Ch 34: Hemichordates and Chordates
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Deuterostomes part 2 - Echinoderms, Hemichordates, Chordates
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Phyla Hemichordata
Acorn worms
deposit feeders
bilateral symmetry
2 of 4 chordate characteristics:
pharyngeal gill slits
allow water to leave and filter nutrients (we had them as embryos)
dorsal hollow nerve cords
marine worms that live in mud, sand, and under rocks
Tornaria larva: very similar to bipinnaria echinoderm larva
3 main body parts: proboscus (before the mouth, sand burrowing) — collar — trunk
mouth between proboscus and collar
class Enteropneusta: gut breathing — reference to gill slits (acorn worms)
Hemichordata Class Pterobranchia (body plan)
“wing gills”
deep oceans
secrete a tube that they live within
have a U-shaped digestive tube
complete with diverticuliti
planula-like larva
closed circulatory system (blood lacks cellular elements and color)
filter feeders
gill slits
excretory: diffusion across body wall
Decentralized NS
diecious (external fertilization)
Phylum Chordata (“cord”)
Small phyla
5% are invertebrates: Two invertebrate groups
Urochordates (sea squirts/tunicates, make up 90% of invertebrate chordates) and cephalochordates (lancelets)
Diverged from common ancestor shared with echinoderms
Because of egg yolk
3 subphylum:
Cephalochordates (lancelets)
Urochordates (tunicates)
Vertebrates
Myxini (hagfish) and Petromyzontida (lamprey)
4 characteristics
Notochord
Dorsal hollow nerve cord
Pharyngeal slits or clefts
Post-anal tail
closed circulatory system (ventral heart)
complete digestive system
Lecithal & microlecithal
latin for yolk
little amount of yolk (humans and echinoderms)
megalecithal = large amount of yolk (chicken)
telolecithal = yolks at one end of the egg — yolk is not evenly distributed between eggs
homolecithal = yolk is evenly distributed between eggs
endostyle and thyroid
1) gland found in pharynx of basal chordates
more of a feeding gland that secretes mucus
2) developed into the thyroid gland
produces T3 and T4
Important for metabolism, energy production, growth, neurological development
Both require iodine
goiter
hypothyroidism (low iodine)
pharyngeal slits
completely perforate into the pharynx
can be used for jaw structures, respiration, or feeding
dorsal hollow nerve cord
anterior end forms brain
fluid with cerebrospinal fluid that we are constantly producing
notochord
humans absorb it and can be in spine
flexible rod
pharynx
connects respiratory system and digestive system
slits:
simple: filter nutrients or for respiration
evolved: become the jaw, glands, or ear bones
Meckel’s cartilage
only ossified part of the skeleton in Chondrichthyes
Cyclostome (jawless vertrebrates)
Class Myxini: Hagfish
Class Petromyzontida: lampreys
swim bladder
buoyancy device (gas or fat bladder); lung derivative
lobe fins
fleshy, muscular fins
Subphylum Cephalochordata (Lancelets)
named for blade-like shape
used to be named Amphioxus, genus is now Branchiostomata
marine suspension feeders/planktonic; retain notochord in the head
Tapered at both ends, laterally flattened
Subphylum Urochordata (Tunicates or sea squirts)
marine, sessile, or planktonic suspension filter feeders
Tail and developed NS in tunicate larva
adult: absorbs tail, becomes sessile, NS degenerates
have an outer protective coat called a tunic
draw in water through an incurrent siphon that filters food particles
do not parasitize but can be very invasive
Fewer HOX genes:
have 9 instead of 13 (less specialization)
monoecious (cross fertilize)
Major transitions in Chrodate history
increase specialization and # of HOX genes as time goes on
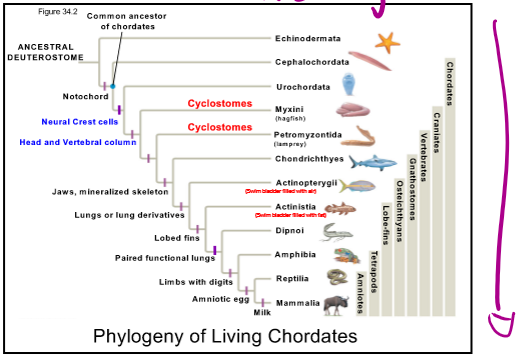
Craniates (vertebrates)
Chordates w/head and vertebrate
cranium encasing the brain
significant muscle formation aroung the gut
smooth muscle: gut muscles that causes peristalsis
Heart on the ventral side
All have cranium (skull), brain, eyes, and other sensory organs
two HOX genes clusters pharyngeal slits, muscles, heart, neural crest cells
they can dislodge and form structures or form facial defects
what is the significance of the development of heads in chordates?
allows for a new way of feeding in active predation and avoiding predators
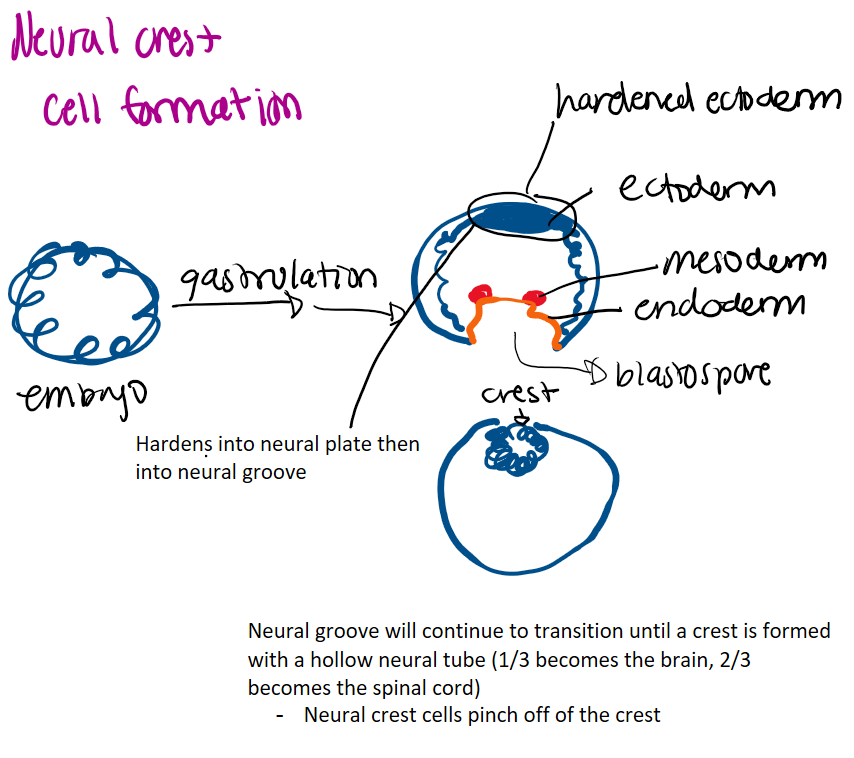
neural crest cell formation
become many kinds of important cells and form many important structures
Subphyla Vertebrata
backbone — more efficient at capturing food, moving, and avoiding predation
Hagfish: basal vertebrates
more complex skeletal and nervous systems
disparity: limbs of different functions, sizes, etc.
expansion of Dlx and HOX genes (second gene duplication)
Dlx: transcription factors (turn genes on)
provide opportunity for more complexity
Have
Vertebral columns: replaces notochord
Dlx gene duplication: homoeotic
Elaboration of the skull: becomes thicker, holds sensory organs
more efficient gills (due to higher metabolic demand) and fins stiffened by bones (fin rays) in aquatic vertebrates
Class Myxini (Cyclostomes)
Hagfishes and Slime Eels
Slime eels: make slime through slime glands
Slime gets in gills of predator and greatly expands to suffocate the predator
Cartilaginous skull
no jaws, vertebrate remnants
very small
retain notochord, move like snakes
marine, scavengers,
Family Petromyzontida (Cyclostomes)
lampreys (latch onto rocks)
ectoparasitic to fish
retain notochord
Non cartilaginous vertebral column (not bone either)
marine and freshwater
jawless, raspy tongues
mineralization
originated in vertebrate mouthparts (first seen in Chondrichthyes jaws)
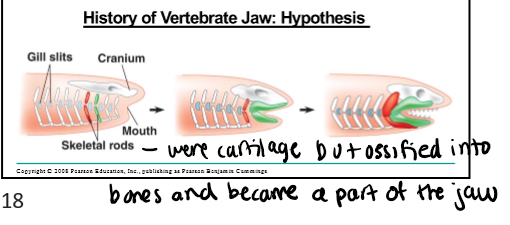
advantages of having a jaw
1) eating/capturing prey/ tearing
2) defense
3) vocalization
4) move/build/grasping things
Clade Gnathostomes
bones (jaws)
expansion of HOX genes
basal chordates: 1 cluster
basal vertebrates: 2 clusters
gnathostomes: 4 clusters
enlarged forebrain
lateral line system forms along with paired fins
Class Chondrichthyes
sharks, rays, etc
cartilaginous skeleton, fusiform body that helps reduce drag
swim quickly, cannot maneuver well
two chambered hearts
gills: ventilate due to higher metabolic demand
Ram ventilation: open mouth and swim through water
buccal pumping: put water in mouth, close jaw, and use muscles to push water over the gills
cloaca: chambered end of the body where the reproductive, digestive, and excretory tracts merge
Reproductive strategies
ovuliparous: laying unfertilized eggs (sharks do not do this)
oviparous: laying fertilized eggs, hatching occurs externally
horn shark
oviviparous: embryo matures inside female, hatches internally, and is born alive BUT they receive nourishment form the yolk ONLY
viviparous: same as oviviparous but embryo receives nourishment from mother
oophagy: nourishment from eggs
embryophagy: embryo eats another embryo
hemotrophic: nourishment by blood (placenta)
animals with gas glands?
Actinopterygii, Actinistia, dipnoii, amphibia, Reptilia, Mammalia
lungs
invagination of endoderm
gills
evagination of the ectoderm
Clade/Superclass Osteichthyes
bony fishes and tetrapods
Class Actinopterygii (ray finned fish)
skin glands that secrete mucus to reduce water resistance
thin, flat, bony scales
swim bladder for buoyancy
lateral line system to detect vibration (how they hear)
operculum - bony flap protecting the gills
2-chambered heart: atria and ventricle
mainly ovuliparous, external fertilization
ossified endoskeleton of CaPO4 which hardens cartilage
Class Sarcopterygii
lobed fins and paired functional lungs
includes coelacanths, lungfishes
rod shaped bones with muscle in pelvic and pectoral fins
“large fin”
Subclass Actinistia
Coelacanths
though to have gone extinct
lobe fins move opposite of each to each like human limbs (cross stepping)
live in deep ocean caves
can’t see bc they live in darkness
Subclass Dipnoii
paired functional lungs
have both lungs and gills
“two ways to breathe”
freshwater
estivate: burrow into the mud and secrete a mucous casing over themselves when over is scarce or ceases, slows metabolism
tetrapods
four limbs
Amphibia, Reptilia, Mammalia
Gnathostomes with four limbs
Adaptations:
4 limbs, feet with digits: supports weight, generation of force, mobility
Pharyngeal clefts: parts of ears, glands, and hyoid (loss of gills)
Ears
Neck: advantageous to sensory adaptations
Pelvic girdle fused to vertebrate: generates force, allows mobility
variable limb function
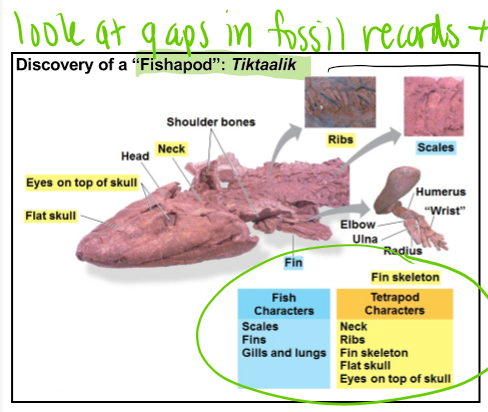
Tiktaalik
“Fishapod”
estimated transition from fish to amphibians
Class Amphibia
amphibians
basal tetrapods
both ways of life
freshwater and terrestrial
Legs, ears, eyelids, voice (larynx)
pulmocutaneous respiration (?)
lungs - simple, buccal pumping
3-chambered heart; pulmonary veins
increased brain size
Urodela, Anura, Apoda
Order Urodela
Salamanders (amphibs)
have tails
Order Anura
Frogs and toads (amphibs)
lack tails
Order Apoda
Caecilians (amphibs)
legless and resemble worms