Lecture 18: Photon Dose Algorithms
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Which algorithms are model based?
convolution superposition and MC and Boltzmann Transport solvers
What are the major advances in dose algoritms?
Splitting radiation dose into primary and secondary components
Tissue densitometry using x-ray CT
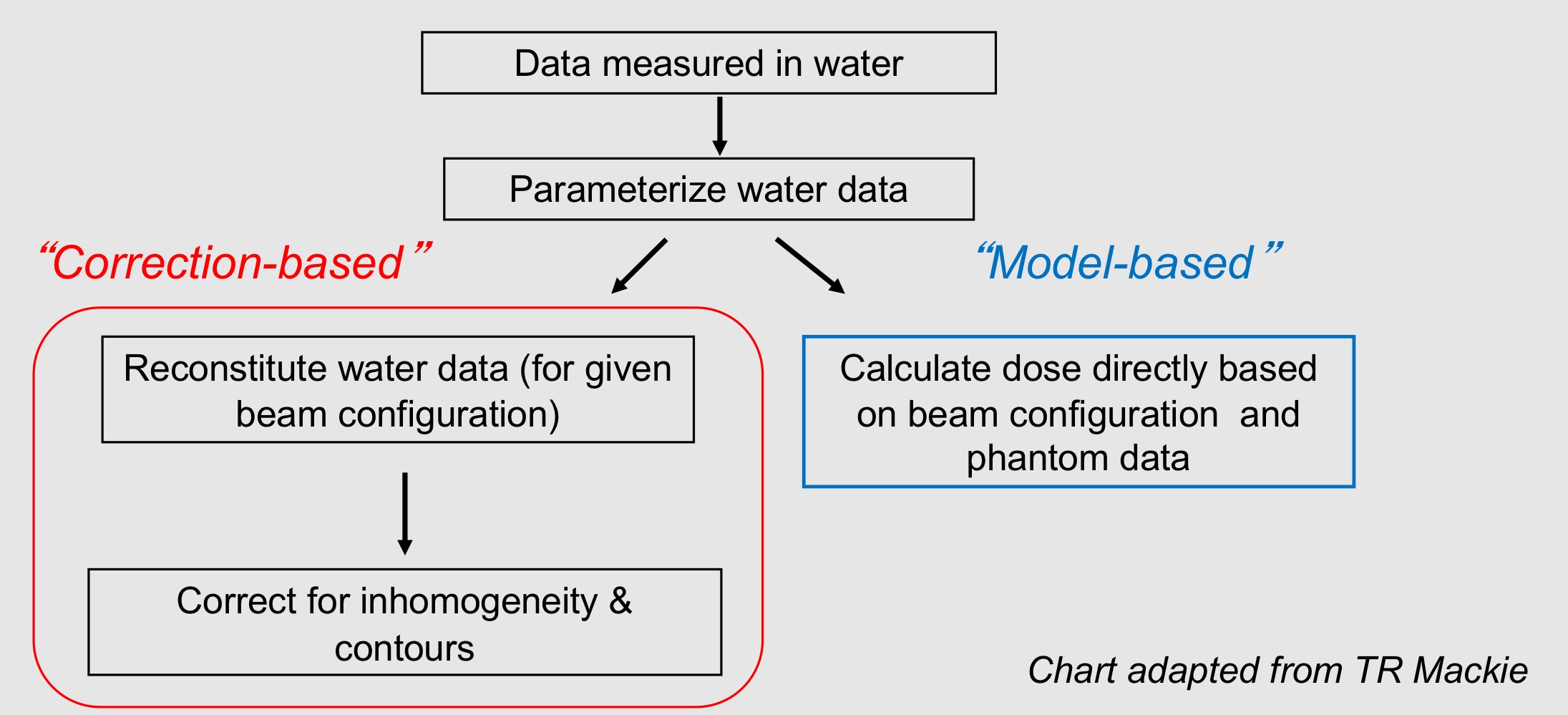
correction-based dose algoritms
corrects dose distribution in water under standard condition to that of the patient deliver, contour and heterogeneity
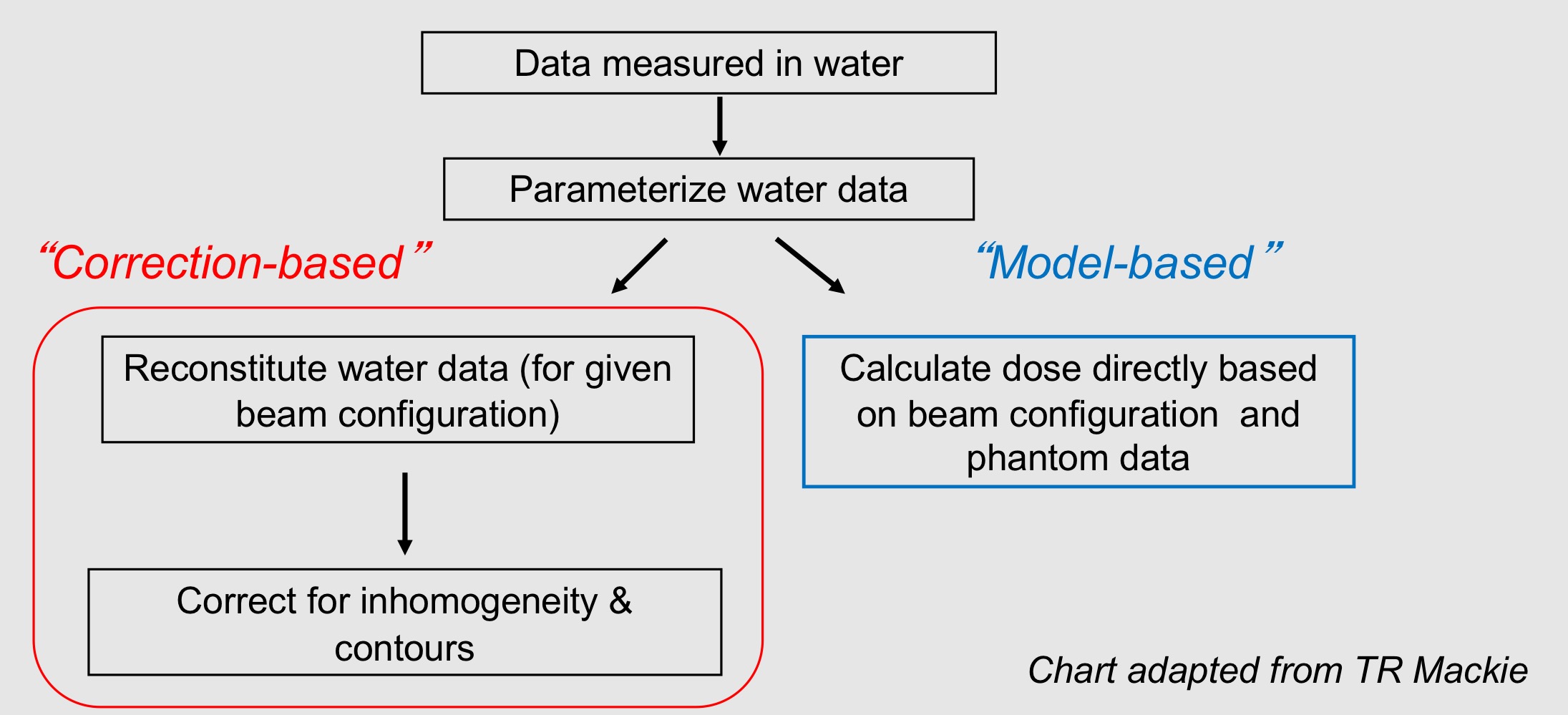
model-based dose algorithms
compute dose from first principle using patient geometry and density data and a model of radiation beam
What two effects should be considered for tissue inhomogeneties?
attenuation of primary beam (distribution of scattered photons)
secondary electron fluence
Purpose of Ray tracing?
Predict path of primary photons throughout patient volume
Reshape kernels for each pair of interaction-dose deposition sites
Most commonly used convolution based method
convolve impulse (TERMA at a point) function with energy deposition kernel
Why is Terma commonly used for convolution based algoritms? Why no collisional Kerma?
Collisional kerma will underestimate the dose; it excludes radiative loss by charged particles
How is Terma computed?
model fluence from linac head and transport it through the patient
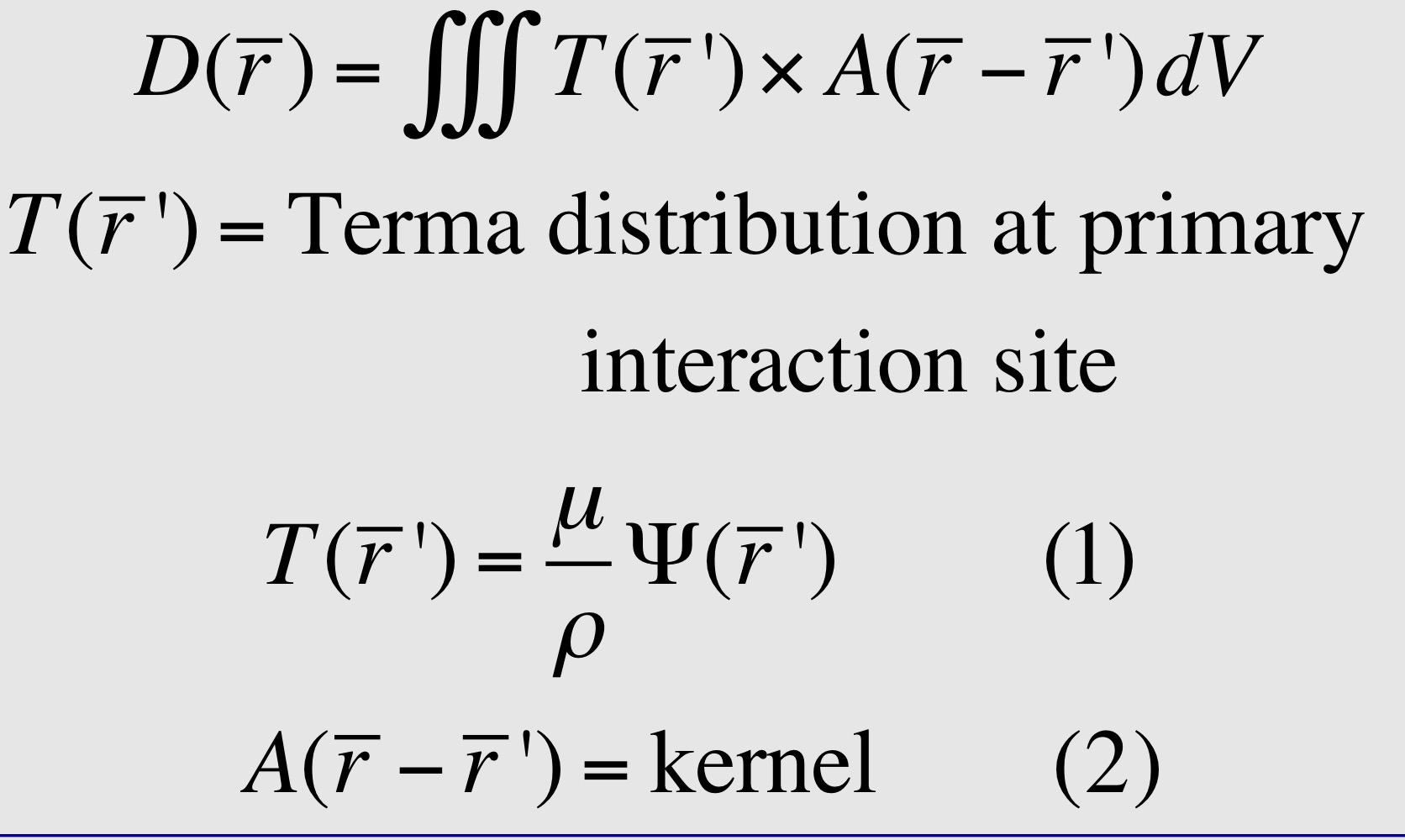
If beam hardening is not being considered, what can be pulled out of the integral?
μ/ρ
What are the real-life complications of spatially invaraint kernels used in convolution-based photon dose algoritms?
tissue inhomogeneities, polyenergetic beams, beam divergence
How are inhomogeneities dealt with in model-based dose calculations with point kernels?
Model incident fluence as it exits Linac head
Project fluence through CT data, compute TERMA at each point as a function of radiological pathlength, attenuating it by μ/ρ
Scale kernel as a function of radiological pathlength between interaction point and dose point
Perform 3D convolution/ superposition
O’Connor’s Theorem
O'Connor's scaling theorem says that the ratio of the fluence of secondary particles to that of primary particles, caused by an external source irradiating a medium in a collimated beam, is the same in two uniform media of the same composition but different density, provided geometrical distances are scaled inversely to density.
Is Monte Carlo an approximation of the Boltzmann Equations?
No, it directly obtains the Boltzmann Transport Equations
How are the boltzmann transport equations implemented clinically?
Linear Boltzmann Transport Equation solver with discrete ordinate approximation
MC will converge if….
infinite particles are used to run
BTE will converge if…
infinitesimally small energy, angle, and space grid sizes are used
What limits the statical accuracy of MC algorithms?
number of histories run
What limits quality of outcome for MC algorithms?
goodness of geometric model, tissue, and underlying physics data
Why are MC algorithms used for MR-guided systems?
Can account for magnetic field
What is a disadvantage of MC algorithms?
Long calculation times
Is MC algorithms more common for electrons or photons?
electrons
What so the BTE solution yield?
It yields the spatial distribution of charged particle fluences. This is converted to the dose distribution
What is the speed of BTE dependent on?
dimensionality of problem
How is electron contamination calculated?
scalar quantity added to the end