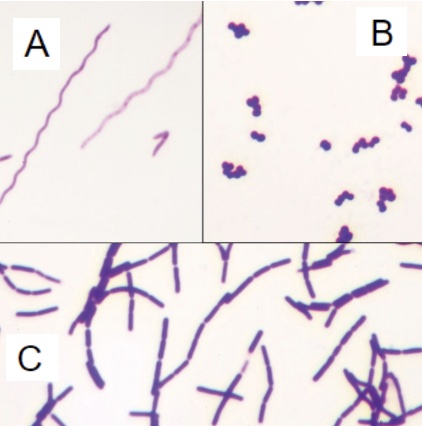
ID the bacillus gram +, coccus gram +, and spirillum gram - bacteria
C, B, A
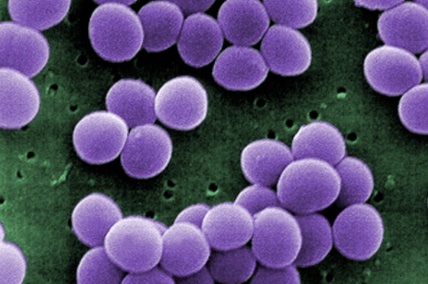
streptococcus, staphylococcus, or diplococcus?
streptococcus
week 9 lab purpose
verify soil isolates are bacteria via PCR and gel electrophoresis
PCR amplification enzyme
DNA Polymerase
what is not a step in PCR
sequencing
denaturation step temperature
95 C
what is NOT in the master mix:
primers
amplify means to _____
copy
The 27F and 1492R primers will anneal to _______, providing a starting point for Taq polymerase.
bacterial DNA
The DNA sequence amplified when the 27F and 1492R primers are used is approx ____ bp
1500
27S and 1492R primers are specifically for the _____ gene on _____ chromosomes
16S rRNA, bacterial
denaturation is
separating DNA strands
Taq polymerase synthesizes primers: T/F
F
T/F: Taq polymerase can only synthesize complementary DNA if it's given a primer.
T
What happens during the coolest stage of PCR?
Primers anneal to complementary seequences
Taq polymerase active temp
72 C
Expected contents of PCR tube when using bacterial chromosome:
millions of 16S rRNA gene sequence copies
Negative Control PCR tube post-reaction if there is NO contamination contains what?
no copies of the desired sequence
Expected Contents of Positive Control PCR Tube
amplified 16S rRNA gene
successful amplification shows as what in the gel?
1500 bp amplicons in a band
how do you confirm no contamination in gel electrophoresis
no band in negative control lane
positive control lane expected result:
1500bp band size
if bacteria can’t be lysed, then PCR reagents can’t access bacterial chromosome. will amplification happen? band?
neither will happen
agarose gel in electrophoresis does what:
separate DNA molecules by size
agarose gel electrophoresis procedure steps:
make solid gel, place in chamber, add buffer, load DNA ladder and all samples, apply current, measure the bands using the DNA ladder
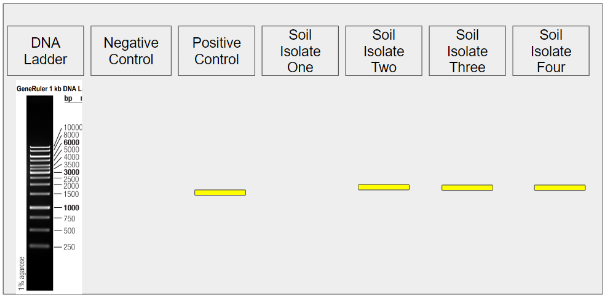
determine reagents contamination using which lane?
negative control
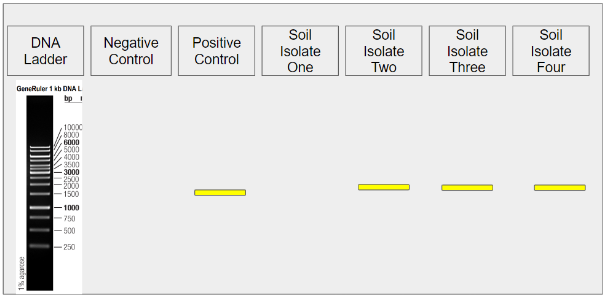
is this the expected result
yes
which lane to check for expected result of gel electrophoresis
positive control lane
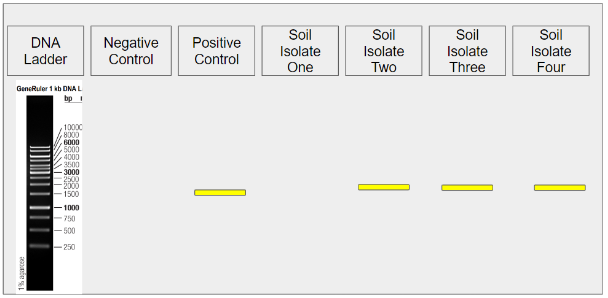
Isolate 1: bacteria or not? And how to confirm?
not bacteria, check if 1500bp band present in the lane
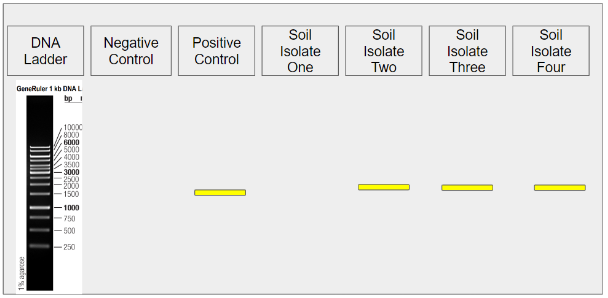
Isolate 2: bacteria or not?
bacteria
motility test - motile bacteria are ___ relative to the inoculation line
disperse from line/diffuse growth pattern
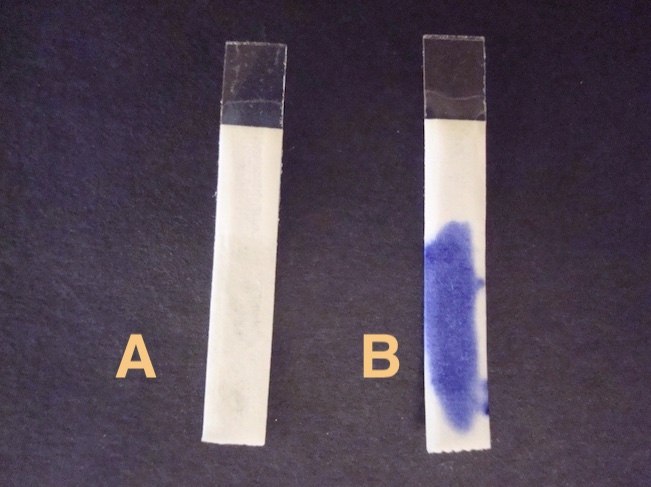
which is cytochrome c oxidase positive?
B
what to add to the oxidase reagent strip before bacteria
water
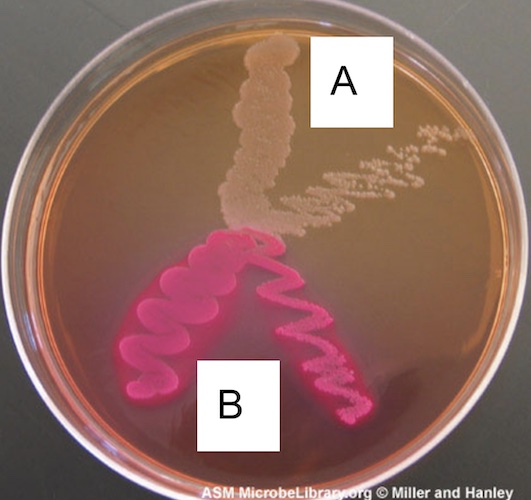
Which one is gram - (macconkey agar)
both
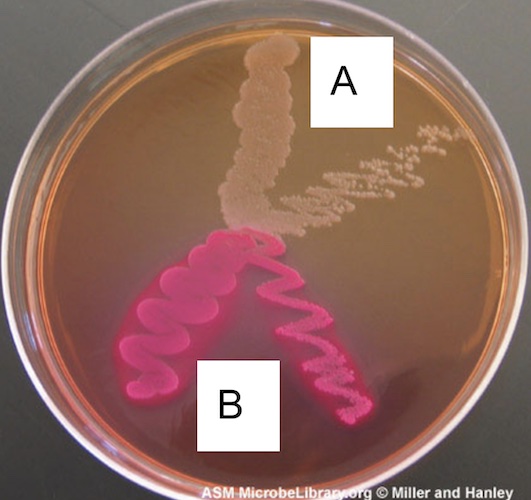
which ferments lactose?
B
MacConkey agar exigence
fecal matter contaminated drinking water
macconkey agar selects for enteric (gut) bacteria using
bile in the agar
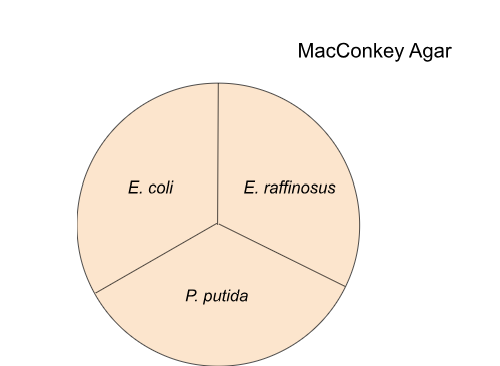
E. Coli will grow/not grow and be what color?
grow, pink/red agar
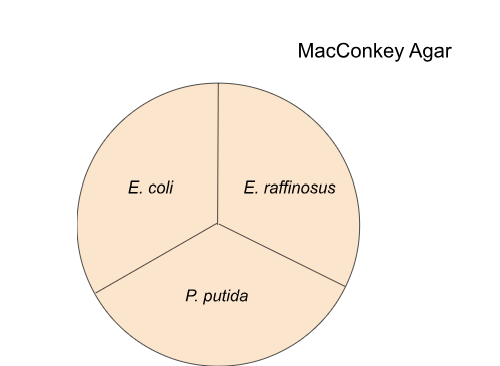
E. raff will grow/not grow and be what color?
card response pending
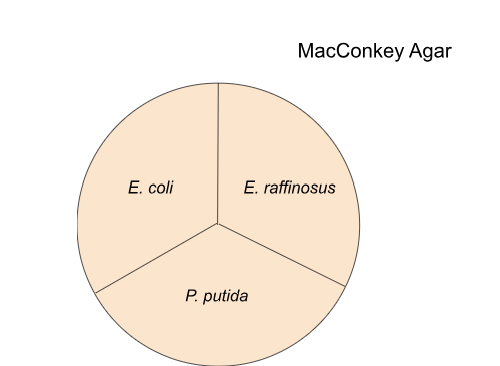
P. Putida grow/not grow and if so what color?
grow, agar color doesn’t change
Gram + bacteria on macconkey agar: grow/not grow
not grow
Why does a clear zone surround beta-hemolytic bacteria?
bacteria break down red blood celss
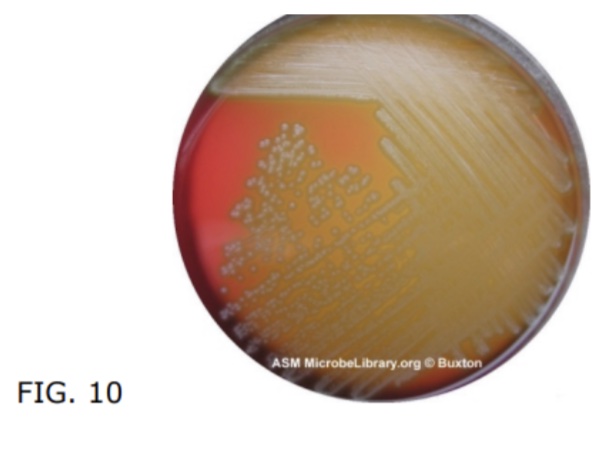
hemolysis type?
alpha
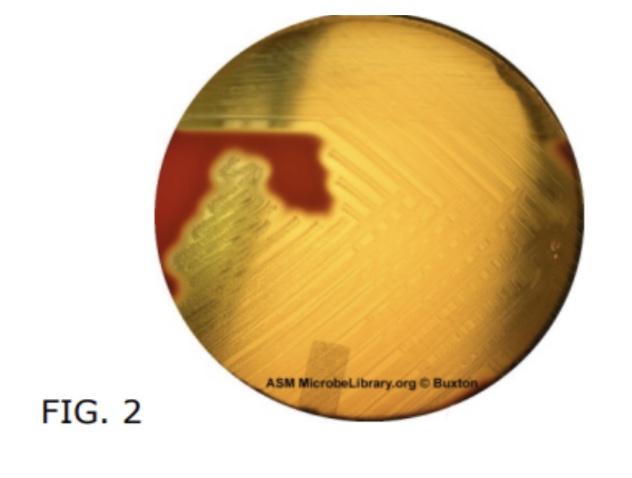
hemolysis type?
beta
on blood agar, E. coli shows
clear zone
on blood agar, E. raff shows
clear zone
on blood agar, P. Putida shows
green
we used ____ blood agar plates
2
catalse + bacteria make ____ bubbles
O2
where do catalase test
fume hood
how much H2O2 in a catalase test sample
1-2 drops
catalase is important because
h2o2 damages cell components
E. raff on blood agar tests Catalase + falsely, because____
Catalase is in mammalian blood
oxidase test is for presence of:
aerobic respiration
catalase test is for
h2o2 breakdown
macconkey agar tests for
lactose fermentation/breakdown
motility test is for
flagella presence
hemolysis test is for
red blood cell breakdown
antibiotic resistance
bacteria grow despite drug that once prevented its growth
antimicrobial resistance mainly driven by
overuse
WHO fact shet reports ___% of UTIs from E. coli were less susceptible to ampicillin
20
The same gene that provides resistance to ampicillin spreads from a strain of E. coli to a different bacterial species (e.g., a Staphylococcus species.). How did this happen?
horizontal gene transfer
antimicrobial resistance occurs naturally too: T/F
true
this mechanism doesn’t drive antibiotic resistance:
Antibiotic inactivation by enzymes
Decreased cellular uptake
Antibiotic target mimicry
Bacterial colony signaling
bacterial colony signaling
bacterium has efflux pump exporting multiple different antimicrobial drugs, therfore giving it multiple resistances, AKA
cross-resistance